Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
Uploaded by
ERICH PINZONCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Section 5 QuizDocument5 pagesSection 5 QuizDede M Iskandar100% (1)
- CheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresSATYAJEET SARFARE (Alumni)No ratings yet
- " A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: True False True False and Not Not and orDocument1 page" A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: True False True False and Not Not and orDario RNo ratings yet
- Finxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetDocument1 pageFinxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetmachnik1486624No ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument7 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To Falseang_chang_1No ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument8 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseJorge LuisNo ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument8 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To Falsetrung_tien_datNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument1 pagePythonmepade9551No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonA HNo ratings yet
- Import: Numpy As NPDocument5 pagesImport: Numpy As NPstaffanyNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Document9 pagesDigital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Washakh Ali Muhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1POEASONo ratings yet
- Python3 TheoryDocument40 pagesPython3 Theorytomtang77No ratings yet
- Python Advance CheatsheetDocument11 pagesPython Advance Cheatsheetibrahimelothmani98No ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument18 pagesPython BasicsMalli Naidu KarpurapuNo ratings yet
- NotespythonDocument7 pagesNotespythonbadoni.sanjay1No ratings yet
- Practical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Document8 pagesPractical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Adarsh Kumar PadhanNo ratings yet
- Pythin LearningsDocument51 pagesPythin LearningsNeha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Abhiram KS Xii S2 Roll No 03Document34 pagesAbhiram KS Xii S2 Roll No 03ABHI CODMNo ratings yet
- Python Example ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython Example Programsesmani84100% (1)
- Python Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument31 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceBosun QuadriNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document24 pagesWeek 8divya.kapoor04No ratings yet
- Python BasicDocument18 pagesPython BasicAman UdyogNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument6 pagesPythonfarzad shaloNo ratings yet
- Phytoncodesxx 2Document12 pagesPhytoncodesxx 2Jennifer VeronaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python TutorialDocument8 pagesDiscrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python Tutorialhuy phanNo ratings yet
- Day - 1.ipynb - ColabDocument16 pagesDay - 1.ipynb - Colabvaishnaviware005No ratings yet
- DanyDocument3 pagesDanydaNyNo ratings yet
- CHEATSHEETDocument23 pagesCHEATSHEETNehemiah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Python Programming ExamplesDocument23 pagesPython Programming ExamplesAbu Al SaidNo ratings yet
- Python Learning Made EasyDocument18 pagesPython Learning Made Easyb dNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument157 pagesPythonSRINIDHINo ratings yet
- Python Summary of Functions and LoopsDocument6 pagesPython Summary of Functions and LoopsheforgiveoursinsNo ratings yet
- Perseprep 1'Document5 pagesPerseprep 1'con.audrey1No ratings yet
- Code2pdf 65ced7de9de3bDocument10 pagesCode2pdf 65ced7de9de3bGenNo ratings yet
- Latihan PythonDocument4 pagesLatihan Pythonrozita100% (1)
- Python Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument35 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceMostafa MirbabaieNo ratings yet
