Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Uploaded by
Joshua Miguel De laraCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- How To Check Client or Fullz Credit Score@BaddestupdateDocument7 pagesHow To Check Client or Fullz Credit Score@Baddestupdatecolton gallahar100% (2)
- 94.cold Forging Cost Estimation SheetDocument5 pages94.cold Forging Cost Estimation SheetVenkateswaran venkateswaranNo ratings yet
- PPR 100 Pipes and Fittings Updated Price List 07 March 2023Document1 pagePPR 100 Pipes and Fittings Updated Price List 07 March 2023Sj interiorNo ratings yet
- Biryani Research PaperDocument11 pagesBiryani Research PaperRaamji Mp100% (1)
- Decideware Marketing Procurement Similar But Different WhitepaperDocument8 pagesDecideware Marketing Procurement Similar But Different WhitepaperlrNo ratings yet
- Organisational EffectivenessDocument25 pagesOrganisational Effectivenessbhagatgourav3100% (1)
- Unit 4 ObDocument15 pagesUnit 4 ObSweety BansalNo ratings yet
- Determining EffectivenessDocument14 pagesDetermining EffectivenessLipika haldarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 OB Organizational Effectiveness ReDocument12 pagesChapter - 15 OB Organizational Effectiveness Rep bbNo ratings yet
- Strategy Organization Design and EffectivenessDocument20 pagesStrategy Organization Design and EffectivenessAnne Kristel RagaNo ratings yet
- Organisational Theory Structure and DesignDocument6 pagesOrganisational Theory Structure and DesignSolve AssignmentNo ratings yet
- Session - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignDocument26 pagesSession - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignBhargavNo ratings yet
- Effective Org - FinalDocument14 pagesEffective Org - FinalISAGANINo ratings yet
- What Is Organization DevelopmentDocument7 pagesWhat Is Organization DevelopmentViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness Is The Degree To Which An Organization Attains ItsDocument46 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness Is The Degree To Which An Organization Attains ItsRoos JansenNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change and Development: Diagnosis Process Book Chapter 5Document17 pagesOrganizational Change and Development: Diagnosis Process Book Chapter 5Kh Aqeel FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Organisational Change and DevelopementDocument7 pagesOrganisational Change and Developementsindu akileshNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structures and DesignDocument28 pagesOrganisation Structures and DesignSantosh Bagwe50% (2)
- Chapter 6 A Organizational EffectivenessDocument3 pagesChapter 6 A Organizational EffectivenessKavya MuraliNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Organization and Its EnviornmentDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 Organization and Its Enviornmentharsh hariharnoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Organizations As SystemsDocument78 pagesLecture 8 Organizations As SystemsgichehaesthernjeriNo ratings yet
- Od Change MGTDocument7 pagesOd Change MGTSrideb SahaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1 - Gael Sebastián González RincónDocument12 pagesActivity 2.1 - Gael Sebastián González Rincónsebgonzalez072006No ratings yet
- PM TheoriesDocument26 pagesPM TheoriesTesfaye KebedeNo ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness: Learning ObjectivesVikasBhatNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational Development?Document3 pagesWhat Is Organizational Development?Yusra Jamil0% (1)
- Organization As A System - FinalDocument19 pagesOrganization As A System - FinalShehnaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1De SaravananNo ratings yet
- The Systems App-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesThe Systems App-WPS Office7lightbrightNo ratings yet
- Organizational DevelopmentDocument6 pagesOrganizational DevelopmentMizan HawladerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Ment Organisation DevelopDocument83 pagesLecture - Ment Organisation DevelopHaribhaskar GovindarajuluNo ratings yet
- Organisation DevelopmentDocument52 pagesOrganisation Developmentshweta_46664100% (7)
- Organisational Structure and HR Alignment Book Notes - CH1Document5 pagesOrganisational Structure and HR Alignment Book Notes - CH1uma sankarNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Organization ManagementDocument38 pagesGroup 3 Organization ManagementSophia Marielle MacarineNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument10 pagesUnit IiiNivas NiviNo ratings yet
- Almeria: Name IDDocument12 pagesAlmeria: Name IDحاتم السعداويNo ratings yet
