Professional Documents
Culture Documents
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
Uploaded by
Jinder RuppanaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesPhysics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualRyanRoseJrbden100% (61)
- Position vs. Time Graphs: Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3Document5 pagesPosition vs. Time Graphs: Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3Sidney BittnerNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-6 Mixed ReviewDocument16 pagesChap 1-6 Mixed ReviewanNo ratings yet
- The PATHFINDER Training ProgramDocument5 pagesThe PATHFINDER Training ProgramLyell E. Petersen100% (1)
- Architects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryDocument558 pagesArchitects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryFlavia ValNo ratings yet
- I Ching TesseractDocument14 pagesI Ching Tesseractthoth11100% (1)
- NTPCDocument158 pagesNTPCAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Sample TestsDocument32 pagesPhysics 11 Sample TestsaayiinkeeNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysicsmoomooyaqiNo ratings yet
- Z - Kinematics 1-D - CombineDocument24 pagesZ - Kinematics 1-D - CombineAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Motion NCert SolutionDocument23 pagesMotion NCert SolutionRamKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Motion NCert SolutionDocument23 pagesMotion NCert SolutionRamKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- 1D Motion - ADocument8 pages1D Motion - AMuhid Ali SanjraniNo ratings yet
- 1a.rectilinear MotionDocument5 pages1a.rectilinear MotionAtulNo ratings yet
- 2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946Document21 pages2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946PRIYATAM IOAANo ratings yet
- Set ADocument2 pagesSet ARoszel cardinoNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document21 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Shreyas MishraNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument53 pagesKINEMATICSSwadhin BarikNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Velocity and AccelerationDocument12 pages2.0 Velocity and AccelerationNazrul IzzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Height and DistanceDocument8 pagesLecture Notes - Height and DistanceDinesh MatlaniNo ratings yet
- 1D MotionDocument6 pages1D Motionxakaka4037No ratings yet
- College Physics - Ch1-Kinematics HomeworkDocument10 pagesCollege Physics - Ch1-Kinematics HomeworkJackieNo ratings yet
- Short Questions: MotionDocument30 pagesShort Questions: MotionGangesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes On Travel GraphsDocument11 pagesTeaching Notes On Travel GraphsottonyembojedidiahNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Document22 pagesPraveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Vibhas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Test Review: Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1 - 3Document8 pagesUnit 1 Test Review: Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1 - 3NathanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineDocument26 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics CH Motion in A Straight Linerw 2 240502 224402Document4 pagesXi Physics CH Motion in A Straight Linerw 2 240502 224402fijiteb766No ratings yet
- Pre-Test in MOTIONFinalDocument5 pagesPre-Test in MOTIONFinalElyzza Wye AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Booklet 1Document7 pagesBooklet 1Raiv LondresNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Rate, Ratio & Proportion: I. L. C. NotesDocument51 pages6.1 Rate, Ratio & Proportion: I. L. C. NotesRain HoNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Velocity SET BDocument6 pagesUnit Test Velocity SET BNandhu RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Class 9 pt1 Two 2023Document2 pagesClass 9 pt1 Two 2023Laxman SdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics:Velocity & Acceleration. - Updated 9/6/06Document5 pagesChapter 2: 1-D Kinematics:Velocity & Acceleration. - Updated 9/6/06Mahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Unit Test (Practice) - Kinematics (Oct 2008 Version) SolutionsDocument6 pagesUnit Test (Practice) - Kinematics (Oct 2008 Version) SolutionsNicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Motion WorksheetDocument8 pagesMotion Worksheetstreetdiary.blogNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Document15 pages11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Sathiya RNo ratings yet
- Assignment EoM EasyDocument3 pagesAssignment EoM EasySohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Motion Practice TestDocument8 pagesMotion Practice TestRanish DhoteNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsDocument27 pagesMotion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Practice Test. MotionDocument3 pagesPractice Test. MotionsatyamheykarNo ratings yet
- Sri Venkateswara College of Education: Chapter 1 Lesson 1 - 2 - 3 TestDocument4 pagesSri Venkateswara College of Education: Chapter 1 Lesson 1 - 2 - 3 TestChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document2 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Monal KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Motion in Straight LineDocument21 pagesCH 3 Motion in Straight LineZeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manual PDFmarcusquyepv100% (13)
