Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP
NCP
Uploaded by
Ginmarie Alcueno Fabillar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pages1) The patient presented with fever and hyperthermia related to dehydration
Original Description:
Original Title
Ncp
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The patient presented with fever and hyperthermia related to dehydration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views4 pagesNCP
NCP
Uploaded by
Ginmarie Alcueno Fabillar1) The patient presented with fever and hyperthermia related to dehydration
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
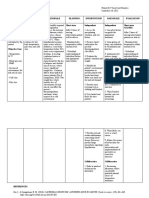
Name: Ginmarie A.
Fabillar Year&Section: BSN-3B
Assessment Nursing Pathophysiology Planning Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Problem Intervention
Subjective •Hyperthermi Fever results •After 4 hrs. Independent: •After 4 hrs.
Data: a related to when something Of nursing Of nursing
dehydration raises the interventions, 1.Monitor 1.Dysrhythmia interventions,
“Mapaso hypothalamic the patient heartrate ands and ECG the patient
ako” as set point, will maintain rhythm. changes are was able to
verbalized triggering core common due to maintain core
by the vasoconstriction temperature electrolyte temperature
patient. and shunting of within 2.Record all imbalance and with in
blood from the normal sources of dehydration normal
Objective periphery to range. fluid loss and direct range.
Cues: decrease heat such as effect of
loss; sometimes urine, hyperthermia
shivering, which vomiting and on blood and
Vital signs: increases heat diarrhea. cardiac tissues.
T- 38.7 production, is
P- 94bpm induced. 3.Promote 2.To monitor
RR- 20cpm surface or potentiates
BP- 140/70 Footnote: Text cooling by fluid and
Author: Larry means of electrolyte
M. Bush tepid sponge loses.
bath.
3.To decrease
4.Wrap temperature by
extremities means through
with cotton evaporation
blankets. and
conduction.
5.Provide
supplemental 4.To minimize
oxygen. shivering.
6.Administer 5.To offset
replacement increased
fluids and oxygen
electrolytes. demands and
consumption
7.Maintain
bedrest. 6.To support
circulating
8.Provide volume and
high calorie tissue
diet, tube perfusion.
feedings, or
parenteral 7.To reduce
nutrition. metabolic
demands and
9.Administer oxygen
antipyretics consumption
orally or
rectally as 8.To increased
prescribed metabolic
by the demands.
physician
9.To facilitate
fast recovery
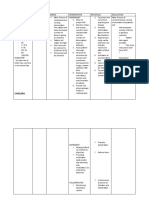
Assessment Nursing Pathophysiology Planning Nursing Rationale Evaluation
Problem Intervention
Subjective Actvity The reflex of After 4 1.Independent: 1.Establishes After 4
Data: intolerance coughing is hours of Evaluate patient's hours of
related to initiated with a nursing patient's capabilities or nursing
“Gin- exhaustion chemical interventions response to needs and interventions
iinubo ako” associated irritation at the patient activity. facilitates the patient
as with peripheral nerve will choice of was able to
verbalized interruptio receptors within demonstrate 2.Provide a interventions demonstrate
by the n in usual the trachea, a quiet Reduces A
patient. sleep main carina, measurable environment stress and measurable
pattern branching points increase in and limit excess increase in
because of of large airways, tolerance in visitors during stimulation, tolerance in
discomfort, and more distal activity with acute phase. promoting activity with
Objective excessive smaller airways. absence of Elevate head rest. absence of
Cues: coughing They are also dyspnea. and encourage dyspnea and
and present in the frequent 2.These excessive
• Dyspnea. dyspnea. pharynx. position measures fatigue.
Laryngeal and changes, deep promotes
V/S taken breathing and maximal
tracheobronchial
as follows: effective inspiration,
receptors
respond to coughing. enhance
T- 37.6
mechanical and expectoratio n
P- 85bpm 3.Encourage
chemical of secretions
RR- 20cpm adequate rest
stimuli. to improve
BP- 110/60 balanced with ventilation.
Footnote: Text moderate
Author: activity. 3.Facilitates
1.Sandeep Promote healing
Sharma adequate process and
2.Muhammad F. nutritional enhances
Hashmi intake. natural
3.Mohamed S. resistance.
Alhajjaj 4. Force fluids 4.Force fluids
to at least to at least
3000 ml per 3000 ml per
day and offer day and offer
warm, rather warm, rather
than cold than cold
fluids. fluids.
