Professional Documents
Culture Documents
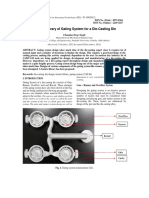
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Uploaded by
karthickCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Blown Film Extrusion ReportDocument12 pagesBlown Film Extrusion ReportAbdul Razak RahmatNo ratings yet
- CIP Session II Quiz-4Document5 pagesCIP Session II Quiz-4munna88% (8)
- Safety in Die CastingDocument33 pagesSafety in Die CastingPra VeeNo ratings yet
- Design ParametersDocument25 pagesDesign ParametersNagaraj RaviNo ratings yet
- Huong Dan Su Dung CnckadDocument245 pagesHuong Dan Su Dung CnckadBlock Serious100% (1)
- Aluminum Die Casting Draft Angles GuideDocument1 pageAluminum Die Casting Draft Angles GuidekotharideepNo ratings yet
- PQ TOS555 How To Check PQ Amplifier (During Pump Run)Document3 pagesPQ TOS555 How To Check PQ Amplifier (During Pump Run)mike100% (1)
- Tool Design TerminologyDocument5 pagesTool Design Terminologyanmol6237No ratings yet
- DC School Text Book: ElectricityDocument88 pagesDC School Text Book: ElectricitymikeNo ratings yet
- 14 Chandan Deep SinghDocument8 pages14 Chandan Deep SinghVinod ChandranNo ratings yet
- Training Program-Die Design19 December 2009Document176 pagesTraining Program-Die Design19 December 2009Kanini Tech I கணினி டெக்100% (1)
- 07 - Castingdesign - BackdraftDocument3 pages07 - Castingdesign - BackdraftAlex Kiko VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual IpeDocument700 pagesLab Manual IpeMominul Islam OpuNo ratings yet
- JIS Standard For Casting MaterialDocument4 pagesJIS Standard For Casting MaterialalliceyewNo ratings yet
- TruMatic enDocument28 pagesTruMatic enAndreja MilovicNo ratings yet
- 2b-CASTING PROCESSESDocument42 pages2b-CASTING PROCESSESIzzat IkramNo ratings yet
- Technical Info About Die CastingDocument5 pagesTechnical Info About Die CastingSanoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument22 pagesInterview QuestionsugeshNo ratings yet
- Beta Die Casting Buyers GuideDocument19 pagesBeta Die Casting Buyers Guidekaniappan sakthivel100% (1)
- Casting ChecklistDocument4 pagesCasting Checklistmihai90No ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Sheet Metal Fabrication Melior Laser Company Intro 05 2013Document14 pagesLaser Cutting Sheet Metal Fabrication Melior Laser Company Intro 05 2013Kirke71No ratings yet
- EC 515 Die Casting DefectsDocument197 pagesEC 515 Die Casting Defectsjuan jose pedrajoNo ratings yet
- 08 - Eng Castingdesign ShrinkagesDocument2 pages08 - Eng Castingdesign ShrinkagesAlex Kiko VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Spencer Electroplating ServiceDocument24 pagesSpencer Electroplating Servicespencer electroplatingNo ratings yet
- Plastic - Die - Engineering - TP IndiaDocument13 pagesPlastic - Die - Engineering - TP IndiaGiyanto NanitNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Low Pressure Die-Casting Aluminum WheelDocument5 pagesNumerical Simulation of Low Pressure Die-Casting Aluminum WheelMostafaNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectDocument5 pagesCasting DefectSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Operator TrainingDocument38 pagesOperator TrainingluisA1923No ratings yet
- Die Design ParametersDocument3 pagesDie Design ParameterspunkhunkNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument22 pagesSurface RoughnessBollu SatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Mold Design For Aluminum Alloy Shell oDocument4 pagesDie Casting Mold Design For Aluminum Alloy Shell ometmlzmuhNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Die Casting GuideDocument2 pagesAluminum Die Casting GuideAndrei Todea0% (1)
- Assab TableDocument8 pagesAssab TableIhfan MohdNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die-CastingDocument12 pagesPressure Die-CastingAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MTripleP IMetalDocument21 pagesIntroduction To MTripleP IMetalKrishna Mohan T.RNo ratings yet
- Injection Moulding Courses BrochureDocument16 pagesInjection Moulding Courses BrochureFa BelNo ratings yet
- 03 - SIPOC Diagram - 2009-06-11Document1 page03 - SIPOC Diagram - 2009-06-11Anand RajaNo ratings yet
- Dievar D20140715Document16 pagesDievar D20140715Keattikhun ChaichanaNo ratings yet