- Describing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsDocument26 pagesDescribing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsRose Ann YamcoNo ratings yet
- Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manualnoisefulrectrix.qn0x100% (16)
- Summative Test in General Physics 1Document4 pagesSummative Test in General Physics 1MengieNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- T1 Ch1 KimPar Basic1 STDVDocument6 pagesT1 Ch1 KimPar Basic1 STDVizzat razaliNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B, AP Physics C WorksheetDocument10 pagesAP Physics B, AP Physics C WorksheetGurukul24x7100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 320 Subhojit Maji 10HNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance ProblamsDocument29 pagesTime and Distance Problamsrenuka mulaNo ratings yet
- NSEA Question Paper 2017Document19 pagesNSEA Question Paper 2017Sparsh SaraogiNo ratings yet
- Class 11th (21-23) Weekly Quiz - 5 PUNE Paper 13.06.2021Document9 pagesClass 11th (21-23) Weekly Quiz - 5 PUNE Paper 13.06.2021Sushma PawarNo ratings yet
- 2 D Kinematics Review 2019Document6 pages2 D Kinematics Review 2019sdshah0604No ratings yet
- Physic MCQDocument32 pagesPhysic MCQTruong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphSomrik LangapNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam-Gen Physics 1Document3 pages1st Quarter Exam-Gen Physics 1Jenny Vhie S. Vinagrera100% (1)
- NSEA Question Paper 2017Document14 pagesNSEA Question Paper 2017EduardNo ratings yet
- Velocity and SpeedDocument9 pagesVelocity and SpeedJenny Teves DayritNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921Document3 pagesAssignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921iitforumNo ratings yet
- Speed Time GraphDocument7 pagesSpeed Time GraphAryan Hossain100% (2)
- 06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument24 pages06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document50 pagesChap 002Eduardo AndradersNo ratings yet
- River VolgaDocument11 pagesRiver Volgaapi-317411236No ratings yet
- Summary of Eric HobsbawmDocument4 pagesSummary of Eric HobsbawmDCNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune EncephalitisDocument26 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune EncephalitisSylvia TrianaNo ratings yet
- Pollitt & Shaorshadze (2011) - The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy PDFDocument31 pagesPollitt & Shaorshadze (2011) - The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy PDFRoz KrakraNo ratings yet
- Cells of Immune System Notes 2Document70 pagesCells of Immune System Notes 2Sudeeksha Ravikoti100% (1)
- Effects Temp On PropsDocument5 pagesEffects Temp On Propsdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Civil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Document1 pageCivil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Joel AganNo ratings yet
- Inverted Nipple PaperDocument7 pagesInverted Nipple PaperFarisah Dewi Batari EmsilNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Neo BehaviorismDocument11 pagesModule 8 Neo BehaviorismDenyseNo ratings yet
- Ratio Detector: SNSCT 16Ec304-Communication Theory Unit-3 K.Sumathi, Ap/EceDocument2 pagesRatio Detector: SNSCT 16Ec304-Communication Theory Unit-3 K.Sumathi, Ap/EceChandu NanduNo ratings yet
- Pump SystemsDocument45 pagesPump SystemsJagdip ShethNo ratings yet
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- DILO SF6 Catalogue 2021 ENDocument214 pagesDILO SF6 Catalogue 2021 ENBadraa BatorgilNo ratings yet
- Plumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..Document203 pagesPlumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..michelghanem100% (2)
- 1T 19-20 LBYKM31 Experiment Manual As of Sept 15 2019Document33 pages1T 19-20 LBYKM31 Experiment Manual As of Sept 15 2019Ammi PinedaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage DC Transmission PDFDocument4 pagesHigh Voltage DC Transmission PDFBMS_SOFTGUYNo ratings yet
- Dolch PhrasesDocument10 pagesDolch PhrasesCharlie Manahan TemonNo ratings yet
- Bharti 2023 BP 6853CDocument17 pagesBharti 2023 BP 6853CmonaranjansharmaNo ratings yet
- The Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNDocument15 pagesThe Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Shining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orDocument1,016 pagesShining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orbatiyeNo ratings yet
- Цацулин CQC Mag 2001-06 J - eng PDFDocument1 pageЦацулин CQC Mag 2001-06 J - eng PDFBudo MediaNo ratings yet
- 预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsDocument15 pages预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsSolo YehNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways Carbon EmissionsDocument9 pagesIndian Railways Carbon EmissionsTechTrip IndiaNo ratings yet
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
Uploaded by
Jinder RuppanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
11 Phy Motioninastraightline tp01
Uploaded by
Jinder RuppanaCopyright:
Available Formats
myCBSEguide
Class 11 - Physics
Motion in A Straight Line Test 01
Question No. 1 to 5 are based on the given text. Read the text carefully and answer the questions:
Tabu lives at A. He was supposed to do to his uncle's house at B. A and B is connected by a straight road 5 km long. But that
day the road was under repair. So, all the buses were following a diversion via C. A to B via C is 7 km. Moreover, this route is
congested There is a traffic signal at C also.
