Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiratory System+
Respiratory System+
Uploaded by
Yasin Abass0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views24 pagesThe respiratory system has upper and lower tracts. The upper tract includes the nose, pharynx and larynx, while the lower tract includes the trachea, bronchi and lungs. The nose filters air and contains smell receptors. The pharynx is a passageway for both air and food. The larynx contains the vocal cords which produce sound. The trachea divides into bronchi which branch into bronchioles and connect to alveoli in the lungs, where gas exchange occurs.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe respiratory system has upper and lower tracts. The upper tract includes the nose, pharynx and larynx, while the lower tract includes the trachea, bronchi and lungs. The nose filters air and contains smell receptors. The pharynx is a passageway for both air and food. The larynx contains the vocal cords which produce sound. The trachea divides into bronchi which branch into bronchioles and connect to alveoli in the lungs, where gas exchange occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views24 pagesRespiratory System+
Respiratory System+
Uploaded by
Yasin AbassThe respiratory system has upper and lower tracts. The upper tract includes the nose, pharynx and larynx, while the lower tract includes the trachea, bronchi and lungs. The nose filters air and contains smell receptors. The pharynx is a passageway for both air and food. The larynx contains the vocal cords which produce sound. The trachea divides into bronchi which branch into bronchioles and connect to alveoli in the lungs, where gas exchange occurs.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 24
Dr/ Sarah Mohamed
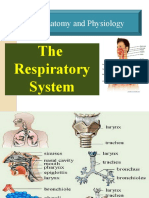
COMPONENTS:
1) Upper Respiratory Tract:
nose , pharynx , larynx
2)Lower Respiratory Tract:
trachea , bronchi , lungs
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS
1. supplies the body with oxygen and disposes of
carbon dioxide.
2. filters inspired air.
3. produces sound.
4. Smell sensation.
5. rids the body of some excess water and heat.
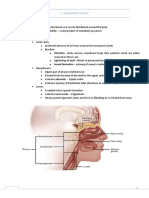
NOSE :
The nose is divided into two regions:
1*The external nose having external nasal opening
2*The internal nasal cavity:
.Lies posterior to the external nose
.Is divided by a midline nasal septum into 2
halves.
.Opens posteriorly into the naso-pharynx via
internal nasal opening.
Internal nasal cavity (cont.):
The cavity has:
1-floor : is formed by the hard and soft palates
separating it from oral cavity below.
2- roof : it is bony separating it form cranial cavity
above.
3-medial wall: is called nasal septum .
4-lateral wall: is bony and receives the opening of
paranasal sinuses.
Internal nasal cavity (cont.):
It is lined by vascular mucous membrane. The upper
part of this mucosa contains smell receptors and so
called (olfactory
mucosa.)
Paranasal Sinuses
Four bones of the skull contain paired air spaces
called the paranasal sinuses – (frontal, ethmoidal,
sphenoidal, maxillary).
Function:
1-Decrease skull bone weight
2-Warm, moisten and filter incoming air
3-Add resonance to voice.
Communicate with the nasal cavity by ducts.
PHARYNX:
*Common space used by both the respiratory
and digestive systems.
*Commonly called the throat.
*It is muscular tube between nose and
larynx.
*Common pathway for both air and food
Pharynx is divided into 3 parts:
1- Nasopharynx: lies behind the nose, showing 2
features:
a)nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoids): lies
behind the nose. When enlarge it cause nasal
obstruction.
b)Opening of eustachian tube which
connect it with middle ear.
2-Oropharynx : continues with oral cavity (contain
tonsils).
3-Laryngeopharynx : continues with larynx.
LARYNX: (VOICE BOX)
*Site : front of neck .
*Structure: formed of group of cartilages connected
to each other by fibrous membrane and small
muscles.
On swallowing , the laryngeal inlet is closed by
epiglottis (one of laryngeal cartilages) , so the
food passes into the esophagus not larynx.
Inside larynx there is 2 vocal cords which are
mucous membrane folds , their vibration produce
the sound.
Trachea:
Length: 10 -12cm.
Site : its upper part in neck while lower in thorax.
in front of esophagus.
Beginning : in the neck at the lower border of
larynx.
End : in the thorax at level of thoracic vertebrae 4
where it divides into right & left bronchus (level
of bifurcation).
Structure: it is formed of incomplete rings of
cartilage arranged above each other to keep
trachea open all the time.
Bronchi :
Trachea divides into 2 main bronchi (right and
left).
Right main bronchus divides into 2 bronchi before
entering the lung while the left bronchus divides
after enter lung.
After entering the lung each bronchus undergoes
repeated branching , the final and smallest
branches are called the bronchioles.
Bronchioles are connected to alveoli , which are
surrounded by a net work of blood capillaries.
Alveoli are the site of gas exchange.
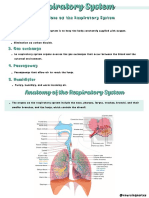
Lung :
Shape: cone shaped with apex above the level of
clavicle and base downwards on diaphragm.
Site : in the thoracic cavity.
Hilum of lung : it present in the medial surface of
lung showing passage of :
1-bronchi
2-pulmonary artery
3-pulmonary vein.
