Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
Uploaded by
Bilal KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Peterbilt Truck 389 Model Family Electrical Schematic ManualDocument6 pagesPeterbilt Truck 389 Model Family Electrical Schematic ManualjhstruckrepairNo ratings yet
- Crown Lift TrucksDocument6 pagesCrown Lift TrucksBarsaManchester50% (2)
- The Perfect Corner 2: A Driver's Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Complex Sections Through the Physics of RacingFrom EverandThe Perfect Corner 2: A Driver's Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Complex Sections Through the Physics of RacingNo ratings yet
- Chevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltFrom EverandChevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- Sony CDX Fs307jdDocument64 pagesSony CDX Fs307jdOana FloreaNo ratings yet
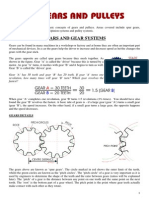
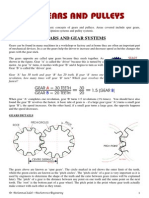
- Gears and PulleysDocument33 pagesGears and PulleysWil Nelson100% (3)
- Important Information About ECBA CertificationDocument4 pagesImportant Information About ECBA Certificationbhushan130No ratings yet
- Differential and Drive AxlesDocument38 pagesDifferential and Drive AxlesShivam Wankhede100% (2)
- Mini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemDocument22 pagesMini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemSonu DasNo ratings yet
- Uses and Applications: Gear RotationDocument11 pagesUses and Applications: Gear RotationKedar BadamiNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument21 pagesProject ReportSanniChChureNo ratings yet
- Gear Basics: Figure1. GearsDocument6 pagesGear Basics: Figure1. GearsHashem Mohamed HashemNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Tem Paper AutomobileDocument20 pagesGaurav Tem Paper AutomobileGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Paper Short QuestionsDocument18 pagesTransmission Paper Short QuestionsAbdurrehman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Final DriveDocument34 pagesFinal DriveArnold ChafewaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Underchassis Servicing, Repair and Maintenance: James D. Artista AETC 2101Document11 pagesAutomobile Underchassis Servicing, Repair and Maintenance: James D. Artista AETC 2101Kirito CabelNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument20 pagesGearsFarhad Noruzi100% (14)
- Training ReportDocument34 pagesTraining ReportVarun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument45 pagesFinal ReportKuppu Raj100% (1)
- 1-Machine Elements 1Document20 pages1-Machine Elements 1Alicemal DüzgünNo ratings yet
- Chalk and Talk Presentation On Gear'Document26 pagesChalk and Talk Presentation On Gear'Darshan HarsoraNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument4 pagesGearsYadanaNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument19 pagesTable of ContentAmrit singhNo ratings yet
- What Is Purpose of Spur GearDocument3 pagesWhat Is Purpose of Spur GearAsad AliNo ratings yet
- SprocketDocument6 pagesSprocketArefin ProttashaNo ratings yet
- Hotchkiss Drive RearDocument17 pagesHotchkiss Drive RearravivpsNo ratings yet
- Actr Mod 2Document18 pagesActr Mod 2jithinkumar22103No ratings yet
- Gears and PulleysDocument33 pagesGears and Pulleyskim haroldNo ratings yet
- Study and Demonstration of Rear Axle AssemblyDocument12 pagesStudy and Demonstration of Rear Axle AssemblySANURASAGARNo ratings yet
- Gear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationDocument24 pagesGear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationHada NanuNo ratings yet
- Differentials ExplainedDocument5 pagesDifferentials ExplainedEngine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- Bevel GearsDocument3 pagesBevel GearsSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is DifferentialDocument9 pagesWhat Is Differentialprem sagarNo ratings yet
- Workshops Pressure, GearDocument6 pagesWorkshops Pressure, GearShubham PopliNo ratings yet
- Workshops Pressure, GearDocument6 pagesWorkshops Pressure, GearShubham PopliNo ratings yet