Tabu got a seat just behind the driver He noticed that the minimum reading in the speedometer was 15km/h. But ultimately the
bus took 1 hour to each B. He could not understand the fallacy.
1. What is the distance and displacement of Tabu?
a. 5 km, 5 km
b. 7 km, 5 km
c. 7 km, 7 km
d. 5 km, 7 km
2. Why the speedometer reading was minimum 15 km/h, but actual time required to cover 7 km was 1 hour?
a. Speedometer was erratic.
b. Halt timing at the traffic signal, slow speed at the congested areas and halt-timing at the bus stops are also to be
taken into account.
c. Both Speedometer was erratic and the actual distance was more than 7 km.
d. Actual distance was more than 7 km.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
3. Speedometer measures
a. None of these
b. Average speed
c. Instantaneous speed
d. Distance traversed
4. If the bus followed ADB path and reached B to (1 hour, then the average speed of the bus would have been
a. 7 km/h
b. 6 km/h
c. None of these
d. 5 km/h
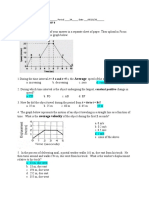
5. Which of the following graphs represents the motion of the bus if it covers AC distance at a speed CB distance at a speed
20 km/h of 15 km/h, CB distance at a speed 20 km/h and total distance is covered in 1 hour including halt at traffic
signal?
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
1/6
myCBSEguide
a.
b.
c.
d.
6. Displacement (x) of a particle is related to time (t) as: x = at + bt2 - ct3 where a, b and care constants of the motion. The
velocity of the particle when its acceleration is zero is given by:
2
a. a + b
2c
2
b. a + b
c
2
c. a +
b
3c
2
d. a + b
4c
7. A car travels a distance s on a straight road in two hours and then returns to the starting point in next three hours. Its
average velocity is:
a. s/5
b. + s
2
s
c. None of these
d. 2s/5
8. In a motion with constant acceleration the velocity is reduced to zero in 5 seconds and after covering a distance of 100
m. The distance covered by the particle in next 5 seconds will be:
a. zero
b. 500 m
c. 250 m
d. 100 m
9. Assertion (A): A negative acceleration of a body can be associated with a speeding up of the body.
Reason (R): The increase in speed of a moving body is independent of its direction of motion.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
2/6
myCBSEguide
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
10. Assertion: Distance and displacement are different physical quantities.
Reason: Distance and displacement have the same dimensions.
a. If both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
b. If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
c. If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
d. If both assertion and reason are false.
11. State True or False:
i. Position-time graph could have negative slope.
a. True
b. False
ii. A body has a constant velocity but varying speed.
a. True
b. False
12. Fill in the blanks:
a. The area under the acceleration-time graph gives ________ for the given time interval.
b. Displacement of an object between two given positions is ________ of the actual path followed by the object in
moving from one position to another.
13. A railway train 400 m long is going from New Delhi railway station to Kanpur. Can we consider the railway train as a
point object?
14. Under what condition the displacement and the distance of a moving object will have the same magnitude?
15. The displacement x of a particle moving in one dimension under the action of constant force is related to the time by the
−
−
equation t = √x − 3 where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Find the velocity of the particle at
1. t = 3s
2. t = 6s.
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
16. A bullet bike moving on a straight road at a speed of 120 kmph is made to stop by a police officer within a 100m
distance. Calculate the retardation of the bike (assumed uniform) and the time it takes for the bike to stop?
