Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3022 Oct 20
3022 Oct 20
Uploaded by
HAMDUOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3022 Oct 20
3022 Oct 20
Uploaded by
HAMDUCopyright:
Available Formats
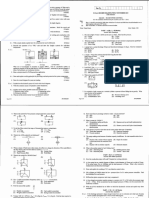
TED (15) 3022 Reg.No.............................
N20-00243
(Revision-2015) Signature..........................
DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/TECHNOLOGY/
MANAGEMENT/COMMERCIAL PRACTICE, NOVEMBER-2020
FLUID MECHANICS AND PNEUMATICS
[Maximum marks: 75] (Time: 2.15 Hours)
om
PART – A
(Answer any three questions in one or two sentences. Each question carries 2 marks)
I. (1). Differentiate between Ideal Fluid and real Fluid.
(2). What are the assumptions made in Bernoulli’s Theorem.
.c
(3). List any four advantages of Fluid power.
(4). List any four applications of air cylinders.
(5). Differentiate between absolute pressure and gauge pressure. (3 x 2 = 6)
ly
PART – B
po
(Answer any four of the following questions. Each question carries 6 marks)
II. (1). Explain the conditions for equilibrium of a floating body.
(2). Explain the differences between orifice and a Notch.
in
(3). List out the minor losses of head in a long pipe.
(4). Explain the principle of working of a weight loaded accumulator.
ad
(5). Explain the principle of working of a positive displacement pump with the help of a figure.
(6). Draw the pneumatic circuit for controlling double acting air cylinder.
(7). List the advantages and applications of a hydro pneumatic system. (4 x 6= 24)
m
PART – C
(Answer any of the three units from the following. Each question carries 15 marks)
UNIT –I
III. (a). Define the following terms.
(i). Specific Volume. (ii). Kinematic Viscosity.
(iii). Specific gravity. (iv). Compressibility. (8)
(b). T tank with length 4m and breadth 6m contains 2.5m deep oil with specific gravity 0.9 find.
(i). Intensity of pressure at the base of the tank.
(ii). Total Pressure on the base of the tank. (7)
OR
IV. (a). A simple U tube manometer containing mercury is used to measure the pressure of oil with
specific gravity 0.8 flowing in a pipeline. Its right limb is open to atmosphere and left limb
is connected to pipe. The centre of the pipe is 90mm below the level of mercury (specific
gravity 13.6) in the right limb. If the difference of mercury levels in the two limbs is 150mm,
om
find the pressure of oil in the pipe. (8)
(b). Explain features of a bourdon tube pressure gauge with the help of a figure. (7)
UNIT-II
.c
V. (a). Explain the principle of working of a venturimeter with the help of a sketch. (8)
(b). A pipe 60 meters long and 150mm in diameter is connected to a water tank at one end and
ly
flows freely into the atmosphere at the other end. Height of water level in the tank is 2.6 meters
above the centre of the pipe. Pipe is horizontal and f = 0.01. Determine the discharge through
po
the pipe in litres per second, if all minor losses are to be considered. (7)
OR
in
VI. (a). List the advantages of triangular notch over rectangular notch. (8)
(b). A venturimeter with a 150mm diameter at inlet and 100mm at throat is laid with its axis
horizontal and is used for measuring the flow of oil with specific gravity 0.9. The oil –
ad
mercury differential manometer shows a gauge difference of 200mm. Coefficient of
discharge of venturimeter is 0.98. Calculate the discharge in litres per minute. (7)
m
UNIT-III
VII. (a). Explain the basic components of a hydraulic system with the help of a diagram. (8)
(b). Explain the principle of a hydraulic Intensifier with a figure. (7)
OR
VIII.(a). List the functions of control valves in a hydraulic system. (8)
(b). Explain the principle of working of a gear pump. (7)
UNIT-IV
IX. (a).Explain the principle of working of an Air lubricator with the help of a diagram. (8)
(b). Compare the characteristics of a hydraulic and pneumatic system. (7)
OR
om
X. (a). Draw the pneumatic circuit for a pneumatic chuck and explain it’s working. (8)
(b). Explain a solenoid operated valve with the help of a diagram. (7)
.c
ly
po
in
ad
m
You might also like
- A1 LanguoDocument164 pagesA1 LanguoAlper Önen100% (1)
- Modeling and Simulation For The Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based On SimulinkDocument4 pagesModeling and Simulation For The Electro-Hydraulic Servo System Based On SimulinkSteven VelandiaNo ratings yet
- B 64483EN 2 - 03 Fanuc Dual Check SafetyDocument240 pagesB 64483EN 2 - 03 Fanuc Dual Check SafetyDmitry100% (4)
- 3051Document4 pages3051Anurag ShajiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Pneumatics: (REVISION - 2015)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics and Pneumatics: (REVISION - 2015)Muhd Shabeeb ANo ratings yet
- B.E / B.Tech (Full Time) D E G R E E End S E M E S T E R Examinations, Nov / D E C 2013Document3 pagesB.E / B.Tech (Full Time) D E G R E E End S E M E S T E R Examinations, Nov / D E C 2013VVCET - MechNo ratings yet
- Anna UniversityDocument3 pagesAnna UniversityupenderNo ratings yet
- New PapersDocument2 pagesNew PapersKripan SR SukrithamNo ratings yet