- Congruence in Organization 2020Document31 pagesCongruence in Organization 2020Maria Araceli JulianoNo ratings yet
- OrganizationtheoriesDocument27 pagesOrganizationtheoriesUmair MoinNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment For OBDocument30 pagesGroup Assignment For OBluldavidyianNo ratings yet
- Organitational Development and ChangeDocument56 pagesOrganitational Development and ChangeSari Marta Krisna IINo ratings yet
- Hazara Univers Ity Manse Hra: AssignmentDocument9 pagesHazara Univers Ity Manse Hra: AssignmentJan Sheer ShahNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational DevelopmentDocument7 pagesWhat Is Organizational Developmentneha9890No ratings yet
- Od15 090520060557 Phpapp02Document31 pagesOd15 090520060557 Phpapp02Shubhs TayalNo ratings yet
- Organization DevelopmentDocument23 pagesOrganization DevelopmentJoseph Anbarasu83% (6)
- Organization and DevelopmentDocument33 pagesOrganization and DevelopmentJoanna GadiaNo ratings yet
- MGMT628-MidTerm-Subjective Solved Spring 2011 by RajpootDocument9 pagesMGMT628-MidTerm-Subjective Solved Spring 2011 by RajpootThe Leo LoverNo ratings yet
- Organizations and Organization Theory: Chapter OneDocument4 pagesOrganizations and Organization Theory: Chapter Onedramane007No ratings yet
- Systems ApproachDocument10 pagesSystems Approachsimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- Organizationalstructure FinalDocument49 pagesOrganizationalstructure FinalSudha YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2Muhammad FarezNo ratings yet
- Ot PPT Chapter 1Document57 pagesOt PPT Chapter 1Nasri IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Organizing - IntroductionDocument13 pagesOrganizing - IntroductionMrigakshi Sharma BarthakurNo ratings yet
- What Is An OD InterventionDocument16 pagesWhat Is An OD InterventionSujith Kumar100% (1)
- Organizational Capacity Development Measurement: Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesOrganizational Capacity Development Measurement: Executive SummaryFritz HaryadiNo ratings yet
- Od Introc1august142023Document41 pagesOd Introc1august142023cartilla.eleizhelNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument9 pagesOrganizational BehaviordonyjosemathewNo ratings yet
- Matthews AssessingOrganizationalEffectiveness 2011Document29 pagesMatthews AssessingOrganizationalEffectiveness 2011sharmaprateek2005No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Theory and Practice of Public AdministrationDocument25 pagesTheory and Practice of Public AdministrationBryan TamayoNo ratings yet
- Concerns of Performance ManagementDocument4 pagesConcerns of Performance ManagementsunithaanugrahaNo ratings yet
- 1, Chapter 3 - Organizational EffectivenessDocument24 pages1, Chapter 3 - Organizational EffectivenessBushra Mubeen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsFrom EverandA Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Handbook for Strategic HR - Section 4: Thinking Systematically and StrategicallyFrom EverandHandbook for Strategic HR - Section 4: Thinking Systematically and StrategicallyNo ratings yet
- Part 6Document8 pagesPart 6Amr YoussefNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Youth Attraction in Bikano at BikanervalaDocument31 pagesA Project Report ON: Youth Attraction in Bikano at Bikanervalamanoj kumar Das67% (3)
- Course: Marketing Research: Faculty of International Economic Relations Semester 1, 2021 - 2022Document2 pagesCourse: Marketing Research: Faculty of International Economic Relations Semester 1, 2021 - 2022Thảo NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IBK Bank - AR SR 2022 - 230512 - 20230605.101636.632Document368 pagesIBK Bank - AR SR 2022 - 230512 - 20230605.101636.632Ivena Oriana 201210003No ratings yet
- Operations StrategyDocument26 pagesOperations Strategysulabhagarwal1985No ratings yet
- Drought in India - Causes, Effects and MeasuresDocument55 pagesDrought in India - Causes, Effects and MeasuresDr Rajendran T100% (6)
- DO 178 ProjectDocument9 pagesDO 178 Projectml12783919No ratings yet
- Grace Corporation: Statement of Management's Responsibility For Financial StatementsDocument14 pagesGrace Corporation: Statement of Management's Responsibility For Financial StatementsLaiza Joyce Sales100% (2)
- Accountancy Project On BRSDocument11 pagesAccountancy Project On BRSBiplab Swain100% (10)
- Industrial VisitDocument8 pagesIndustrial VisitmarySibiliaNo ratings yet
- 110 KV Outsourcing BP PDFDocument4 pages110 KV Outsourcing BP PDFKamiki BigiliNo ratings yet