- Machine ElementsDocument20 pagesMachine ElementsDidar KoçyiğitNo ratings yet
- Drive Shaft PDFDocument14 pagesDrive Shaft PDFnamduong368No ratings yet
- GearsDocument21 pagesGearsabduallah rabahNo ratings yet
- Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore: Minor Project:-Submitted ToDocument16 pagesSushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore: Minor Project:-Submitted ToVikas PandeyNo ratings yet
- Bda20303 Chapter 1-Gear SystemDocument27 pagesBda20303 Chapter 1-Gear SystemWan SamiraNo ratings yet
- Good Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CDocument29 pagesGood Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CSrikar ChinmayaNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument15 pagesSteering SystemSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Automotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesDocument10 pagesAutomotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesMohammad YahyaNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Gears: Introduction: The Slip and Creep in The Belt or Rope Drives Is A Common Phenomenon, in TheDocument50 pages4.0 Gears: Introduction: The Slip and Creep in The Belt or Rope Drives Is A Common Phenomenon, in TheSham SundarNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument8 pagesSteering Systemnehascribd1No ratings yet
- GEARS Types and UsesDocument9 pagesGEARS Types and UsesAllia TuboroNo ratings yet
- Front Axle and Steering SystemsDocument35 pagesFront Axle and Steering SystemsRohit ChaubalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LSD in TrucksDocument1 pageAnalysis of LSD in TrucksdipinrajdkNo ratings yet
- Transmission Paper Short QuestionsDocument5 pagesTransmission Paper Short QuestionsAtif SultanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-09 at 11.38.39 AMDocument26 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-09 at 11.38.39 AMishuhaiq7No ratings yet
- What Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramDocument14 pagesWhat Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramTisha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Chainless BycycleDocument14 pagesChainless BycycleABHISHEK CHOUDHARINo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemsDocument19 pagesTransmission SystemsIshu PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Car BibleDocument3 pagesCar BibleSoheil YadNo ratings yet
- MCT 311 Lesson 5Document16 pagesMCT 311 Lesson 5Moussa SaidNo ratings yet
- Steering Gears Steering MechanismsDocument23 pagesSteering Gears Steering MechanismsthiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument29 pagesSteering SystemNauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Rack and Pinion Gears InformationDocument6 pagesRack and Pinion Gears InformationifyNo ratings yet
- Gear Drive, Belt and Chain Drive - Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesGear Drive, Belt and Chain Drive - Lecture NotesVarun KavvampalliNo ratings yet
- SteeringDocument36 pagesSteeringHimanshu Yadav100% (1)
- The Slot Car Handbook: The definitive guide to setting-up and running Scalextric sytle 1/32 scale ready-to-race slot carsFrom EverandThe Slot Car Handbook: The definitive guide to setting-up and running Scalextric sytle 1/32 scale ready-to-race slot carsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- P120NF10Document15 pagesP120NF10marpre1983No ratings yet
- Maintenance Checklist Shekar AugerDocument1 pageMaintenance Checklist Shekar Augershamsheer ikramNo ratings yet
- Schindler Ahead: Smart Urban MobilityDocument8 pagesSchindler Ahead: Smart Urban MobilityMileNo ratings yet
- CBRE CONSULTANTS Professional PracticeDocument7 pagesCBRE CONSULTANTS Professional PracticeHoney DaveNo ratings yet
- DIL44 TQFP44 1 TIF 70 0076 Adapter ManualDocument2 pagesDIL44 TQFP44 1 TIF 70 0076 Adapter ManualEnkhbaatar TumenjargalNo ratings yet
- Citizen Science Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCitizen Science Lesson Planapi-266870910No ratings yet
- Toyota KZJ95 Coolant Temperature Gauge Modification - Forum IH8-1Document17 pagesToyota KZJ95 Coolant Temperature Gauge Modification - Forum IH8-1Mouhamed FofanaNo ratings yet