17. Give example of a motion where x > 0, v < 0 and a > 0 at a particular instant.
18. A motor car moving at a speed of 72 km/h cannot come to stop in less than 3.0 seconds while for a truck this time
interval is 5.0 second. On a highway, the car is behind the truck both moving 72 km/h. The truck gives a signal that it is
going to stop at an emergency. At what distance the car should be from the truck so that it does not bump onto (collide
with) the truck? The human response time is 0.5 s. (Comment: This is to illustrate why vehicles carry the message on the
rear side. Keep safe distance).
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
3/6
myCBSEguide
Class 11 - Physics
Motion in A Straight Line Test 01
Solution
1. (b) 7 km, 5 km
Explanation: Distance is the actual path covered ic., 3 + 4 = 7 km. Displacement is the otraight line distance from A to
−−−−−−
B i.e., √3 + 4 = 5 km.
2 2
2. (b) Halt timing at the traffic signal, slow speed at the congested areas and halt-timing at the bus stops are also to be taken
into account.
Explanation: Halt timing at the traffic signal, slow speed at the congested areas and halt-timing at the bus stops are also
to be taken into account.
3. (c) Instantaneous speed
Explanation: A speedometer is a gauge that measures and displays the instantaneous speed of a vehicle.
4. (b) 6 km/h
Explanation: Average speed =
Total distance traversed
Total time taken
= = 6 km/h
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
5. (b)
Explanation:
6. (c) a + b
3c
Explanation: The displacement x = at + bt2 - ct3
velocity = a + 2bt - 3ct2
acceleration = 2b - 3c ⋅ 2t
i.e., acceleration is zero at time t =
2b b
=
6c 3c
2
∴ Velocity (at t = b
3c
) = a + 2b b
3c
− 3c
b
9c
2 2 2
2b b b
= a + − = a +
3c 3c 3c
7. (c) None of these
Explanation: average velocity is zero, as car returns to the starting point.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
4/6
myCBSEguide
8. (d) 100 m
Explanation: During the first 5 seconds of the motion, the acceleration is -ve and during the next 5 seconds it becomes
positive. (Example: a stone thrown upwards, coming to momentary rest at the highest point.) The distance covered
remains same during the two intervals of time.
9. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: A body having negative acceleration can be associated with speeding up, if object moves along negative
X-direction with increasing speed.
10. (b) If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: If both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
11. State True or False:
i. (a) True
Explanation: True
ii. (b) False
Explanation: False
12. Fill in the blanks:
a. change in velocity
b. independent
13. Yes, because length of the train is smaller as compared to the distance between New Delhi and Kanpur.
14. Distance and displacement have the same magnitude when the object moves in a straight line.
−
−
15. Here, t = √x − 3
−
−
√x = t + 3
x = (t + 3)2
i. v =
dx
= 2(t + 3)
dt
At t = 3 s, v = 2(3 + 3) = 12m/s
ii. At t = 6 s, v = 2(6 + 3) = 18m/s
To practice more questions & prepare well for exams, download myCBSEguide App. It provides complete study
material for CBSE, NCERT, JEE (main), NEET-UG and NDA exams. Teachers can use Examin8 App to create similar
papers with their own name and logo.
16. Given,
Initial velocity of the bike, u = 120 km/h = 33.33 m/s
As bike stops, so final velocity, v = 0
Distance taken to stop, s = 100 m
Let, 'a' be the retardation experienced by the bike.
From the equation of motion, we have
v2 – u2 = 2as
(0)2 - 33.332 = 2 × 100 × a
a = − = - 5.55 m/s
1111
200
Now, using the first equation of motion we get
v = u + at
t= = = 6 sec.
v−u 0−33.33
a −5.55
17. Let us consider function of motion
x(t) = A + Be …(i)
−γt
Where γ and A, is a constant B is amplitude
x (t) is displacement at time t, where A > B andγ >0
dx(t)
v(t) =
dt
= 0 + (−γ)Be
−γt −γt
= −γBe
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
5/6
myCBSEguide
d d −γt 2 −γt
a(t) = [v(t)] = (−γB exp ) = (γ B exp )
dt dt
From (i) ∴ A > B so x is always + ve i.e., x > 0.