- Process Parameter CalculationDocument2 pagesProcess Parameter CalculationmaheshNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturability Analysis of Die-Cast Parts: Pvmrao@mech - Iitd.ac - in Tkkundra@mech - Iitd.ac - inDocument12 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturability Analysis of Die-Cast Parts: Pvmrao@mech - Iitd.ac - in Tkkundra@mech - Iitd.ac - indamonlanglois100% (1)
- HASCO-General Mould Components IndexDocument7 pagesHASCO-General Mould Components IndexНикола МедићNo ratings yet
- DFM ProDocument57 pagesDFM ProMahesh KarpeNo ratings yet
- Vacuum CastingDocument5 pagesVacuum CastingHarpreetSinghNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Any ExceptionsDocument3 pagesInstructions:: Any ExceptionsAkhmad FathoniNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming TechnologyDocument42 pagesMetal Forming TechnologydedybarokahNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Die Casting Process FlowDocument13 pagesAluminum Die Casting Process FlowPrabish KumarNo ratings yet
- Forging Die Design & SimulationDocument8 pagesForging Die Design & SimulationKumar SatyamNo ratings yet
- Die Casting ProposalDocument11 pagesDie Casting ProposalAbubakar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Workflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-LtdDocument6 pagesWorkflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-Ltdluan_ba100% (1)
- Solidcast IranDocument239 pagesSolidcast IranMario Farfan Cantoya NetoNo ratings yet
- Brochure For HPDC ProcessDocument4 pagesBrochure For HPDC Processramaswamykama786No ratings yet
- Casting Technology: DC School Text BookDocument23 pagesCasting Technology: DC School Text BookmikeNo ratings yet
- Cold Shut DefectsDocument3 pagesCold Shut Defectsvivek1312No ratings yet
- Casting ModuleDocument113 pagesCasting ModuleAshok KhannaNo ratings yet
- CNC Turning Programming Fundementalsls, Step by StepDocument14 pagesCNC Turning Programming Fundementalsls, Step by Stepschriener50% (2)
- Tolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsDocument3 pagesTolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsShankar V IyerNo ratings yet
- Training at CaparoDocument36 pagesTraining at Caparopilaniabhupesh_81404No ratings yet
- ÖDEV Materials-17-01348-V3Document24 pagesÖDEV Materials-17-01348-V3Serkan APAYNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances Enhance: Piercing PlasmaDocument2 pagesRecent Advances Enhance: Piercing Plasmaraymond wilburnNo ratings yet
- Weld Defect Formation in Rail Thermite Welds PDFDocument12 pagesWeld Defect Formation in Rail Thermite Welds PDFbhuNo ratings yet
- Foundry DefectsDocument74 pagesFoundry DefectsdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Foundry DefectsDocument74 pagesFoundry DefectsdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Pipemill Fluxes FinalDocument1 pagePipemill Fluxes Finaltanveer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Products Production Stages and MachineryDocument97 pagesProducts Production Stages and MachineryAdham ElHelwNo ratings yet
- ME8793 Process Planning and Cost EStimation UNIT 4 QBDocument13 pagesME8793 Process Planning and Cost EStimation UNIT 4 QBLEO PRAVIN PNo ratings yet
- PREBOND-110 (Rust Converter-Cum Epoxy Primer)Document6 pagesPREBOND-110 (Rust Converter-Cum Epoxy Primer)raahul_nNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Rapid Tooling 1Document19 pagesLecture 15 Rapid Tooling 1shanur begulajiNo ratings yet
- Tungaloy Tungdrill Twisted TDX KorthalsborrDocument20 pagesTungaloy Tungdrill Twisted TDX KorthalsborrWilserWeltecNo ratings yet
- Typical Anchors Used in Cement PlantsDocument1 pageTypical Anchors Used in Cement PlantsEhab Attia SelimNo ratings yet
- Corner JointDocument2 pagesCorner JointTayyab HussainNo ratings yet
- VBFDocument2 pagesVBFshridharkotnisNo ratings yet
- 20050602014857.orion AlloysDocument25 pages20050602014857.orion AlloysdtweetyNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Process: Okky Helja Octora SR 2006492843Document11 pagesDie Casting Process: Okky Helja Octora SR 2006492843Okky Helja100% (1)
- LT4422 Bonding Selector Guide 2Document2 pagesLT4422 Bonding Selector Guide 2sandbad1No ratings yet
- Objectives, Evaluation, and The Improvement of Education: Studies in Educational EvaluationDocument12 pagesObjectives, Evaluation, and The Improvement of Education: Studies in Educational EvaluationSandro ToninNo ratings yet
