Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CON3101
CON3101
Uploaded by
clam2014Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CON3101
CON3101
Uploaded by
clam2014Copyright:
Available Formats
CONNECTIONS
Bolted Splices in Compression – Splice Plate Member Checks
Author: Kevin Cowie, Alistair Fussell
Affiliation: Steel Construction New Zealand Inc.
Date: 24th February 2012
Ref: CON3101
Key Words
Splices, Bolted Splice, Compression, Bolted Beam Splice, Bolted Compression Splice
Introduction
The Steel Construction New Zealand publication Steel Connect (SCNZ 14.1 and SCNZ 14.2) provides structural
engineers with a rapid and cost-effective way to specify the majority of structural steelwork connections, in
accordance with accepted fabrication industry norms. Specification of these connections also facilitates the
development of reliable cost estimates by designers, fabricators, consulting quantity surveyors and constructors.
Steel Connect contains bolted beam splice (BBS) and bolted welded beam splice (BWBS) connections. An
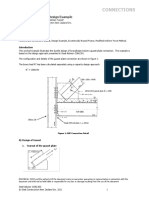
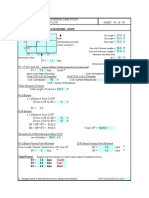
example of a bolted beam splice connection is shown in figure 1. A number of limit states are checked. The
connection capacity is based on the limit state that results in the lowest joint capacity. In Steel Connect there
are checks for the flange splice design tension loads and a flange plate compactness requirement. However
there are no specific checks for flange plate member (buckling) under compression axial forces. This article sets
out the plate member axial capacity requirements.
Figure 1: Bolted Splice – Non Bearing (Hyland et al, 2008)
Splice Plate Member Axial Compression Design Strength Limit
The splice plate member axial compression capacity is determined using clauses 6.3.2 and 6.3.3 of NZS 3404
(SNZ, 2007). The flange splice plate will be treated as a column element.
The effective length (Le) of the splice plate compression member is:
Le k eL
where:
L = length between bolt rows each side of the splice
k e = the member effective length factor determined in accordance with 4.8.3 NZS 3404
ke 0.7
Disclaimer: SCNZ and the author(s) of this document make no warrantee, guarantee or representation in connection with this
document and shall not be held liable or responsible for any loss or damage resulting from the use of this document
Steel Advisor CON3101
© Steel Construction New Zealand Inc. 2012 1
The splice plate member axial compression capacity is:
Nic c Nis
where:
Nis = the design section capacity of the splice plate
Le fyi
n kf
r 250
r = radius of gyration
kf = the form factor, taken as 1.0
fyi=plate yield stress (MPa)
Values of the member slenderness reduction factor ( c ) may be obtained directly from table 6.3.3(2) NZS 3404
using the value of the modified member slenderness ( n) and the appropriate member constant ( b ) given in
table 6.3.3(1) NZS 3404. For splice plates b = 0 should be used.
Alternatively, c may be calculated as follows.
2
90
c 1 1
2
1
90
2
2
90
n a b
0.00326 13.5 0
2100 n 13.5
a 2
n 15.3 n 2050
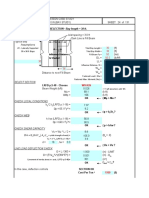
Example of Determining Flange Splice Member Axial Compression Design Strength Limit
An 8mm thick flange plate is selected for a bolted splice. The distance between bolt rows is 90mm. The yield
stress (fyi) is 250 MPa. What is the flange compression splice plate member axial compression capacity
expressed as a percentage of plate section capacity?
