Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dehydration Secondary To Diarrhea - NPD
Dehydration Secondary To Diarrhea - NPD
Uploaded by
Lovely Grace Pore0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesThis document discusses dehydration secondary to diarrhea. It notes that diarrhea commonly occurs in children aged 6 months to 5 years old due to factors like poor sanitation, food intake, and inadequate water supplies. The digestion process becomes too fast during diarrhea to allow for proper nutrient absorption. Symptoms of severe diarrhea include dehydration. If dehydration caused by diarrhea is treated medically, the outcomes are more positive. However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious issues like seizures, brain damage, and even death.
Original Description:
NURSING PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGRAM
Original Title
DEHYDRATION SECONDARY TO DIARRHEA _ NPD
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses dehydration secondary to diarrhea. It notes that diarrhea commonly occurs in children aged 6 months to 5 years old due to factors like poor sanitation, food intake, and inadequate water supplies. The digestion process becomes too fast during diarrhea to allow for proper nutrient absorption. Symptoms of severe diarrhea include dehydration. If dehydration caused by diarrhea is treated medically, the outcomes are more positive. However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious issues like seizures, brain damage, and even death.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
28 views3 pagesDehydration Secondary To Diarrhea - NPD
Dehydration Secondary To Diarrhea - NPD
Uploaded by
Lovely Grace PoreThis document discusses dehydration secondary to diarrhea. It notes that diarrhea commonly occurs in children aged 6 months to 5 years old due to factors like poor sanitation, food intake, and inadequate water supplies. The digestion process becomes too fast during diarrhea to allow for proper nutrient absorption. Symptoms of severe diarrhea include dehydration. If dehydration caused by diarrhea is treated medically, the outcomes are more positive. However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious issues like seizures, brain damage, and even death.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
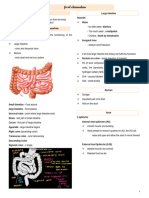
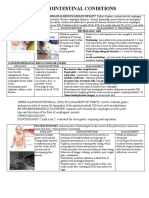
DEHYDRATION SECONDARY TO DIARRHEA
NURSING PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DIAGRAM
Predisposing Factors
Age Poor sanitation Food Intake Inadequate
water
Diarrhea typically A lack of personal Eating foods supplies
occurs in children hygiene and that upset the Storing water
aged 6 months to availability of digestive in containers
5 years, and is handwashing system. without lids,
most common facility. use of dippers
among children 2- to draw water
4 years old. from water
storage
containers
Precipitating Factors
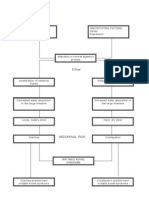
Digestion Process
Malabsorption of food (poor
absorption) where the food
moves too fast through your
bowels for nutrients to be
absorbed
The digestion process becomes
too fast to allow for the large
intestine to absorb the excess
liquid.
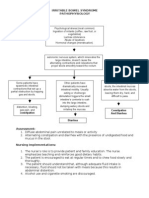
The main symptom of diarrhea is loose or watery
stool, it also includes bloating or cramps in the
abdomen, a strong and urgent need to have a bowel
movement, nausea (upset stomach).
If you have severe diarrhea, you may experience
symptoms like fever, weight loss, dehydration,
severe pain, and vomiting.
Diagnostic Test & Laboratory Test
Blood test, Stool test, Breath test, Flexible
sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, Upper endoscopy
DIARRHEA
Therefore, there is progression deterioration and affecting
its function.
Affected absorption fluid feeling thirsty and lightheaded, dry
and electrolytes mouth, tiredness, having dark
colored, strong-smelling urine,
passing urine less often than usual.
Affected secretion of chloride Excessive fatigue, muscle weakness,
ions and water breathing problems, frequent
vomiting, prolonged diarrhea,
excessive thirst, high blood pressure.
