Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Format
Drug Study Format
Uploaded by
HAIDER JULAILI0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesThis document summarizes information on the drugs Diazepam and Ipratropium, including their mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, dosages, and nursing responsibilities. Diazepam is a sedative that works by potentiating GABA and produces muscle relaxation. It is used for anxiety disorders and muscle spasms but has contraindications in pregnancy, acute conditions, and lactation. Side effects include drowsiness, confusion, and hypotension. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for adverse reactions and therapeutic effectiveness. Ipratropium is a bronchodilator that works as a muscarinic receptor antagonist to inhibit parasympathetic effects and bronchodilation. It is used
Original Description:
DRUGSTUDY
Original Title
Drug-Study-Format
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes information on the drugs Diazepam and Ipratropium, including their mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, dosages, and nursing responsibilities. Diazepam is a sedative that works by potentiating GABA and produces muscle relaxation. It is used for anxiety disorders and muscle spasms but has contraindications in pregnancy, acute conditions, and lactation. Side effects include drowsiness, confusion, and hypotension. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for adverse reactions and therapeutic effectiveness. Ipratropium is a bronchodilator that works as a muscarinic receptor antagonist to inhibit parasympathetic effects and bronchodilation. It is used
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views7 pagesDrug Study Format
Drug Study Format
Uploaded by
HAIDER JULAILIThis document summarizes information on the drugs Diazepam and Ipratropium, including their mechanisms of action, indications, contraindications, side effects, dosages, and nursing responsibilities. Diazepam is a sedative that works by potentiating GABA and produces muscle relaxation. It is used for anxiety disorders and muscle spasms but has contraindications in pregnancy, acute conditions, and lactation. Side effects include drowsiness, confusion, and hypotension. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for adverse reactions and therapeutic effectiveness. Ipratropium is a bronchodilator that works as a muscarinic receptor antagonist to inhibit parasympathetic effects and bronchodilation. It is used
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
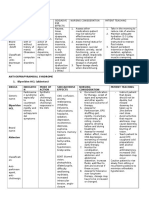
Drug Mechanism of action/Side effects Indication/Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities
Brand name: Mechanism of Action: Indication: Nursing Responsibilities:
Diazepam - Depress the CNS, probably by potentiating GABA, Management of anxiety disorders, short-term
an inhibitory neurotransmitter. relief of anxiety symptoms, spasticity associated Remember to apply the 10 rights of drug administration
with upper motor neuron disorders, adjunct before giving the appropriate drug to the client
Generic name: - Produces skeletal muscle relaxation by inhibiting therapy for muscle spasms. preoperatively.
Valium spinal polysynaptic afferent pathways. 1. Right drug
Contraindication: 2. Right patient
- Has anticonvulsant properties due to enhanced
Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to 3. Right dose
presynaptic inhibition.
Classification: benzodiazepines; psychoses, acute narrow-angle 4. Right route
Anticonvulsant, Therapeutic effects: glaucoma, shock, coma, acute alcoholic
5. Right time and frequency
Sedative, Skeletal intoxication; pregnancy (cleft lip or palate,
(1) Relief of Anxiety 6. Right documentation
muscle relaxants inguinal hernia, cardiac defects, microcephaly,
(2) Sedation pyloric stenosis when used in first trimester; 7. Right history and assessment
(3) Amnesia neonatal withdrawal syndrome reported in 8. Drug approach and right to refuse
newborns); lactation. 9. Right drug-drug interaction and evaluation
Route: IV (4) Skeletal muscle relaxant
10.Right education and information
(5) Decreased seizure activity
Dosage: 3 mg Monitor for adverse reactions.