- DL 2291Document2 pagesDL 2291Chetan MruthyunjayaNo ratings yet
- ME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument9 pagesME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticssureshNo ratings yet
- ME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument6 pagesME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsSuresh VeluNo ratings yet
- College - Be - 2010 - 2010nov - Mech - Me 2305 - Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument3 pagesCollege - Be - 2010 - 2010nov - Mech - Me 2305 - Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics9600257003No ratings yet
- 4022 Automobile Engineering - QPDocument2 pages4022 Automobile Engineering - QPMuhd Shabeeb ANo ratings yet
- CE1310 - Applied Hydraulics & PneumaticsDocument10 pagesCE1310 - Applied Hydraulics & PneumaticsShyam MechNo ratings yet
- AHP Question BankDocument11 pagesAHP Question Bankduraiprakash83No ratings yet
- H&P Question Bank PDFDocument10 pagesH&P Question Bank PDFHarish RajaNo ratings yet
- QP FMM 22445 ME4I Summer 2022Document5 pagesQP FMM 22445 ME4I Summer 2022Shantanu WaghmareNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityAK 7No ratings yet
- ME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument12 pagesME 1305 Applied Hydraulics and PneumaticsNarayana SamyNo ratings yet
- AHP 16 MarksDocument4 pagesAHP 16 MarksvelavansuNo ratings yet
- ME 2305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Instuitute of Research and TechnologyDocument10 pagesME 2305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Dhanalakshmi Srinivasan Instuitute of Research and TechnologyAnonymous p8bHAAxNo ratings yet
- KOM PapersDocument30 pagesKOM PapersjrravikirankopelliNo ratings yet
- AHPMEDocument1 pageAHPMEStephen JacsiNo ratings yet
- ME1305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics May Jun 2007Document4 pagesME1305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics May Jun 2007Mechtrix MohanNo ratings yet
- HM&S - Me16323Document2 pagesHM&S - Me16323Chary100% (1)
- Indian Maritime University: (A Central University, Govt. of India)Document2 pagesIndian Maritime University: (A Central University, Govt. of India)rahul rajNo ratings yet
- Oew GekDocument2 pagesOew GekHtet Wai Yan AungNo ratings yet
- 13fi-,zp.c:1l: Pectncn 879Document3 pages13fi-,zp.c:1l: Pectncn 879Athisayaraj RajNo ratings yet
- (Time: 3 Hours) (Total Marks: 70) : Printed Pages: 3Document3 pages(Time: 3 Hours) (Total Marks: 70) : Printed Pages: 3Awanish SinghNo ratings yet
- ME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsDocument4 pagesME8694 Hydraulics and PneumaticsHarry HarryNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics July 2017 (2010 Scheme)Document1 pageHydraulics July 2017 (2010 Scheme)MaruthiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Fluid PowerDocument4 pagesIndustrial Fluid Powersumit ChimkarNo ratings yet
- CBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)Document2 pagesCBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)Swaroop SomannaNo ratings yet
- CBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)Document2 pagesCBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)Swaroop SomannaNo ratings yet
- MECH-ND-2020-ME 2305-Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics-582039598-ME2305-ME1305-APPLIED HYDRAULICS AND PNEUMATICSDocument2 pagesMECH-ND-2020-ME 2305-Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics-582039598-ME2305-ME1305-APPLIED HYDRAULICS AND PNEUMATICSDharma RajaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Hydraulic Machines July 2023Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics Hydraulic Machines July 2023arjunguttula11No ratings yet
- 08 May 2019Document2 pages08 May 2019Ramesh SagapariyaNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoMr Business ToolNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics Year/Sem: III/VDocument8 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Question Bank Sub. Code/Name: ME1305 Applied Hydraulics and Pneumatics Year/Sem: III/VVVCET - MechNo ratings yet
- Scan 9 Dec 2019Document4 pagesScan 9 Dec 2019Keerthi VarmanNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBharat GelotNo ratings yet
- Design of Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems-April-2011Document2 pagesDesign of Hydraulics and Pneumatic Systems-April-2011SasiKumar Petchiappan100% (1)
- 3021 Oct 20Document2 pages3021 Oct 20akkgptcktmNo ratings yet
- 22445-2023-Winter-Question-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document4 pages22445-2023-Winter-Question-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Pratham DalviNo ratings yet
- CBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)Document2 pagesCBCS Scheme: Fluid Power Systems (Model QP)SyedNo ratings yet
- Ahp 2013 Imp PDFDocument3 pagesAhp 2013 Imp PDFganeshkumarNo ratings yet
- Me1025 5 Sem PDFDocument2 pagesMe1025 5 Sem PDFRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- T1402 Marine BoilersDocument2 pagesT1402 Marine BoilersSTUDENTS OF DOE CUSATNo ratings yet