- Uts Tom 2021Document4 pagesUts Tom 2021Randhy WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- PMP Notes From Andy CroweDocument21 pagesPMP Notes From Andy Crowereddysham4u100% (2)
- Vineetha RESUME PDFDocument3 pagesVineetha RESUME PDFvineetha yalamanchaliNo ratings yet
- Betriebsanleitung + PB CMB3 SF E2!1!00Document42 pagesBetriebsanleitung + PB CMB3 SF E2!1!00Andres GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AlienFX SDK 5.2 User GuideDocument22 pagesAlienFX SDK 5.2 User GuideAlina TitaNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab4-2 MST STUDENTDocument19 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab4-2 MST STUDENTAlejandro SantosNo ratings yet
- World Payments Report 2019Document48 pagesWorld Payments Report 2019felixnovus100% (1)
- Data Extraction From Electric Vehicles Through OBD and Application of Carbon Footprint EvaluationDocument6 pagesData Extraction From Electric Vehicles Through OBD and Application of Carbon Footprint EvaluationRichard MancillaNo ratings yet
- Biopython: Python Tools For Computational Biology: Brad Chapman ChangDocument5 pagesBiopython: Python Tools For Computational Biology: Brad Chapman Changmalla ashwiniNo ratings yet
- Weller WSA350 Datasheet-2487208Document2 pagesWeller WSA350 Datasheet-2487208Diego rangel hernandezNo ratings yet
- Seeed OPL For Customer 20151021Document105 pagesSeeed OPL For Customer 20151021Google TempNo ratings yet
- Air - Fuel Ratio Tuning - Rich Vs Lean - TurbobygarrettDocument2 pagesAir - Fuel Ratio Tuning - Rich Vs Lean - TurbobygarrettDhirendra DubeyNo ratings yet
- Muzaffarpur To GwaliorDocument1 pageMuzaffarpur To GwaliorOmprakash VermaNo ratings yet
- RSP CalibrationDocument23 pagesRSP CalibrationHanyi JangNo ratings yet
- MT6592 Mediatek PDFDocument53 pagesMT6592 Mediatek PDFpop678100% (1)
- Cyber-Physical System in Automotive Domain PDFDocument11 pagesCyber-Physical System in Automotive Domain PDFBrankoNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Sunanda Sinha, S.S. ChandelDocument14 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Sunanda Sinha, S.S. ChandelAzizul MohamadNo ratings yet
- MixRite 2 5 Product Page 280615Document2 pagesMixRite 2 5 Product Page 280615RicardoArturoPerezNo ratings yet
- TD190164 Ball Valves SEDDocument12 pagesTD190164 Ball Valves SEDPablo Andres CartesNo ratings yet
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
Uploaded by
Bilal KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
How Does A Differential Work Diagram, Animation, and Images
Uploaded by
Bilal KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
What is a Di!erential and How Does
it Work with Di!erential Diagram
May 10, 2022 Knowledge Base
While you might already know that every time you
round a corner in a wheeled machine a di!erential is
being put to work, you might still wonder exactly
how it works, what it does, and how all its parts
come together to pull o! its tasks. Whether you’re
simply an inquisitive reader in search of knowledge
or you have a di!erential disassembled in your shop,
we’ve put together this simple overview of
di!erentials — with images and videos — to help
demystify di!erentials.
▲ Inside the di!erential gears work in
coordination to allow the di!erential to
change the direction of power, send
power to each wheel, and allow each
wheel to operate independently. »
Click video to play/pause animation.
❱❱ What is a Di"erential?
At its most basic, a di!erential is a system of
interconnected gears powered through a driveshaft
that (most commonly) accomplishes four tasks:
The Di!erential Changes the Direction of Power
If you imagine the power being output from an
engine traveling along driveshafts to the wheels, it
will immediately be clear that for each powered
wheel that energy will need to be converted 90
degrees. To do this, a di!erential uses a drive pinion
connected perpendicularly to a ring gear. As the
drive pinion rotates, the teeth in the drive pinion
turn the ring gear and rotate the force 90 degrees so
it can be applied to the wheels.