- Epreuve Orale Du Brevet - Guide-2.fr - enDocument4 pagesEpreuve Orale Du Brevet - Guide-2.fr - enmuhtadiNo ratings yet
- Es23 12Document2 pagesEs23 12yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Sae1045 1018Document2 pagesSae1045 1018kevinjunNo ratings yet
- ME364 Forming SheetDocument11 pagesME364 Forming SheetVed Prakash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DiplomaManufacturingProcessImportant2 3MarksQuestions AnswersEnglish PDFDocument36 pagesDiplomaManufacturingProcessImportant2 3MarksQuestions AnswersEnglish PDFSathya NarayananNo ratings yet
- 4jer en - Tze00086 PDFDocument6 pages4jer en - Tze00086 PDFr0ll3rNo ratings yet
- CoatedDocument3 pagesCoatedmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Chap6.1 - Casting-1Document31 pagesChap6.1 - Casting-1Nex LeeNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8Document9 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8muraliNo ratings yet
- 1 Manufacturing TechnologyDocument2 pages1 Manufacturing TechnologyNarasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- Remelting For Highest StandardsDocument12 pagesRemelting For Highest StandardsX800XLNo ratings yet
- Fabrication CostDocument6 pagesFabrication CostChong Cong100% (1)
- Daily ReportDocument17 pagesDaily ReportAgung Tri SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Mid 2Document13 pagesTest Bank Mid 2mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- National Curriculum Framework For School EducationDocument628 pagesNational Curriculum Framework For School EducationSharjeel ShaikhNo ratings yet
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Uploaded by
karthickOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Diecasting Defect Analysis Chart - 19.11.19
Uploaded by
karthickCopyright:
Available Formats
ALUMINIUM HIGH PRESSURE DIE CASTING DEFECTS ANALYSIS CHART
DEFECT TYPE
SHOT END PARAMETERS METAL VOLUME CLAMPING & EJECTION DIE SURFACE VACUUM & VENTING DIE CONSTRUCTION METAL
SHORT FILL
MAIN CAUSES:Metal is frozen before the cavity 1 3 6 7 8 14 15 16 17 24 28 29 31 36 37 38 41 42 43 44 46
is filled or by insufficient metal being ladled.
Metal can cool down too much
in the shot sleeve
Metal may loosing too much heat Too much metal when prefil is used may cause the Some parts of the die
in the runner and cavity change over point to be too late and therefore the may be too cold.
metal may cool down too much before second stage
COLD SHUT
MAIN CAUSES:Metal is frozen when 1 3 6 7 8 14 15 16 24 28 29 31 36 37 38 41 42 44 46
two metal fronts join.
Die expansion at cavity fill May affect fill pattern.
can cause a second layer Oxide layers could be forming
Dies being forged apart with continued Source of oxide layer
to form over the casting. during prefill.
feeding after cavity fill.
SCALING
MAIN CAUSES:Layers of metal and oxides can
be created by poor shot end control and/or bad 2 3 4 5 6 10 13 14 15 16 17 23 28 41 47
gate and runner design.
Poor runner design can cause
In correct first stage velocity can cause Sticking plunger can cause entrained air during Interrupted or uneven cavity fill. Damaged shot sleeve layering during cavity fill.
sit to be entrained in the metal first stage or variable velocity during cavity fill. can be a sourceof entrained air.
BLISTER
MAIN CAUSES:Trapped gases are in csting
when the die is opened when the casting is still 3 4 5 6 14 15 16 18 21 28 30 36 37 38 39 41 42 44
weak.This allows the compressed gas to expand
and cause a blister.
Check operating window of PQ sq diagram Steam produced form water in the If the die is poorly constructed and Die is more likely to flash
to determine if pressure and projected area cavity can cause sever flash. finished then itmay not shut off if metal is very hot.
is not too high.
FLASH
MAIN CAUSES:Metal pressure is too high upon the
projected area of the casting at the end of cavity fill. 10 13 19 23
2 7 9 25 31 35 39 41 44
This creates a force across the parting line which is
too great for the clamping force of the machine.The
die is then forced apart which allows metal to escape.
Normally second stage velocity Broken tie bar(s) or cracked platten(s) This cause is very likely Metal cmposition may cause some
change affects metal pressure. may cause flash to occur suddenly. if flash ocurs suddenly. metal to solidify at too high a temperature
in the shot sleeve.