From (ii) v is always negative from (ii) v < 0
From (iii) a is always again positive a >0
As the value of γ Be can varies from 0 to + ∞
2 −γ
18. For truck u = 72× m/s = 20m/s
5
18
v = 0, a = ?, t = 5sec
v = u + at
0 = 20 + a × 5
= -4m/s2
−20
a = 5
For car t = 3 s, u = 20m/s, v = 0, a = ac
V = u + at
0 = 20 + ac
3
ac= −20
3
m/s
2
Let car is distance x metre behind the truck. Car takes time ‘t’ to stop after observing the signal given by truck to stop.
Time of response for human = 0.5 second
Time t includes the time to stop the car and responding time both. So time taken by car to stop after applying breaks is (t
– 0.5) second.
vc = u + act
0=20 − 20
3
(t – 0.5) ...(i)
For truck driver, there is no responding time he applies breaks with passing signal to car back side, so
v = u + at
0 = 20 - 4t ...(ii)
Equating (i) and (ii) equation.
20 - 4t= 20 − (t − 0.5)
−20
3
−20
−4t = − (t − 0.5)
3
12t = 20t - 10
-20t + 12t = -10
-8t = -10
seconds
10 5
t = = = 1.25
8 4
Distance travelled by car and truck in sec
5
5 5 5 1 2
S = 20 × + (−4) × × (∵ S = ut + at )
4 4 4 2
S = 25 −
25
8
= 25-3.125 = 21.875 m
Car travel first 0.5 sec with speed of uniform but after this responding time 0.5 sec breaks are applied and then retarding
−20
motion starts for car s
1 2
c = (20 × .5) × 20(1.25 − 0.5) + ×( ) (1.25 − 0.5)
2 3
= 10 + 20 × 0.75 −
10
3
× 0.75 × 0.75 = 10 + 15 - 7.5 × 0.25
Sc = 25 - 1.875 = 23.125 m
Sc - S = 23.125 - 21.875 = 1.25 m.
So avoid bump onto the truck, the car must be behind at least 1.25 m.
Copyright © myCBSEguide.com. Mass distribution in any mode is strictly prohibited.
6/6
You might also like
- Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesPhysics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualRyanRoseJrbden100% (61)
- Position vs. Time Graphs: Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3Document5 pagesPosition vs. Time Graphs: Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3Sidney BittnerNo ratings yet
- Chap 1-6 Mixed ReviewDocument16 pagesChap 1-6 Mixed ReviewanNo ratings yet
- The PATHFINDER Training ProgramDocument5 pagesThe PATHFINDER Training ProgramLyell E. Petersen100% (1)
- Architects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryDocument558 pagesArchitects Illustrated Pocket DictionaryFlavia ValNo ratings yet
- I Ching TesseractDocument14 pagesI Ching Tesseractthoth11100% (1)
- NTPCDocument158 pagesNTPCAnand GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Sample TestsDocument32 pagesPhysics 11 Sample TestsaayiinkeeNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument10 pagesPhysicsmoomooyaqiNo ratings yet
- Z - Kinematics 1-D - CombineDocument24 pagesZ - Kinematics 1-D - CombineAryan SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Motion NCert SolutionDocument23 pagesMotion NCert SolutionRamKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- Motion NCert SolutionDocument23 pagesMotion NCert SolutionRamKumarSharmaNo ratings yet
- 1D Motion - ADocument8 pages1D Motion - AMuhid Ali SanjraniNo ratings yet
- 1a.rectilinear MotionDocument5 pages1a.rectilinear MotionAtulNo ratings yet
- 2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946Document21 pages2 Kinematics 1-D FINAL 1664995471946PRIYATAM IOAANo ratings yet
- Set ADocument2 pagesSet ARoszel cardinoNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document21 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Shreyas MishraNo ratings yet
- KINEMATICSDocument53 pagesKINEMATICSSwadhin BarikNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Velocity and AccelerationDocument12 pages2.0 Velocity and AccelerationNazrul IzzNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Height and DistanceDocument8 pagesLecture Notes - Height and DistanceDinesh MatlaniNo ratings yet
- 1D MotionDocument6 pages1D Motionxakaka4037No ratings yet
- College Physics - Ch1-Kinematics HomeworkDocument10 pagesCollege Physics - Ch1-Kinematics HomeworkJackieNo ratings yet