The Di!erential Divides Power Between Wheels on
the Same Axle
In the case of front and rear di!erentials, two
powered wheels exist at opposite ends of the
di!erential. At the same time as the direction of
power is rotated, the di!erential also splits the
power and sends power to each of the wheels.
The Di!erential Alters Torque Through Gear
Reduction
Because of the configuration of the di!erential, a
di!erential can also be used to transfer power with a
high rotational force into output with a lower speed,
higher torque force.
The Di!erential Allows Wheels to Turn at Di!erent
Speeds Relative to Each Other
With the exception of a locked di!erential, one of
the most important functions of the di!erential is
undoubtedly its ability to allow each wheel to rotate
at di!erent speeds. If you’ve ever pushed a cart
where wheels are directly fixed to each other in a
solid axle, you already know that since the rotation
of each wheel is locked, turning becomes more
di"cult. By connecting the axles (and in turn the
wheels) in a way that allows for changes in the
rotational speed of each, the di"culties of cornering
are greatly reduced.
▲ A pulled apart view of the di!erential
gives a better look at how each part
works inside the di!erential.
❱❱ How Does a Di"erential Work to
Allow Each Wheel to Turn
Independently?
Every time a wheeled machine rounds a corner, the
distance each wheel needs to travel is no longer
equal. As the inside wheel carves a path along part
of a smaller curve, the outside wheel must cover a
longer path that can be amplified by the sharpness
of the curve and the width of the axles. Without a
di!erential this di!erence would force either the
inside wheel to slip as it rotates too fast or the
outside wheel to skid as it rotates too slow.
Overtime, this constant imbalance would wear
heavily on tires, axles, and the entire machine.
To correct this problem, the di!erential connects
each axle through side gears and spider gears that
allow a loose connection of the axles instead of a
fixed connection. With each side gear mounted in a
mirror fashion and connected to each other through
spider gears mounted between them the side gears
can either rotate in unison or, when a di!erence in
force is detected, independently of one another.
As should be clear in the animation above, at times
when one wheel is experiencing less resistance a
look inside a di!erential would show the spider
gears rotating to allow each wheel to turn at
di!erent speeds.
❱❱ What Are The Most Common
Types of Di"erentials?
While the open (or standard) di!erential solves the
issue of correcting for di!erent rotational speeds of
each wheel, the di!erential also introduces a new
issue into the drive system: correcting for road
conditions where the resistance of one wheel is
greatly reduced through a loss of traction. To correct
this a few modifications to the standard di!erential
have been implemented.
Open (Or Standard) Di!erential
This type of di!erential is the one demonstrated in
the above animation. In it, no system is
implemented to correct for slippage when wheels
encounter imperfect road conditions. However due
to its reliability and the reduced complexity of its
design compared to other di!erential types, it is the
most common type of di!erential.
Locked Di!erential
A locked di!erential simply trades o! the
advantages of the wheels turning at di!erent speeds
for the advantages of the wheels always turning in
unison by eliminating the independence of each
axle. This e!ect can either be manually controlled
and able to turn on and o! or permanent. It is most
common in vehicles where di"cult road conditions
(or even the non-existence of roads) is the standard
and not the exception.
Limited Slip Di!erential
The limited slip di!erential is a marriage of the open
di!erential and the locked di!erential wherein the
di!erential routinely acts like an open di!erential
but under certain conditions can be influenced to act
like a locked di!erential. This e!ect can be created
either through a viscous coupling or through a clutch
system, and is most often found in high
performance cars.
▲ Here, a freshly rebuilt di!erential sits
at the center of a rear axle.
❱❱ Where On a Machine is A
Di"erential?
Depending on a machine and how power is divided
and delivered to each of the wheels, a di!erential
can exist at the front of the machine along the front
axle, at the rear of the machine along the rear axle,
or at the center of the machine dividing the front
and rear axles.