COLDFLAKES
MAIN CAUSES:Metal is allowed to cool too
much in the shot sleeve.The solid particles are
3 8 15 16 17 24 29 31 41 42 44 46
then injected in to the cavity.These flakes are
often clearly visible on the surface of the casting
with the naked dye.
Sources of metal flakes. Too cold.
SHOT LUBE STAIN
MAIN CAUSES:This defect occurs when too
24 27 29
much shot (tip) lube is used.
Percentage of solids too high A lip on the shot sleeve & low
It is possible to reduce some Die and shot sleeve
at cavity fill.Second stage Air trapped in cavity. ejector pins,for example can cause
porosity under intensification. may be too cold.
air to be entrapped in the metal.
AIR POROSITY velocity may be the cause of this.
MAIN CAUSES:This defect is caused by trapped
air in the casting which can come from several
sources.It can be caused by poor shot end 3 4 5 6 8 11 12 14 15 16 17 24 28 29 31 36 37 38 41 43 44
control,poor venting and overflow function
or bad gating and runner design.
If the die is too cold then air
The casting shrinks as it cools.This cause Changing volume affects wave may be trapped during cavity fill
the casting to grip die components more acceleration and change over point. as two metal fronts meet
DRAG MARKS as it is left longer in the die. (similar to cold shut).
MAIN CAUSES:Insufficient draft or an undercut
causing a casting to be damaged on the surface
when it is ejected.This effect may be reduced 18 19 20 21 22 30 32 33 34 35 39 40 41 42 43 44
by changing the temperature at which the casting
is ejected.Poor surface finish of the die can
be another cause.
Metal too weak when
Varying change over point when prefil is Metal adhesion is a sigh that the die is too hot in that area and
ejecting and SOLDERING
used can cause variation in heat load on Can cause uneven die temperature. may cause other problems such as drag marks and soldering.
can occurhere also.
different parts of the die.
HOT TEARING/CRACKING
MAIN CAUSES:This defect is caused by metal
shrinking during solidification while under 1 7 8 9 11 12 14 15 16 17 24 28 30 32 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
tension.At the last place to solidify a tear
or crack develops which can be seen at the
surface (Not HOT SHORTNESS)
Adjusting these parameters may fix the Excessive Fe,Cu and Zn
problem with out dealing with the root cause. Damage from ejection. can cause hot shortness.
HOT SHORTNESS
MAIN CAUSES:The composition of the alloy
causes the metal to be too weak at high
temperatures (after soldification).This then can 18 20 21 22 30 32 40 42 44 45 46
cause cracks in the surface of the casting
to appear in regions of high stress when the
casting is cooling (and contracting).NOTE:This Shrinkage not fed.Sometimes it is not
defect can occur in conjuction with hot cracking. possible to feed shrinkage due to the
location of the gate.
SINK
MAIN CAUSES:A sink is caused by a shrinkage
cavity being near the surface of the casting.This 1 7 8 9 11 12 14 15 16 17 24 28 30 32 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
causes the surface of the casting to collapse into
the cavity as soldification occurs.Sinks are caused
by the same things as shrinkage porosity as well
as very poor thermal control of the die because
Sources of entrained air. Sources of entrained air.
hot spots are required for sinks to form.
EXPLODED METAL
MAIN CAUSES:A combination of porosity and
3 4 5 14 15 16 17 18 21 25 26 27 30 32 36 37 38 41 42 43
the casting being ejected before it has solidified
completely.This allows the trapped gasses
to burst out of the casting along with any
unsolidified metal. Poor fill patern may concentrate
Oversize biscut can explode. Poor Thermal control. heat load in a small area of the die.
WARPAGE
MAIN CAUSES:A casting can deform after
ejecting during the time it is cooling down
to room temperature.The root cause can 18 21 22 24 30 32 33 34 40 41 42 43 44 46
sometimes be the casting geometry or the alloy
specification.Warpage can be minimised by ejecting
at a lower temerature.Uneven die temperature
Variation in volume changes the
is a major cause of this type of defect.
Prefill can sometimes help reduce effective change over point.This can Die may need to be polished.
soldering in some areas. change heat distribution in the die.
SOLDERING
MAIN CAUSES:Chemical attack and bonding
of aluminium to die steel.This causes aluminium 2 5 9 15 16 17 30 32 33 34 39 41 42 44 46
to be torn away from the casting during ejection.
Soldering can be reduced be a change in ally
and/or a reduction in die/metal temperature.
