Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cosas Lineas 64
Cosas Lineas 64
Uploaded by
Mohammed GamilCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- B. Velde (Auth.) - Introduction To Clay Minerals - Chemistry, Origins, Uses and Environmental Significance-Springer Netherlands (1992) PDFDocument205 pagesB. Velde (Auth.) - Introduction To Clay Minerals - Chemistry, Origins, Uses and Environmental Significance-Springer Netherlands (1992) PDFLeonardo TejedorNo ratings yet
- 5.0. Setting Out DCC20063Document20 pages5.0. Setting Out DCC20063nursyahzanani100% (1)
- AISC Design Guide 16 Errata - Flush and Extend Multiple-Row Moment End-Plate Connections PDFDocument4 pagesAISC Design Guide 16 Errata - Flush and Extend Multiple-Row Moment End-Plate Connections PDFFernando Gutiérrez UrzúaNo ratings yet
- Design of Slabs To EC2Document12 pagesDesign of Slabs To EC2smartman35100% (2)
- Cosas Lineas 63Document1 pageCosas Lineas 63Mohammed GamilNo ratings yet
- Cosas Lineas 62Document1 pageCosas Lineas 62Mohammed GamilNo ratings yet
- The Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignDocument8 pagesThe Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignNIE100% (2)
- JUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-ParametersDocument6 pagesJUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-Parameterssultan1786No ratings yet
- Answer Key, Problem Set 2: Answers: (A) Order Is 2 (B) K 0.0226 M S (C) (AB) StrategyDocument15 pagesAnswer Key, Problem Set 2: Answers: (A) Order Is 2 (B) K 0.0226 M S (C) (AB) StrategyecclesiaNo ratings yet
- Pedestal - DesignDocument6 pagesPedestal - DesignMatthew KedeNo ratings yet
- Factor - TransversalDocument11 pagesFactor - TransversalSarah Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials - 9780073380285 - Exercise 155 - QuizletDocument5 pagesMechanics of Materials - 9780073380285 - Exercise 155 - QuizletAmirali SahebzamaniNo ratings yet
- Anchorage To PedestalDocument30 pagesAnchorage To PedestalIsprotec IngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Factor Method Wind Load - Transversal SectionDocument11 pagesFactor Method Wind Load - Transversal SectionSarah Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- B C D F E: - BC - BC Relº - CD - CD Rel - DE - DE Rel - DF - DF RelDocument2 pagesB C D F E: - BC - BC Relº - CD - CD Rel - DE - DE Rel - DF - DF RelXesar AbelNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Barrier WallDocument1 pageVehicular Barrier Walljklo12No ratings yet
- LdgPiles PILE DESIGN SPREADSHEETDocument7 pagesLdgPiles PILE DESIGN SPREADSHEETCivilax.comNo ratings yet
- Trial and Error Eccentric Distance Find Balance Section .: Use Re Bar (DB/RB) CB 11.611Document3 pagesTrial and Error Eccentric Distance Find Balance Section .: Use Re Bar (DB/RB) CB 11.611Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Efor. Error' (B) - (B) : Q.1) ThefollowingtablelepresentthefielddataintlaversingusingtheodoliteandsteelDocument10 pagesEfor. Error' (B) - (B) : Q.1) Thefollowingtablelepresentthefielddataintlaversingusingtheodoliteandsteelmarwan hazaNo ratings yet
- ME 482/582 Chapter 2 HW Solution: U A B C T T T UDocument6 pagesME 482/582 Chapter 2 HW Solution: U A B C T T T UPhạm Hữu PhướcNo ratings yet
- B Dot AlgorithmDocument4 pagesB Dot AlgorithmHussein AbdulwahabNo ratings yet
- DIgSILENT Time-Overcurrent Plot1Document1 pageDIgSILENT Time-Overcurrent Plot1Javier PillcoNo ratings yet
- Cross Section LevelingDocument2 pagesCross Section LevelingMohamed NkNo ratings yet
- TBD1Document1 pageTBD1MichenerparkNo ratings yet
- RRRRDocument2 pagesRRRRAek JanNo ratings yet
- Filled Composite Column Design Based On AISC 360-10/16 & ACI 318-19Document1 pageFilled Composite Column Design Based On AISC 360-10/16 & ACI 318-19Prolay MannaNo ratings yet
- RRRR 1Document2 pagesRRRR 1Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Sta 1+500Document20 pagesSta 1+500rismanNo ratings yet
- App BDocument11 pagesApp Bakakak01No ratings yet