Hopefully, how a di!erential works and what it does
should be clear now, but if you’re interested in
learning more, why not take a video trip into one of
the Recon and Rebuild shops and see a di!erential
being rebuilt? You can watch that in our How to
Rebuild a Front and Rear Axle post. Or keep scrolling
for a gallery of disassembled di!erentials and
diagrams.
At H&R, we’ve earned a reputation as a top source
EMAIL US
for rebuilt transmissions for wheel loaders,
articulated trucks, and other heavy construction
equipment. We know that reputation comes from
our commitment to our rebuild process and the
expert knowledge our parts technicians bring to
every project. If you’re in search of a replacement
di!erential, reach out to our Parts Specialists and
they’ll connect you to our deep inventory and
provide fast information about availability and
pricing.
LET US
SEARCH FOR
YOU
Don't see what you are looking
for? With access to specialized
search tools and our extensive
vendor network, our parts
specialists are here to search for
you and to connect you to your
parts, fast and simple.
Call: 800-333-0650
★ Di"erential Image and Diagram
Gallery
▲ A hub, bearings, gears, and carriers
from a di!erential are waiting for a tech
to put together for a di!erential
rebuild.
▲ The ring gear rests on its side.
During a rebuild, a ring gear must be
closely inspected to ensure teeth are
not damaged and replaced if they are
worn.
▲ The spider gears are set out, with
the spider in the center, in anticipation
for assembly and insertion into the
di!erential.
▲ Here, an assembled di!erential with
the back case removed gives a clear
picture of the internals of the part.
▲ The ring gear, side gears, and other
parts are laid out on a workbench
before being incorporated into the
di!erential.
▲ An H&R parts technician puts on
some of the final touches before
completing this di!erential rebuild.
▲ At each side of the di!erential, an
axle connects the di!erential to a wheel
and transfers power to the wheel.
▲ Bearings facilitate movement of
axles and allow the internal of the
di!erential to rotate freely.
▲ A pinion shaft at the end of the
center axle of the machine transfers
power to the di!erential.
▲ A large ring gear connects to the
pinion drive and rotates the direction of
force 90 degrees.
▲ Side gears connected to shafts allow
the turning of the ring gear to turn the
wheels of the machine or — when the
spider gears are put into motion —
each wheel to rotate independently.
▲ Spider gears are held together in a
spider shaft, and while the shaft rotates
in unison with the ring gear, the spider
gears only turn when there is an
imbalance in the rotational speed of
each wheel.
Knowledge Base Series
This article is part of the H&R Construction
Equipment Parts knowledge base series,
designed to speak informatively and
passionately about topics in the heavy
equipment industry. From 10-year-old
excavator enthusiasts to passionate parts
tinkerers looking to learn more, the aim of the
series is to provide basic information to any
and all inquisitive minds.
← Previous Next →
RELATED POSTS
1. What Are the Parts of a Bulldozer
Undercarriage with Undercarriage
Diagram
2. How an Excavator Swivel (Rotary
Distributor) Works with Excavator
Swivel Diagram
3. What is a Swing Drive with Swing
Drive Diagram
Search posts here...
Categories
Inside H&R
Dismantled Machines
Construction Equipment Parts
Final Drive
Swing Drive and Slewing Ring
How To
Knowledge Base
GET A PART QUOTE
First Name *
Last Name *
Email *
Machine Make
Please Select
Machine Model
Part Number
Part Description *
Stay Up-to-Date with Deals and News
Yes, sign me up for the H&R news and updates
email (unsubscribe at any time).
Please verify that you are human *
protected by reCAPTCHA
Privacy - Terms
Submit
Recent Posts
Discover 7 of the Oldest, Man-Made Structures on Earth
June 5, 2023
Big Shots: May 2023
May 30, 2023
Discover 6 of the Biggest Construction Projects in History
May 19, 2023
RSS Feed
Sitemap Advanced Search Legal Information
Careers Contact Us All States Ag Parts
Summit Supply
SUBSCRIBE HERE FOR H&R NEWSLETTER
Get all the latest information on Events, Sales and O!ers.