- Practice On If ConditionDocument2 pagesPractice On If ConditionManohar DattNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument17 pagesPythonNishantNo ratings yet
- Python 02 ExpressionDocument41 pagesPython 02 ExpressionYI-LIN CHANGNo ratings yet
- Python CheatsheetDocument28 pagesPython CheatsheetMunguntuya AltangerelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To R: 1 Getting StartedDocument14 pagesIntroduction To R: 1 Getting StartedOlalekan K ObisesanNo ratings yet
- A3 Python CheatsheetDocument1 pageA3 Python CheatsheetleeNo ratings yet
- AI LabDocument7 pagesAI Labsethhemant567No ratings yet
- Python Control Struct - VerboseDocument2 pagesPython Control Struct - VerbosemansourNo ratings yet
- Error Related QuestionsDocument5 pagesError Related QuestionsHarsh SatyarthiNo ratings yet
- What Is PythonDocument10 pagesWhat Is Pythonskylarzhang66No ratings yet
- Python ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython ProgramsShyam MukhiyaNo ratings yet
- Mis 211Document17 pagesMis 211Reem MajedNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab Record 21 OriginalDocument64 pagesAcs Lab Record 21 OriginalBomma DineshNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet - StarLABDocument2 pagesPython Cheat Sheet - StarLABAlexNo ratings yet
- Practical Lab:Introduction To Python ProgrammingDocument15 pagesPractical Lab:Introduction To Python Programmingtala massadNo ratings yet
- 02 - Introduction To PythonDocument23 pages02 - Introduction To PythoniknowthissabrinaNo ratings yet
- Python EnglishDocument17 pagesPython EnglishAntoni Essone BibangNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument25 pagesPython Cheat SheetAbhisekh NayakNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet & ReferenceDocument23 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & ReferenceMostafa MirbabaieNo ratings yet
- "Hello World": PrintDocument7 pages"Hello World": PrintMuhammad TalalNo ratings yet
- 3 - PythonDocument33 pages3 - PythonJohn David LoberosNo ratings yet
- PythonprogDocument5 pagesPythonprogAnonymous buSPtQ8F0uNo ratings yet
- Lose WiFi Connection After Suspend Ubuntu 20.04 - Unix & Linux Stack ExchangeDocument4 pagesLose WiFi Connection After Suspend Ubuntu 20.04 - Unix & Linux Stack ExchangeShahinuzzamanAdaNo ratings yet
- GUI Programming With Python - Message Widget in TkinterDocument3 pagesGUI Programming With Python - Message Widget in TkinterNguyễn HọcNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-Class DiagramDocument35 pagesLab 3-Class Diagramsayed omranNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Pembayaran Parkir PROJECT 6Document26 pagesAplikasi Pembayaran Parkir PROJECT 6Setyo Aji WibowoNo ratings yet
- AS - QB - VII - More On HTMLDocument7 pagesAS - QB - VII - More On HTMLsaidabade26No ratings yet
- Google Chrome Os 8952 x3R1D5pDocument16 pagesGoogle Chrome Os 8952 x3R1D5pPavithra deviNo ratings yet
- GV75 @track Air Interface Firmware Update R1.02Document13 pagesGV75 @track Air Interface Firmware Update R1.02João Paulo Machado ClaroNo ratings yet
- Creational Design Patterns:: Elements of Reusable Object - Oriented SoftwareDocument39 pagesCreational Design Patterns:: Elements of Reusable Object - Oriented SoftwareKumar Arikrishnan100% (1)
- Chapter 14Document40 pagesChapter 14Trần Nguyễn An TânNo ratings yet
- 16x8 LED Dot Matrix With MAX7219 ModuleDocument9 pages16x8 LED Dot Matrix With MAX7219 ModuleIvan AldasNo ratings yet
- Introduction Actionscript 3.0Document37 pagesIntroduction Actionscript 3.0RopsonNo ratings yet
- What Is AutosarDocument19 pagesWhat Is AutosarSyrine hammouda100% (1)
- AccentureDocument4 pagesAccentureapi-3710084No ratings yet
- The Game Asset PipelineDocument31 pagesThe Game Asset PipelineWagner de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 SqaDocument31 pagesLecture 7 Sqaarshiya khanNo ratings yet
- Studio 5000: Ordering GuideDocument3 pagesStudio 5000: Ordering GuideMarcelo SantosNo ratings yet