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Limit in Rebar ContentDocument17 pagesLimit in Rebar ContentNgoc Ba NguyenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1 Stadia Interval FactorDocument12 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 1 Stadia Interval FactorTherese Myekkah GendiveNo ratings yet
- Bolted Moment ConnectionDocument18 pagesBolted Moment ConnectionAlpha50% (2)
- Semiconductor KF10N60P/F: Technical DataDocument7 pagesSemiconductor KF10N60P/F: Technical DataHugo FloresNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Robotics Mechanics and Control 4Th Edition Craig 0133489795 9780133489798 Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Robotics Mechanics and Control 4Th Edition Craig 0133489795 9780133489798 Full Chapter PDFscott.osborn956100% (26)
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Chapter 19 (Probability Distributions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument5 pagesForm 4: Chapter 19 (Probability Distributions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsJing Wen LeongNo ratings yet
- Ce368-M7 - Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument1 pageCe368-M7 - Doubly Reinforced BeamRanilyn L. AndalesNo ratings yet
- NC 9303 1733 005 0 Perhitungan Balok Konsol GBK: As Max ofDocument3 pagesNC 9303 1733 005 0 Perhitungan Balok Konsol GBK: As Max ofRafli Hasuna HakimNo ratings yet
- DSP-based Control of Variable Speed Drives 1037Document1 pageDSP-based Control of Variable Speed Drives 1037SuganthiVasanNo ratings yet
- Vertical Vs Mean Effective StressDocument1 pageVertical Vs Mean Effective StressseraiwangiNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining WallDocument2 pagesDesign of Retaining WallassssssssssaaaaaawwNo ratings yet
- Losa Maciza en Dos Direcciones. LOSA DE TANQUES ELEVADOSDocument7 pagesLosa Maciza en Dos Direcciones. LOSA DE TANQUES ELEVADOSEstefania PerezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry MC 2Document10 pagesTrigonometry MC 2wrq6j4z42jNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION (2.1) : Free Body: CDDocument14 pagesSOLUTION (2.1) : Free Body: CDehab elsawyNo ratings yet
- ME2103Document1 pageME2103Bhaskar B SarkarNo ratings yet
- Column Interaction DiagramDocument4 pagesColumn Interaction Diagramshangz1511No ratings yet
- Column Interaction DiagramDocument3 pagesColumn Interaction DiagramAli Al-BashaNo ratings yet
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Chuong 7+8Document3 pagesChuong 7+8Pham TuyenNo ratings yet
- Listing Obtained. Obtaining Separating: Municipals Municipals EmployeesDocument2 pagesListing Obtained. Obtaining Separating: Municipals Municipals EmployeesSiti Nur HanisNo ratings yet
- Wing SectionsDocument4 pagesWing SectionsOUESLATI RajaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt Calculation For Sign PostDocument5 pagesAnchor Bolt Calculation For Sign PostaselabambarandageNo ratings yet
- Vortrag Bulus UmutDocument34 pagesVortrag Bulus UmutUmut BulusNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1devashishkumar693No ratings yet
- Concrete Slab For 20kpaDocument3 pagesConcrete Slab For 20kpaEngin eeringNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byDocument1 pageDesign Criteria: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byCesar Romero VilchezNo ratings yet
- BC 148Document2 pagesBC 148Sagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Schottky-Gate Effect Transistor Without Junction: New Silicon Carbide Bipolar Mode FieldDocument3 pagesSchottky-Gate Effect Transistor Without Junction: New Silicon Carbide Bipolar Mode FieldMamidala Jagadesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem 12-105Document53 pagesProblem 12-105adam johnsonNo ratings yet
- Sharp Microelectronics - pq1cg41h2 - E-1203196Document6 pagesSharp Microelectronics - pq1cg41h2 - E-1203196Syed Khawar MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Computers and Geotechnics: Navid Bahrani, Peter K. KaiserDocument12 pagesComputers and Geotechnics: Navid Bahrani, Peter K. Kaiserzimbazimba75No ratings yet