- Apple Business Manager Getting Started GuideDocument11 pagesApple Business Manager Getting Started GuideHeidi BonillaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PROPOSAL SEC A - Group 3Document25 pagesBUSINESS PROPOSAL SEC A - Group 3sanandi DASNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation StatementDocument7 pagesBank Reconciliation StatementAhmed DeoNo ratings yet
- Tess Zero Accident Program For ZAP Conf 09Document29 pagesTess Zero Accident Program For ZAP Conf 09Armin GomezNo ratings yet
- Odoo v15Document5 pagesOdoo v15t.nominerdene99No ratings yet
- A Toolbox For Innovation and Customer-Centricity-Microsoft Press (2014)Document574 pagesA Toolbox For Innovation and Customer-Centricity-Microsoft Press (2014)Obuka ObukaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis (Leisure and Entertainment World)Document7 pagesSynopsis (Leisure and Entertainment World)Sejal SarafNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Coca ColaDocument16 pagesRatio Analysis of Coca ColaAlwina100% (1)
- Prachi Jain - PGFA2036Document5 pagesPrachi Jain - PGFA2036NISHA CHANDANI Jaipuria JaipurNo ratings yet
- Tds On Provison of Expenses (Tax Gls Open For Direct Manual Posting On 17.04.23 & 18.04.23 Only by Corporate Office) Urgent & Statuary ComplianceDocument1 pageTds On Provison of Expenses (Tax Gls Open For Direct Manual Posting On 17.04.23 & 18.04.23 Only by Corporate Office) Urgent & Statuary ComplianceArvind Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- ASIAN Paints DistrbnDocument12 pagesASIAN Paints Distrbnapi-3719687100% (9)
- June Current Affair Magazine Jokta AcademyDocument76 pagesJune Current Affair Magazine Jokta AcademyAshish ParmarNo ratings yet
- DataStage Solution BriefDocument5 pagesDataStage Solution Briefbane komnenovicNo ratings yet
- Concrete Construction Practical Problems and Solutions Akhtar H. Surahyo 9780195797770 Amazon - Com Books PDFDocument3 pagesConcrete Construction Practical Problems and Solutions Akhtar H. Surahyo 9780195797770 Amazon - Com Books PDFJiabin LiNo ratings yet
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Uploaded by
Joshua Miguel De laraOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Organizations and Organizational Effectiveness
Uploaded by
Joshua Miguel De laraCopyright:
Available Formats
ORGANIZATIONS AND ORGANIZATIONAL EFFECTIVENESS
ORGANIZATIONS - A social unit of people that is structured and managed to meet a need or to
pursue collective goals. All organizations have a management structure that determines
relationships between the different activities and the members, and subdivides and assigns roles,
responsibilities, and authority to carry out different tasks. Organizations are open systems-they
affect and are affected by their environment.
CONCEPT OF ORGANIZATIONAL EFFECTIVE
• Organizational effectiveness is defined as an extent to which an organization achieves its
predetermined objectives with the given amount of resources and means without placing
undue strain on its members.
• However, the concept of organizational effectiveness is not simple because there are many
approaches in conceptualizing this term. Such approaches can be grouped into following
three approaches:
• Goal Approach - Effectiveness refers to maximization of profits by providing an
efficient service that leads to high productivity and good employee morale. Several
variables such as high productivity, employees’ high morale, satisfaction, profit
maximizations, turnover, employee efficiency, quality, accidents, and motivation,
which help in measuring organizational effectiveness. However, none of the single
variable has proved to be entirely satisfactory.
• Function Approach - Parson states that since it has been assumed that an
organization is identified in terms of its goal, focus towards attainment of these
goals should also aim at serving the society. Thus, the vital question in determining
effectiveness is how well an organization is doing for the super-ordinate system.
The limitation of this approach is that when organizations have autonomy to follow
its independent courses of action, it is difficult to accept that the ultimate goal of
organization will be to serve the society. As such, it cannot be applied for measuring
organizational effectiveness in terms of its contributions to social system.
Both the goal and functional approach do not give adequate consideration to the
conceptual problem of the relations between the organization and its environment.
• System Resource Approach - System-resource approach of organizational
effectiveness emphasizes on inter-dependency of processes that relate the
organization to its environment. The interdependence takes the form of input
through output transactions and includes scarce and valued resources such as
physical, economic and human for which every organization competes.
