Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histology Points of Indentifications 1st Year-1
Histology Points of Indentifications 1st Year-1
Uploaded by
Sikandar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesThis document provides identification points for 46 different tissues in the human body. It lists the key characteristics to identify each tissue under a microscope, such as their cell shape, layering, presence of glands or cartilage, and other distinguishing microscopic features. Some of the tissues included are simple squamous epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, cardiac muscle, nerve, lymph node, mammary gland, lung, cartilage and bone. This guide aims to help first year medical students learn to distinguish different tissues by their histological characteristics.
Original Description:
Histology identification points
Original Title
Histology Points of Indentifications 1st year-1-converted
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides identification points for 46 different tissues in the human body. It lists the key characteristics to identify each tissue under a microscope, such as their cell shape, layering, presence of glands or cartilage, and other distinguishing microscopic features. Some of the tissues included are simple squamous epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, cardiac muscle, nerve, lymph node, mammary gland, lung, cartilage and bone. This guide aims to help first year medical students learn to distinguish different tissues by their histological characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views3 pagesHistology Points of Indentifications 1st Year-1
Histology Points of Indentifications 1st Year-1
Uploaded by
SikandarThis document provides identification points for 46 different tissues in the human body. It lists the key characteristics to identify each tissue under a microscope, such as their cell shape, layering, presence of glands or cartilage, and other distinguishing microscopic features. Some of the tissues included are simple squamous epithelium, stratified squamous epithelium, cardiac muscle, nerve, lymph node, mammary gland, lung, cartilage and bone. This guide aims to help first year medical students learn to distinguish different tissues by their histological characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Histology Points of Identification
1st year MBBS
No. Tissue Identification points
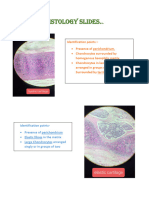
1. Simple Squamous • Elongated cells with bulging nuclei on side – view
epithelium • single layer of squamous (flattened) cells with rounded
central nuclei on surface- view
2. Simple Cuboidal • Height and width of cells equal.
Epithelium • Single layer of cubical cells with central rounded nuclei
3. Simple Columnar • Height of cells is more than width.
Epithelium • Single layer of elongated cells containing elongated nuclei
towards their bases.
4. Pseudostratifled • Single layer of cells; all cells rest on basement membrane.
epithelium • Some cells columnar and others cuboidal.
• The nuclei of cells are at different levels; giving a false
appearance of many layers.
5. Stratified • Basal layer of cuboidal / columnar cells
Squamous • Middle 2-3 layer of polygonal cells
epithelium • Multilayered
• Superficial flattened cells.
6. Stratified Cuboidal • Basal layer of cuboidal or columnar
epithelium • Multilayered
• Surface cells are cuboidal in shape.
7. Stratified columnar • Basal cells are cuboidal in shape
epithelium • Multilayered
• Surface cells are columnar in shape
8. Transitional • Deepest cuboidal cells
Epithelium • Dome cells in surfacelayer
• Pear shaped cells in middle layer
9. Adipose tissue • Empty looking
(white Fat) • Large ovoid closely packed cells
• Marginal nucleus (signet-ring appearance)
10. Adipose tissue • Central nucleus
(Brown Fat) • Empty looking
• Small ovoid closely packed cells
11. Tendon(Dense • C.T covering fibers and bundies.
Regular collagenous • Parallel running collagen fibers with nuclei of fibroblasts in
Connective tissue) between
12 Ligament(Dense • Elastic fibers slightly overlapping with nuclei of fibroblastsin
Regular elastic between
Connective tissue) • Nuclei of fibroblasts are larger
13 Loos Areolar C.T • C.T cells in between
• Irregularly arranged fibers of all types
14. Mucoid C. T • Fibroblasts with nuclei in ground substance
(embryonic) • Loosely arranged collagen fibers
15. Cartilage-hyaline • Isogenous group of cartilage cells in lacunae
• Pearly bluish, homogeneous and glassy appearance of matrix
• Perichondrium
Histology Points of Identification
1st year MBBS
19. Cartilage- elastic • Elastic fibers in matrix
• Perichondrium
20. Cartilage-white • Chondrocytes in rows
fibrous • Collagen fibers in matrix
(fibrocartilage) • Perichondrium is absent
21. Compact bone • Central and volkman’s canal
• Characteristic lamellae
• Typical bone cells
22 Spongy bone • Few haversian systems
• Hemopoietic (bone marrow) tissue
• Trabeculae of bone matrix
23. Smooth muscles • Central single nucleus
• Non- satiated
• Spindle shaped cells
• Tapering edges
24. Skeletal muscles • Striated
• Multiple peripheral nuclei
• Non- branching
25. Cardiac muscles • Branching
• Center nuclei
• Intercalated discs
• Striated
26. Nerve (peripheral) • Bundles of nerve fibers (myelinated & unmyelinated) both in
cross and longitudinal sections
• Myelin sheath is visible as unstained areas.