Lobes of lungs:
Each lung is divided into lobes , right one
divides into 3 lobes while left divides into two.
Pleura :
It is the covering of lung.
pleura is formed of 2 layers :
1- parietal layer: outer , lines the thoracic cavity.
2- visceral layer: inner , covers the lungs.
Pleural cavity: it present between the 2 layer ,
containing serous fluid which act as lubricant.
You might also like
- Holistic DentistryDocument13 pagesHolistic Dentistrydnybell67% (3)
- Liver MCQ SurgeryDocument114 pagesLiver MCQ Surgerydrnsatyaprasad100% (3)
- Ultherapy Patient BrochureDocument2 pagesUltherapy Patient BrochureSusantiNo ratings yet
- OHIP BillingDocument37 pagesOHIP BillingSyedKashifAliNo ratings yet
- Respiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiration, Types of Respiration and Anatomy of Human Respiratory Systemegfr3yfgNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Respiratory SystemDocument37 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory SystemPal SedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemDocument82 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Respiratory SystemMaria Angelique Ofciar100% (2)
- Lect 3Document8 pagesLect 3علي الاسديNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System s2 2019Document56 pagesRespiratory System s2 2019noviantyramadhani12No ratings yet
- Respiratory FinalsDocument4 pagesRespiratory FinalsAlliana Pauline AbanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Respiratory System (Vizconde, Ehreiz Raiden C. BSN2A)Raiden VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesRespiratory SystemShivani Sriram100% (1)
- Respiratory System AnatomyDocument38 pagesRespiratory System AnatomyAbdirazak AliNo ratings yet
- Zoo 1 PPT 10 Respiratory (2015)Document17 pagesZoo 1 PPT 10 Respiratory (2015)Zucc mahnutNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - HandoutsDocument35 pagesRESPIRATORY DISTURBANCES - Handoutsfebie pachecoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - NotesDocument4 pagesRespiratory System - NotessNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedDocument43 pagesThe Respiratory System: ASTIKA NUR ROHMAH, S.Kep., NS., M.BiomedAdek KhazeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemKhushi JainNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument53 pagesRespiratory SystemRotan CirebonNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemJay DaxiniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy RespiratoryDocument68 pagesAnatomy RespiratorydofezdsNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemNandita Halder100% (1)
- Anatomy of The Respiratory System 1Document8 pagesAnatomy of The Respiratory System 1Grace Noviyanthi SinambelaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument21 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory Systemsameeha semiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. Aim: To Study The Human Respiratory System. RequirementsDocument6 pagesExperiment No. Aim: To Study The Human Respiratory System. RequirementsRohan Saste100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationDocument48 pagesChapter 10 Respiratory System PresentationMary Jane LubricoNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AnjuDocument38 pagesRESPIRATORY SYSTEM Anjuanju rachel jose100% (1)
- X Respiratory SystemDocument31 pagesX Respiratory SystemHannah DiñosoNo ratings yet
- 2- الجاهزة20.02.2022 lower Respiratory system physiologyDocument32 pages2- الجاهزة20.02.2022 lower Respiratory system physiologybessan alfqeatNo ratings yet
- UNIT 8 (Respiratory System)Document6 pagesUNIT 8 (Respiratory System)Workinesh Kaynabo KambaloNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Document13 pagesSupplementary Material 3.1 Basic Concepts and Assessment (N) - 2Kent Borro CantomayorNo ratings yet
- OxygenationDocument20 pagesOxygenationKhie-An OcampoNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesParts and Functions of Respiratory Systemjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- 2020 Respiratory SystemDocument146 pages2020 Respiratory Systemsyafi zulNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2nd-U-3 Respiratory SystemDocument113 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-3 Respiratory Systemsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Group1 Review of Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesGroup1 Review of Respiratory Systemjohn obinaNo ratings yet
- Animalphysio2nd 180428184330Document28 pagesAnimalphysio2nd 180428184330environmentalgyanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemMiss Glozirie An BacangNo ratings yet
- 4 Respiratory System (Report Revised)Document35 pages4 Respiratory System (Report Revised)ARra OdezaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System Consists of 2 PartsDocument3 pagesThe Respiratory System Consists of 2 PartsAquardoleo ValentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22 Notes Respiratory SystemDocument36 pagesChapter 22 Notes Respiratory SystemMarilia BonorinoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory NotesDocument6 pagesRespiratory NotesBethany CrawfordNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThe Respiratory SystemNada RonaldNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument16 pagesRespiratory System PDFMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document6 pagesChapter 15Holy HaeinNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Sakina Dept. Anatomi Dan Histologi FK UnairDocument52 pagesRespiratory System: Sakina Dept. Anatomi Dan Histologi FK UnairFhyrha MyuceNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemKatherineMysterieuxNo ratings yet