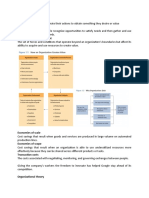
Factors Affecting Organizational Effectiveness
• Causal Variables are those independent variables that determine the course of
developments within an organization and the objectives achieved by an organization. It
includes organization and management’s policies, decisions, business and leadership
strategies, skills and behavior.
• Intervening variables according to Likert are those variables that will reflect the internal
state and health of the organization. An example are loyalties, attitudes, motivations,
performance goals and perceptions of all the members and their collective capacity for
effective interaction, communication and decision-making.
• End-Result variables are the dependent variables that will reflect the achievements of the
organization such as productivity, costs, loss and earnings.
Inter-Relationship of Variables
• The inter-relationship may be visualized as psychological process where the causal
variables acting upon the organism or intervening variables and creating certain responses
or end-result variables.
Organizational Effectiveness Model
• The organizational effectiveness model can be presented in a more complex way. An
example of these are the three different levels such as the individual, group and
organizational levels in order to make the organization more effective. The effective
organization is built of effective individuals who work collectively in groups.
5 Major reasons why organizations exist:
• To increase specialization and the division of labor
• Division of labor allows specialization
• Specialization allows individuals to become experts at their job
• To use large-scale technology
• Economies of scale: cost savings that result when goods and services are produced in large
volume
References:
https://www.mbaknol.com/modern-management-concepts/concept-of-organizational-
effectiveness/
https://www.slideserve.com/adria-lee/organization-theory-chapter-3-organizing-in-a-changing-
global-environment-gareth-r-jones
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/organization.html
https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/how-can-organizing-changing-global-environment-
333149
https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/todays-environment-which-more-important-340013
You might also like
- How To Check Client or Fullz Credit Score@BaddestupdateDocument7 pagesHow To Check Client or Fullz Credit Score@Baddestupdatecolton gallahar100% (2)
- 94.cold Forging Cost Estimation SheetDocument5 pages94.cold Forging Cost Estimation SheetVenkateswaran venkateswaranNo ratings yet
- PPR 100 Pipes and Fittings Updated Price List 07 March 2023Document1 pagePPR 100 Pipes and Fittings Updated Price List 07 March 2023Sj interiorNo ratings yet
- Biryani Research PaperDocument11 pagesBiryani Research PaperRaamji Mp100% (1)
- Decideware Marketing Procurement Similar But Different WhitepaperDocument8 pagesDecideware Marketing Procurement Similar But Different WhitepaperlrNo ratings yet
- Organisational EffectivenessDocument25 pagesOrganisational Effectivenessbhagatgourav3100% (1)
- Unit 4 ObDocument15 pagesUnit 4 ObSweety BansalNo ratings yet
- Determining EffectivenessDocument14 pagesDetermining EffectivenessLipika haldarNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15 OB Organizational Effectiveness ReDocument12 pagesChapter - 15 OB Organizational Effectiveness Rep bbNo ratings yet
- Strategy Organization Design and EffectivenessDocument20 pagesStrategy Organization Design and EffectivenessAnne Kristel RagaNo ratings yet
- Organisational Theory Structure and DesignDocument6 pagesOrganisational Theory Structure and DesignSolve AssignmentNo ratings yet
- Session - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignDocument26 pagesSession - 1 Significance of Organization Structure and DesignBhargavNo ratings yet
- Effective Org - FinalDocument14 pagesEffective Org - FinalISAGANINo ratings yet
- What Is Organization DevelopmentDocument7 pagesWhat Is Organization DevelopmentViraja GuruNo ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness Is The Degree To Which An Organization Attains ItsDocument46 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness Is The Degree To Which An Organization Attains ItsRoos JansenNo ratings yet
- Organizational Change and Development: Diagnosis Process Book Chapter 5Document17 pagesOrganizational Change and Development: Diagnosis Process Book Chapter 5Kh Aqeel FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Organisational Change and DevelopementDocument7 pagesOrganisational Change and Developementsindu akileshNo ratings yet