Affected excretion of waste Vomiting, bloody diarrhea (loose
and toxins stool/poop), stomach pain
DIAGNOSTIC TEST & IMAGING TEST
Physical Exam, Vital signs, Urinalysis, Blood test,
DEHYDRATION
If treated If not treated
Medical Surgical Nursing Seizures
Management Management Management
- Acute pain
- Loperamide - Diarrhea
(Imodium) - High risk for fluid Brain Damage
- Bismuth volume deficit
subsalicylate - Fatigue
(Pepto-Bismol) - Knowledge DEATH
- Rifaximin Deficient
You might also like
- The Memory Healer ProgramDocument100 pagesThe Memory Healer Programdancingelk2189% (18)
- Methods in Behavioral Research 12th Edition Cozby Solutions Manual DownloadDocument8 pagesMethods in Behavioral Research 12th Edition Cozby Solutions Manual DownloadJeffrey Gliem100% (16)
- Assignment of International RelationsDocument7 pagesAssignment of International RelationsAlina MinhasNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument45 pagesCase Studymejul100% (2)
- Constipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Document20 pagesConstipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Vaidya M.R. PoornimaNo ratings yet
- Constipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Document26 pagesConstipation and Bowel Obstructions PP Rat 10.2020Osman Bin SaifNo ratings yet
- Digestive Care Package AdvancedDocument22 pagesDigestive Care Package AdvancedWwNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea NCP Pedia WardDocument4 pagesDiarrhea NCP Pedia WardKyle DapulagNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2Document20 pagesNursing Management of Gastro Intestinal Problem 2wyneNo ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination: Anatomy and Physiology of GitDocument3 pagesBowel Elimination: Anatomy and Physiology of GitEmmanuelRodriguezNo ratings yet
- Diare Dehidrasi BeratDocument40 pagesDiare Dehidrasi BeratcutietimothyNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea (Diare)Document9 pagesDiarrhea (Diare)Eki MegaraniNo ratings yet
- Anal Fissure Secondary To Chronic ConstipationDocument3 pagesAnal Fissure Secondary To Chronic ConstipationLovely Grace PoreNo ratings yet
- (Roselle Balicas) - Chrome - LNKDocument8 pages(Roselle Balicas) - Chrome - LNKRose CasBalNo ratings yet
- DiareDocument5 pagesDiarefarisNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On GIT Laxatives & Purgatives: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasDocument13 pagesDrugs Acting On GIT Laxatives & Purgatives: Dr. Syed Muneeb Anjum (PH.D.) Ips, UvasSultan Abdul Hamid IINo ratings yet
- (S) Digestive SystemDocument31 pages(S) Digestive SystemRehanNo ratings yet
- AGE ReadingDocument7 pagesAGE ReadingyasiraNo ratings yet
- Persistent Diarrhea-Sept2009Document43 pagesPersistent Diarrhea-Sept2009Mega Dwi PutriNo ratings yet
- Kegawatan Pada Diare Dehidrasi BeratDocument40 pagesKegawatan Pada Diare Dehidrasi BeratAkram BatjoNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction DR WelmanDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction DR Welmanluthfiyya syafiqaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction DR WelmanDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction DR Welmanluthfiyya syafiqaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction DR WelmanDocument10 pagesIntestinal Obstruction DR Welmanluthfiyya syafiqaNo ratings yet
- Care of The Child With Gastrointestinal Dysfunction: Betsy Johnson, MSN, CPNP-PCDocument66 pagesCare of The Child With Gastrointestinal Dysfunction: Betsy Johnson, MSN, CPNP-PCGelsey Gelsinator JianNo ratings yet
- Laxatives and Anti-DiarrhealDocument28 pagesLaxatives and Anti-DiarrhealimnasNo ratings yet
- Approach To Diagnosis and Therapy of The: Patient With Acute DiarrheaDocument8 pagesApproach To Diagnosis and Therapy of The: Patient With Acute DiarrheaUtari DesyaNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument6 pagesBowel Elimination2022105340No ratings yet
- Handout 6. Esavs Constipation & Megacolon 2021Document8 pagesHandout 6. Esavs Constipation & Megacolon 2021UTARI PUTRINo ratings yet