- Control SpeedDocument4 pagesControl SpeedNghiep Hua CongNo ratings yet
- OS Activity2Document18 pagesOS Activity2Prince PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- ComEd1 Module2week3and4Document18 pagesComEd1 Module2week3and4Jean AviezaNo ratings yet
- TOSCA AUTOMATION TRAINING (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesTOSCA AUTOMATION TRAINING (AutoRecovered)mrigank guptaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument41 pagesLogRae RarNo ratings yet
- Oop Lab Manual 2023-24Document25 pagesOop Lab Manual 2023-24hitendrazope2004No ratings yet
- Cs PDFDocument255 pagesCs PDFjoshi_rljNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Generative Drawing: A Self-Paced WorkbookDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Generative Drawing: A Self-Paced WorkbookgmconNo ratings yet
- Algorithm and Flowchart Unit - 1Document10 pagesAlgorithm and Flowchart Unit - 1Akshay PophaliNo ratings yet
- CST8288 ReviewDocument84 pagesCST8288 Reviewsaika sairaiNo ratings yet
- Don't Upgrade To Wii Firmware 4.2 or 4.3!: USB Loader GuideDocument11 pagesDon't Upgrade To Wii Firmware 4.2 or 4.3!: USB Loader GuideJesaca ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Sai CVDocument11 pagesSai CVKaushal KishoreNo ratings yet
- ANALYSISTABS - Daily Project Status UpdateDocument5 pagesANALYSISTABS - Daily Project Status UpdateRamdhan WijayaNo ratings yet
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
Uploaded by
ERICH PINZONOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
CheatSheet Python 2 - Data Structures
Uploaded by
ERICH PINZONCopyright:
Available Formats
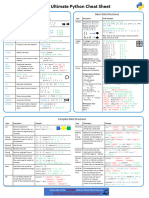
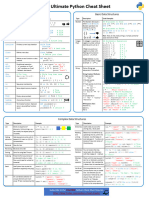
Python Cheat Sheet: Basic Data Types
“A puzzle a day to learn, code, and play” → Visit finxter.com
Description Example
Boolean The Boolean data type is a truth value, either ## 1. Boolean Operations
True or False. x, y = True, False
print(x and not y) # True
The Boolean operators ordered by priority: print(not x and y or x) # True
not x → “if x is False, then x, else y”
x and y → “if x is False, then x, else y” ## 2. If condition evaluates to False
x or y → “if x is False, then y, else x” if None or 0 or 0.0 or '' or [] or {} or set():
# None, 0, 0.0, empty strings, or empty
These comparison operators evaluate to True: # container types are evaluated to False
1 < 2 and 0 <= 1 and 3 > 2 and 2 >=2 and
print("Dead code") # Not reached
1 == 1 and 1 != 0 # True
Integer, An integer is a positive or negative number ## 3. Arithmetic Operations
Float without floating point (e.g. 3). A float is a x, y = 3, 2
positive or negative number with floating point print(x + y) # = 5
precision (e.g. 3.14159265359). print(x - y) # = 1
print(x * y) # = 6
The ‘//’ operator performs integer division. print(x / y) # = 1.5
The result is an integer value that is rounded print(x // y) # = 1
toward the smaller integer number print(x % y) # = 1s
(e.g. 3 // 2 == 1). print(-x) # = -3
print(abs(-x)) # = 3
print(int(3.9)) # = 3
print(float(3)) # = 3.0
print(x ** y) # = 9
String Python Strings are sequences of characters. ## 4. Indexing and Slicing
s = "The youngest pope was 11 years old"
The four main ways to create strings are the print(s[0]) # 'T'
following. print(s[1:3]) # 'he'
print(s[-3:-1]) # 'ol'
1. Single quotes print(s[-3:]) # 'old'
'Yes' x = s.split() # creates string array of words
2. Double quotes print(x[-3] + " " + x[-1] + " " + x[2] + "s")
"Yes"
# '11 old popes'
3. Triple quotes (multi-line)
"""Yes
## 5. Most Important String Methods
We Can"""
y = " This is lazy\t\n "
4. String method
print(y.strip()) # Remove Whitespace: 'This is lazy'
str(5) == '5' # True
print("DrDre".lower()) # Lowercase: 'drdre'
5. Concatenation
print("attention".upper()) # Uppercase: 'ATTENTION'
"Ma" + "hatma" # 'Mahatma'
print("smartphone".startswith("smart")) # True
print("smartphone".endswith("phone")) # True
print("another".find("other")) # Match index: 2
These are whitespace characters in strings.