- Organisation Structures and DesignDocument28 pagesOrganisation Structures and DesignSantosh Bagwe50% (2)
- Chapter 6 A Organizational EffectivenessDocument3 pagesChapter 6 A Organizational EffectivenessKavya MuraliNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Organization and Its EnviornmentDocument6 pagesUNIT 1 Organization and Its Enviornmentharsh hariharnoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Organizations As SystemsDocument78 pagesLecture 8 Organizations As SystemsgichehaesthernjeriNo ratings yet
- Od Change MGTDocument7 pagesOd Change MGTSrideb SahaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.1 - Gael Sebastián González RincónDocument12 pagesActivity 2.1 - Gael Sebastián González Rincónsebgonzalez072006No ratings yet
- PM TheoriesDocument26 pagesPM TheoriesTesfaye KebedeNo ratings yet
- Organizational Effectiveness: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 pagesOrganizational Effectiveness: Learning ObjectivesVikasBhatNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational Development?Document3 pagesWhat Is Organizational Development?Yusra Jamil0% (1)
- Organization As A System - FinalDocument19 pagesOrganization As A System - FinalShehnaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document20 pagesUnit 1De SaravananNo ratings yet
- The Systems App-WPS OfficeDocument12 pagesThe Systems App-WPS Office7lightbrightNo ratings yet
- Organizational DevelopmentDocument6 pagesOrganizational DevelopmentMizan HawladerNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Ment Organisation DevelopDocument83 pagesLecture - Ment Organisation DevelopHaribhaskar GovindarajuluNo ratings yet
- Organisation DevelopmentDocument52 pagesOrganisation Developmentshweta_46664100% (7)
- Organisational Structure and HR Alignment Book Notes - CH1Document5 pagesOrganisational Structure and HR Alignment Book Notes - CH1uma sankarNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Organization ManagementDocument38 pagesGroup 3 Organization ManagementSophia Marielle MacarineNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument10 pagesUnit IiiNivas NiviNo ratings yet
- Almeria: Name IDDocument12 pagesAlmeria: Name IDحاتم السعداويNo ratings yet
- Congruence in Organization 2020Document31 pagesCongruence in Organization 2020Maria Araceli JulianoNo ratings yet
- OrganizationtheoriesDocument27 pagesOrganizationtheoriesUmair MoinNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment For OBDocument30 pagesGroup Assignment For OBluldavidyianNo ratings yet
- Organitational Development and ChangeDocument56 pagesOrganitational Development and ChangeSari Marta Krisna IINo ratings yet
- Hazara Univers Ity Manse Hra: AssignmentDocument9 pagesHazara Univers Ity Manse Hra: AssignmentJan Sheer ShahNo ratings yet
- What Is Organizational DevelopmentDocument7 pagesWhat Is Organizational Developmentneha9890No ratings yet
- Od15 090520060557 Phpapp02Document31 pagesOd15 090520060557 Phpapp02Shubhs TayalNo ratings yet
- Organization DevelopmentDocument23 pagesOrganization DevelopmentJoseph Anbarasu83% (6)
- Organization and DevelopmentDocument33 pagesOrganization and DevelopmentJoanna GadiaNo ratings yet
- MGMT628-MidTerm-Subjective Solved Spring 2011 by RajpootDocument9 pagesMGMT628-MidTerm-Subjective Solved Spring 2011 by RajpootThe Leo LoverNo ratings yet
- Organizations and Organization Theory: Chapter OneDocument4 pagesOrganizations and Organization Theory: Chapter Onedramane007No ratings yet
- Systems ApproachDocument10 pagesSystems Approachsimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- Organizationalstructure FinalDocument49 pagesOrganizationalstructure FinalSudha YadavNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document6 pagesTutorial 2Muhammad FarezNo ratings yet
- Ot PPT Chapter 1Document57 pagesOt PPT Chapter 1Nasri IBRAHIMNo ratings yet
- Organizing - IntroductionDocument13 pagesOrganizing - IntroductionMrigakshi Sharma BarthakurNo ratings yet
- What Is An OD InterventionDocument16 pagesWhat Is An OD InterventionSujith Kumar100% (1)
- Organizational Capacity Development Measurement: Executive SummaryDocument12 pagesOrganizational Capacity Development Measurement: Executive SummaryFritz HaryadiNo ratings yet
- Od Introc1august142023Document41 pagesOd Introc1august142023cartilla.eleizhelNo ratings yet
- Organizational BehaviorDocument9 pagesOrganizational BehaviordonyjosemathewNo ratings yet