- MODULE I Injection Molding ProcessDocument40 pagesMODULE I Injection Molding ProcessAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2-001.2 (Basis) PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 2-001.2 (Basis) PDFJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Introduction of New IGBT Generation 7: Application NoteDocument15 pagesIntroduction of New IGBT Generation 7: Application NoteBrunophb2012No ratings yet
- Attendance' Policies: Physics 197 - Mesa College - Fall 2020 Course Syllabus - 48712 - Moonday LabDocument7 pagesAttendance' Policies: Physics 197 - Mesa College - Fall 2020 Course Syllabus - 48712 - Moonday LabJohnsonNo ratings yet
- Di (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexDocument5 pagesDi (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexGoutam BissoyiNo ratings yet
- MCQ DomDocument179 pagesMCQ DomArputha RajNo ratings yet
- Microwave GeneratorDocument4 pagesMicrowave Generatorroby72No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties: Part 1: MME 293 Lecture 01Document42 pagesMechanical Properties: Part 1: MME 293 Lecture 01Pranto AminNo ratings yet
- Osama Al-Rashayda 20171563 Experiment No.5 Single Phase Induction MotorDocument5 pagesOsama Al-Rashayda 20171563 Experiment No.5 Single Phase Induction MotorOsama RashaydaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding Physics: Attempt The Following Questions On Your Own What Is Physics?Document8 pages1.1 Understanding Physics: Attempt The Following Questions On Your Own What Is Physics?Ushma PunatarNo ratings yet
- Rupture Disc SizingDocument9 pagesRupture Disc SizingShruti JoshiNo ratings yet
- 15 Yrs of Geotechnical Limit State Design in AustraliaDocument6 pages15 Yrs of Geotechnical Limit State Design in AustraliaJackNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Problem SetsDocument23 pagesMachine Design Problem SetsMAX LAPINGCAO100% (1)
- FVD Englishcatalog 20220922Document6 pagesFVD Englishcatalog 20220922NATHANEASTBOUNDNo ratings yet
- " The Power of Instruction Is Seldom of Much Efficacy Except in Those Happy Dispositions Where It Is Almost Superfluous." - Nevertheless, One Tries!Document6 pages" The Power of Instruction Is Seldom of Much Efficacy Except in Those Happy Dispositions Where It Is Almost Superfluous." - Nevertheless, One Tries!Sirf LaundeNo ratings yet
- Review of Transformations - Translations, Reflections, Rotations and Dilations. - Print - QuizizzDocument8 pagesReview of Transformations - Translations, Reflections, Rotations and Dilations. - Print - Quizizzsheher banuNo ratings yet
- Final Hoody.1Document81 pagesFinal Hoody.1muslimwaqar2002No ratings yet
- Research Focus - John Victor ChristyDocument1 pageResearch Focus - John Victor Christyjohnvchristy7No ratings yet
- The Leading-Edge Diesel Rotary Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemDocument36 pagesThe Leading-Edge Diesel Rotary Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemEhab AllazyNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Proline Promass 84X: Coriolis FlowmeterDocument34 pagesTechnical Information Proline Promass 84X: Coriolis FlowmeterAntonio LoretoCortesNo ratings yet
- NPS-MRI-0070E - NSM-S15P PRE Manual - EN V1.3Document81 pagesNPS-MRI-0070E - NSM-S15P PRE Manual - EN V1.3ьшчNo ratings yet
- En 10228-2 1998Document6 pagesEn 10228-2 19989823458877No ratings yet
- Acceleration Cases 2023Document8 pagesAcceleration Cases 2023pragathi mudavathNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Math 2Document7 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Math 2Lovely Amor CatipayNo ratings yet
Cosas Lineas 64
Cosas Lineas 64
Uploaded by
Mohammed GamilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cosas Lineas 64
Cosas Lineas 64
Uploaded by
Mohammed GamilCopyright:
Available Formats
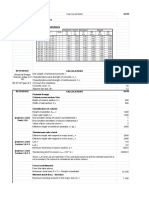
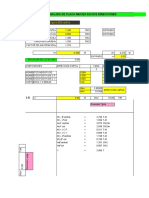
B
T+B
S
T
(Level Sight)
B.M
1.0
A
T = S (1 − B/4S)2 = SK
T = Vertical distance of transit below lower support for taking level sight.