• Ordinary C.T is seen as endo-,peri- & epineurium
27. Sensory ganglion • Central medulla is made up of nerve fibers
• Cell bodies are collected in groups towards periphery
• Cells are psuedounipolar
28. Autonomic ganglion • Cell bodies are scattered diffusely
• Cells are multipolar with irregular shapes
32. Lymph Node • Hilum containing efferent lymphatics
• Lymph nodules without central arteriole are situated in the
cortex.
• Medullary cords
33. Palatine tonsil • Characteristics non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelial
covering
• Tonsillar epithelium crypts
34. Pharyngeal tonsil • Lymphatic tissue is more diffuse and (usually not arranged as
typical nodules)
• Covering epithelium is pseudostratified columnar ciliated
epithelium with patches of non-keratinized stratified
squamous epithelium
• Plicae and pleats of surface epithelium are present instead of
crypts.
35. Lingual tonsil • Epithelium is non- keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
• Lymphatic tissue is present as typical nodules as well as
diffused
Histology Points of Identification
1st year MBBS
• Each nodule has single crypt
36. Thymus • Characteristics lobules having cortex and medulla
• Thymic corpuscles
37. Spleen • Red pulp (splenic cords & venous sinuses)
• White pulp (containing splenic nodules with definite central
arterioles)
• No differentiation into cortex and medulla
38. Thin skin • Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
• Dermal papillae
• Hair roots and follicles
• Sebaceous glands
• Coiled tubular sweat glands
39. Thick skin • Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium with five distinct
layers
• No hair roots and follicles
40. Mammary gland – • Cord like tubules lined by simple cuboidal epithelium
inactive state • Much more inter tubular
• Absence of alveoli
42. Mammary gland • Scanty connective tissue stroma
(lactating state) • Alveoli of various sizes and shapes and full of secretions
• Highly development ducts
44. Trachea • pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
• c- Shaped hyaline cartilage
• Trachealis muscle
• Tracheal glands
45. Lung • Serosa
• Alveoli (lined by simple squamous epithelium)
• Bronchioles and bronchi
46 Epiglottis • Elastic cartilage
• Stratified squamous non-keratinized and pseudostratified
ciliated columnar epithelia containing goblet cells
COMPILED BY : MOHSIN FIAZ
You might also like
- Important For ExamDocument11 pagesImportant For ExamJagveer ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document4 pagesChapter 4Rhea Mae TabayagNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument97 pagesTissuesnalakaNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 4: Classification of Tissues Martini Chapter 4Document66 pagesLab Activity 4: Classification of Tissues Martini Chapter 4CHULA ANAK BINANo ratings yet
- 4 - Practical 4 Histology, EpitheliumDocument16 pages4 - Practical 4 Histology, EpitheliumAMIRA HELAYELNo ratings yet
- EpitheliaDocument1 pageEpitheliaTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- 10 TissueDocument60 pages10 Tissuebeyonduck100% (1)
- Module 3 - BIOSCI2Document30 pagesModule 3 - BIOSCI2Jahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- Histology: The Study of Tissues: - Four TypesDocument17 pagesHistology: The Study of Tissues: - Four TypeswlkernanNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues and Cell ModificationsDocument40 pagesBody Tissues and Cell ModificationsKrystin DiamosNo ratings yet
- Basic Histology-1Document51 pagesBasic Histology-1Zechariah NggitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissues: Zona Occludens Anchoring JunctionsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Tissues: Zona Occludens Anchoring JunctionsrenjiniNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 22Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 22Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- M4 TiisuesDocument8 pagesM4 TiisuesGemarela Salas CapitenioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4, Tissues, Part 2: Histology The Study of Tissues Tissue A Collection of Cells That Perform RelatedDocument31 pagesChapter 4, Tissues, Part 2: Histology The Study of Tissues Tissue A Collection of Cells That Perform RelatedSajid NadafNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument18 pagesHistologyGlavinorNo ratings yet
