Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 1 Social Psychology As A Scince
Unit 1 Social Psychology As A Scince
Uploaded by
Annika MadridOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1 Social Psychology As A Scince
Unit 1 Social Psychology As A Scince
Uploaded by
Annika MadridCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 1: Social Psychology
as a Science
Week Week 1
Date @June 14, 2023
Files
Notes tested on quiz
Unit/mod M1 U1
💡 Psychology
➥ science that seeks to measure, explain, and sometimes
change the behavior of human and animals.
Gordon Alport
➥ The scientific study of how an individual’s thoughts,
feelings, and behaviors are influenced by other people
Four Key Aspects
Influenced by other people
➝ Social psychology is the study of how other people
affect us
➝ Social aspect is one of the most important in social
psychology
Thoughts, feelings, and behaviors
➝ How other people affect every aspect of individual’s
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 1
life, including thoughts (cognitions), feelings
(affect), and behaviors
Thoughts (cognitions) – how individuals process
information about other people
and how they store the information in their memory.
Feelings (affect) – how people form a prejudice
against out groups and their
affection for friends and lovers.
Behavior – to understand why various kinds of actions
toward other people occur
or do not occur.
Individual’s perspective
➝ Take the perspective of individuals in a social
setting, rather than focusing only on objective features
of the situation.
Scientific study - Social psychologists rely on direct
tests of their ideas
➝ Rely on direct tests of their ideas
➝ Scientific evidence is necessary before a proposal
will be taken seriously; it is not enough merely to
speculate about an event and generate a plausible
explanation.
Herman Melville
➥ Our lives are connected by a thousand invisible threads
➥ Social Psychology aims to illuminate those threads, and
it does so by asking
questions that have intrigued us all:
How much of our social world is just in our heads?
Would you be cruel if ordered?
To help, or to help oneself?
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 2
➣ The Power of the Situation
We are creatures of our cultures and contexts
Evil situations sometimes overwhelm good intentions,
inducing people to follow falsehoods or comply with
cruelty
➣ The Power of the Person
We are also the creators of our social worlds
If a group is evil, its members contribute to (or
resist) its being so. Facing the same situation,
different people may react differently
➣ The Importance of Cognition
People react differently partly because they think
differently
Social reality is something we construct subjectively.
Our beliefs about ourselves also matter
➣ The Applicability of Social Psychological Principles
Social psychologists are more and more applying their
concepts and methods to current social concerns, such as
emotional well-being, health, courtroom decision-making,
prejudice reduction, environmental design and
conservation, and the quest for peace
SOCIOLOGY SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY PERSONALITY PSYCHOLOGY
Provides general Studies the Studies the
laws and theories psychological characteristics that
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 3
about societies, not processes people make individuals
individuals have in common with unique and different
one another that from one another.
make them
susceptible to
social influence.
Historical Background of Social Psychology
Emerged as a field distinct from other disciplines and from
other areas of psychology sometime in the middle 20th
century, perhaps most clearly during the 1950s
“Modern” social psychology has existed for only 50 or 60
years
Ancient Greek
Plato
Father of Western Philosophy
Suggested that people experience the world in three
distinct ways: in thought, in emotion, and in action.
Thus, the triumvirate of cognitive (thoughts),
affective(feelings), and behavioral aspects of experience
is very old.
Elements of the Self – Appetitive, Spirited, Mind
Allegory of the Cave
True Lie
Plato’s “crowd mind” speculations: “even when the wisest
individuals when assembled into a crowd might be
transformed into an irrational mob.”
Aristotle
Argued forcefully that living a good life and achieving
personal happiness are both dependent on providing
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 4
benefits to other people in addition to the self.
Aristotle’s view was that the connection with others forms
an essential part of who we are.
This idea is consistent with social psychological work on
the self-concept, which has shown that our social
relationships are important components of how we define
ourselves.
The concept of social norms can be traced back to one of
the greatest ideas of philosophy:
“Social Contract” – the idea that to survive and
prosper, human groups had to develop some basic
rules of social and moral conduct.
Middle 19th Century
➥ field of psychology separated from philosophy and became a
distinct discipline
1898 –An American psychologist,
NORMAN TRIPLETT,
American psychologist
conducted the first American empirical study that could
be classified as social psychological in nature.