Side Effects: Monitor for therapeutic effectiveness. Maximum effect
Frequency: BID may require 1-2 weeks; patient tolerance to therapeutic
Body as a whole: throat and chest pain effects may develop after 4 weeks of treatment
Observe necessary preventive precautions for suicidal
CNS: drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, confusion,
tendencies that may be present in anxiety states
paradoxic rage, dizziness, vertigo, amnesia, vivid
accompanied by depression.
dreams, headache, slurred speech, and tremor
Observe patient closely and monitor vital signs when
CV: Hypotension, tachycardia, edema, cardiovascular diazepam is given parenterally; hypotension, muscular
collapse weakness, tachycardia, and respiratory depression may
occur.
Special Senses: blurred vision, diplopia, nystagmus
Lab tests: Periodic CBC and liver function tests during
GI: xerostomia, nausea, constipation, and hepatic prolonged therapy.
dysfunction
Urogenital: incontinence, urinary retention, Supervise ambulation. Adverse reactions such as
gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities, ovulation drowsiness and ataxia are more likely to occur in older
failure adults and debilitated or those receiving larger doses.
Monitory I&O ration including urinary and bowel
Respiratory: hiccups, cough, and laryngospasm. -
Other: pain, venous thrombosis, phlebitis at injection elimination.
site
Drug Mechanism of action/Side effects Indication/Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities
Brand name: Mechanism of Action: Indication: Nursing Responsibilities:
Ipratropium Ipratropium acts as an antagonist of the muscarinic Bronchodilators that relax muscles in the airways
acetylcholine receptor. This effect produces the and increase air flow to the lungs. Remember to apply the 10 rights of drug administration
inhibition of the parasympathetic nervous system in before giving the appropriate drug to the client
Generic name: the airways and hence, inhibit their function. The Contraindication: preoperatively.
Atrovent function of the parasympathetic system in the airway Contraindicated with hypersensitivity to atropine 1. Right drug
is to generate bronchial secretions and constriction or its derivatives, soy bean or peanut allergies 2. Right patient
and hence, the inhibition of this action can lead to (aerosol). 3. Right dose
bronchodilation and fewer secretions. 4. Right route
Classification:
Anticholinergics 5. Right time and frequency
Side Effects: 6. Right documentation
7. Right history and assessment
Body as a whole: headache, pain, influenza, chest 8. Drug approach and right to refuse
Route: Inhalation 9. Right drug-drug interaction and evaluation
pain
Dosage: 10. Right education and information
GI: Nausea
500mcg/2.5 mg
per 2.5ml Respiratory: Bronchitis, dyspnea, coughing, Monitor respiratory status; auscultate lungs before and
pneumonia, bronchospasm, pharyngitis, sinusitis, after inhalation.
Frequency: Q6H
rhinitis
Monitor signs of paradoxical bronchospasm (wheezing,
cough, dyspnea, tightness in chest and throat), especially
at higher or excessive doses. If condition occurs, advise
patient to withhold medication and notify physician
immediately.
Be alert for signs of allergic reactions, including
pulmonary symptoms (tightness in the throat and chest,
wheezing, cough, dyspnea) or skin reactions (rash,
pruritus, urticaria). Notify physician or nursing staff
immediately if these reactions occur.
Assess blood pressure periodically and compare to
normal values. Report low blood pressure (hypotension),
especially if patient experiences dizziness or syncope.
Report treatment failure (exacerbation of respiratory
symptoms) to physician.
Teach patient proper use of inhaler.
Drug Mechanism of action/Side effects Indication/Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities
Brand name: Mechanism of Action: Indication: Nursing Responsibilities:
Phenytoin Has antiepileptic activity without causing general Control of tonic-clonic(grandma) and complex
depression stabilizes neuronal membranes and partial (temporal lobe) seizures. Observe ten rights in giving medication.