Collaborative: Collaborative:
Administer Administer
medications as medications
prescribe: as prescribe:
mucolytics or mucolytics or
expectorants expectorants
You might also like
- TBDY 2018 EnglishDocument608 pagesTBDY 2018 EnglishaygunbayramNo ratings yet
- Anemia NCPDocument10 pagesAnemia NCPCharmz_asherah100% (10)
- Cues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues: Subjective/ Objective Background of The Disease Nursing Diagnosis Goal/ Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMaria Margaret Macasaet0% (1)
- The British Student's Guide To Obtaining Your Visa To Study at The Islamic University of Madinah v.2Document76 pagesThe British Student's Guide To Obtaining Your Visa To Study at The Islamic University of Madinah v.2Nouridine El KhalawiNo ratings yet
- Glycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaDocument306 pagesGlycine As A Lixiviant For The Leaching of Low Grade Copper Gold Ores Bennson Chemuta TandaJavierAntonioGuardiolaEsparzaNo ratings yet
- Computer Siwes Web DesignDocument16 pagesComputer Siwes Web DesignKareemSeyeGanzboy0% (1)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goals of Care Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharles Dave AgustinNo ratings yet
- ROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPDocument6 pagesROSABIA, Micaela Pauline J. .-BSN-2A-ISDH-GS-NURSERY-NCPkimberly quitonNo ratings yet
- المستند (7) Document3 pagesالمستند (7) Mawadh AlsbhiNo ratings yet
- Medical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameDocument4 pagesMedical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5 Patient's NameHadeer Mahmoud Abuslima100% (1)
- NCP Form Hyper ThermDocument1 pageNCP Form Hyper ThermomarskyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJobelyn TunayNo ratings yet
- Colle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesColle Ofn: Nursing Care PlanDara Sophia EncarguezNo ratings yet
- NCPsDocument11 pagesNCPsJobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis NCPDocument6 pagesGastroenteritis NCPKaguraNo ratings yet
- Date/Tim e Cues Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals Objectives Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesDate/Tim e Cues Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Basis Goals Objectives Criteria Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationpjcolitaNo ratings yet
- NCP No. 2Document2 pagesNCP No. 2Lorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanLegendX100% (1)
- Lacanlale, Kristle Anne F. BSN 1Y-2-Irr 1 Group 2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument4 pagesLacanlale, Kristle Anne F. BSN 1Y-2-Irr 1 Group 2: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationKristle Anne Federigan - LacanlaleNo ratings yet
- Subjective: Diarrhea Related To Watery Short Term: IndependentDocument4 pagesSubjective: Diarrhea Related To Watery Short Term: IndependentEmma Lyn SantosNo ratings yet
- Fluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Document2 pagesFluid Volume Deficit Related To Loose Watery Stool Diarrhea)Jesse James Advincula Edjec100% (15)
- NCP 4Document2 pagesNCP 4ako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoDocument2 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: Sto: DX StoBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- Volume 1Document2 pagesVolume 1roxybiscanteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Nursinng Evaluation Subjective DataDocument17 pagesNursing Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Nursinng Evaluation Subjective DataJake AllegoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Classwork Format Level I CCMC-CN Second Semester A.Y. 2020-2021Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Classwork Format Level I CCMC-CN Second Semester A.Y. 2020-2021Mary Ella Mae PilaNo ratings yet
- 6 NCPDocument8 pages6 NCPKlint IntervencionNo ratings yet
- "Nilalagnat Ang Anak Ko." AsDocument2 pages"Nilalagnat Ang Anak Ko." AsgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- Assesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssesment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTrisha Suazo100% (1)
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPmahangin85% (20)
- PNEUMONIADocument8 pagesPNEUMONIARica ParcasioNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan No. 2: Cue Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan No. 2: Cue Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationJIRAH MAY NAELGANo ratings yet
- Abenoja NcplanDocument3 pagesAbenoja NcplanOfficial ZEYNNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument9 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The LiverDocument2 pagesCirrhosis of The LiverBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationzeavhinNo ratings yet
- Risk NCP - PESCADERO 4CDocument1 pageRisk NCP - PESCADERO 4COrlando VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Prado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Document52 pagesPrado, Catherine BSN IIB (Activity 1 Case Scenario)Catherine PradoNo ratings yet