Triplett was curious about a pattern he noticed in
bicycle racing times. His topic became known as “social
facilitation.”
1908
WILLIAM McDOUGAL(English Psychologist) & EDWARD ROSS
(American sociologist)
Publication of the first two textbooks bearing the name
Social Psychology
Early Decades in the 20th Century
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 5
➥ view on BEHAVIORISM strengthened
1930’s to 1940’s
Two critical events occurred that had the most important
impact on the development of Social Psychology:
Great Depression in the U.S.
World War II
Kurt Lewin
➥ The father of modern social psychology
➥ Was instrumental in establishing social psychology as a
respected field of scientific inquiry
1950’s to 1960’s – Social Psychology flourished.
1970’s – scientific maturity.
1970 to present – recognition of gender and racial bias;
culture specificity.
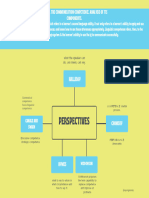
Major Theoretical Perspective in Social
Psychology
Socio-Cultural Perspective
➥ Social behavior resides in the social group that we find
ourselves going along ‘’social currents.’’
“CRAZES” - products of the ‘’mob mind.’’
➥ an irrational unanimity of interest, feeling, opinion,
or deed in a body of communicating individuals, which
results from suggestion and imitation.
‘’Social Norms’’ – rules about appropriate behavior.
‘’Culture’’ – is a set of beliefs, customs, habits, and
language shared by people living in a particular time
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 6
and place.
Evolutionary Perspective
➥ Human social behaviors are rooted in physical and
psychological predispositions that helped our ancestors
survive and reproduce.
‘’Natural Selection’’ – process by which characters help
animals survive are passed on to their offspring.
Social Learning Perspective
➥ Social behavior is driven by each individual’s past
learning experiences with reward and punishment.
➥ Emphasize unique experiences in a particular family,
school, or peer group.
Social Cognitive Perspective
➥ Social behavior is driven by each person’s subjective
interpretations of events in the social world.
Kurt Lewin – a person’s interpretation of a situation is
related to his goals at the time.
Interaction between inner experience and the outside
world.
Unit 1: Social Psychology as a Science 7
You might also like
- Social Psychology ReviewerDocument10 pagesSocial Psychology ReviewerTin EupenaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Social Psychology: Prepared By: Mr. Gerald M. Llanes, LPT, RPMDocument76 pagesAn Introduction To Social Psychology: Prepared By: Mr. Gerald M. Llanes, LPT, RPMGerald M. LlanesNo ratings yet
- Defination and Scop of Social Psychology PDFDocument75 pagesDefination and Scop of Social Psychology PDFjyotikanoujiyaNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology IntroDocument20 pagesSocial Psychology Introsimranarora2007100% (1)
- Chapter 1.1 - Social Psychology As A DisciplineDocument38 pagesChapter 1.1 - Social Psychology As A DisciplineKARLA MAE REVANONo ratings yet
- Social Psychology - ReviewerDocument7 pagesSocial Psychology - Reviewermaxsrn92No ratings yet
- A Short Story Written by Filipino AuthorDocument16 pagesA Short Story Written by Filipino AuthorCatheryl Padilla SalenNo ratings yet
- MPC-004 Advanced Social PsychologyDocument264 pagesMPC-004 Advanced Social PsychologyKiran TarlekarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Social PsychologyDocument22 pagesUNIT 1 Social PsychologySammie Tanyah GandahNo ratings yet
- Extrovertion QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesExtrovertion QuestionnaireMicah Eureka TagleNo ratings yet
- Social PsychologyDocument9 pagesSocial PsychologyRachelle BlancoNo ratings yet
- Virreyy's Group PsychologyDocument35 pagesVirreyy's Group PsychologyJoshua Nathaniel J. NegridoNo ratings yet
- 1 EDITED 12022024 080356pmDocument32 pages1 EDITED 12022024 080356pmBabar HassanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 AP Psychology History of Psychology-1Document30 pagesCH 1 AP Psychology History of Psychology-1SNOWNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document2 pagesLecture 1Claudia StokicNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document3 pagesLesson 1marie fayeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Social Psychology 1Document6 pagesIntroduction To Social Psychology 1geksxxwpNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Introduction To Social Psychology What Is Social Psychology?Document51 pagesUnit 1-Introduction To Social Psychology What Is Social Psychology?Ananta ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Social PsychologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Social PsychologyAnjali Jha100% (1)