prevents hyper excitability caused by excessive For patient requiring a loading dose. 1. Right drug
Generic name: stimulation, limits the spread of seizure activity from Prevention and treatment of seizures occurring 2. Right patient
Dilantin an active focus, also effective in treating cardiac during neurosurgery. 3. Right dose
arrhythmias, especially those induced by digitalis, Status Epilepticus 4. Right route
antiarrhythmic properties are very similar to those of 5. Right time and frequency
lidocaine, both are class IB antiarrhythmic. Contraindication: 6. Right documentation
Classification:
Anticonvulsant Contraindicated in patient hypersensitive to 7. Right history and assessment
Side Effects: hydantoin and those with sinus bradycardia, SA 8. Drug approach and right to
CNS: ataxia, slurred speech, dizziness, insomnia, 9. refuse
nervousness, twitching, headache, mental confusion, block, second or third degree AV block or 10. Right drug-drug interaction and evaluation
decreased coordination. Adams-Stokes syndrome. 11. Right education and information
Route: Oral Use cautiously in patients with hepatic dysfunction,
CV: periarteritis nodosa hypotension, myocardial infarction, diabetes, or
Dosage: 100 mg
respiratory depression, in elderly or debilitated patients
EENT: nystagmus, diplopia, blurred vision
Frequency: TID and in those receiving other hydantoin derivatives.
GI: gingival hyperplasia, nausea, vomiting, Elderly patients tend to metabolize phenytoin slowly and
constipation may need reduced dosages.
Phenytoin requirements usually increase during
Hematologic: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, pregnancy.
megaloblastic anemia, agrunolocytosis Stop drug if rash appears.
Use only clear solution for injection. A slight yellow
Hepatic: toxic hepatitis
color is acceptable. Don’t refrigerate.
Metabolic: hyperglycemia Don’t give I.M. unless dosage adjustments are made;
drug may precipitate at injection site, cause pain, and be
Muscuskeletal: osteomalacia absorbed erratically.
Divided doses given with or after meals may decrease
Skin: Purpuric dermatitis, photosensitivity reactions,
adverse GI reactions.
necrosis, inflammation at injection site, discoloration
Advise patient to avoid alcohol.
of skin if given by IV push in back of hand
Other: hirsutism, lymphadenopathy Warn patient not to stop drug abruptly because seizures
may worsen.
Stress importance of good oral hygiene and regular dental
examinations.
Caution patient that drug may have color pink, red or
reddish brown urine.
Drug Mechanism of action/Side effects Indication/Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities
Brand name: Mechanism of Action: Indication: Nursing Responsibilities:
Hydralazine Acts directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause Hypertension
vasodilation, primarily arteriolar, decreasing Eclampsia Observe ten rights in giving medication.
peripheral resistance; maintains or increases renal and 1. Right drug
Generic name:
cerebral flow. Contraindication: 2. Right patient
Apresoline
Hypersensitivity 3. Right dose
Side Effects: CAD 4. Right route
CNS: Headache, peripheral neuritis, dizziness, Mitral valvular rheumatic heart disease 5. Right time and frequency
Classification: tremors, psychotic reactions characterized by
Antihypertensive 6. Right documentation
depression, disorientation, anxiety
7. Right history and assessment
CV: Palpitations, tachycardia, angina pectoris, 8. Drug approach and right to
Route: Oral hypotension, paradoxical press or 9. refuse
response, orthostatic hypotension 10. Right drug-drug interaction and evaluation
Dosage: 10 mg, 11. Right education and information
25 mg, 5 mg, 100 GI: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
mg constipation, paralytic ileus
Before
GU: Difficult micturition, impotence - Check BP Arrange for CBC, LE cell preparations and
Hematologic: Blood Dyscrasias ANA titers beforetherapy.
Frequency: Q6H
- Assess for contraindicated conditions.
Hypersensitivity: Rash, urticaria, pruritus, fever, - Assess bowel sounds.
chills, arthralgia, eosinophilia, rarely, hepatitis, - Assess voiding pattern.
obstructive jaundice During
Other: Nasal congestion, flushing, edema, muscle - Give oral drug with food.
cramps, splenomegaly, dyspnea, lupus-like syndrome, - Use parenteral drug immediately after opening ampule.
possible carcinogenesis. - Instruct to take drug exactly as prescribed.