Determine modified member slenderness ( n)
Le fy
n kf
r 250
where:
Le k eL 0.7 x 90 63mm
r 0.289tif 0.289 x 8 2.312
kf 1.0
fy 250MPa
63 250
n 1 27.2
2.312 250
Steel Advisor CON3101
© Steel Construction New Zealand Inc. 2012 2
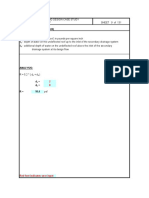
Determine member slenderness reduction factor ( c )
Using table 6.3.3(2) NZS 3404 for b 0:
c 0.95
splice plate member axial compression capacity is 95% of splice plate section capacity
References
Hyland C., Cowie K., Clifton C., Structural Steelwork Connections Guide: Design Procedures, SCNZ 14.1 2007,
Steel Construction New Zealand (Inc), Manukau City, 2008
Hyland C., Cowie K., Bird G., Structural Steelwork Connections Guide: Connection Tables, SCNZ 14.2 2007, Steel
Construction New Zealand (Inc), Manukau City, 2008
SNZ, Steel Structures Standard (Incorporating Amendments 1 and 2), NZS 3404:1997, Standards New Zealand,
Wellington, 2007
Steel Advisor CON3101
© Steel Construction New Zealand Inc. 2012 3
You might also like
- NZS 4297-2020 Engineering Design of Earth BuildingsDocument63 pagesNZS 4297-2020 Engineering Design of Earth Buildingsclam2014No ratings yet
- Broadway Ledger AnglesDocument8 pagesBroadway Ledger AnglesxpertsteelNo ratings yet
- Pages From ASME PTB-4-2013 - Section VIII-Division 1 Example Problem ManualDocument4 pagesPages From ASME PTB-4-2013 - Section VIII-Division 1 Example Problem Manualzguy360No ratings yet
- Testing Procedure of Ball ValveDocument2 pagesTesting Procedure of Ball Valverajesh100% (2)
- Anchor BoltDocument15 pagesAnchor BoltRyan Wiratama67% (3)
- Aerospace Lug AnalysisDocument51 pagesAerospace Lug AnalysisAnthony GravagneNo ratings yet
- Mech 2Document82 pagesMech 2Erwin100% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ductile Iron Pipes and Fittings - Electrosteel Casting LTD PDFDocument44 pagesDuctile Iron Pipes and Fittings - Electrosteel Casting LTD PDFSmith780512No ratings yet
- Con 1201Document4 pagesCon 1201rubyNo ratings yet
- 16 Jib Crane ANA5201Document5 pages16 Jib Crane ANA5201vodugu123100% (1)
- Watertank GSDocument38 pagesWatertank GSSushobhit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Con 1303Document8 pagesCon 1303chef100% (1)
- Bow String Girder Steel Members Design As Per IRC Code Bow-String Girder - DesignDocument967 pagesBow String Girder Steel Members Design As Per IRC Code Bow-String Girder - DesignStructural Spreadsheets100% (1)
- Design For Steel Structures (Jackets)Document12 pagesDesign For Steel Structures (Jackets)Kathia Lorena Espinoza RojasNo ratings yet
- 200801007DistortionalBuckling PDFDocument22 pages200801007DistortionalBuckling PDFSalah InhgaruoNo ratings yet
- TDS Lec 6Document94 pagesTDS Lec 6YAHAMPATH ARACHCHIGE PASAN MADURA YahampathNo ratings yet
- Analisa Anchor BoltDocument7 pagesAnalisa Anchor BoltGunawan NamakuNo ratings yet
- Anchor Bolts Design of Headed Anchor BoltsDocument12 pagesAnchor Bolts Design of Headed Anchor BoltsDoug LambNo ratings yet
- RC Slab Bridge DecksDocument24 pagesRC Slab Bridge DecksKeyur Patel100% (1)
- Unrestrained BeamDocument3 pagesUnrestrained BeamGanesh Konar100% (1)
- Design of Anchor Bolts in PedestalsDocument10 pagesDesign of Anchor Bolts in PedestalsVertical Starter100% (6)
- Strength Analysis of BeamsDocument40 pagesStrength Analysis of BeamsHussain Al AmerNo ratings yet
- Analyses On Reinforced Concrete Cross SectionsDocument31 pagesAnalyses On Reinforced Concrete Cross Sectionsshamsukarim2009No ratings yet
- Design Provisions of BS 5950 Part 1Document21 pagesDesign Provisions of BS 5950 Part 1ISMAEL SHAIK86% (7)
- Concrete Column DesignDocument2 pagesConcrete Column Designheherson juanNo ratings yet
- Coposite Profiled BeamDocument50 pagesCoposite Profiled BeamManu C PeringelilNo ratings yet
- Watertank GS PDFDocument24 pagesWatertank GS PDFManoj RautNo ratings yet
- Analyses On Reinforced Concrete Cross SectionsDocument35 pagesAnalyses On Reinforced Concrete Cross SectionsnavaleriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07-Unit 05 - Design For Shear PDFDocument19 pagesChapter 07-Unit 05 - Design For Shear PDFMohamed AbdNo ratings yet
- BRG-S-T-D-RD 85+835-1X30Document19 pagesBRG-S-T-D-RD 85+835-1X30Aziz ul HakeemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Flexural MembersDocument27 pagesLecture 4 Flexural MembersEdwin RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Strength Design of Structural Masonry - 2017 10 12Document70 pagesStrength Design of Structural Masonry - 2017 10 12Ricardo Muñiz DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Design of Water Tanks: by Dr. G.S.Suresh, Professor, Civil Engineering Department, NIE, MysoreDocument24 pagesDesign of Water Tanks: by Dr. G.S.Suresh, Professor, Civil Engineering Department, NIE, MysoreKawan EngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewDocument47 pagesLecture 4-2-2 - Design of Compression Members NewHarold Jackson MtyanaNo ratings yet