A = Horizontal distance between points of support - obtained from structure list of plan & profile.
0.9 B = Vertical distance between points of support - obtained from plan & profile, tower site data
sheets or field measurement.
S = Sag.
K = (1−B/4s)2–Determined from curve below.
EXAMPLE
A = 1400.0'
0.8 B = 60.0'
S = 49.1' @ 608F
S = 51.2' @ 908F
B/S = 60.0/49.1 = 1.22 @608 F B/S = 60.0 / 51.2 = 1.17 @ 908 F
K = 0.482 @ 608 F K = 0.501 @ 908F
0.7 T = (49.1) (0.482) = 23.66' @ 608 F T = (51.2) (0.501) = 25.65' @ 908 F
5
( )
Change in "T" for 58F = (25.65−23.66) 30 = 0.33'
0.6
"K" Factor
0.5
0.4
0.3
For most accurate results, use that
part of curve drawn in solid line.
0.2
0.1
0.0
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0
Ratio (B/S)
Sag is based on parabolic functions. If sag exceeds 5% of span, do not use this chart.
FIGURE 14.18 Conductor sagging by horizontal line of sight.
14.6.3.2 Sagging by Transit Methods
IEEE Guide Std. 524–1993 lists three methods of sagging conductor with a transit: ‘‘Calculated Angle of
Sight,’’ ‘‘Calculated Target Method,’’ and ‘‘Horizontal Line of Sight.’’ The method best suited to a
particular line sagging situation may vary with terrain and line design.
ß 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
You might also like
- B. Velde (Auth.) - Introduction To Clay Minerals - Chemistry, Origins, Uses and Environmental Significance-Springer Netherlands (1992) PDFDocument205 pagesB. Velde (Auth.) - Introduction To Clay Minerals - Chemistry, Origins, Uses and Environmental Significance-Springer Netherlands (1992) PDFLeonardo TejedorNo ratings yet
- 5.0. Setting Out DCC20063Document20 pages5.0. Setting Out DCC20063nursyahzanani100% (1)
- AISC Design Guide 16 Errata - Flush and Extend Multiple-Row Moment End-Plate Connections PDFDocument4 pagesAISC Design Guide 16 Errata - Flush and Extend Multiple-Row Moment End-Plate Connections PDFFernando Gutiérrez UrzúaNo ratings yet
- Design of Slabs To EC2Document12 pagesDesign of Slabs To EC2smartman35100% (2)
- Cosas Lineas 63Document1 pageCosas Lineas 63Mohammed GamilNo ratings yet
- Cosas Lineas 62Document1 pageCosas Lineas 62Mohammed GamilNo ratings yet
- The Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignDocument8 pagesThe Capacity Spectrum Method As A Tool For Seismic DesignNIE100% (2)
- JUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-ParametersDocument6 pagesJUAS 2019 - Tutorial 2: 1.) S-Parameterssultan1786No ratings yet
- Answer Key, Problem Set 2: Answers: (A) Order Is 2 (B) K 0.0226 M S (C) (AB) StrategyDocument15 pagesAnswer Key, Problem Set 2: Answers: (A) Order Is 2 (B) K 0.0226 M S (C) (AB) StrategyecclesiaNo ratings yet
- Pedestal - DesignDocument6 pagesPedestal - DesignMatthew KedeNo ratings yet
- Factor - TransversalDocument11 pagesFactor - TransversalSarah Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials - 9780073380285 - Exercise 155 - QuizletDocument5 pagesMechanics of Materials - 9780073380285 - Exercise 155 - QuizletAmirali SahebzamaniNo ratings yet
- Anchorage To PedestalDocument30 pagesAnchorage To PedestalIsprotec IngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Factor Method Wind Load - Transversal SectionDocument11 pagesFactor Method Wind Load - Transversal SectionSarah Mae GonzalesNo ratings yet