Changed metal velocity can increase heat
Low levels of Fe (less than 0.6-0.7%) can cause soldering.
transfer to a problem area in some cases
SHRINKAGE POROSITY
MAIN CAUSES:This defect is caused by metal
reducing its volume during soldification and 1 7 8 9 11 12 14 15 16 17 24 28 30 32 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
an inability to feed shrinkage with more metal
before soldification.Hot spots cn also cause
shrinkage porosity to be concentrated in a
specific zones.See 'SINK' Oxide & sludge can
Shrinkage can occur when biscut Improved gating and runner design can be associated with
is too short for intensification. Die is too cold. enhance feeding of shrinkage in some area. shrinkage porosity.
HEAT CHECKING
MAIN CAUSES:This defect is caused by the
surface of the tool steel continually expanding 2 7 13 24 29 30 31 41 42 43 44
& contracting during use.Excessively cold dies
& die flexing accelerate this effect.
Metal freeszing off in runners,
Affects the change over point with respect to the
gate(s) and the cavity during Changing metal composition or type can
metal in the runner and die.This may be the cause Sources of porosity.
prefill can disrupt the fill pattern improve pressure tightness.
LEAKER and any resulting cold flakes can
of entraained air since the shot sleeve may not be
full at the change over point.
MAIN CAUSES:Causes of leaks in castings cause leakes as well.
where pressure tightness is required can be oxide
folds and/or inclusions and/or porosity
in conjuction with a surface defect which 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 11 12 14 15 16 17 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 36 37 38 39 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
completes the path for a leak.A close analysis
of the leaking area may reveal which of the many
causes is causing the leak.
DISCOLOURED SURFACE
MAIN CAUSES:Oxide films (dross) and/or
residues in the cavity and/or particles in the metal
6 25 26 27 29 31 33 35 42 44 45 46 47
and/or excess die lube can cause the surface
to be discoloured.Also it can be caused by a part
of the die being too cold causing the casting
to have darker regions or 'smears' on the surface. If prefill is used,the metal may be too cold and Die surface is too cold or there
cause staining/streaking on the casting surface. is too much die lube on the die surface.
BREAK OUT
MAIN CAUSES:Metal flakes (cold flakes)which
6 29 31 41 43 44 45 46 47
get caught in the gate during cavity fill can break
out unevenly when the casting is trimmed.
If the gate is partially frozen during All flux will not be used if the metal
Solidified metal in these areas can
cavity fill,break-out can occur. is too cold.Also sludge can form
be pushed down the shot sleeve
if the metal temperature is too low.
and then into the casting.
INCLUSIONS
MAIN CAUSES:The main causes of this type 15 16 17 35 44 44 46 47
of defect are dirty/contaminated metal and/or
poor melt handling practice.
Poor ejector pin location can be a contributor
along with these causes.
EJECTOR DAMAGE
MAIN CAUSES:In broad terms,it can be defined 18 20 21 22 24 29 30 32 33 34 39 40 42 43 44 46
as excessive pressure on the casting surface
by the ejector pin (s) during ejection.
EROSION/CAVITATION Metal flow is not atomised. Metal flow has 'collapsed' into a 'solid' stream. Metal freezing in runner & gate causing the
effective gate & runner area to change.
MAIN CAUSES:Erosion is caused
by direct molten metal impingment of die steel.
Cavitation type erosion is caused by turbulance
which causes low pressure regions in the flowing
8 9 29 31 39 41 42 44 45
metalThese low pressure regions cause voids
to form which can collapse at the die surface
& cause erosion.
Damage to the casting when the die is opening. Root cause can be poor die surface,bad csting
CRACKED CASTING geomerty and metal out of specification
MAIN CAUSES:A crack in the casting can (see HOT SHORTNESS)
be caused by mechanical damage when the die
is opened or when the casting is ejeted.This
classification excludes HOT CRACKING & 18 19 20 21 22 24 28 29 30 31 32 35 39 40 42 43
cracking at the surface due to SHRINKAGE
POROSITY.Also,this definition excludes
HOT SHORTNESS.