- NCP DiarrheaDocument2 pagesNCP DiarrheaVince John SevillaNo ratings yet
- GROUP 8 NCP Patient FDocument12 pagesGROUP 8 NCP Patient FasdasdNo ratings yet
- NCP Cumadcad FeverDocument2 pagesNCP Cumadcad FeverPatrick PaternoNo ratings yet
- Name: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralDocument2 pagesName: Grace AGE: 28 Gender: Female Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: GeneralRainier IbarretaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- Assessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessmen T Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKimmy DoraNo ratings yet
- Prado NCPDocument4 pagesPrado NCPalleah pradoNo ratings yet
- Case Study #1 (NCM116RC)Document4 pagesCase Study #1 (NCM116RC)Dexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Ncpdrug StudyDocument4 pagesNcpdrug StudyMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationer balotNo ratings yet
- I. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesI. Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- As Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ADocument2 pagesAs Fluid Volume Deficit (FVD), Hypovolemia) Is ATanya Alyssa Untalan AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP Deficit Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesNCP Deficit Fluid VolumeKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- Pae Clinical Case Week 8Document10 pagesPae Clinical Case Week 8ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypokalemia Nursing Care PlanIan Lelis100% (1)
- C. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Document5 pagesC. Case Study thesis-NCP (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- IndependentDocument2 pagesIndependentR Hornilla ArcegaNo ratings yet
- NCP MeningitisDocument2 pagesNCP MeningitisARISNo ratings yet
- PPPPDocument4 pagesPPPPRoshin Mae E. TejeroNo ratings yet
- NCP Aguda 3Document2 pagesNCP Aguda 3Erryl Justine AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- Physiological Ecology: How Animals Process Energy, Nutrients, and ToxinsFrom EverandPhysiological Ecology: How Animals Process Energy, Nutrients, and ToxinsNo ratings yet
- Air Is Allowed To Flow From A Large Reservoir ThroDocument3 pagesAir Is Allowed To Flow From A Large Reservoir Throsid202pkNo ratings yet
- Overtime in NursingDocument5 pagesOvertime in NursingallisonNo ratings yet
- AP Technical Education Service Rules-178Document29 pagesAP Technical Education Service Rules-178Neeraja CNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Good Research PracticeDocument9 pagesGuidelines On Good Research PracticeAndre SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Chants de Noël 2021-AccordéonDocument9 pagesChants de Noël 2021-Accordéontilan.dossogneNo ratings yet
- Writing Strategy and Tips - CAE PDFDocument11 pagesWriting Strategy and Tips - CAE PDFAntoSeitanNo ratings yet
- Alvaro - Now Creatives Freelancer AgreementDocument10 pagesAlvaro - Now Creatives Freelancer AgreementEdward Rey EbaoNo ratings yet
- 78-2017ernakulam, KannurDocument13 pages78-2017ernakulam, KannurBingo MeNo ratings yet
- Cini Manual PDF FreeDocument536 pagesCini Manual PDF FreeJaeIlLee100% (1)
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionKhizar ShahNo ratings yet
- A KissDocument3 pagesA KissTrần Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- Diet PlanDocument4 pagesDiet PlanRahul BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Coats Tire ChangerDocument32 pagesCoats Tire ChangergomooneyNo ratings yet
- BMW IcebreakersDocument2 pagesBMW IcebreakersdunamisbzNo ratings yet
- El Educador Como Gestor de Conflictos 13 To 74Document62 pagesEl Educador Como Gestor de Conflictos 13 To 74AlExa Garzón100% (1)
- The Scarlet Letter Analysis EssayDocument8 pagesThe Scarlet Letter Analysis Essayurdpzinbf100% (2)
- Vampires Werewolves and Witches Oh MyDocument51 pagesVampires Werewolves and Witches Oh Myangelg29850% (1)
- Committes of Health in IndiaDocument5 pagesCommittes of Health in IndiaRaghavendr Kore100% (1)
- 080930-Antarctica TourismDocument15 pages080930-Antarctica TourismVân PhươngNo ratings yet
- Subcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1Document4 pagesSubcontract Agreement (Jenesis) V.1.1sigit l.prabowoNo ratings yet
- BF Necromancer Supplement r11Document13 pagesBF Necromancer Supplement r11Michael KirchnerNo ratings yet
- Chocolate Chip Cookies (Easy Soft Chewy) - Cafe DelitesDocument1 pageChocolate Chip Cookies (Easy Soft Chewy) - Cafe DelitesNina MabantaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics AssignmentDocument3 pagesBusiness Analytics AssignmentDevansh RaiNo ratings yet
- LTE ENB Feature Description SLR 2 4 V2 0 en PDF 1Document1,021 pagesLTE ENB Feature Description SLR 2 4 V2 0 en PDF 1Swati SiwachNo ratings yet
- Emcee ScriptDocument6 pagesEmcee ScriptJasper MomoNo ratings yet
- (1912) Book of Home Building & DecorationDocument264 pages(1912) Book of Home Building & DecorationHerbert Hillary Booker 2nd100% (2)