- B C D F E: - BC - BC Relº - CD - CD Rel - DE - DE Rel - DF - DF RelDocument2 pagesB C D F E: - BC - BC Relº - CD - CD Rel - DE - DE Rel - DF - DF RelXesar AbelNo ratings yet
- Vehicular Barrier WallDocument1 pageVehicular Barrier Walljklo12No ratings yet
- LdgPiles PILE DESIGN SPREADSHEETDocument7 pagesLdgPiles PILE DESIGN SPREADSHEETCivilax.comNo ratings yet
- Trial and Error Eccentric Distance Find Balance Section .: Use Re Bar (DB/RB) CB 11.611Document3 pagesTrial and Error Eccentric Distance Find Balance Section .: Use Re Bar (DB/RB) CB 11.611Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Efor. Error' (B) - (B) : Q.1) ThefollowingtablelepresentthefielddataintlaversingusingtheodoliteandsteelDocument10 pagesEfor. Error' (B) - (B) : Q.1) Thefollowingtablelepresentthefielddataintlaversingusingtheodoliteandsteelmarwan hazaNo ratings yet
- ME 482/582 Chapter 2 HW Solution: U A B C T T T UDocument6 pagesME 482/582 Chapter 2 HW Solution: U A B C T T T UPhạm Hữu PhướcNo ratings yet
- B Dot AlgorithmDocument4 pagesB Dot AlgorithmHussein AbdulwahabNo ratings yet
- DIgSILENT Time-Overcurrent Plot1Document1 pageDIgSILENT Time-Overcurrent Plot1Javier PillcoNo ratings yet
- Cross Section LevelingDocument2 pagesCross Section LevelingMohamed NkNo ratings yet
- TBD1Document1 pageTBD1MichenerparkNo ratings yet
- RRRRDocument2 pagesRRRRAek JanNo ratings yet
- Filled Composite Column Design Based On AISC 360-10/16 & ACI 318-19Document1 pageFilled Composite Column Design Based On AISC 360-10/16 & ACI 318-19Prolay MannaNo ratings yet
- RRRR 1Document2 pagesRRRR 1Aek JanNo ratings yet
- Sta 1+500Document20 pagesSta 1+500rismanNo ratings yet
- App BDocument11 pagesApp Bakakak01No ratings yet
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Limit in Rebar ContentDocument17 pagesLimit in Rebar ContentNgoc Ba NguyenNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1 Stadia Interval FactorDocument12 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 1 Stadia Interval FactorTherese Myekkah GendiveNo ratings yet
- Bolted Moment ConnectionDocument18 pagesBolted Moment ConnectionAlpha50% (2)
- Semiconductor KF10N60P/F: Technical DataDocument7 pagesSemiconductor KF10N60P/F: Technical DataHugo FloresNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Robotics Mechanics and Control 4Th Edition Craig 0133489795 9780133489798 Full Chapter PDFDocument27 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Robotics Mechanics and Control 4Th Edition Craig 0133489795 9780133489798 Full Chapter PDFscott.osborn956100% (26)
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Form 4: Chapter 19 (Probability Distributions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsDocument5 pagesForm 4: Chapter 19 (Probability Distributions) SPM Practice Fully Worked SolutionsJing Wen LeongNo ratings yet
- Ce368-M7 - Doubly Reinforced BeamDocument1 pageCe368-M7 - Doubly Reinforced BeamRanilyn L. AndalesNo ratings yet
- NC 9303 1733 005 0 Perhitungan Balok Konsol GBK: As Max ofDocument3 pagesNC 9303 1733 005 0 Perhitungan Balok Konsol GBK: As Max ofRafli Hasuna HakimNo ratings yet