- Matthews AssessingOrganizationalEffectiveness 2011Document29 pagesMatthews AssessingOrganizationalEffectiveness 2011sharmaprateek2005No ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument22 pagesHuman Resource ManagementAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Theory and Practice of Public AdministrationDocument25 pagesTheory and Practice of Public AdministrationBryan TamayoNo ratings yet
- Concerns of Performance ManagementDocument4 pagesConcerns of Performance ManagementsunithaanugrahaNo ratings yet
- 1, Chapter 3 - Organizational EffectivenessDocument24 pages1, Chapter 3 - Organizational EffectivenessBushra Mubeen SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Building Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsFrom EverandBuilding Winning Organisations: A complete guide to sustaining best-in-class performance for all organisationsNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsFrom EverandA Guide to Collaboration: Working Models of Comprehensive Community ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Handbook for Strategic HR - Section 4: Thinking Systematically and StrategicallyFrom EverandHandbook for Strategic HR - Section 4: Thinking Systematically and StrategicallyNo ratings yet
- Part 6Document8 pagesPart 6Amr YoussefNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON: Youth Attraction in Bikano at BikanervalaDocument31 pagesA Project Report ON: Youth Attraction in Bikano at Bikanervalamanoj kumar Das67% (3)
- Course: Marketing Research: Faculty of International Economic Relations Semester 1, 2021 - 2022Document2 pagesCourse: Marketing Research: Faculty of International Economic Relations Semester 1, 2021 - 2022Thảo NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IBK Bank - AR SR 2022 - 230512 - 20230605.101636.632Document368 pagesIBK Bank - AR SR 2022 - 230512 - 20230605.101636.632Ivena Oriana 201210003No ratings yet
- Operations StrategyDocument26 pagesOperations Strategysulabhagarwal1985No ratings yet
- Drought in India - Causes, Effects and MeasuresDocument55 pagesDrought in India - Causes, Effects and MeasuresDr Rajendran T100% (6)
- DO 178 ProjectDocument9 pagesDO 178 Projectml12783919No ratings yet
- Grace Corporation: Statement of Management's Responsibility For Financial StatementsDocument14 pagesGrace Corporation: Statement of Management's Responsibility For Financial StatementsLaiza Joyce Sales100% (2)
- Accountancy Project On BRSDocument11 pagesAccountancy Project On BRSBiplab Swain100% (10)
- Industrial VisitDocument8 pagesIndustrial VisitmarySibiliaNo ratings yet
- 110 KV Outsourcing BP PDFDocument4 pages110 KV Outsourcing BP PDFKamiki BigiliNo ratings yet
- Apple Business Manager Getting Started GuideDocument11 pagesApple Business Manager Getting Started GuideHeidi BonillaNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PROPOSAL SEC A - Group 3Document25 pagesBUSINESS PROPOSAL SEC A - Group 3sanandi DASNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation StatementDocument7 pagesBank Reconciliation StatementAhmed DeoNo ratings yet
- Tess Zero Accident Program For ZAP Conf 09Document29 pagesTess Zero Accident Program For ZAP Conf 09Armin GomezNo ratings yet
- Odoo v15Document5 pagesOdoo v15t.nominerdene99No ratings yet
- A Toolbox For Innovation and Customer-Centricity-Microsoft Press (2014)Document574 pagesA Toolbox For Innovation and Customer-Centricity-Microsoft Press (2014)Obuka ObukaNo ratings yet
- Synopsis (Leisure and Entertainment World)Document7 pagesSynopsis (Leisure and Entertainment World)Sejal SarafNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis of Coca ColaDocument16 pagesRatio Analysis of Coca ColaAlwina100% (1)
- Prachi Jain - PGFA2036Document5 pagesPrachi Jain - PGFA2036NISHA CHANDANI Jaipuria JaipurNo ratings yet
- Tds On Provison of Expenses (Tax Gls Open For Direct Manual Posting On 17.04.23 & 18.04.23 Only by Corporate Office) Urgent & Statuary ComplianceDocument1 pageTds On Provison of Expenses (Tax Gls Open For Direct Manual Posting On 17.04.23 & 18.04.23 Only by Corporate Office) Urgent & Statuary ComplianceArvind Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- ASIAN Paints DistrbnDocument12 pagesASIAN Paints Distrbnapi-3719687100% (9)
- June Current Affair Magazine Jokta AcademyDocument76 pagesJune Current Affair Magazine Jokta AcademyAshish ParmarNo ratings yet
- DataStage Solution BriefDocument5 pagesDataStage Solution Briefbane komnenovicNo ratings yet
- Concrete Construction Practical Problems and Solutions Akhtar H. Surahyo 9780195797770 Amazon - Com Books PDFDocument3 pagesConcrete Construction Practical Problems and Solutions Akhtar H. Surahyo 9780195797770 Amazon - Com Books PDFJiabin LiNo ratings yet