After
- Withdraw drug gradually.
- Discontinue if blood dyscrasias occur.
- Arrange for pyridoxine therapy if pt develops symptoms
of peripheral neuritis.
- Monitor for orthostatic hypotension.
- Report persistent or severe constipation, unexplained fever
or malaise, muscle or joint aching, chest pain, rash,
numbness, tingling.
- Do proper documentation
Drug Mechanism of action/Side effects Indication/Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities
Brand name: Mechanism of Action: Indication: Nursing Responsibilities:
Sodium Sodium bicarbonate raises blood and urinary pH by Treatment of metabolic acidosis, promotion of
Bicarbonate dissociation to provide bicarbonate ions, which gastric, systemic and urine alkalinization in the Observe ten rights in giving medication.
neutralizes the hydrogen ion concentration. It also case of intoxication with weak organic acids. 12. Right drug
neutralizes gastric acid via production of carbon 13. Right patient
Generic name: dioxide. Contraindication: 14. Right dose
Sodium Metabolic or respiratory alkalosis, hypernatremia, 15. Right route
Bicarbonate Side Effects: severe pulmonary edema, hypocalcaemia, 16. Right time and frequency
Metabolic alkalosis, mood changes, tiredness, hypochlorhydria 17. Right documentation
shortness of breath, muscle weakness, irregular
heartbeat, muscle hyper tonicity, twitching, 18. Right history and assessment
Classification: 19. Drug approach and right to
hypernatraemia, hyperosmolality, hypocalcaemia,
Antacids 20. refuse
hypokalemia, stomach cramps, flatulence.
21. Right drug-drug interaction and evaluation
22. Right education and information
Route: Oral
Obtain patient history including drug history and any
Dosage: 325 mg hypersensitivity.
Frequency: TID Assess respiratory and pulse rate, rhythm, depth, lung
sounds and notify the physician.
Assess for carbon dioxide in GI tract, may lead to
perforation if ulcer is severe.
Test and monitor urine pH, urinary output, during
beginning treatment.
If patient has edematous tendency, notify physician.
If patient is vomiting withhold medication and
immediately inform the physician.
If the patient exhibits shortness of breath and hyperpnea,
immediately inform the physician.
Inform physician if relief is not obtained or if the patient
demonstrate any symptoms suggest bleeding, such as
black tarry stools or coffee ground emesis.
Caution patient to immediately report to physician if
symptoms such as nausea, vomiting and anorexia occurs.
You might also like
- Official History of 86th DivisionDocument344 pagesOfficial History of 86th DivisionFilipNo ratings yet
- Pregabalin LYricaDocument2 pagesPregabalin LYricaKristine Young100% (3)
- Biperiden (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBiperiden (Drug Study)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- JRC JHS-183 SOFTWARE 04 2019 E JD-1387-19 RevDocument26 pagesJRC JHS-183 SOFTWARE 04 2019 E JD-1387-19 RevSKY MARINENo ratings yet
- Er-Drug StudyDocument41 pagesEr-Drug Studyrc_lacampuinganyahooNo ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - AnticonvulsantsDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - AnticonvulsantsZam PamateNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- MIni CaseSTUDY pediaWARDDocument10 pagesMIni CaseSTUDY pediaWARDDANIELLA MALARANG MELNo ratings yet
- Appendix-B (4) (2068)Document21 pagesAppendix-B (4) (2068)namah odatNo ratings yet
- Demerol DrugDocument2 pagesDemerol DrugMsOrange100% (1)
- Drug AnalysisDocument49 pagesDrug Analysisjomalaw6714No ratings yet
- 3 E. Drug StudyDocument4 pages3 E. Drug StudySarrah MaramagNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Document5 pagesAnti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Ronilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy: Signs & Symptoms / Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Ncps / Health TeachingsDocument22 pagesCerebral Palsy: Signs & Symptoms / Pathophysiology / Drug Studies / Ncps / Health TeachingsGeoffrey Sintaan RiveraNo ratings yet