- DSP-based Control of Variable Speed Drives 1037Document1 pageDSP-based Control of Variable Speed Drives 1037SuganthiVasanNo ratings yet
- Vertical Vs Mean Effective StressDocument1 pageVertical Vs Mean Effective StressseraiwangiNo ratings yet
- Design of Retaining WallDocument2 pagesDesign of Retaining WallassssssssssaaaaaawwNo ratings yet
- Losa Maciza en Dos Direcciones. LOSA DE TANQUES ELEVADOSDocument7 pagesLosa Maciza en Dos Direcciones. LOSA DE TANQUES ELEVADOSEstefania PerezNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry MC 2Document10 pagesTrigonometry MC 2wrq6j4z42jNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION (2.1) : Free Body: CDDocument14 pagesSOLUTION (2.1) : Free Body: CDehab elsawyNo ratings yet
- ME2103Document1 pageME2103Bhaskar B SarkarNo ratings yet
- Column Interaction DiagramDocument4 pagesColumn Interaction Diagramshangz1511No ratings yet
- Column Interaction DiagramDocument3 pagesColumn Interaction DiagramAli Al-BashaNo ratings yet
- Electric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelDocument2 pagesElectric Chiller Replacement 8000 RT Step Down Building: Project Name Design by Building Name Floor/ LevelAek JanNo ratings yet
- Chuong 7+8Document3 pagesChuong 7+8Pham TuyenNo ratings yet
- Listing Obtained. Obtaining Separating: Municipals Municipals EmployeesDocument2 pagesListing Obtained. Obtaining Separating: Municipals Municipals EmployeesSiti Nur HanisNo ratings yet
- Wing SectionsDocument4 pagesWing SectionsOUESLATI RajaNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt Calculation For Sign PostDocument5 pagesAnchor Bolt Calculation For Sign PostaselabambarandageNo ratings yet
- Vortrag Bulus UmutDocument34 pagesVortrag Bulus UmutUmut BulusNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1devashishkumar693No ratings yet
- Concrete Slab For 20kpaDocument3 pagesConcrete Slab For 20kpaEngin eeringNo ratings yet
- Design Criteria: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byDocument1 pageDesign Criteria: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byCesar Romero VilchezNo ratings yet
- BC 148Document2 pagesBC 148Sagar ShahNo ratings yet
- Schottky-Gate Effect Transistor Without Junction: New Silicon Carbide Bipolar Mode FieldDocument3 pagesSchottky-Gate Effect Transistor Without Junction: New Silicon Carbide Bipolar Mode FieldMamidala Jagadesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Problem 12-105Document53 pagesProblem 12-105adam johnsonNo ratings yet
- Sharp Microelectronics - pq1cg41h2 - E-1203196Document6 pagesSharp Microelectronics - pq1cg41h2 - E-1203196Syed Khawar MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Computers and Geotechnics: Navid Bahrani, Peter K. KaiserDocument12 pagesComputers and Geotechnics: Navid Bahrani, Peter K. Kaiserzimbazimba75No ratings yet
- MODULE I Injection Molding ProcessDocument40 pagesMODULE I Injection Molding ProcessAntonius PrakosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 2-001.2 (Basis) PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 2 2-001.2 (Basis) PDFJamiel CatapangNo ratings yet