- The First Five ChaptersDocument52 pagesThe First Five ChaptersOdaa BultumNo ratings yet
- Advanced SP AddDocument59 pagesAdvanced SP AddOdaa BultumNo ratings yet
- CH 01 Lecture What Is PsychologyDocument8 pagesCH 01 Lecture What Is Psychologyhpadgett27No ratings yet
- Social Psychology PDFDocument115 pagesSocial Psychology PDFDr. Deepti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Social Psychology 1MBDocument260 pagesAdvanced Social Psychology 1MBRahul PalNo ratings yet
- PsychologyDocument12 pagesPsychologySruthy MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment of The Social PsychologyDocument56 pagesAssignment of The Social PsychologySagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Psych 109 - REVIEWERDocument21 pagesPsych 109 - REVIEWERChanGie Rhyl UbayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Notes Intro To Social PsychologyDocument4 pagesLecture 1 Notes Intro To Social PsychologyCeline SinghNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To Social PsychologyDocument5 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To Social PsychologyAayushNo ratings yet
- Manual 1introductionDocument24 pagesManual 1introductionL YNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Science of Social PsychologyDocument23 pagesAn Introduction To The Science of Social PsychologyReyhan KüçükyeğenNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Social Psychology : 1.0 ObjectivesDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Social Psychology : 1.0 ObjectivesKanishk BansalNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Science of Social PsychologyDocument24 pagesAn Introduction To The Science of Social PsychologyEmma EmsNo ratings yet
- 1.2-1.4 PSYCH 1100 Reviewer NotesDocument6 pages1.2-1.4 PSYCH 1100 Reviewer Notesdynes.sebastianNo ratings yet
- Unit 1. Social PsychologyDocument23 pagesUnit 1. Social Psychologythf6smhryjNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Social PsychologyDocument6 pagesChapter1 Social PsychologyKAYLE NICOLE ILIJAYNo ratings yet
- Understanding Social Psychology: Dr. Rashmi SinghDocument24 pagesUnderstanding Social Psychology: Dr. Rashmi SinghAndrew ShapiroNo ratings yet
- Introductory Report RIDHI BHATIA (220243)Document16 pagesIntroductory Report RIDHI BHATIA (220243)ridhi bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Social PsychologyDocument95 pagesIntroduction To Social PsychologySagar SunuwarNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology - ReviewerDocument3 pagesSocial Psychology - Reviewersheila minminNo ratings yet
- Social PsychologyDocument3 pagesSocial PsychologyCarlyn HarfordNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of PsychologyDocument20 pagesThe Evolution of PsychologyyamiNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition Laura King PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition Laura King PDF Full Chapterlizarddecernkqwvy100% (23)
- Solution Manual For The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition Laura KingDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For The Science of Psychology An Appreciative View 5th Edition Laura Kingpromiser.mulleinjh0l100% (48)
- Social PsychologyDocument9 pagesSocial Psychologyanshu1508No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Social PsychologyDocument79 pagesChapter 1 Social PsychologyBCNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PsychologyDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Psychologysbnm836No ratings yet
- HHS Sociology Chapter 01 PDFDocument34 pagesHHS Sociology Chapter 01 PDFRingle JobNo ratings yet
- Sociology4You 2001 PDFDocument600 pagesSociology4You 2001 PDFNelmar Basiasmith100% (2)
- Human BehaviourDocument66 pagesHuman Behaviournor hanis100% (1)
- Social Psychology.Document6 pagesSocial Psychology.Maryam NisarNo ratings yet