- 4.1 - Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument94 pages4.1 - Tissue Level of OrganizationEmman ImbuidoNo ratings yet
- Tissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumDocument9 pagesTissue Type Sketch Function Location Notes Simple Squamous EpitheliumKaitlin NooneyNo ratings yet
- Tissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPDocument41 pagesTissues (Histology) : Joash Nathaniel S. Tan, PTRPLleana Tan100% (1)
- Histology Lecture Chapter 3 PrelimDocument8 pagesHistology Lecture Chapter 3 PrelimFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGDocument54 pagesBody Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument41 pagesHuman TissuesMae Ann Mejico EspirituNo ratings yet
- Histology - Epithelial TissuesDocument4 pagesHistology - Epithelial TissuesKrissa OmandamNo ratings yet
- Histology of The Nervous System 2011Document33 pagesHistology of The Nervous System 2011Ng Bing JueNo ratings yet
- Anaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialDocument7 pagesAnaphy and Physiology - Review MaterialKennethNo ratings yet
- ClassificationofTissue EpithDocument16 pagesClassificationofTissue Epithrickflairdrip15No ratings yet
- Lecture-1 With AnnonationDocument39 pagesLecture-1 With AnnonationShaily NainNo ratings yet
- Histology ParticalDocument58 pagesHistology ParticalmagholNo ratings yet
- Histo Paper 2Document117 pagesHisto Paper 2SATVIK RAMNo ratings yet
- Cells & TissuesDocument17 pagesCells & TissuesClaraNo ratings yet
- Lec Activity4tissues CastroDocument9 pagesLec Activity4tissues CastropelielNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and Tissuesgrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- 1 Cells and TissuesDocument3 pages1 Cells and TissuesELI GOZONNo ratings yet
- HMM1414 Chapter 5 Part 1Document56 pagesHMM1414 Chapter 5 Part 1Luqman Al-Bashir FauziNo ratings yet
- 4b Epithelial TissueallDocument43 pages4b Epithelial Tissueallapi-159564163No ratings yet
- Week 4 - TissuesDocument41 pagesWeek 4 - TissuesJuvy CambeNo ratings yet
- Tissue - SeeleyDocument61 pagesTissue - SeeleyJuli Damayanty Harahap100% (1)
- Zoo Lab UwUDocument38 pagesZoo Lab UwUHannah Danniella NapolesNo ratings yet
- Cartilagedr 190528154146Document30 pagesCartilagedr 190528154146Dr.Aman SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument5 pagesHistologySNo ratings yet
- 4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument49 pages4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- EP TissueDocument16 pagesEP Tissueكرار 2No ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals PowerNotesDocument3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals PowerNotesananyatripathy84No ratings yet
- Chapter 4-TissuesDocument32 pagesChapter 4-TissueszainmaryamNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabDocument34 pagesMidterm Study Guide For Anatomy and Physiology 1 LabkabukibearNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - HistologyDocument25 pagesLab 3 - HistologyRite2summaiya SumiNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue EdDocument95 pagesConnective Tissue EdGirmay GebrehiwotNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- TISSUESDocument59 pagesTISSUESWHWHWHWHWWH WWGHWHGWGHW100% (1)
- 02 HistologyDocument9 pages02 HistologyJinnwen MandocdocNo ratings yet
- Week 3Document112 pagesWeek 3Anne nicole P. CasemNo ratings yet
- Bio100 - Le3 ReviewerDocument20 pagesBio100 - Le3 ReviewerMariel De Leon GinesNo ratings yet
- FSC111 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocument75 pagesFSC111 - Cell Structure and FunctionKenneth SilvaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument10 pagesTissuesdenniesjrelefante101622No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument60 pagesTissuesLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- 2.animal TissuesDocument50 pages2.animal TissuesAhmed OrabyNo ratings yet
- Histology Laboratory Practicals Velez Medtech Reviewer 2018 FullDocument31 pagesHistology Laboratory Practicals Velez Medtech Reviewer 2018 FullFilicidad EleseoNo ratings yet