METAL VOLUME CLAMPING AND EJECTION DIE SURFACE VACUUM & VENTING DIE CONSTRUCTION METAL
l r
et
c al l ge
sm ne un ts
s pl s po
S e e p le
to
in
ng
o an is s rt w h y
SE
d rt ch o
la ac ac o d e e nit ki rfl fin n ld di
gh on rn rn
sh ui hi
n er u tic lo
w
ov
e
ce ut si
g co or
. w hi fu fu g/ /g at g /S d/
AU w igh oo low oo hig oo ear oo late settin ity too ity too arly ate ow igh t settin
h ly g lo g ac lin o n
or rfa rc de & n
se se on sm h e w be to io te d/ de ot ry an at
io e
do do oo l ni or
t
ng /m cl in
g oo e lu n es /la su un er l/h et ed ac
C ha hi
g sh lo w cy ak g/
C ub er ra
y pe ratio adh on an ve nn tro om old at fic rn
lo h t t tt tt n c oc e l l h h n on t lo rl ay ty g or ru ci fu
LEGEND FOR COLOUR
ity lo el le ro e ec oo oo g
Le tin ge ng pr sp nt so ee ft on ge in pe
LE re to re to loc loc po po erat e ve e v on to on to on to on to we r ho nde ricte n tim g m ce to lay t lay t e to erat ity/ hea lun plu ld t ie s die pra nce eta uum too ven t sl dra an al c ting hot ntam of s lding
o o ity in in io o o o o ig d o o in y l tin d /c
IB essu ressu ge ve ge ve over over decel stag stag ificati ificati ificati ificati shot d pou d lau onst icatio ockin n for n de n de g forc ar op in cav g oil uch p ough too co too ho uch d ough die s be co ces/M g vac m on tive ie/sho uate ating herm lt cas is too si co s out in ho =most likely cause (s)
SS etal pr etal p rst sta rst sta hange hange rong econd econd ntens ntens ntens ntens rong locke locke ube c olidif orn l jectio jectio jectio ockin rregul ater eakin oo m ot en ie is ie is oo m ot en rong ie lu irty fa eakin acuu neffec oor d nadeq oor g oor t ifficu etal etal lloy i ross
PO 1. M 2. M 3. Fi 4. Fi 5. C 6. C 7. W 8. S 9. S 10. I 11. I 12. I 13. I 14. W 15. B 16. B 17. T 18. S 19. W 20. E 21. E 22. E 23. L 24. I 25. W 26. L 27. T 28. N 29. D 30. D 31. T 32. N 33. W 34. D 35. D 36. L 37. V 38. I 39. P 40. I 41. P 42. P 43. D 44. M 45. M 46. A 47. D
=possible cause (s)
=least likely cause (s)
Main Reference:"Die Casting Defects"
North American Die Casting Association - NADCA
You might also like
- Blown Film Extrusion ReportDocument12 pagesBlown Film Extrusion ReportAbdul Razak RahmatNo ratings yet
- CIP Session II Quiz-4Document5 pagesCIP Session II Quiz-4munna88% (8)
- Safety in Die CastingDocument33 pagesSafety in Die CastingPra VeeNo ratings yet
- Design ParametersDocument25 pagesDesign ParametersNagaraj RaviNo ratings yet
- Huong Dan Su Dung CnckadDocument245 pagesHuong Dan Su Dung CnckadBlock Serious100% (1)
- Aluminum Die Casting Draft Angles GuideDocument1 pageAluminum Die Casting Draft Angles GuidekotharideepNo ratings yet
- PQ TOS555 How To Check PQ Amplifier (During Pump Run)Document3 pagesPQ TOS555 How To Check PQ Amplifier (During Pump Run)mike100% (1)
- Tool Design TerminologyDocument5 pagesTool Design Terminologyanmol6237No ratings yet
- DC School Text Book: ElectricityDocument88 pagesDC School Text Book: ElectricitymikeNo ratings yet
- 14 Chandan Deep SinghDocument8 pages14 Chandan Deep SinghVinod ChandranNo ratings yet
- Training Program-Die Design19 December 2009Document176 pagesTraining Program-Die Design19 December 2009Kanini Tech I கணினி டெக்100% (1)
- 07 - Castingdesign - BackdraftDocument3 pages07 - Castingdesign - BackdraftAlex Kiko VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual IpeDocument700 pagesLab Manual IpeMominul Islam OpuNo ratings yet
- JIS Standard For Casting MaterialDocument4 pagesJIS Standard For Casting MaterialalliceyewNo ratings yet
- TruMatic enDocument28 pagesTruMatic enAndreja MilovicNo ratings yet
- 2b-CASTING PROCESSESDocument42 pages2b-CASTING PROCESSESIzzat IkramNo ratings yet
- Technical Info About Die CastingDocument5 pagesTechnical Info About Die CastingSanoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionDocument22 pagesInterview QuestionsugeshNo ratings yet
- Beta Die Casting Buyers GuideDocument19 pagesBeta Die Casting Buyers Guidekaniappan sakthivel100% (1)