- Short Questions: MotionDocument30 pagesShort Questions: MotionGangesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes On Travel GraphsDocument11 pagesTeaching Notes On Travel GraphsottonyembojedidiahNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Document22 pagesPraveen Kumar Pachauri: IIT-JEE - 2020 - 2021Vibhas SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Test Review: Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1 - 3Document8 pagesUnit 1 Test Review: Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 1 - 3NathanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineDocument26 pagesNCERT Grade 11 Physics CH 03 Motion in A Straight LineBhagyaNo ratings yet
- Xi Physics CH Motion in A Straight Linerw 2 240502 224402Document4 pagesXi Physics CH Motion in A Straight Linerw 2 240502 224402fijiteb766No ratings yet
- Pre-Test in MOTIONFinalDocument5 pagesPre-Test in MOTIONFinalElyzza Wye AlbaoNo ratings yet
- Booklet 1Document7 pagesBooklet 1Raiv LondresNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Rate, Ratio & Proportion: I. L. C. NotesDocument51 pages6.1 Rate, Ratio & Proportion: I. L. C. NotesRain HoNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Velocity SET BDocument6 pagesUnit Test Velocity SET BNandhu RamkumarNo ratings yet
- Class 9 pt1 Two 2023Document2 pagesClass 9 pt1 Two 2023Laxman SdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics:Velocity & Acceleration. - Updated 9/6/06Document5 pagesChapter 2: 1-D Kinematics:Velocity & Acceleration. - Updated 9/6/06Mahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Unit Test (Practice) - Kinematics (Oct 2008 Version) SolutionsDocument6 pagesUnit Test (Practice) - Kinematics (Oct 2008 Version) SolutionsNicholas ChevalierNo ratings yet
- Motion WorksheetDocument8 pagesMotion Worksheetstreetdiary.blogNo ratings yet
- 11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Document15 pages11 Phy ln3 Problems 1629708307Sathiya RNo ratings yet
- Assignment EoM EasyDocument3 pagesAssignment EoM EasySohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Motion Practice TestDocument8 pagesMotion Practice TestRanish DhoteNo ratings yet
- Motion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsDocument27 pagesMotion and Time: Check Your Progress Factual QuestionsRahul RajNo ratings yet
- Practice Test. MotionDocument3 pagesPractice Test. MotionsatyamheykarNo ratings yet
- Sri Venkateswara College of Education: Chapter 1 Lesson 1 - 2 - 3 TestDocument4 pagesSri Venkateswara College of Education: Chapter 1 Lesson 1 - 2 - 3 TestChandra ReddyNo ratings yet
- Work Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Document2 pagesWork Book # 1: Distance & Displacement, Speed &velocity, Average Speed & Average Velocity 1Monal KumarNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Motion in Straight LineDocument21 pagesCH 3 Motion in Straight LineZeel ShahNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manual PDFmarcusquyepv100% (13)
- Describing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsDocument26 pagesDescribing Motion: Third Quarter PhysicsRose Ann YamcoNo ratings yet
- Physics 5th Edition Walker Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesPhysics 5th Edition Walker Solutions Manualnoisefulrectrix.qn0x100% (16)
- Summative Test in General Physics 1Document4 pagesSummative Test in General Physics 1MengieNo ratings yet
- Kinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Document3 pagesKinematics P ME KNM 01-02-03Raghav MishraNo ratings yet
- T1 Ch1 KimPar Basic1 STDVDocument6 pagesT1 Ch1 KimPar Basic1 STDVizzat razaliNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B, AP Physics C WorksheetDocument10 pagesAP Physics B, AP Physics C WorksheetGurukul24x7100% (1)
- Assignment 3Document3 pagesAssignment 320 Subhojit Maji 10HNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance ProblamsDocument29 pagesTime and Distance Problamsrenuka mulaNo ratings yet
- NSEA Question Paper 2017Document19 pagesNSEA Question Paper 2017Sparsh SaraogiNo ratings yet
- Class 11th (21-23) Weekly Quiz - 5 PUNE Paper 13.06.2021Document9 pagesClass 11th (21-23) Weekly Quiz - 5 PUNE Paper 13.06.2021Sushma PawarNo ratings yet