Email Address SUBSCRIBE
MENU
Home
About Us
Construction Equipment Parts
Shop Parts
Equipment
Final Drive Finder
Blog
Contact Us
RESOURCES
Careers
Credit Application
Marketing Information
Legal Information
AFFILIATED COMPANIES
All States Ag Parts
Summit Supply
ArrowWe use cookies
Material to provide a
personalized
PARTS BOOKS site experience. By
continuing to use & browse this site, Got
Bobcat Parts Book
you agree to our Privacy Policy. It
Caterpillar Parts Book
You might also like
- Peterbilt Truck 389 Model Family Electrical Schematic ManualDocument6 pagesPeterbilt Truck 389 Model Family Electrical Schematic ManualjhstruckrepairNo ratings yet
- Crown Lift TrucksDocument6 pagesCrown Lift TrucksBarsaManchester50% (2)
- The Perfect Corner 2: A Driver's Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Complex Sections Through the Physics of RacingFrom EverandThe Perfect Corner 2: A Driver's Step-by-Step Guide to Optimizing Complex Sections Through the Physics of RacingNo ratings yet
- Chevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltFrom EverandChevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (17)
- Sony CDX Fs307jdDocument64 pagesSony CDX Fs307jdOana FloreaNo ratings yet
- Gears and PulleysDocument33 pagesGears and PulleysWil Nelson100% (3)
- Important Information About ECBA CertificationDocument4 pagesImportant Information About ECBA Certificationbhushan130No ratings yet
- Differential and Drive AxlesDocument38 pagesDifferential and Drive AxlesShivam Wankhede100% (2)
- Mini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemDocument22 pagesMini Project Report: Differential Gear SystemSonu DasNo ratings yet
- Uses and Applications: Gear RotationDocument11 pagesUses and Applications: Gear RotationKedar BadamiNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument21 pagesProject ReportSanniChChureNo ratings yet
- Gear Basics: Figure1. GearsDocument6 pagesGear Basics: Figure1. GearsHashem Mohamed HashemNo ratings yet
- Gaurav Tem Paper AutomobileDocument20 pagesGaurav Tem Paper AutomobileGaurav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transmission Paper Short QuestionsDocument18 pagesTransmission Paper Short QuestionsAbdurrehman HashmiNo ratings yet
- Final DriveDocument34 pagesFinal DriveArnold ChafewaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Underchassis Servicing, Repair and Maintenance: James D. Artista AETC 2101Document11 pagesAutomobile Underchassis Servicing, Repair and Maintenance: James D. Artista AETC 2101Kirito CabelNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument20 pagesGearsFarhad Noruzi100% (14)
- Training ReportDocument34 pagesTraining ReportVarun AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument45 pagesFinal ReportKuppu Raj100% (1)
- 1-Machine Elements 1Document20 pages1-Machine Elements 1Alicemal DüzgünNo ratings yet
- Chalk and Talk Presentation On Gear'Document26 pagesChalk and Talk Presentation On Gear'Darshan HarsoraNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument4 pagesGearsYadanaNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument19 pagesTable of ContentAmrit singhNo ratings yet
- What Is Purpose of Spur GearDocument3 pagesWhat Is Purpose of Spur GearAsad AliNo ratings yet
- SprocketDocument6 pagesSprocketArefin ProttashaNo ratings yet
- Hotchkiss Drive RearDocument17 pagesHotchkiss Drive RearravivpsNo ratings yet
- Actr Mod 2Document18 pagesActr Mod 2jithinkumar22103No ratings yet
- Gears and PulleysDocument33 pagesGears and Pulleyskim haroldNo ratings yet
- Study and Demonstration of Rear Axle AssemblyDocument12 pagesStudy and Demonstration of Rear Axle AssemblySANURASAGARNo ratings yet