- Casting ChecklistDocument4 pagesCasting Checklistmihai90No ratings yet
- Laser Cutting Sheet Metal Fabrication Melior Laser Company Intro 05 2013Document14 pagesLaser Cutting Sheet Metal Fabrication Melior Laser Company Intro 05 2013Kirke71No ratings yet
- EC 515 Die Casting DefectsDocument197 pagesEC 515 Die Casting Defectsjuan jose pedrajoNo ratings yet
- 08 - Eng Castingdesign ShrinkagesDocument2 pages08 - Eng Castingdesign ShrinkagesAlex Kiko VillalobosNo ratings yet
- Spencer Electroplating ServiceDocument24 pagesSpencer Electroplating Servicespencer electroplatingNo ratings yet
- Plastic - Die - Engineering - TP IndiaDocument13 pagesPlastic - Die - Engineering - TP IndiaGiyanto NanitNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulation of Low Pressure Die-Casting Aluminum WheelDocument5 pagesNumerical Simulation of Low Pressure Die-Casting Aluminum WheelMostafaNo ratings yet
- Casting DefectDocument5 pagesCasting DefectSaurabhNo ratings yet
- Operator TrainingDocument38 pagesOperator TrainingluisA1923No ratings yet
- Die Design ParametersDocument3 pagesDie Design ParameterspunkhunkNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument22 pagesSurface RoughnessBollu SatyanarayanaNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Mold Design For Aluminum Alloy Shell oDocument4 pagesDie Casting Mold Design For Aluminum Alloy Shell ometmlzmuhNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Die Casting GuideDocument2 pagesAluminum Die Casting GuideAndrei Todea0% (1)
- Assab TableDocument8 pagesAssab TableIhfan MohdNo ratings yet
- Pressure Die-CastingDocument12 pagesPressure Die-CastingAyush PandeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MTripleP IMetalDocument21 pagesIntroduction To MTripleP IMetalKrishna Mohan T.RNo ratings yet
- Injection Moulding Courses BrochureDocument16 pagesInjection Moulding Courses BrochureFa BelNo ratings yet
- 03 - SIPOC Diagram - 2009-06-11Document1 page03 - SIPOC Diagram - 2009-06-11Anand RajaNo ratings yet
- Dievar D20140715Document16 pagesDievar D20140715Keattikhun ChaichanaNo ratings yet
- Process Parameter CalculationDocument2 pagesProcess Parameter CalculationmaheshNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturability Analysis of Die-Cast Parts: Pvmrao@mech - Iitd.ac - in Tkkundra@mech - Iitd.ac - inDocument12 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturability Analysis of Die-Cast Parts: Pvmrao@mech - Iitd.ac - in Tkkundra@mech - Iitd.ac - indamonlanglois100% (1)
- HASCO-General Mould Components IndexDocument7 pagesHASCO-General Mould Components IndexНикола МедићNo ratings yet
- DFM ProDocument57 pagesDFM ProMahesh KarpeNo ratings yet
- Vacuum CastingDocument5 pagesVacuum CastingHarpreetSinghNo ratings yet
- Instructions:: Any ExceptionsDocument3 pagesInstructions:: Any ExceptionsAkhmad FathoniNo ratings yet
- Metal Forming TechnologyDocument42 pagesMetal Forming TechnologydedybarokahNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Die Casting Process FlowDocument13 pagesAluminum Die Casting Process FlowPrabish KumarNo ratings yet
- Forging Die Design & SimulationDocument8 pagesForging Die Design & SimulationKumar SatyamNo ratings yet
- Die Casting ProposalDocument11 pagesDie Casting ProposalAbubakar MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Workflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-LtdDocument6 pagesWorkflow of Injection Molding Simulation & Verification: Ffinno-Technologies-Co-Ltdluan_ba100% (1)
- Solidcast IranDocument239 pagesSolidcast IranMario Farfan Cantoya NetoNo ratings yet
- Brochure For HPDC ProcessDocument4 pagesBrochure For HPDC Processramaswamykama786No ratings yet
- Casting Technology: DC School Text BookDocument23 pagesCasting Technology: DC School Text BookmikeNo ratings yet
- Cold Shut DefectsDocument3 pagesCold Shut Defectsvivek1312No ratings yet
- Casting ModuleDocument113 pagesCasting ModuleAshok KhannaNo ratings yet
