Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillo
DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillo
Uploaded by
karl eiron delos santosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillo
DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillo
Uploaded by
karl eiron delos santosCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY
Name of the Patient Mr. Ramon Del Poso Age: 64 years old Sex:Male Name of Student Angelica Mae E. Ronquillo
Civil Status: _____________ Religion: _____ Rm/Bed No. _Area: Station 2 Level/ Block: BSN Level 3 Block A
Address : ___________________________ Date Submitted: May 18, 2023 Date of Admission:May 13, 2023
Diagnosis: DM TYPE 2 UNCONTROLLED, UGIB, ANEMIA Rating: ________________________
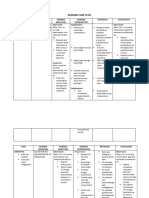
Drug Classification/ Indication/ Side Effects Adverse Nursing Consideratio
Name/Dosage/ Mechanism of Action Contraindication Reactions ns
Route/Frequenc
y/ Drug Order
Generic name: PHARMACOTHER Indication: (Byetta): CNS: Headache, Before:
Omeprazole APEUTIC: Duodenal and gastric Frequent (44%): dizziness, Check and
Benzimidazole ulcer. Nausea. fatigue. verify doctor’s
Brand name: Gastroesophageal Occasional (13%– GI: Diarrhea, order regarding
Empraz reflux disease 6%): Diarrhea, abdominal pain,
the medication.
CLINICAL: including severe vomiting, dizziness, nausea, mild
Observe 10
Usual dosage/ Proton pump inhibitor erosive esophagitis anxiety, dyspepsia. transient
frequency: (4 to 8 wk Rare (less than increases in liver rights: Right
40 mg once daily THERAPEUTIC treatment). Long- 6%): Weakness. function tests. patient, drug,
given via infusion EFFECT: term treatment of Urogenital: He dose, time, and
over 20-30 Increases gastric pH, pathologic (Bydureon): maturia, route.
minutes until oral reduces gastric acid hypersecretory proteinuria. Make a
administration is production. conditions such as 5% or greater: Skin: Rash.
medication
possible. Zollinger-Ellison Nausea, diarrhea,
ACTION: syndrome, multiple headache, card with the
Usual route: Inhibits hydrogen- endocrine adenomas, constipation, complete
IV potassium adenosine and systemic vomiting, dyspepsia, doctor’s order,
triphosphatase mastocytosis. In injec-tion site name of the
Drug order: (H+/K+ ATP pump), combination with pruritus or nodule patient, bed
an enzyme on the clarithromycin to
Omeprazole 40 surface of
gastric treat duodenal ulcers number and
mg q12 parietal cells. associated room/ward.
with Helicobacter Obtain and
pylori. record vital
PHARMACOKINE
TICS signs.
Contraindication: Ask the
Absorption: Poorly Hypersensitivity to client’s full
absorbed from GI omeprazole, other name to verify
tract; 30–40% reaches proton pump his identity.
systemic circulation. inhibitors.
Educate and
Onset: 0.5–3.5 h. Concomitant use
with products explain the
Peak: Peak inhibition
of gastric acid containing medication to
secretion: 5 d. rilpivirine. the client, how
Metabolism: Metabol it works, why
ized in liver. it is given to
Elimination: 80% him, and the
excreted in urine, 20% Caution use:
possible side
in feces. May increase risk of
fractures, effects.
Half-Life: 0.5–1.5 h.
gastrointestinal
INTERACTIONS: infections. Hepatic
Drug: rug: Concomit impairment, pts of
ant administration Asian descent. During:
of diazepam and Position patient
omeprazole may appropriately
increase diazepam for medication
concentrations. administration.
Concomitant Follow the
administration directions on
of phenytoin and the medicine
omeprazole may label. IV
infusion:
increase phenytoin le Reconstitute
vels. Concomitant with 100 mL of
administration dextrose 5% or
of warfarin and NaCl 0.9% inj.
omeprazole may
increase warfarin lev After:
els.
Remind the
client to report
all adverse
reactions and
to notify
prescriber.
Monitor the
patient’s vital
signs
frequently.
Lab tests:
Monitor
urinalysis for
hematuria and
proteinuria.
Periodic liver
function tests
with prolonged
use.
Evaluate the
effectiveness
of the
medication.
Wash your
hands properly
Document the
time, location,
dose, and
medication
given to the
patient.
Patient and Family
Education:
Report any
changes in
urinary
elimination
such as pain or
discomfort
associated with
urination, or
blood in urine.