- A. Related FactorsDocument10 pagesA. Related FactorsEva YuliaNo ratings yet
- Diarrhoea in Children: An ApproachDocument78 pagesDiarrhoea in Children: An ApproachNP SinghNo ratings yet
- Dehydration: Royal Medical Services Provider Unit Nursing Continuing Education and Training DepartmentDocument34 pagesDehydration: Royal Medical Services Provider Unit Nursing Continuing Education and Training DepartmentJanuaryNo ratings yet
- 2016 Investigation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDocument10 pages2016 Investigation of Chronic DiarrhoeaDanielaRojasNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea in ChildrenDocument42 pagesDiarrhea in ChildrenIPNATC NEPALNo ratings yet
- Constipation in Children: Muzal KadimDocument43 pagesConstipation in Children: Muzal KadimAnonymous G20oAbl6p8No ratings yet
- Daud Khan 1045Document31 pagesDaud Khan 1045Iqra BatoolNo ratings yet
- Ibs 2Document1 pageIbs 2Alan James Sy Cañizares100% (1)
- Constipation and Bladder and Bowel Control - Oct 2013Document4 pagesConstipation and Bladder and Bowel Control - Oct 2013Dr.Kamlesh BariNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea: Group 4: Surya Patricya Serikat Niscaya Theresia Yuni Venggy Reylandhie Yustina NayDocument15 pagesDiarrhea: Group 4: Surya Patricya Serikat Niscaya Theresia Yuni Venggy Reylandhie Yustina NayvenggyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System DisordersDocument117 pagesDigestive System DisordersSusan Batan BandongNo ratings yet
- Elimination: Dumip-Ig, Maricel Gregorio, Kristine Milagrosa, Nina JesusaDocument30 pagesElimination: Dumip-Ig, Maricel Gregorio, Kristine Milagrosa, Nina JesusaKristine Las GregorioNo ratings yet
- Prepared By: Melody Gay M. Igcasenza, PTRP, RNDocument122 pagesPrepared By: Melody Gay M. Igcasenza, PTRP, RNtishpatNo ratings yet
- Stomach and Intestine Lesson 15Document25 pagesStomach and Intestine Lesson 15Neil AngNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument1 pagePa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403No ratings yet
- GI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Document85 pagesGI Sympt Mokhtar (2015)Abdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Diet in Gastro Intestinal and Liver Disorders: ObjectivesDocument19 pagesDiet in Gastro Intestinal and Liver Disorders: ObjectivesIyappan SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Case Report Diarrhea: Adviser By: Dr. Alfred, Sp. A Writen By: Meylinda (1261050133)Document18 pagesCase Report Diarrhea: Adviser By: Dr. Alfred, Sp. A Writen By: Meylinda (1261050133)Norma Diona PurbaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2Document52 pagesCase Study 2mejulNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument4 pagesBowel EliminationWarner Yague Pacariem Jr.No ratings yet
- Bowel Elimination ProblemsDocument69 pagesBowel Elimination ProblemsjonaNo ratings yet
- Bowel EliminationDocument59 pagesBowel EliminationRekha DehariyaNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Chronic Diarrhea: Parijat R. Tripathi Anshu SrivastavaDocument9 pagesApproach To A Child With Chronic Diarrhea: Parijat R. Tripathi Anshu SrivastavaTrọng PhướcNo ratings yet
- Stomach and Intestine Lesson 15Document25 pagesStomach and Intestine Lesson 15Nicholson SalgadoNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting GitDocument8 pagesDrugs Affecting GitReysel MonteroNo ratings yet
- EliminationDocument9 pagesEliminationJeffrey TrayaNo ratings yet
- Regurgitation, The Result of Gastroesophageal Reflux, Occurs Commonly in The 1st Year of LifeDocument7 pagesRegurgitation, The Result of Gastroesophageal Reflux, Occurs Commonly in The 1st Year of LifeImam AlifurqonNo ratings yet
- GerdDocument9 pagesGerdPriyaNo ratings yet
- Patofisiologi DiareDocument45 pagesPatofisiologi DiareAngela Kristiana Intan100% (1)
- Gastrointestinal - BoardsDocument7 pagesGastrointestinal - BoardsSoojung NamNo ratings yet
- AGE MarchDocument46 pagesAGE MarchJefelson Eu Palaña NahidNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea PPTDocument82 pagesDiarrhea PPTIshwar HavaragiNo ratings yet
- PPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENDocument31 pagesPPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaNo ratings yet
- COULOMB Quick Start GuideDocument128 pagesCOULOMB Quick Start GuideJordan RileyNo ratings yet
- 1.8V To 28V Input, PWM Step-Up Controllers in MAX: General Description FeaturesDocument18 pages1.8V To 28V Input, PWM Step-Up Controllers in MAX: General Description FeaturesStoica VictorNo ratings yet
- Gladys Mutindi Proposal (1) (1)Document20 pagesGladys Mutindi Proposal (1) (1)robin wanjalaNo ratings yet
- Kirishitan Yashiki 切支丹屋敷 - Myōgadani 茗荷谷Document3 pagesKirishitan Yashiki 切支丹屋敷 - Myōgadani 茗荷谷trevorskingleNo ratings yet
- VACTERL-Hydrocephaly, DK-Phocomelia, and Cerebro-Cardio-Radio-Reno-Rectal CommunityDocument6 pagesVACTERL-Hydrocephaly, DK-Phocomelia, and Cerebro-Cardio-Radio-Reno-Rectal CommunitySarly FebrianaNo ratings yet
- EWC DraftDocument5 pagesEWC Draftdboyd616No ratings yet
- Johns 10e Irm ch09Document42 pagesJohns 10e Irm ch09Jacob WeiseNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument2 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-549061305No ratings yet
- Tindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanDocument15 pagesTindahan Pinoy NG Laguna Business PlanRica Kathrine Reyes AustriaNo ratings yet
- Borrowing Costs and Government Grants ProblemsDocument1 pageBorrowing Costs and Government Grants Problemstough mamaNo ratings yet
- Moral Decision Making in International Sales Negotiations: Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing July 2001Document23 pagesMoral Decision Making in International Sales Negotiations: Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing July 2001ihda0farhatun0nisakNo ratings yet
- The Way To The Other World in Medieval Literature & ArtDocument19 pagesThe Way To The Other World in Medieval Literature & ArtRKEColeNo ratings yet
- The Micah 6-8 Tricola and Its Influence On Jesus' Denunciation of The Pharisees in Matthew 23Document44 pagesThe Micah 6-8 Tricola and Its Influence On Jesus' Denunciation of The Pharisees in Matthew 23Josh GelattNo ratings yet
- Beginner Elementary Placement TestDocument5 pagesBeginner Elementary Placement TestALEJANDRA GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- JIS College of Engineering: Vision and Mission of The DepartmentDocument4 pagesJIS College of Engineering: Vision and Mission of The DepartmentAnushka SikdarNo ratings yet
- Enraf-Nonius Endomed 484 EN PDFDocument7 pagesEnraf-Nonius Endomed 484 EN PDFAgustya PutriNo ratings yet
- Greek Verb and Noun WorksheetsDocument5 pagesGreek Verb and Noun WorksheetsEleftheria ChatzimichaliNo ratings yet
- EpicorImplementation UserGuide 101400Document695 pagesEpicorImplementation UserGuide 101400Edgar del Bene100% (1)
- Galaxy Morphology: By: Amie Sulaiman Saron Ephraim Stephannie GrijalvaDocument16 pagesGalaxy Morphology: By: Amie Sulaiman Saron Ephraim Stephannie GrijalvaBudi AfriyansyahNo ratings yet
- Certificate of ComplianceDocument14 pagesCertificate of ComplianceCheryl Sasing CabahugNo ratings yet
- Understanding Emotions From An Indian PerspectiveDocument29 pagesUnderstanding Emotions From An Indian PerspectiveRatan SikderNo ratings yet
- AmoebaDocument3 pagesAmoebaMark Louie DolotaNo ratings yet
- Adez V Ca GR No. 100643Document4 pagesAdez V Ca GR No. 100643Mary Rose CaronNo ratings yet
- Culture of Colombia VS Culture of JapanDocument3 pagesCulture of Colombia VS Culture of JapanKaterine GómezNo ratings yet
- Music Therapy Session Assessment Raglio Et Al., 2017 - Clinical Psychology & PsychotherapyDocument15 pagesMusic Therapy Session Assessment Raglio Et Al., 2017 - Clinical Psychology & PsychotherapyNic Loc OnteNo ratings yet
- LPLT12448 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Document6 pagesLPLT12448 : LPL - Lpl-Rohini (National Reference Lab) Sector - 18, Block - E Rohini DELHI 110085Kumar ManglamNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument2 pagesLetterrazishadab100% (1)