- Introduction of New IGBT Generation 7: Application NoteDocument15 pagesIntroduction of New IGBT Generation 7: Application NoteBrunophb2012No ratings yet
- Attendance' Policies: Physics 197 - Mesa College - Fall 2020 Course Syllabus - 48712 - Moonday LabDocument7 pagesAttendance' Policies: Physics 197 - Mesa College - Fall 2020 Course Syllabus - 48712 - Moonday LabJohnsonNo ratings yet
- Di (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexDocument5 pagesDi (M M M) Terphenyl-Embedded Decaphyrin and Its Bis-Rh (I) ComplexGoutam BissoyiNo ratings yet
- MCQ DomDocument179 pagesMCQ DomArputha RajNo ratings yet
- Microwave GeneratorDocument4 pagesMicrowave Generatorroby72No ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties: Part 1: MME 293 Lecture 01Document42 pagesMechanical Properties: Part 1: MME 293 Lecture 01Pranto AminNo ratings yet
- Osama Al-Rashayda 20171563 Experiment No.5 Single Phase Induction MotorDocument5 pagesOsama Al-Rashayda 20171563 Experiment No.5 Single Phase Induction MotorOsama RashaydaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Understanding Physics: Attempt The Following Questions On Your Own What Is Physics?Document8 pages1.1 Understanding Physics: Attempt The Following Questions On Your Own What Is Physics?Ushma PunatarNo ratings yet
- Rupture Disc SizingDocument9 pagesRupture Disc SizingShruti JoshiNo ratings yet
- 15 Yrs of Geotechnical Limit State Design in AustraliaDocument6 pages15 Yrs of Geotechnical Limit State Design in AustraliaJackNo ratings yet
- Machine Design Problem SetsDocument23 pagesMachine Design Problem SetsMAX LAPINGCAO100% (1)
- FVD Englishcatalog 20220922Document6 pagesFVD Englishcatalog 20220922NATHANEASTBOUNDNo ratings yet
- " The Power of Instruction Is Seldom of Much Efficacy Except in Those Happy Dispositions Where It Is Almost Superfluous." - Nevertheless, One Tries!Document6 pages" The Power of Instruction Is Seldom of Much Efficacy Except in Those Happy Dispositions Where It Is Almost Superfluous." - Nevertheless, One Tries!Sirf LaundeNo ratings yet
- Review of Transformations - Translations, Reflections, Rotations and Dilations. - Print - QuizizzDocument8 pagesReview of Transformations - Translations, Reflections, Rotations and Dilations. - Print - Quizizzsheher banuNo ratings yet
- Final Hoody.1Document81 pagesFinal Hoody.1muslimwaqar2002No ratings yet
- Research Focus - John Victor ChristyDocument1 pageResearch Focus - John Victor Christyjohnvchristy7No ratings yet
- The Leading-Edge Diesel Rotary Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemDocument36 pagesThe Leading-Edge Diesel Rotary Uninterruptible Power Supply SystemEhab AllazyNo ratings yet
- Technical Information Proline Promass 84X: Coriolis FlowmeterDocument34 pagesTechnical Information Proline Promass 84X: Coriolis FlowmeterAntonio LoretoCortesNo ratings yet
- NPS-MRI-0070E - NSM-S15P PRE Manual - EN V1.3Document81 pagesNPS-MRI-0070E - NSM-S15P PRE Manual - EN V1.3ьшчNo ratings yet
- En 10228-2 1998Document6 pagesEn 10228-2 19989823458877No ratings yet
- Acceleration Cases 2023Document8 pagesAcceleration Cases 2023pragathi mudavathNo ratings yet
- Plane Trigonometry: Math 2Document7 pagesPlane Trigonometry: Math 2Lovely Amor CatipayNo ratings yet