- A & P RespiratoryDocument18 pagesA & P Respiratoryamirul haakimNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKelly Camero ÜNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Respiratory SystemIftikharNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument71 pagesRespiratory SystemmarygracetamborlnhsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - PDF - 79624Document7 pagesRespiratory System - PDF - 79624Mohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesWeek 3 Respiratory SystemangeliaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument77 pagesRespiratory SystemYour Materials100% (1)
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemКрістіна БаландаNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesRespiratory SystemSumita GhoshNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument57 pagesAnatomy of Respiratory SystemRyan Larsen100% (1)
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory SystemTricia CabiliNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJuma SammyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument74 pagesRespiratory SystemJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- Minor Surgical Procedures in Maxillofacial SurgeryDocument65 pagesMinor Surgical Procedures in Maxillofacial SurgerydrzibranNo ratings yet
- Dental ReviewDocument5 pagesDental ReviewUmarsyah AliNo ratings yet
- Code Blue Policy - Adult Care Sites - Calgary ZoneDocument9 pagesCode Blue Policy - Adult Care Sites - Calgary ZoneLLyreONo ratings yet
- Coronary Atherosclerosis Current Management and Treatment ChourmouziosDocument472 pagesCoronary Atherosclerosis Current Management and Treatment ChourmouziosMarcelo Andrade100% (1)
- Kegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksDocument57 pagesKegawatan Respirasi Pada Keganasan Rongga ToraksChristian HarnatNo ratings yet
- Nihms 818708Document22 pagesNihms 818708bela RachmanNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Card AnswersDocument29 pagesOphthalmology Card AnswersRaihan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Credentialing Pathways For Aesthetic Medicine Practice in Pakistan 13th JUNE 2022Document14 pagesCredentialing Pathways For Aesthetic Medicine Practice in Pakistan 13th JUNE 2022tasawwur zahoorNo ratings yet
- Right Heart Failure and Cardiorenal Syndrome 2020Document18 pagesRight Heart Failure and Cardiorenal Syndrome 2020Raul FernandoNo ratings yet
- Conservative Removal of Caries With CarisolvDocument5 pagesConservative Removal of Caries With CarisolvDontoNo ratings yet
- 5b9f87df82236UG Syllabus (MBBS) AIIMS RaipurDocument8 pages5b9f87df82236UG Syllabus (MBBS) AIIMS RaipurBri MinNo ratings yet
- Instrument Used in ExodontaDocument32 pagesInstrument Used in ExodontaNoor Abdullah AlNo ratings yet
- MyopiaDocument83 pagesMyopiaOphthalmology DiscussionNo ratings yet
- Risk Factor Analysis FOR Long-Term Unfavorable Ocular Outcomes in Children Treated FOR RETINOPATHY OF PREMATURITYDocument7 pagesRisk Factor Analysis FOR Long-Term Unfavorable Ocular Outcomes in Children Treated FOR RETINOPATHY OF PREMATURITYSalma HamdyNo ratings yet
- A5 Brochure - Revise - Centre Pinning - With IndoscopeDocument32 pagesA5 Brochure - Revise - Centre Pinning - With IndoscopeGerman DrumsNo ratings yet
- Endodontic SurgeryDocument21 pagesEndodontic SurgeryFusea RaduNo ratings yet
- OCO Biomedical 2013 Product Catalog 10-2013Document28 pagesOCO Biomedical 2013 Product Catalog 10-2013eddy1012805361No ratings yet
- Castro, Almeacor D. - Digestive ExerciseDocument4 pagesCastro, Almeacor D. - Digestive ExerciseJaja Dofitas CastroNo ratings yet
- Stepwise Provisional Versus Systematic Culotte For Stenting of True Coronary Bifurcation Lesions - Five-Year Follow-Up of The Multicentre Randomised EBC TWO Trial - EuroInterventionDocument9 pagesStepwise Provisional Versus Systematic Culotte For Stenting of True Coronary Bifurcation Lesions - Five-Year Follow-Up of The Multicentre Randomised EBC TWO Trial - EuroInterventionValentin CHIONCELNo ratings yet
- SANTHOSH JENNIFER MARIA LABEX 24 Ant. Abd Wall and CavityDocument9 pagesSANTHOSH JENNIFER MARIA LABEX 24 Ant. Abd Wall and CavityJENNIFER MARIA SANTHOSHNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Surgery DR NISHTHADocument23 pagesGlaucoma Surgery DR NISHTHAnishtha singhNo ratings yet
- Heparin Sodium Injection, USP: RX Only DescriptionDocument29 pagesHeparin Sodium Injection, USP: RX Only DescriptionArchie TobiasNo ratings yet
- Va Medica: Consensus Report Italiano Sul Trattamento Con Tossina Botulinica Per Uso EsteticoDocument13 pagesVa Medica: Consensus Report Italiano Sul Trattamento Con Tossina Botulinica Per Uso EsteticoEmiliano Prandelli100% (1)
- Brittni Mckane Clin Onc AssignDocument18 pagesBrittni Mckane Clin Onc Assignapi-569589889No ratings yet
- Symmetry Surgical® Bookwalter® Self-Retaining Retractor Catalog Literature - Bookwalter CatalogDocument36 pagesSymmetry Surgical® Bookwalter® Self-Retaining Retractor Catalog Literature - Bookwalter CatalogBruno PinaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument15 pagesCoronary Artery Diseasektae337No ratings yet