- Gear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationDocument24 pagesGear Boxes in Automobiles PresentationHada NanuNo ratings yet
- Differentials ExplainedDocument5 pagesDifferentials ExplainedEngine Tuning UpNo ratings yet
- Bevel GearsDocument3 pagesBevel GearsSaurabh SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is DifferentialDocument9 pagesWhat Is Differentialprem sagarNo ratings yet
- Workshops Pressure, GearDocument6 pagesWorkshops Pressure, GearShubham PopliNo ratings yet
- Workshops Pressure, GearDocument6 pagesWorkshops Pressure, GearShubham PopliNo ratings yet
- Machine ElementsDocument20 pagesMachine ElementsDidar KoçyiğitNo ratings yet
- Drive Shaft PDFDocument14 pagesDrive Shaft PDFnamduong368No ratings yet
- GearsDocument21 pagesGearsabduallah rabahNo ratings yet
- Sushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore: Minor Project:-Submitted ToDocument16 pagesSushila Devi Bansal College of Technology, Indore: Minor Project:-Submitted ToVikas PandeyNo ratings yet
- Bda20303 Chapter 1-Gear SystemDocument27 pagesBda20303 Chapter 1-Gear SystemWan SamiraNo ratings yet
- Good Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CDocument29 pagesGood Morning .?: Presentation On Vehicle Steering Systems by Pari, D.J & K.CSrikar ChinmayaNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument15 pagesSteering SystemSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- Automotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesDocument10 pagesAutomotive (2) Lab: EXP2: Manual Transmission and TransaxlesMohammad YahyaNo ratings yet
- 4.0 Gears: Introduction: The Slip and Creep in The Belt or Rope Drives Is A Common Phenomenon, in TheDocument50 pages4.0 Gears: Introduction: The Slip and Creep in The Belt or Rope Drives Is A Common Phenomenon, in TheSham SundarNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument8 pagesSteering Systemnehascribd1No ratings yet
- GEARS Types and UsesDocument9 pagesGEARS Types and UsesAllia TuboroNo ratings yet
- Front Axle and Steering SystemsDocument35 pagesFront Axle and Steering SystemsRohit ChaubalNo ratings yet
- Analysis of LSD in TrucksDocument1 pageAnalysis of LSD in TrucksdipinrajdkNo ratings yet
- Transmission Paper Short QuestionsDocument5 pagesTransmission Paper Short QuestionsAtif SultanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-05-09 at 11.38.39 AMDocument26 pagesScreenshot 2023-05-09 at 11.38.39 AMishuhaiq7No ratings yet
- What Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramDocument14 pagesWhat Is A Gearbox? (Transmission) - Types, Parts, Function & DiagramTisha GaikwadNo ratings yet
- Chainless BycycleDocument14 pagesChainless BycycleABHISHEK CHOUDHARINo ratings yet
- Transmission SystemsDocument19 pagesTransmission SystemsIshu PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Car BibleDocument3 pagesCar BibleSoheil YadNo ratings yet
- MCT 311 Lesson 5Document16 pagesMCT 311 Lesson 5Moussa SaidNo ratings yet
- Steering Gears Steering MechanismsDocument23 pagesSteering Gears Steering MechanismsthiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Steering SystemDocument29 pagesSteering SystemNauman KhanNo ratings yet
- Rack and Pinion Gears InformationDocument6 pagesRack and Pinion Gears InformationifyNo ratings yet
- Gear Drive, Belt and Chain Drive - Lecture NotesDocument26 pagesGear Drive, Belt and Chain Drive - Lecture NotesVarun KavvampalliNo ratings yet
- SteeringDocument36 pagesSteeringHimanshu Yadav100% (1)