- Scope, Goal and Relationships of Social Psychology With Other DesciplinesDocument11 pagesScope, Goal and Relationships of Social Psychology With Other DesciplinesSerah LalaiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The History and Science of PsychologyDocument22 pagesIntroduction To The History and Science of PsychologyHayaton IRNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Social Psychology: What You Will LearnDocument22 pagesModule 2: Social Psychology: What You Will LearnDebora AndgziaNo ratings yet
- AtiyaDocument4 pagesAtiyamtariqmtariq021No ratings yet
- Ku Eps 100 NotesDocument86 pagesKu Eps 100 Notesfrancis kimaniNo ratings yet
- Social Psychology by Farhan GondalDocument12 pagesSocial Psychology by Farhan GondalFarhan Amjad GondalNo ratings yet
- Uts MidDocument6 pagesUts MidShekinah BandiezNo ratings yet
- UNDERSTANDING THE SELF - Module 1Document5 pagesUNDERSTANDING THE SELF - Module 1Glenndel RosauroNo ratings yet
- Kesulitan Menulis Siswa SDDocument11 pagesKesulitan Menulis Siswa SDlely.nurullailyNo ratings yet
- Dll-Pr1-Week 3Document5 pagesDll-Pr1-Week 3Heilene Ethel AngcayaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 05 - 26 - KULIAH BISNIS - Prodi D4Document38 pages2018 - 05 - 26 - KULIAH BISNIS - Prodi D4ardi wijanaNo ratings yet
- Lalitha PriyankaDocument8 pagesLalitha PriyankaSri Lalitha YanamandraNo ratings yet
- Depression 2023Document12 pagesDepression 2023RAUL PEREYENo ratings yet
- Student Learning OutcomesDocument43 pagesStudent Learning OutcomesRenell Frias100% (1)
- Chatgpt in and For Second Language Acquisition A Call For Systematic ResearchDocument6 pagesChatgpt in and For Second Language Acquisition A Call For Systematic Researchparawnareman99No ratings yet
- Language ContactDocument2 pagesLanguage ContactMA PAULINE DHAY PEREZNo ratings yet
- 300+ Artificial Intelligence MCQ Questions & Answers - LetsfindcourseDocument10 pages300+ Artificial Intelligence MCQ Questions & Answers - Letsfindcoursedevid mandefro100% (2)
- Vivien MonushDocument4 pagesVivien MonushVivien MonushNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Presentation SeminarDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence Presentation Seminarsidharth joshiNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument38 pagesEmotional IntelligenceMostafa ShershNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 11Document5 pagesKelompok 11SunAlfiNo ratings yet
- One of The Common Languages Used by Many Counties Around The World IsDocument3 pagesOne of The Common Languages Used by Many Counties Around The World Isdelavwega0405No ratings yet
- LT5 Pardo QuestionsDocument2 pagesLT5 Pardo QuestionsKathrynn CanalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Consumer BehaviorDocument61 pagesChapter 3 Consumer BehaviorFatima AbboudNo ratings yet
- Education 655Document7 pagesEducation 655Krizia May AguirreNo ratings yet
- Data Science UIN IB RevisedDocument27 pagesData Science UIN IB Revisedpustakafti2No ratings yet
- Gender Differences in Reading Strategies Among Vocational High School StudentsDocument7 pagesGender Differences in Reading Strategies Among Vocational High School StudentsReko upbNo ratings yet
- Mid Test AplicomDocument3 pagesMid Test AplicomAgatri TefaNo ratings yet
- General PsychoDocument179 pagesGeneral Psychomj6857322No ratings yet
- Delivery Plan 2022 1Document4 pagesDelivery Plan 2022 1api-659744227No ratings yet
- Drills IIDocument21 pagesDrills IIEricka Shane EspejoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of L1 Metaphorical Comprehension On L2 Metaphorical Comprehension of Iraqi EFL LearnersDocument7 pagesThe Impact of L1 Metaphorical Comprehension On L2 Metaphorical Comprehension of Iraqi EFL LearnersSuzan ShanNo ratings yet
- FCE Use of English Part 1, Test 19 - SleepDocument2 pagesFCE Use of English Part 1, Test 19 - SleepsupernaturalhousethingsNo ratings yet
- Young Learners' Motivation For Learning EnglishDocument15 pagesYoung Learners' Motivation For Learning Englishalfirahmadi222No ratings yet
- PSY 411 PPT 2 Models of TeachingDocument4 pagesPSY 411 PPT 2 Models of TeachingSheena NuguidNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document1 pageTopic 4ALINA DONIGA .No ratings yet
- Opinion Noam Chomsky The False Promise of ChatGPT - The New York TimesDocument15 pagesOpinion Noam Chomsky The False Promise of ChatGPT - The New York TimesRespaldo CBNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Learning Theories and Their Impact To EppDocument29 pagesContemporary Learning Theories and Their Impact To EppMeng VillareNo ratings yet