- FluoxetineDocument2 pagesFluoxetineSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalDocument10 pagesDRUG STUDY - BSN III Center For Behavioral Sciences: Generic Name: Psychosis Adult: PO Adverse Effects CNS:ExtrapyramidalChris Denver BancaleNo ratings yet
- DS DR RodasDocument7 pagesDS DR RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDrug Study - LevetiracetamCath Bril100% (4)
- Drugstudy ForcasestudyDocument22 pagesDrugstudy ForcasestudyRovic Selga TrisinioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Cns Drugs Summary Review Notes FinalDocument12 pagesCns Drugs Summary Review Notes Finalمريم حجيNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug-StudyDocument3 pagesTramadol Drug-StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic ClassDocument4 pagesPharmacologic ClassBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyDimple calloNo ratings yet
- Anxiolytic and Hypnotic DrugsDocument3 pagesAnxiolytic and Hypnotic Drugsskoee dbswjNo ratings yet
- Temazepam (Restoril)Document1 pageTemazepam (Restoril)E100% (2)
- CNS Drugs - Summary - Review Notes - Final-1Document12 pagesCNS Drugs - Summary - Review Notes - Final-1Fatima AlmarzooqNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug Study PDFDocument3 pagesTramadol Drug Study PDFMa. Eloisa YrogirogNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Rivotril DrugDocument2 pagesRivotril DrugMery Ong BenitezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tramadol)Document1 pageDrug Study (Tramadol)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormDocument3 pagesDrug Study FormKC KENT LORILLANo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyXio PauNo ratings yet
- THPDocument3 pagesTHPtonmoyNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument3 pagesDiazepamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument1 pageDiazepamGracia Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAlex Silvano0% (1)
- Drug Study EditedDocument8 pagesDrug Study EditedAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- YAWAADocument10 pagesYAWAAZyrene CapulongNo ratings yet
- W9 PharmacologyDocument5 pagesW9 PharmacologyEh paano kung HindiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study On Certain DrugsDocument10 pagesDrug Study On Certain DrugsMelvin D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Yanga - NCP, Drug Study, FdarDocument7 pagesYanga - NCP, Drug Study, Fdar3amabelle arevaloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Muscle Relaxant, Antiseizure & Antiparkinson'sDocument12 pagesDrug Study - Muscle Relaxant, Antiseizure & Antiparkinson'sKristineNo ratings yet
- For MaDocument9 pagesFor MaKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationDocument3 pagesClassification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameterDocument5 pagesDrug Classification Indication Action and Pharmacokinetics Contraindication Adverse Effect Monitoring ParameteryssatNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMAE RACHELLE LAMOSTENo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand NameDocument2 pagesDrug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Intervention Generic Name: Haloperidol (Haldol) Brand Namemyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Week 9 PharmaDocument19 pagesWeek 9 PharmaRachelle CambaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyPRINCESS MARIZHAR OMARNo ratings yet
- CT Week 7 PharmaDocument15 pagesCT Week 7 PharmaJoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Amiodarone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAmiodarone Drug StudyDexter Niel Ortilano CPAC-SNNo ratings yet
- 33 Psych EmergenciesDocument3 pages33 Psych EmergenciesGAPL WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesPharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous Systempatty janeNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: BenzodiazepineDocument5 pagesTherapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: Benzodiazepine Therapeutic Class: Anxiolytic Pharmacologic Class: BenzodiazepineAriadne MangondatoNo ratings yet