- Solution 4 & 5: Ntnu TMR 4195 Design of Offshore StructuresDocument12 pagesSolution 4 & 5: Ntnu TMR 4195 Design of Offshore StructuresflcwkNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Structure - Steel Design Tension MembersDocument24 pagesDesign of Steel Structure - Steel Design Tension MembersshingkeongNo ratings yet
- BracingDocument5 pagesBracingإبراهيم طلعتNo ratings yet
- 50NB Tubler ConnectionDocument11 pages50NB Tubler ConnectionDass MNo ratings yet
- Warehouse A: ProjectDocument145 pagesWarehouse A: ProjectCHEA VANNAINo ratings yet
- (PDF) 13.1a Beam-Column Joints Design Examples - pp.269-277 - CIVL3320 - 2017!05!08 - CompressDocument5 pages(PDF) 13.1a Beam-Column Joints Design Examples - pp.269-277 - CIVL3320 - 2017!05!08 - CompressAndres NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Section - This Chapter Will Discuss The Following TopicsDocument22 pagesAnalysis of Section - This Chapter Will Discuss The Following TopicsBatepola BacNo ratings yet
- Flexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsFrom EverandFlexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsSean M. GarnerNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsFrom EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsNo ratings yet
- Materials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationFrom EverandMaterials Science and Technology of Optical FabricationNo ratings yet
- The Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryFrom EverandThe Fatigue Strength of Transverse Fillet Welded Joints: A Study of the Influence of Joint GeometryNo ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysFrom EverandFriction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysNo ratings yet
- Ageing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityFrom EverandAgeing and Life Extension of Offshore Structures: The Challenge of Managing Structural IntegrityNo ratings yet
- Steel and Its Heat Treatment: Bofors HandbookFrom EverandSteel and Its Heat Treatment: Bofors HandbookRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsFrom EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsNo ratings yet
- Joining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsFrom EverandJoining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsSergio T. Amancio FilhoNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- Hertz-Halding2022 Book SustainableLightConcreteStructDocument219 pagesHertz-Halding2022 Book SustainableLightConcreteStructclam2014No ratings yet
- SS 674 2021 Fibre Concrete - Design of Fibre Concrete StructuresDocument48 pagesSS 674 2021 Fibre Concrete - Design of Fibre Concrete Structuresclam2014100% (1)
- Structural Steel Sets The Framework For Massive Airport RedevelopmentDocument4 pagesStructural Steel Sets The Framework For Massive Airport Redevelopmentclam2014No ratings yet
- Structure White Paper - Crane Girder - FinalDocument61 pagesStructure White Paper - Crane Girder - Finalclam2014No ratings yet
- IB - BLSTMB Pro1200 With FPDocument22 pagesIB - BLSTMB Pro1200 With FPclam2014No ratings yet
- Steel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3Document4 pagesSteel: Built To Last: Case Study No 3clam2014No ratings yet
- Aci 364.9T-03 (11) : Racks in A EpairDocument3 pagesAci 364.9T-03 (11) : Racks in A Epairclam2014No ratings yet
- SCNZ Case Study 13 - WebDocument4 pagesSCNZ Case Study 13 - Webclam2014No ratings yet
- Case Study No 6 Customhouse QuayDocument4 pagesCase Study No 6 Customhouse Quayclam2014No ratings yet
- Interior Roof GirderDocument5 pagesInterior Roof Girderclam2014No ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Noncompact and Slender Concrete-Filled Steel Tube (CFT) Beam-ColumnsDocument20 pagesAnalysis and Design of Noncompact and Slender Concrete-Filled Steel Tube (CFT) Beam-Columnsclam2014No ratings yet
- Issues On Using Welded Built-Up Box Columns in Steel Special Moment FramesDocument13 pagesIssues On Using Welded Built-Up Box Columns in Steel Special Moment Framesclam2014No ratings yet
- Project: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Gravity Loads (Load Tables) SHEET 7 of 131Document1 pageProject: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Gravity Loads (Load Tables) SHEET 7 of 131clam2014No ratings yet
