Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Some Types of Probability
Some Types of Probability
Uploaded by
Eliza Mae SorianoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Some Types of Probability
Some Types of Probability
Uploaded by
Eliza Mae SorianoCopyright:
Available Formats
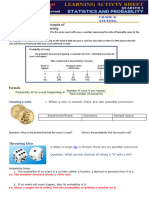
Some types of Probability
1. Experimental Probability It is based on the number of possible outcomes by the total number
of trials. When tossing a coin, the total possible outcomes are two, heads and tails. The total
number of trials is determined by the total times the coin is flipped. If the coin is flipped 50
times and it lands on heads 28 times, then the experimental probability of head is 28/50.
2. Theoretical Probability It is an approach that bases the probability on the possible chances of
something to happen. For example, if you want to know the theoretical probability that a die
will land on a number ―3‖ when rolled, you must determine how many possible outcomes
there are. On a die, there are six numbers that are equally likely to occur, offering six
possibilities. To land on a three, you have a one-in-six, or 1:6, chance of it landing on a ―3‖. So,
the P(3) = 1/6.
3. Subjective Probability It is based on a person‘s own personal reasoning and judgment. It is
the probability that the outcome a person is expecting will actually occur. There are no formal
calculations for subjective probability but instead it is based on a person‘s own knowledge and
feelings. For example, during a sport‘s game, a fan of one team may state that the team they are
rooting for will win. The person bases his decision on facts or opinions regarding the game, the
two teams and the likelihood of the team winning.
You might also like
- Leson 1.1 Notes Probability and Statistics - Virtual SC CourseDocument3 pagesLeson 1.1 Notes Probability and Statistics - Virtual SC CourseAlibinSabahNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IADocument4 pagesMathematics IAPranay Manikanta JainiNo ratings yet
- On ProbabilityDocument13 pagesOn ProbabilitySridhar PantNo ratings yet
- IA Draft MathDocument17 pagesIA Draft MathSara RisticNo ratings yet
- Different Types of ProbabilitiesDocument16 pagesDifferent Types of Probabilitieslunok mariitNo ratings yet
- Probability: Probability Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With Calculating The Likelihood of A Given Event'sDocument4 pagesProbability: Probability Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With Calculating The Likelihood of A Given Event'sjhanelleNo ratings yet
- Statistics 3 - ProbabilityDocument31 pagesStatistics 3 - Probabilityأمجد هاتف منفي جفالNo ratings yet
- Theory of ProbabilityDocument51 pagesTheory of ProbabilityVeronica Sanders57% (7)
- 8401 Assignment No 1Document12 pages8401 Assignment No 1Urooj KhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Project File Term 2Document19 pagesMaths Project File Term 2Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Probability: Tossing A CoinDocument4 pagesProbability: Tossing A Coinxanga007No ratings yet
- CUF Feb16 PDFDocument3 pagesCUF Feb16 PDFIrma Estela Marie EstebanNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics - Yayo 2Document7 pagesProbability and Statistics - Yayo 2riskyNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Module 7Document5 pagesBiostatistics Module 7JANE CASSANONo ratings yet
- Maths Probability Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesMaths Probability Investigatory ProjectPalash KurkuteNo ratings yet
- Probability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsFrom EverandProbability with Permutations: An Introduction To Probability And CombinationsNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Module 7 8Document10 pagesBiostatistics Module 7 8JANE CASSANONo ratings yet
- Probability TheoryDocument221 pagesProbability TheoryJoy Hazel RomeroNo ratings yet
- LS3 Probability JHSDocument34 pagesLS3 Probability JHSJaysanAledZurc100% (1)
- Probability - WikipediaDocument18 pagesProbability - Wikipediaهجو مطرNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Probability and StatisticsDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Probability and StatisticsimtiazbscNo ratings yet
- Stat & Prob - Learning Activity Sheets - 3rd - Basic Concepts of ProbabilityDocument3 pagesStat & Prob - Learning Activity Sheets - 3rd - Basic Concepts of ProbabilityQueeny CabasonNo ratings yet
- Probability and SamplingDocument20 pagesProbability and SamplingTsitsi AbigailNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Gambling Theory: Know the Odds!From EverandIntroduction to Gambling Theory: Know the Odds!Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chapter 13Document18 pagesChapter 13Pawan NayakNo ratings yet