print("cheat".replace("ch", "m")) # 'meat'
● Newline \n
print(','.join(["F", "B", "I"])) # 'F,B,I'
● Space \s
print(len("Rumpelstiltskin")) # String length: 15
● Tab \t print("ear" in "earth") # Contains: True
You might also like
- Section 5 QuizDocument5 pagesSection 5 QuizDede M Iskandar100% (1)
- CheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresDocument1 pageCheatSheet Python 2 Data StructuresSATYAJEET SARFARE (Alumni)No ratings yet
- " A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: True False True False and Not Not and orDocument1 page" A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: True False True False and Not Not and orDario RNo ratings yet
- Finxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetDocument1 pageFinxter WorldsMostDensePythonCheatSheetmachnik1486624No ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument7 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To Falseang_chang_1No ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument8 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseJorge LuisNo ratings yet
- Basic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To FalseDocument8 pagesBasic Data Structures Keywords: Types Evaluate To Falsetrung_tien_datNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument1 pagePythonmepade9551No ratings yet
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonDocument9 pages1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Merged Programming PythonA HNo ratings yet
- Import: Numpy As NPDocument5 pagesImport: Numpy As NPstaffanyNo ratings yet
- Digital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Document9 pagesDigital Image Processing Lab Manual# 1Washakh Ali Muhammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1POEASONo ratings yet
- Python3 TheoryDocument40 pagesPython3 Theorytomtang77No ratings yet
- Python Advance CheatsheetDocument11 pagesPython Advance Cheatsheetibrahimelothmani98No ratings yet
- Python BasicsDocument18 pagesPython BasicsMalli Naidu KarpurapuNo ratings yet
- NotespythonDocument7 pagesNotespythonbadoni.sanjay1No ratings yet
- Practical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Document8 pagesPractical Assignment Xi SC (CS) - 2022-23Adarsh Kumar PadhanNo ratings yet
- Pythin LearningsDocument51 pagesPythin LearningsNeha KhatriNo ratings yet
- Abhiram KS Xii S2 Roll No 03Document34 pagesAbhiram KS Xii S2 Roll No 03ABHI CODMNo ratings yet
- Python Example ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython Example Programsesmani84100% (1)
- Python Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument31 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceBosun QuadriNo ratings yet
- Week 8Document24 pagesWeek 8divya.kapoor04No ratings yet
- Python BasicDocument18 pagesPython BasicAman UdyogNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument6 pagesPythonfarzad shaloNo ratings yet
- Phytoncodesxx 2Document12 pagesPhytoncodesxx 2Jennifer VeronaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python TutorialDocument8 pagesDiscrete Structures Lab 1 Python Basics: 1 Python Installation 2 Python Tutorialhuy phanNo ratings yet
- Day - 1.ipynb - ColabDocument16 pagesDay - 1.ipynb - Colabvaishnaviware005No ratings yet
- DanyDocument3 pagesDanydaNyNo ratings yet
- CHEATSHEETDocument23 pagesCHEATSHEETNehemiah GarciaNo ratings yet
- Python Programming ExamplesDocument23 pagesPython Programming ExamplesAbu Al SaidNo ratings yet
- Python Learning Made EasyDocument18 pagesPython Learning Made Easyb dNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument157 pagesPythonSRINIDHINo ratings yet
- Python Summary of Functions and LoopsDocument6 pagesPython Summary of Functions and LoopsheforgiveoursinsNo ratings yet
- Perseprep 1'Document5 pagesPerseprep 1'con.audrey1No ratings yet
- Code2pdf 65ced7de9de3bDocument10 pagesCode2pdf 65ced7de9de3bGenNo ratings yet
- Latihan PythonDocument4 pagesLatihan Pythonrozita100% (1)
- Python Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceDocument35 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & Quick ReferenceMostafa MirbabaieNo ratings yet
- Practice On If ConditionDocument2 pagesPractice On If ConditionManohar DattNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument17 pagesPythonNishantNo ratings yet
- Python 02 ExpressionDocument41 pagesPython 02 ExpressionYI-LIN CHANGNo ratings yet
- Python CheatsheetDocument28 pagesPython CheatsheetMunguntuya AltangerelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To R: 1 Getting StartedDocument14 pagesIntroduction To R: 1 Getting StartedOlalekan K ObisesanNo ratings yet
- A3 Python CheatsheetDocument1 pageA3 Python CheatsheetleeNo ratings yet