- The Slot Car Handbook: The definitive guide to setting-up and running Scalextric sytle 1/32 scale ready-to-race slot carsFrom EverandThe Slot Car Handbook: The definitive guide to setting-up and running Scalextric sytle 1/32 scale ready-to-race slot carsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Band Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsFrom EverandBand Saw (Missing Shop Manual): The Tool Information You Need at Your FingertipsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- P120NF10Document15 pagesP120NF10marpre1983No ratings yet
- Maintenance Checklist Shekar AugerDocument1 pageMaintenance Checklist Shekar Augershamsheer ikramNo ratings yet
- Schindler Ahead: Smart Urban MobilityDocument8 pagesSchindler Ahead: Smart Urban MobilityMileNo ratings yet
- CBRE CONSULTANTS Professional PracticeDocument7 pagesCBRE CONSULTANTS Professional PracticeHoney DaveNo ratings yet
- DIL44 TQFP44 1 TIF 70 0076 Adapter ManualDocument2 pagesDIL44 TQFP44 1 TIF 70 0076 Adapter ManualEnkhbaatar TumenjargalNo ratings yet
- Citizen Science Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesCitizen Science Lesson Planapi-266870910No ratings yet
- Toyota KZJ95 Coolant Temperature Gauge Modification - Forum IH8-1Document17 pagesToyota KZJ95 Coolant Temperature Gauge Modification - Forum IH8-1Mouhamed FofanaNo ratings yet
- Uts Tom 2021Document4 pagesUts Tom 2021Randhy WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- PMP Notes From Andy CroweDocument21 pagesPMP Notes From Andy Crowereddysham4u100% (2)
- Vineetha RESUME PDFDocument3 pagesVineetha RESUME PDFvineetha yalamanchaliNo ratings yet
- Betriebsanleitung + PB CMB3 SF E2!1!00Document42 pagesBetriebsanleitung + PB CMB3 SF E2!1!00Andres GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AlienFX SDK 5.2 User GuideDocument22 pagesAlienFX SDK 5.2 User GuideAlina TitaNo ratings yet
- CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab4-2 MST STUDENTDocument19 pagesCCNPv7.1 SWITCH Lab4-2 MST STUDENTAlejandro SantosNo ratings yet
- World Payments Report 2019Document48 pagesWorld Payments Report 2019felixnovus100% (1)
- Data Extraction From Electric Vehicles Through OBD and Application of Carbon Footprint EvaluationDocument6 pagesData Extraction From Electric Vehicles Through OBD and Application of Carbon Footprint EvaluationRichard MancillaNo ratings yet
- Biopython: Python Tools For Computational Biology: Brad Chapman ChangDocument5 pagesBiopython: Python Tools For Computational Biology: Brad Chapman Changmalla ashwiniNo ratings yet
- Weller WSA350 Datasheet-2487208Document2 pagesWeller WSA350 Datasheet-2487208Diego rangel hernandezNo ratings yet
- Seeed OPL For Customer 20151021Document105 pagesSeeed OPL For Customer 20151021Google TempNo ratings yet
- Air - Fuel Ratio Tuning - Rich Vs Lean - TurbobygarrettDocument2 pagesAir - Fuel Ratio Tuning - Rich Vs Lean - TurbobygarrettDhirendra DubeyNo ratings yet
- Muzaffarpur To GwaliorDocument1 pageMuzaffarpur To GwaliorOmprakash VermaNo ratings yet
- RSP CalibrationDocument23 pagesRSP CalibrationHanyi JangNo ratings yet
- MT6592 Mediatek PDFDocument53 pagesMT6592 Mediatek PDFpop678100% (1)
- Cyber-Physical System in Automotive Domain PDFDocument11 pagesCyber-Physical System in Automotive Domain PDFBrankoNo ratings yet
- Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Sunanda Sinha, S.S. ChandelDocument14 pagesRenewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews: Sunanda Sinha, S.S. ChandelAzizul MohamadNo ratings yet
- MixRite 2 5 Product Page 280615Document2 pagesMixRite 2 5 Product Page 280615RicardoArturoPerezNo ratings yet
- TD190164 Ball Valves SEDDocument12 pagesTD190164 Ball Valves SEDPablo Andres CartesNo ratings yet