- DiazepamDocument2 pagesDiazepam1adie1907No ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Advers Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindic Ation Advers Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesSalwa ZeinNo ratings yet
- Narcolepsy, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesFrom EverandNarcolepsy, A Simple Guide to the Condition, Treatment and Related DiseasesRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- Handling of Synthetic Silica and Silicate: Technical Bulletin Fine Particles 28Document32 pagesHandling of Synthetic Silica and Silicate: Technical Bulletin Fine Particles 28devang asherNo ratings yet
- Advantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencesDocument3 pagesAdvantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencescidracNo ratings yet
- Jaimon Joy CVDocument4 pagesJaimon Joy CVjaimonjoyNo ratings yet
- Citrobacter Freundii: (Atcc 8090™)Document2 pagesCitrobacter Freundii: (Atcc 8090™)carlosNo ratings yet
- Energol HLP-HM 32Document5 pagesEnergol HLP-HM 32fidan muradovaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Non-Isothermal Reactors DesignDocument16 pagesChapter Four Non-Isothermal Reactors Designمصطفى العباديNo ratings yet
- Permian Basin & Eagle Ford Shale From A Global Perspective - Art Berman 2018Document16 pagesPermian Basin & Eagle Ford Shale From A Global Perspective - Art Berman 2018Cliffhanger100% (1)
- 02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisDocument27 pages02 Introduction To Numerical AnalysisBruhNo ratings yet
- 1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance IedxcelDocument14 pages1 Formulae Equations and Amount of Substance Iedxcelshafiqur rahmanNo ratings yet
- ALFOplus User ManualDocument110 pagesALFOplus User ManualAntonio Bezerra0% (2)
- Example Lab ReportDocument20 pagesExample Lab ReportbobtentpegNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz 2 (30 Items) - NurseslabsDocument35 pagesFundamentals of Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz 2 (30 Items) - NurseslabsCHINGANGBAM ANJU CHANUNo ratings yet
- Revision TourDocument2 pagesRevision TourSanskruti ChavanNo ratings yet
- 3 Ways To Unlock The Power of Your Subconscious Mind PDFDocument2 pages3 Ways To Unlock The Power of Your Subconscious Mind PDFRajeswari RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing Q1W1Document39 pagesCreative Writing Q1W1Jhun Ar-Ar Roa RamosNo ratings yet
- 5 Commandments of DatingDocument8 pages5 Commandments of DatingBariki MwasagaNo ratings yet
- E BooksDocument130 pagesE BooksprakashpatelkNo ratings yet
- GemologyDocument7 pagesGemologyManish MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Part 1 Tissues and The IntegumentaryDocument28 pagesLab 3 - Part 1 Tissues and The IntegumentaryNatalie PembertonNo ratings yet
- Stress EssayDocument7 pagesStress EssayMangala RaniNo ratings yet
- Civil Polytechnic Engineering-Transportation Engineering Semester 4 Text BooksDocument226 pagesCivil Polytechnic Engineering-Transportation Engineering Semester 4 Text BooksROHITHNo ratings yet
- Witn (SBG) - Maimun SalehDocument4 pagesWitn (SBG) - Maimun SalehRafly AndrianzaNo ratings yet
- BBC Knowledge Asia Edition September 2015Document100 pagesBBC Knowledge Asia Edition September 2015Кристина Харченко100% (1)
- Duplicate: Invoice: DO NumberDocument2 pagesDuplicate: Invoice: DO NumberLiau Zhan HongNo ratings yet
- DroughtDocument4 pagesDroughtSarvesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Blessing of Medals of Sts Benedict and Anthony of PaduaDocument4 pagesBlessing of Medals of Sts Benedict and Anthony of PaduaJuan Jaylou AnteNo ratings yet
- Anaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationDocument2 pagesAnaesthetic and Respiratory Equipment - Laryngoscopes For Tracheal IntubationAisha MughalNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of SHMP and Advanced Scale Inhibitors For Control of and Scales in RO DesalinationDocument10 pagesEvaluation of SHMP and Advanced Scale Inhibitors For Control of and Scales in RO DesalinationKool LokeshNo ratings yet