- AI LabDocument7 pagesAI Labsethhemant567No ratings yet
- Python Control Struct - VerboseDocument2 pagesPython Control Struct - VerbosemansourNo ratings yet
- Error Related QuestionsDocument5 pagesError Related QuestionsHarsh SatyarthiNo ratings yet
- What Is PythonDocument10 pagesWhat Is Pythonskylarzhang66No ratings yet
- Python ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython ProgramsShyam MukhiyaNo ratings yet
- Mis 211Document17 pagesMis 211Reem MajedNo ratings yet
- Acs Lab Record 21 OriginalDocument64 pagesAcs Lab Record 21 OriginalBomma DineshNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet - StarLABDocument2 pagesPython Cheat Sheet - StarLABAlexNo ratings yet
- Practical Lab:Introduction To Python ProgrammingDocument15 pagesPractical Lab:Introduction To Python Programmingtala massadNo ratings yet
- 02 - Introduction To PythonDocument23 pages02 - Introduction To PythoniknowthissabrinaNo ratings yet
- Python EnglishDocument17 pagesPython EnglishAntoni Essone BibangNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat SheetDocument25 pagesPython Cheat SheetAbhisekh NayakNo ratings yet
- Python Cheat Sheet & ReferenceDocument23 pagesPython Cheat Sheet & ReferenceMostafa MirbabaieNo ratings yet
- "Hello World": PrintDocument7 pages"Hello World": PrintMuhammad TalalNo ratings yet
- 3 - PythonDocument33 pages3 - PythonJohn David LoberosNo ratings yet
- PythonprogDocument5 pagesPythonprogAnonymous buSPtQ8F0uNo ratings yet
- Lose WiFi Connection After Suspend Ubuntu 20.04 - Unix & Linux Stack ExchangeDocument4 pagesLose WiFi Connection After Suspend Ubuntu 20.04 - Unix & Linux Stack ExchangeShahinuzzamanAdaNo ratings yet
- GUI Programming With Python - Message Widget in TkinterDocument3 pagesGUI Programming With Python - Message Widget in TkinterNguyễn HọcNo ratings yet
- Lab 3-Class DiagramDocument35 pagesLab 3-Class Diagramsayed omranNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Pembayaran Parkir PROJECT 6Document26 pagesAplikasi Pembayaran Parkir PROJECT 6Setyo Aji WibowoNo ratings yet
- AS - QB - VII - More On HTMLDocument7 pagesAS - QB - VII - More On HTMLsaidabade26No ratings yet
- Google Chrome Os 8952 x3R1D5pDocument16 pagesGoogle Chrome Os 8952 x3R1D5pPavithra deviNo ratings yet
- GV75 @track Air Interface Firmware Update R1.02Document13 pagesGV75 @track Air Interface Firmware Update R1.02João Paulo Machado ClaroNo ratings yet
- Creational Design Patterns:: Elements of Reusable Object - Oriented SoftwareDocument39 pagesCreational Design Patterns:: Elements of Reusable Object - Oriented SoftwareKumar Arikrishnan100% (1)
- Chapter 14Document40 pagesChapter 14Trần Nguyễn An TânNo ratings yet
- 16x8 LED Dot Matrix With MAX7219 ModuleDocument9 pages16x8 LED Dot Matrix With MAX7219 ModuleIvan AldasNo ratings yet
- Introduction Actionscript 3.0Document37 pagesIntroduction Actionscript 3.0RopsonNo ratings yet
- What Is AutosarDocument19 pagesWhat Is AutosarSyrine hammouda100% (1)
- AccentureDocument4 pagesAccentureapi-3710084No ratings yet
- The Game Asset PipelineDocument31 pagesThe Game Asset PipelineWagner de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 SqaDocument31 pagesLecture 7 Sqaarshiya khanNo ratings yet
- Studio 5000: Ordering GuideDocument3 pagesStudio 5000: Ordering GuideMarcelo SantosNo ratings yet
- Control SpeedDocument4 pagesControl SpeedNghiep Hua CongNo ratings yet
- OS Activity2Document18 pagesOS Activity2Prince PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- ComEd1 Module2week3and4Document18 pagesComEd1 Module2week3and4Jean AviezaNo ratings yet
- TOSCA AUTOMATION TRAINING (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesTOSCA AUTOMATION TRAINING (AutoRecovered)mrigank guptaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument41 pagesLogRae RarNo ratings yet
- Oop Lab Manual 2023-24Document25 pagesOop Lab Manual 2023-24hitendrazope2004No ratings yet
- Cs PDFDocument255 pagesCs PDFjoshi_rljNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Generative Drawing: A Self-Paced WorkbookDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Generative Drawing: A Self-Paced WorkbookgmconNo ratings yet
- Algorithm and Flowchart Unit - 1Document10 pagesAlgorithm and Flowchart Unit - 1Akshay PophaliNo ratings yet
- CST8288 ReviewDocument84 pagesCST8288 Reviewsaika sairaiNo ratings yet
- Don't Upgrade To Wii Firmware 4.2 or 4.3!: USB Loader GuideDocument11 pagesDon't Upgrade To Wii Firmware 4.2 or 4.3!: USB Loader GuideJesaca ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Sai CVDocument11 pagesSai CVKaushal KishoreNo ratings yet
- ANALYSISTABS - Daily Project Status UpdateDocument5 pagesANALYSISTABS - Daily Project Status UpdateRamdhan WijayaNo ratings yet