- Aisc 09 PDFDocument3 pagesAisc 09 PDFclam2014No ratings yet
- (Option Ii) Interior Floor Girder Selection Live Load Reduction Check - Bay Width 36 FTDocument2 pages(Option Ii) Interior Floor Girder Selection Live Load Reduction Check - Bay Width 36 FTclam2014No ratings yet
- Engineering Journal: Third Quarter 2021 - Volume 58, No. 3Document72 pagesEngineering Journal: Third Quarter 2021 - Volume 58, No. 3clam2014No ratings yet
- Lateral Load Flow Calculations - Roof: Pi P (Ki / Sum Ki)Document4 pagesLateral Load Flow Calculations - Roof: Pi P (Ki / Sum Ki)clam2014No ratings yet
- Interior Floor Fill Beam Selection - Bay Length 30 FTDocument3 pagesInterior Floor Fill Beam Selection - Bay Length 30 FTclam2014No ratings yet
- Aisc 05 PDFDocument1 pageAisc 05 PDFclam2014No ratings yet
- Project: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Project Plan SHEET 1 of 131Document5 pagesProject: Steel Building Design Case Study Subject: Project Plan SHEET 1 of 131clam2014No ratings yet
- Eaton Vickers PVH Variable Axial Piston Pump: Industrial Applications Mobile ApplicationsDocument9 pagesEaton Vickers PVH Variable Axial Piston Pump: Industrial Applications Mobile ApplicationsPedro LandazuriNo ratings yet
- Piping Class Spec. - 1C23 (Lurgi)Document5 pagesPiping Class Spec. - 1C23 (Lurgi)otezgidenNo ratings yet
- S/N Codes and Standards Revision American Petroleum Institute (API)Document11 pagesS/N Codes and Standards Revision American Petroleum Institute (API)Benedict OgbaghaNo ratings yet
- Orbu SPC 44 0 22Document98 pagesOrbu SPC 44 0 22geverett2765No ratings yet
- Dump Vessel DV15: Without TAIL GATEDocument33 pagesDump Vessel DV15: Without TAIL GATEAqshoNo ratings yet
- BV3D BV3DZDocument4 pagesBV3D BV3DZYOGESH GOPALNo ratings yet
- 2BK3 2014 CygnusDocument54 pages2BK3 2014 CygnusCarlos Barba PNo ratings yet
- Asme B16.39-1998Document20 pagesAsme B16.39-1998absolutvacio82No ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue: Passion PRODocument129 pagesParts Catalogue: Passion PROEdar Jhon Montenegro RimarachinNo ratings yet
- Chinese Standard For Pressure VesselDocument40 pagesChinese Standard For Pressure VesselirfanlarikhotmailcomNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification of ValvesDocument28 pagesTechnical Specification of ValvesDhananjay BhaldandNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test ReportDocument6 pagesSaudi Aramco Test ReportGOSP3 QC MechanicalNo ratings yet
- Algunos Estandares de La Valvula de Control Entre OtrasDocument9 pagesAlgunos Estandares de La Valvula de Control Entre OtrasDoris Alfaro TorrezNo ratings yet
- Wide FlangeDocument32 pagesWide FlangeFathoniNo ratings yet
- DCEM2100 OPS.B5pdfDocument71 pagesDCEM2100 OPS.B5pdfSebastian TorresNo ratings yet
- HS550UTV 4 Parts CatalogueDocument67 pagesHS550UTV 4 Parts CatalogueСтојаковић ЂуроNo ratings yet
- OIL Offloading Hoses Brochure 2020 WDocument24 pagesOIL Offloading Hoses Brochure 2020 WTaufiq WibawaNo ratings yet
- Tal-Ge-Png-Iso-1cc003501 - 01 (As Built)Document1 pageTal-Ge-Png-Iso-1cc003501 - 01 (As Built)Jan pierre Arismendis paibaNo ratings yet
- WSA 109 - Flange Assembly Torque Calculator v5Document12 pagesWSA 109 - Flange Assembly Torque Calculator v5MouchartStéphanieNo ratings yet
- Mud ValvesDocument4 pagesMud ValvesFabio Peres de LimaNo ratings yet
- MKWD LWUA ADB Package 3 Technical Details and DrawingsDocument195 pagesMKWD LWUA ADB Package 3 Technical Details and DrawingsRoland AnaumNo ratings yet
- DOC-NA-ME-500 - Piping Class PDFDocument12 pagesDOC-NA-ME-500 - Piping Class PDFedscesc10No ratings yet
- EEMUA 145 1987 90 100 Copper Nickel Alloy Piping For Offshore Applications Specification Fla 2 PDFDocument25 pagesEEMUA 145 1987 90 100 Copper Nickel Alloy Piping For Offshore Applications Specification Fla 2 PDFz4zarrar100% (1)
- Fugitive Emission Standards: ISO 15848 Iso 15848 Tightness ClassesDocument1 pageFugitive Emission Standards: ISO 15848 Iso 15848 Tightness ClassesSatish ShewaleNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Vibration Problems at Compressor StationsDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Vibration Problems at Compressor StationsMuhd Fadzlee ZNo ratings yet
- Metaris Vane ProductsDocument20 pagesMetaris Vane ProductsFernanda DomecgNo ratings yet
- Gray Iron Gate Valves, Flanged and Threaded Ends: MSS SP-70-2011Document16 pagesGray Iron Gate Valves, Flanged and Threaded Ends: MSS SP-70-2011LUISNo ratings yet
- Treated Water PumpDocument8 pagesTreated Water PumpKELVIN TECHNOLOGIESNo ratings yet