- Ful ReportDocument70 pagesFul Reportchyralis100% (1)
- Gout DietDocument2 pagesGout DietMarina Tomasenco - Danici100% (1)
- Cheikhelard Et Al - 2012 - Gynecologic Clinical Examination of The Child and AdolescentDocument10 pagesCheikhelard Et Al - 2012 - Gynecologic Clinical Examination of The Child and AdolescentBerry BancinNo ratings yet
- Course Code: GPB-713 Course Title: Principles of Plant BreedingDocument24 pagesCourse Code: GPB-713 Course Title: Principles of Plant BreedingAvulavenkatarambabu RambabuNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of A Fall Ball For All Jamie A Swenson Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of A Fall Ball For All Jamie A Swenson Online PDF All Chapternandddbolt100% (7)
- NCM 117-Somatic DisordersDocument5 pagesNCM 117-Somatic DisordersJa DimasNo ratings yet
- Bb3 WHO Classification of Tumors of Haemopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 4th 2008 PGDocument422 pagesBb3 WHO Classification of Tumors of Haemopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues 4th 2008 PGLoredana Milea Ex Lefter100% (1)
- A Systematic Review of Warfarin Use in Post-Bariatric Surgery PatDocument6 pagesA Systematic Review of Warfarin Use in Post-Bariatric Surgery PatGestne AureNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento Vs ECCDocument3 pagesSarmiento Vs ECCEmily LeahNo ratings yet
- Neb Ul Ization 2Document31 pagesNeb Ul Ization 2RegineJoyCarinoNo ratings yet
- Aquate Shrimp Helps Provide Economic Benefit To Shrimp Farmers in HondurasDocument4 pagesAquate Shrimp Helps Provide Economic Benefit To Shrimp Farmers in HondurasInternational Aquafeed magazineNo ratings yet
- Cefalea LancetDocument2 pagesCefalea LancetJohana Zamudio RojasNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy-Induced Secondary MalignanciesDocument9 pagesChemotherapy-Induced Secondary MalignanciesSupandy HasanNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Part - II Qmaths - inDocument91 pagesGeneral Knowledge Part - II Qmaths - inPradeep Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Science Investigatory Project: Universidad de ManilaDocument7 pagesScience Investigatory Project: Universidad de ManilaCassandra AgustinNo ratings yet
- CoViTris2020 and ChloViD2020 A Striking PDFDocument16 pagesCoViTris2020 and ChloViD2020 A Striking PDFgygyNo ratings yet
- Caso Clínico - Neisseria GonorrhoeaeDocument7 pagesCaso Clínico - Neisseria GonorrhoeaeRigobertoNo ratings yet
- Obesity and Anticipated Difficult Airway - A Comprehensive Approach With Videolaryngoscopy, Ramp Position, Sevoflurane and Opioid Free AnaesthesiaDocument8 pagesObesity and Anticipated Difficult Airway - A Comprehensive Approach With Videolaryngoscopy, Ramp Position, Sevoflurane and Opioid Free AnaesthesiaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Leaflet Covid 19 - Pregnant Women PDFDocument2 pagesLeaflet Covid 19 - Pregnant Women PDFBindar AdrianNo ratings yet
- Rosácea PDFDocument5 pagesRosácea PDFRegiane AmorimNo ratings yet
- Revised Research Title Group1Document7 pagesRevised Research Title Group1Nornisah H. PangandamanNo ratings yet
- Astro-Diagnosis, A Guide To Healing, Chapters XXX - XXXIIIDocument14 pagesAstro-Diagnosis, A Guide To Healing, Chapters XXX - XXXIIIOmSilence2651100% (1)
- Infectious Diseases IIDocument57 pagesInfectious Diseases IIAhmad MakhloufNo ratings yet
- Idsa Amr Guidance v3.0Document174 pagesIdsa Amr Guidance v3.0Sejla KotoricNo ratings yet
- OSOM Regs 08Document12 pagesOSOM Regs 08Aymen ElatrashNo ratings yet
- Gecc 125 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyDocument24 pagesGecc 125 - Biodiversity and Healthy SocietyMARIA JEZZA LEDESMANo ratings yet
- 14-Improving SVM Performance For Type II Diabetes Prediction With An Improved Non-Linear Kernel Insights From The PIMA DatasetDocument9 pages14-Improving SVM Performance For Type II Diabetes Prediction With An Improved Non-Linear Kernel Insights From The PIMA Datasetbeefypixel761No ratings yet
- Shoulder PresentationDocument8 pagesShoulder PresentationvincentsharonNo ratings yet
- Introductory Pharmacology - Cancer ChemotherapyDocument9 pagesIntroductory Pharmacology - Cancer ChemotherapyTyler Rosolowski100% (2)