Report severe
diarrhea; drug
may need to be
discontinued.
You might also like
- flgx213 (2) Pkjun2015Document6 pagesflgx213 (2) Pkjun2015Jason Van Den HeeverNo ratings yet
- Vic 2019 CatalogDocument893 pagesVic 2019 CatalogAnna Mae Marantan100% (1)
- Elevator Control SystemDocument15 pagesElevator Control SystemAdityaGupta100% (1)
- "My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingDocument3 pages"My Breasts Are Sore and Tender But There Is No Milk Coming Out and Im Also in Pain Due To Uterine CrampingBAGUIO CATSNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)Document13 pagesNursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)vinda astri permatasari100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryDocument64 pagesNormal Spontaneous DeliveryMichellin Andres MarianoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study East AveDocument15 pagesDrug Study East AveSean Philippe CabralNo ratings yet
- Burn - Daily Physical AssessmentDocument8 pagesBurn - Daily Physical AssessmentkrishcelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of FluoxetineDocument2 pagesDrug Study of FluoxetineLance De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Otitis MediaDocument4 pagesNCP Otitis MediaZillah KorrenNo ratings yet
- HydroxyzineDocument4 pagesHydroxyzineGeorge Smith AbeledaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilityJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Assess Ability To Learn or Perform Desired Health-Related CareDocument6 pagesAssess Ability To Learn or Perform Desired Health-Related CareMarielle J GarciaNo ratings yet
- PEDIA CASE 3 FinalDocument9 pagesPEDIA CASE 3 FinalXandra BnnNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OkDocument4 pagesDrug Study OkLene ThereseNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument5 pagesBrand NameJunrey AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument27 pagesCase StudyMikko Anthony Pingol AlarconNo ratings yet
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study For PneumoniaDocument5 pagesDrugs Study For PneumoniaLucelle ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Asthma Case StudyDocument39 pagesAsthma Case StudyYzel Vasquez AdavanNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy and SoapieDocument17 pagesDrugstudy and SoapieYasi EcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Health HistoryDocument2 pagesHealth HistoryFaisaliah UngkakayNo ratings yet
- Case Study Final PortraitDocument11 pagesCase Study Final PortraitZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Hypertension CASE REPORTDocument57 pagesHypertension CASE REPORTJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- KamanJan ChloroquineDocument3 pagesKamanJan Chloroquinekimberly_caberteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - AmoxicillinDocument2 pagesDrug Study - AmoxicillinVANESSA PAULA ALGADORNo ratings yet
- I Patient Assessment Data BaseDocument12 pagesI Patient Assessment Data BaseJanice_Fernand_1603No ratings yet
- Hypertension (HTP)Document4 pagesHypertension (HTP)Charmagne Joci EpantoNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia and Risk For AspirationDocument3 pagesHyperthermia and Risk For AspirationAlmyr RimandoNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Cataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DDocument7 pagesCataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DKismet SummonsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MMMCDocument14 pagesDrug Study MMMCKathleen Pagulayan Intalan-GloriosoNo ratings yet
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 pagesCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Acute Pain Related To Inflammatory Response Secondary To InfectionTammy De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanningDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanningAthena Irish LastimosaNo ratings yet
- Vital Signs TPRDocument21 pagesVital Signs TPRfloremer guimalanNo ratings yet
- Ru Ward ClassDocument12 pagesRu Ward ClassAmal MUTIANo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY (Gastro)Document3 pagesCASE STUDY (Gastro)Jake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGail SantosNo ratings yet
- Ongoing AppraisalDocument2 pagesOngoing AppraisalLouisa Marie MirandaNo ratings yet
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoNo ratings yet
- Guada A. Dumapit RN, ManDocument18 pagesGuada A. Dumapit RN, ManAnne B. BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care PlansDocument10 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Bronchitis Nursing Care Planscy belNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelNo ratings yet