- CNC Turning Programming Fundementalsls, Step by StepDocument14 pagesCNC Turning Programming Fundementalsls, Step by Stepschriener50% (2)
- Tolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsDocument3 pagesTolerances For Aluminium Die CastingsShankar V IyerNo ratings yet
- Training at CaparoDocument36 pagesTraining at Caparopilaniabhupesh_81404No ratings yet
- ÖDEV Materials-17-01348-V3Document24 pagesÖDEV Materials-17-01348-V3Serkan APAYNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances Enhance: Piercing PlasmaDocument2 pagesRecent Advances Enhance: Piercing Plasmaraymond wilburnNo ratings yet
- Weld Defect Formation in Rail Thermite Welds PDFDocument12 pagesWeld Defect Formation in Rail Thermite Welds PDFbhuNo ratings yet
- Foundry DefectsDocument74 pagesFoundry DefectsdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Foundry DefectsDocument74 pagesFoundry DefectsdanielsasikumarNo ratings yet
- Pipemill Fluxes FinalDocument1 pagePipemill Fluxes Finaltanveer ahmedNo ratings yet
- Products Production Stages and MachineryDocument97 pagesProducts Production Stages and MachineryAdham ElHelwNo ratings yet
- ME8793 Process Planning and Cost EStimation UNIT 4 QBDocument13 pagesME8793 Process Planning and Cost EStimation UNIT 4 QBLEO PRAVIN PNo ratings yet
- PREBOND-110 (Rust Converter-Cum Epoxy Primer)Document6 pagesPREBOND-110 (Rust Converter-Cum Epoxy Primer)raahul_nNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15 Rapid Tooling 1Document19 pagesLecture 15 Rapid Tooling 1shanur begulajiNo ratings yet
- Tungaloy Tungdrill Twisted TDX KorthalsborrDocument20 pagesTungaloy Tungdrill Twisted TDX KorthalsborrWilserWeltecNo ratings yet
- Typical Anchors Used in Cement PlantsDocument1 pageTypical Anchors Used in Cement PlantsEhab Attia SelimNo ratings yet
- Corner JointDocument2 pagesCorner JointTayyab HussainNo ratings yet
- VBFDocument2 pagesVBFshridharkotnisNo ratings yet
- 20050602014857.orion AlloysDocument25 pages20050602014857.orion AlloysdtweetyNo ratings yet
- Die Casting Process: Okky Helja Octora SR 2006492843Document11 pagesDie Casting Process: Okky Helja Octora SR 2006492843Okky Helja100% (1)
- LT4422 Bonding Selector Guide 2Document2 pagesLT4422 Bonding Selector Guide 2sandbad1No ratings yet
- Objectives, Evaluation, and The Improvement of Education: Studies in Educational EvaluationDocument12 pagesObjectives, Evaluation, and The Improvement of Education: Studies in Educational EvaluationSandro ToninNo ratings yet
- Epreuve Orale Du Brevet - Guide-2.fr - enDocument4 pagesEpreuve Orale Du Brevet - Guide-2.fr - enmuhtadiNo ratings yet
- Es23 12Document2 pagesEs23 12yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Sae1045 1018Document2 pagesSae1045 1018kevinjunNo ratings yet
- ME364 Forming SheetDocument11 pagesME364 Forming SheetVed Prakash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DiplomaManufacturingProcessImportant2 3MarksQuestions AnswersEnglish PDFDocument36 pagesDiplomaManufacturingProcessImportant2 3MarksQuestions AnswersEnglish PDFSathya NarayananNo ratings yet
- 4jer en - Tze00086 PDFDocument6 pages4jer en - Tze00086 PDFr0ll3rNo ratings yet
- CoatedDocument3 pagesCoatedmatteo2009No ratings yet
- Chap6.1 - Casting-1Document31 pagesChap6.1 - Casting-1Nex LeeNo ratings yet
- Material Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8Document9 pagesMaterial Data Sheet: Casting Material: Stainless Steel CF8muraliNo ratings yet
- 1 Manufacturing TechnologyDocument2 pages1 Manufacturing TechnologyNarasimha Murthy InampudiNo ratings yet
- Remelting For Highest StandardsDocument12 pagesRemelting For Highest StandardsX800XLNo ratings yet
- Fabrication CostDocument6 pagesFabrication CostChong Cong100% (1)
- Daily ReportDocument17 pagesDaily ReportAgung Tri SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Mid 2Document13 pagesTest Bank Mid 2mhd slmnNo ratings yet
- National Curriculum Framework For School EducationDocument628 pagesNational Curriculum Framework For School EducationSharjeel ShaikhNo ratings yet