- B.E. / B.Tech Degree Examinations April / May 2021 Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesB.E. / B.Tech Degree Examinations April / May 2021 Mechatronics EngineeringAravinth100% (1)
- Me206 QPDocument2 pagesMe206 QPMohammed Jihad PmNo ratings yet
- FMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Document8 pagesFMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyulud100% (1)
- 151406-151903-Fluid Power EngineeringDocument2 pages151406-151903-Fluid Power EngineeringHerat HirparaNo ratings yet
- HP Question Paper 2023Document3 pagesHP Question Paper 2023Monika BNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document8 pagesSet No. 129viswa12No ratings yet
- FMHM 8Document8 pagesFMHM 829viswa12No ratings yet
- Code No: 13006Document4 pagesCode No: 13006SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Hydraulic Machines July 2022Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics Hydraulic Machines July 2022530-M-004 AVINASH SAI GANGADANo ratings yet
- r05222202 Prime Movers and Mechanical ComponentsDocument9 pagesr05222202 Prime Movers and Mechanical ComponentsSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Hybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignFrom EverandHybrid Systems Based on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: Modelling and DesignNo ratings yet
- Jensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewDocument11 pagesJensen: Unit 4 Pretest ReviewKarma TenzinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Evapotranspiration 2014 - 2Document23 pagesChapter 3 - Evapotranspiration 2014 - 2smdunaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Utm PSC Sho CiDocument5 pages2021 Utm PSC Sho Cisawsheng59No ratings yet
- Articles On Caste and Class in Early India 2016Document210 pagesArticles On Caste and Class in Early India 2016Aquib RahmaniNo ratings yet
- Schmidt Bender Catalog 2020 en USDocument48 pagesSchmidt Bender Catalog 2020 en USKyle YangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in EnglishMary Jane MiravallesNo ratings yet
- Anova CFDDocument13 pagesAnova CFDHaydar YahyaNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Speed Control Using C++Document77 pagesDC Motor Speed Control Using C++eraditya2001100% (11)
- The Python Quiz Book Michael Driscoll Full ChapterDocument67 pagesThe Python Quiz Book Michael Driscoll Full Chaptersaul.sumbry682100% (7)
- Pressure Transmitter AzbilDocument2 pagesPressure Transmitter Azbilehsan shahpariNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Dosis Serbuk Biji Kelor (Moringa Oliefera) Terhadap Kadar Biochemical Oxygen Demand Air Limbah Rumah Pemotongan Ayam TAHUN 2021Document9 pagesPengaruh Dosis Serbuk Biji Kelor (Moringa Oliefera) Terhadap Kadar Biochemical Oxygen Demand Air Limbah Rumah Pemotongan Ayam TAHUN 2021meiliaNo ratings yet
- Payback BC MethodDocument1 pagePayback BC MethodJam LarsonNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument6 pagesScienceInkspireNo ratings yet
- EE 302 Final Exam and Histogram F12 PDFDocument4 pagesEE 302 Final Exam and Histogram F12 PDFAnonymous BKSqKEQhnuNo ratings yet
- 24-12-2021 - Hand Written Notes - Shankar IAS AcademyDocument13 pages24-12-2021 - Hand Written Notes - Shankar IAS AcademyThakre ShubhamNo ratings yet
- The Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin - 1968 - The New Visionaries - Sobre Unbuilt - Impresso - Arthur RosenblattDocument12 pagesThe Metropolitan Museum of Art Bulletin - 1968 - The New Visionaries - Sobre Unbuilt - Impresso - Arthur RosenblattThais AnastacioNo ratings yet
- Draft List of Disadvantaged CommunitiesDocument43 pagesDraft List of Disadvantaged CommunitiesrkarlinNo ratings yet
- Jarso DoyoDocument82 pagesJarso DoyoDawit NegussieNo ratings yet
- Cooling Tower Performance CalculationDocument11 pagesCooling Tower Performance CalculationJason Thomas100% (1)
- The Structure and Functions of Language - John R. Searle 2014Document14 pagesThe Structure and Functions of Language - John R. Searle 2014Agustín AlemNo ratings yet
- JHS Detailed Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesJHS Detailed Lesson PlanJewelNo ratings yet
- Jokta AcademyDocument1 pageJokta Academyjokta academyNo ratings yet
- MaximumDocument3 pagesMaximumJowiNo ratings yet
- Iranian Ice Repositories - An Example of Traditional Indigenous ArchitectureDocument12 pagesIranian Ice Repositories - An Example of Traditional Indigenous Architectureadekpadek100% (1)
- De Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Mon Tieng Anh Lop 11 Truong THPT Pham Cong Binh Vinh Phuc Nam 2016 2017 Co Dap AnDocument9 pagesDe Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Mon Tieng Anh Lop 11 Truong THPT Pham Cong Binh Vinh Phuc Nam 2016 2017 Co Dap AnLê Thị Kiều OanhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Problem SetDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry Problem SetBermonica Alvior SatuitoNo ratings yet
- Virtual Labs: Greener and Economic Approach For Learning The Pharma-LabDocument8 pagesVirtual Labs: Greener and Economic Approach For Learning The Pharma-LabRocio MontanoNo ratings yet