- University of Northern PhilippinesDocument6 pagesUniversity of Northern PhilippinesCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationDocument6 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Acute Pain As Evidence by Increased RespirationCamille T. SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP GeDocument14 pagesNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process in Drug TherapyDocument32 pagesNursing Process in Drug TherapyChaseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 1 Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Short TermYumeko JabamiNo ratings yet
- Case Pres A1-RhdDocument11 pagesCase Pres A1-RhdCharm TanyaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyAlisse Sales De-PazNo ratings yet
- EndometriosisDocument6 pagesEndometriosissalamredNo ratings yet
- CiprofloxacinDocument2 pagesCiprofloxacinx483xDNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeDocument4 pagesPathophysiology Cushing S SyndromeMaria Luisa VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Dengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andDocument5 pagesDengue: Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever, Resulting in Bleeding, Low Levels of Blood Platelets andFrance John Evangelista TorresNo ratings yet
- HTP Uti (Artillo)Document2 pagesHTP Uti (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis Group CDocument40 pagesAcute Appendicitis Group CHeart TolenadaNo ratings yet
- Sample Letter Templates (4th Year)Document49 pagesSample Letter Templates (4th Year)Yna LafuenteNo ratings yet
- The Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeFrom EverandThe Ride of Your Life: What I Learned about God, Love, and Adventure by Teaching My Son to Ride a BikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Efm Cip UfDocument6 pagesEfm Cip UfDaneAoneNo ratings yet
- MBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsDocument4 pagesMBA (3 Semester Program) : Financial EconometricsNaqeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Admission Letter CsabDocument1 pageAdmission Letter Csabsuraj mohantyNo ratings yet
- Schematic/Electrical Parts: 36021V5J, V7J 36026V5J, V7J 42026 & 42030V6J With "H" ControlsDocument55 pagesSchematic/Electrical Parts: 36021V5J, V7J 36026V5J, V7J 42026 & 42030V6J With "H" ControlsJose Moreno TorbiscoNo ratings yet
- Aluminium FormworkDocument14 pagesAluminium FormworkebinVettuchirayil100% (6)
- Michael Stephen ResumeDocument2 pagesMichael Stephen ResumeMichael MololuwaNo ratings yet
- Input Output I F 0 1 Inputs Output A B F 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1: Logic GatesDocument2 pagesInput Output I F 0 1 Inputs Output A B F 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1: Logic GatesSam JordanNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction of Diaphragm Walls Embedded in Rock For A Metro ProjectDocument27 pagesDesign and Construction of Diaphragm Walls Embedded in Rock For A Metro ProjectCEG BangladeshNo ratings yet
- Emad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFDocument8 pagesEmad 21522379 Type A KWH PDFEMAD ABDULRAHMAN ABDULLAH HASAN MASHRAH -No ratings yet
- Ipc 2581BDocument9 pagesIpc 2581BlaxenovNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving ProblemsDocument22 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving Problemsnoahzaec100% (2)
- MODULE 4 - E-TechDocument19 pagesMODULE 4 - E-TechElijah GloriaNo ratings yet
- Ode and NameDocument670 pagesOde and Namenavneetkpatil8409No ratings yet
- E4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTDocument12 pagesE4-E5 - Text - Chapter 3. OUTSOURCING - CONTRACT MANAGEMENTAGM S&M-CMNo ratings yet
- GVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFDocument28 pagesGVC To IVC To SVC (Ganges Valley Civilization To Indus Valley Civilization To Sarasvati Valley Civilization) PDFanjanaNo ratings yet
- Vermicast Production For Supporting Plant Growth OrganicallyDocument4 pagesVermicast Production For Supporting Plant Growth OrganicallyJhenalyn Perlada100% (2)
- Secret CodesDocument6 pagesSecret CodesUMANo ratings yet
- Pulse Amplitude ModulationDocument19 pagesPulse Amplitude ModulationShubhangBaghelNo ratings yet
- Siemens 7UT613 7UT633 V4.6 Trafo PTT User Manual ENUDocument6 pagesSiemens 7UT613 7UT633 V4.6 Trafo PTT User Manual ENUkoke404No ratings yet
- ISA 706 (Revised)Document19 pagesISA 706 (Revised)karnanNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Document405 pagesCompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Calisto Junior100% (1)
- Imam Ash Shafi'EeDocument3 pagesImam Ash Shafi'EeAmalia AmiraNo ratings yet
- Egurukul OrbitDocument8 pagesEgurukul OrbitbetsyNo ratings yet
- Ignou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19Document7 pagesIgnou Assignment Wala Ehi 1 Solved Assignment 2018-19NEW THINK CLASSES100% (1)
- Paws of DestinyDocument2 pagesPaws of Destinytest dataNo ratings yet
- 8344 20466 1 PBDocument11 pages8344 20466 1 PBpetra taeNo ratings yet
- Critical Areas of Structural Concerns On Bulk Carriers / Dry Cargo ShipsDocument5 pagesCritical Areas of Structural Concerns On Bulk Carriers / Dry Cargo ShipsHUNG LE THANHNo ratings yet