- 2 D Kinematics Review 2019Document6 pages2 D Kinematics Review 2019sdshah0604No ratings yet
- Physic MCQDocument32 pagesPhysic MCQTruong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphDocument4 pagesLesson 3 Velocity - Time GraphSomrik LangapNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Exam-Gen Physics 1Document3 pages1st Quarter Exam-Gen Physics 1Jenny Vhie S. Vinagrera100% (1)
- NSEA Question Paper 2017Document14 pagesNSEA Question Paper 2017EduardNo ratings yet
- Velocity and SpeedDocument9 pagesVelocity and SpeedJenny Teves DayritNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921Document3 pagesAssignment 01 Rectillinear Motion AJN Sir-2921iitforumNo ratings yet
- Speed Time GraphDocument7 pagesSpeed Time GraphAryan Hossain100% (2)
- 06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDocument24 pages06/30/11 - Moneysaver - Lewis-Clark EditionDavid ArndtNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document50 pagesChap 002Eduardo AndradersNo ratings yet
- River VolgaDocument11 pagesRiver Volgaapi-317411236No ratings yet
- Summary of Eric HobsbawmDocument4 pagesSummary of Eric HobsbawmDCNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune EncephalitisDocument26 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune EncephalitisSylvia TrianaNo ratings yet
- Pollitt & Shaorshadze (2011) - The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy PDFDocument31 pagesPollitt & Shaorshadze (2011) - The Role of Behavioural Economics in Energy and Climate Policy PDFRoz KrakraNo ratings yet
- Cells of Immune System Notes 2Document70 pagesCells of Immune System Notes 2Sudeeksha Ravikoti100% (1)
- Effects Temp On PropsDocument5 pagesEffects Temp On Propsdina gunasekeraNo ratings yet
- Civil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Document1 pageCivil Works CW05 R1 (Submission Drawings 16.03.22)Joel AganNo ratings yet
- Inverted Nipple PaperDocument7 pagesInverted Nipple PaperFarisah Dewi Batari EmsilNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Neo BehaviorismDocument11 pagesModule 8 Neo BehaviorismDenyseNo ratings yet
- Ratio Detector: SNSCT 16Ec304-Communication Theory Unit-3 K.Sumathi, Ap/EceDocument2 pagesRatio Detector: SNSCT 16Ec304-Communication Theory Unit-3 K.Sumathi, Ap/EceChandu NanduNo ratings yet
- Pump SystemsDocument45 pagesPump SystemsJagdip ShethNo ratings yet
- "7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofDocument29 pages"7 Streams of Income For The Average Nigerian": by Oluwatoyin Omotoso ofOliver Dennis100% (1)
- DILO SF6 Catalogue 2021 ENDocument214 pagesDILO SF6 Catalogue 2021 ENBadraa BatorgilNo ratings yet
- Plumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..Document203 pagesPlumbing 2008 Includes FU Calculation Fire Fighting..michelghanem100% (2)
- 1T 19-20 LBYKM31 Experiment Manual As of Sept 15 2019Document33 pages1T 19-20 LBYKM31 Experiment Manual As of Sept 15 2019Ammi PinedaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage DC Transmission PDFDocument4 pagesHigh Voltage DC Transmission PDFBMS_SOFTGUYNo ratings yet
- Dolch PhrasesDocument10 pagesDolch PhrasesCharlie Manahan TemonNo ratings yet
- Bharti 2023 BP 6853CDocument17 pagesBharti 2023 BP 6853CmonaranjansharmaNo ratings yet
- The Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNDocument15 pagesThe Properties of Determinants:: 11 22 II NNVivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Shining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orDocument1,016 pagesShining The Light I ... by Robert Shapiro Tom... (Z-Lib - orbatiyeNo ratings yet
- Цацулин CQC Mag 2001-06 J - eng PDFDocument1 pageЦацулин CQC Mag 2001-06 J - eng PDFBudo MediaNo ratings yet
- 预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsDocument15 pages预习内容:Chapter 3 Solving Radical EquationsSolo YehNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways Carbon EmissionsDocument9 pagesIndian Railways Carbon EmissionsTechTrip IndiaNo ratings yet