- Module 5 BCC ProbabilityDocument10 pagesModule 5 BCC ProbabilityJean Rose RamillaNo ratings yet
- Presented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrDocument30 pagesPresented By, Name-Ankita Rath ROLL NO-17STAT008 P.G. Dept. of Statistics 2 YrSoumya Ranjan SatapathyNo ratings yet
- Probability-Math Is FunDocument5 pagesProbability-Math Is Funapi-233663523No ratings yet
- SRDS Lecture 1 Brief Introduction To ProbabilityDocument42 pagesSRDS Lecture 1 Brief Introduction To Probabilityprraaddeej chatelNo ratings yet
- Probability DefinitionsDocument8 pagesProbability DefinitionsMahtab UddinNo ratings yet
- Statistics - 2Document1 pageStatistics - 2for4569No ratings yet
- PROBABLITYDocument2 pagesPROBABLITYkkoolwal17No ratings yet
- Combinatorics and ProbabilityDocument17 pagesCombinatorics and ProbabilityHedi mar NecorNo ratings yet
- Probability 120904030152 Phpapp01Document25 pagesProbability 120904030152 Phpapp01gioluisreyes1No ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument23 pagesProbabilityMusicNo ratings yet
- Unit-8 Block 4 Statistics in PsychologyDocument32 pagesUnit-8 Block 4 Statistics in PsychologyRashmi NNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1Marc Kristjan CamarilloNo ratings yet
- The Probability of An Event - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesThe Probability of An Event - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Weaver - ProbabilityDocument4 pagesWeaver - ProbabilityMauro SellittoNo ratings yet
- GEELECDS Introduction To ProbabilityDocument2 pagesGEELECDS Introduction To ProbabilityIbrahim FerrarizNo ratings yet
- Probability SLMDocument8 pagesProbability SLMviswa nadhNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument88 pagesProbability DistributionJay KumarNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Experemental Ang TheoreticalDocument11 pagesDifferentiating Experemental Ang TheoreticalShuyen AmistadNo ratings yet
- Probability IntroDocument6 pagesProbability Intrograzell1234No ratings yet
- Concepts of ProbabilityDocument32 pagesConcepts of ProbabilityRushina SinghiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: ProbabilityDocument13 pagesChapter 2: ProbabilityMatthew MiradorNo ratings yet
- Week 8 (Prob & Prob Dist)Document26 pagesWeek 8 (Prob & Prob Dist)Sucklaj ShahidNo ratings yet
- National College of Business Administration & Economics: Probability & StatisticsDocument5 pagesNational College of Business Administration & Economics: Probability & StatisticsAleena HassanNo ratings yet
- Matematik Tambahan Tugasan SuhaimiDocument20 pagesMatematik Tambahan Tugasan SuhaimiFaiz AbidinNo ratings yet
- History of ProbabilityDocument3 pagesHistory of ProbabilityJeffery Ooi100% (1)
- ProbabilityDocument1 pageProbabilityAniNo ratings yet
- PROBABILITYDocument4 pagesPROBABILITYNatalie Irish VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Probability Had Its Origins in Games of Chance and Gambling. Probability Originated From A Gambler's Dispute in 1654Document3 pagesThe Theory of Probability Had Its Origins in Games of Chance and Gambling. Probability Originated From A Gambler's Dispute in 1654Satyajith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Probability ThesisDocument4 pagesProbability Thesisnawei27No ratings yet
- Block-4 BAGDocument34 pagesBlock-4 BAGStartedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Probability and Normal DistributionDocument12 pagesLesson 1 Probability and Normal DistributionJOHN ALIDONNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument23 pagesProbabilityGaron, Margaret MaeNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminology in ProbabilityDocument4 pagesBasic Terminology in ProbabilityKashaf Amjad100% (1)
- ProbabilityDocument126 pagesProbabilitydawit tesfaNo ratings yet
- Probability Study GuideDocument9 pagesProbability Study GuideereklezaalishviliNo ratings yet
- Journalism - Photojournalism Continuation (Part 2)Document45 pagesJournalism - Photojournalism Continuation (Part 2)Eliza Mae SorianoNo ratings yet
- Journalism - Photojournalism Continuation (Part 1)Document34 pagesJournalism - Photojournalism Continuation (Part 1)Eliza Mae SorianoNo ratings yet
- Journalism - Photojournalism (Part 1) RecordedDocument34 pagesJournalism - Photojournalism (Part 1) RecordedEliza Mae SorianoNo ratings yet
- English 7 - CGDocument26 pagesEnglish 7 - CGEliza Mae SorianoNo ratings yet
- Science 4 CGDocument17 pagesScience 4 CGEliza Mae SorianoNo ratings yet