Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 BJT Biasing
6 BJT Biasing
Uploaded by
Maaliao Reoneil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pagesThis document discusses transistor biasing in 3 sentences:
Transistor biasing involves applying DC voltages to turn on a transistor so it can amplify an AC signal. The bias establishes an operating point called the Q-point in the active, cutoff, or saturation regions. Common biasing circuits include voltage divider, emitter-biased, collector feedback, and emitter follower configurations which are analyzed using exact or approximate methods.
Original Description:
Math
Original Title
6 BJT Biasing (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses transistor biasing in 3 sentences:
Transistor biasing involves applying DC voltages to turn on a transistor so it can amplify an AC signal. The bias establishes an operating point called the Q-point in the active, cutoff, or saturation regions. Common biasing circuits include voltage divider, emitter-biased, collector feedback, and emitter follower configurations which are analyzed using exact or approximate methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pages6 BJT Biasing
6 BJT Biasing
Uploaded by
Maaliao ReoneilThis document discusses transistor biasing in 3 sentences:
Transistor biasing involves applying DC voltages to turn on a transistor so it can amplify an AC signal. The bias establishes an operating point called the Q-point in the active, cutoff, or saturation regions. Common biasing circuits include voltage divider, emitter-biased, collector feedback, and emitter follower configurations which are analyzed using exact or approximate methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
ECE 220:
TRANSISTORS
Bipolar Junction Transistor Biasing
Prepared by: Engr. Arcel Salem
2nd Sem. AY 2022-2023
BIASING
Biasing: The DC voltages applied to a transistor in order to turn it
ON so that it can amplify the AC signal
ECE220 Engr. Salem
OPERATING POINT
• The DC input establishes an
operating or quiescent point called
the Q-point
ECE220 Engr. Salem
THREE STAGES OF OPERATION
• Active or Linear Region of Operation
• Base-Emitter junction is forward biased
• Base-Collector junction is reversed biased
• Cutoff Region of Operation
• Base-Emitter junction is reverse biased
• Saturation Region of Operation
• Base-Emitter junction is forward biased
• Base-Collector junction is forward biased
ECE220 Engr. Salem
DC BIASING CIRCUITS
• Voltage-divider bias circuit
• Emitter-biased circuit
• Collector-feedback bias
• Emitter follower configuration
ECE220 Engr. Salem
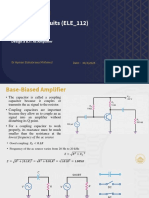
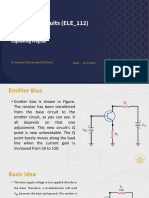
Voltage Divider Bias
• This is the very stable bias circuit
• The currents and voltages are nearly independent of any variations in β.
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Exact Analysis
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Exact Analysis
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Voltage Divider Bias Analysis
ECE220 Engr. Salem
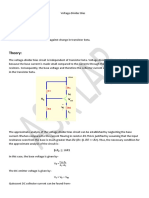
Example
Determine the dc bias voltage 𝑉𝐶𝐸 and the current 𝐼𝐶 for the voltage-divider
configuration shown below using exact analysis.
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Approximate Analysis
• This analysis can be used only when specific conditions are met.
• Conditions for approximate analysis:
𝛃𝐑 𝐄 ≥ 𝟏𝟎𝐑 𝟐
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Approximate Analysis
𝐑 𝟐 𝐕𝐂𝐂
𝐕𝐁 =
𝐑𝟏 + 𝐑𝟐
𝐕𝐄
𝐈𝐄 =
𝐑𝐄
𝐈 𝐂𝐐 = 𝐈 𝐄
𝐕𝐂𝐄𝐐 = 𝐕𝐂𝐂 − 𝐈𝐂 (𝐑 𝐂 + 𝐑 𝐄 )
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Example
Determine the dc bias voltage 𝑉𝐶𝐸 and the current 𝐼𝐶 for the voltage-divider
configuration shown below using approximate analysis.
ECE220 Engr. Salem
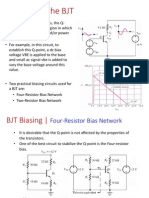
Collector Feedback Configuration
• Also called DC Bias with Voltage
Feedback
• Another way to improve the stability of a
bias circuit is to add a feedback path from
collector to base.
• In this bias circuit the Q-point is only
slightly dependent on the transistor beta, β.
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Collector Feedback Configuration
• Transistor Saturation Level
𝐕𝐂𝐂 − 𝐕𝐁𝐄
𝐈𝐁 = 𝐕𝐂𝐂
𝐑 𝐁 + 𝛃(𝐑 𝐂 + 𝐑 𝐄 ) 𝐈𝐂𝐬𝐚𝐭 = 𝐈𝐂𝐦𝐚𝐱 =
𝐑𝐂 + 𝐑𝐄
• Transistor Cutoff
𝐕𝐂𝐄 = 𝐕𝐂𝐂 − 𝐈𝐂 (𝐑 𝐂 + 𝐑 𝐄 ) 𝐕𝐂𝐄 = 𝐕𝐂𝐂
ECE220 Engr. Salem
Emitter Follower Configuration
• Voltage is taken off from collector: Saturation
𝐕𝐄𝐄 − 𝐕𝐁𝐄
𝐈𝐁 =
𝐑 𝐁 + (𝛃 + 𝟏)𝐑 𝐄
𝐕𝐂𝐄 = 𝐕𝐄𝐄 − 𝐈𝐄 𝐑 𝐄
ECE220 Engr. Salem
REFERENCES
• Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10th & 11th edition by
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
• Electronic Devices, 9th edition by Thomas L. Floyd
ECE220 Engr. Salem
You might also like
- Electronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewDocument86 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits Lab NewleevasusanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report JFET Transistor CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report JFET Transistor Characteristicsbravo5charlie40% (5)
- Manual de Reemplazo de SemiconductoresDocument5 pagesManual de Reemplazo de SemiconductoresCarlos Leonardo Cremonese Verna50% (8)
- 5 Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument27 pages5 Bipolar Junction TransistorsMaaliao ReoneilNo ratings yet
- 9 Voltage RegulatorsDocument20 pages9 Voltage RegulatorsMaaliao ReoneilNo ratings yet
- Diode Circuit AnalysisDocument26 pagesDiode Circuit AnalysisJANUBAS, GLORIBETH L.No ratings yet
- 4 Power Supply FiltersDocument9 pages4 Power Supply FiltersfritzramirezcanawayNo ratings yet
- 4 RectifiersDocument15 pages4 RectifiersJANUBAS, GLORIBETH L.No ratings yet
- Clippers ClampersDocument13 pagesClippers ClampersJANUBAS, GLORIBETH L.No ratings yet
- Chap 4 DC Biasing BJTDocument44 pagesChap 4 DC Biasing BJTUgeswran ThamalinggamNo ratings yet
- Lecnotes - Bipolar Junction Transistor - Part 2Document63 pagesLecnotes - Bipolar Junction Transistor - Part 2Fausto ArambuloNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesDocument20 pagesSinusoidal Steady State Analysis: Chapter ObjectivesPartha MishraNo ratings yet
- Small Signal Amplifiers Eet3Document67 pagesSmall Signal Amplifiers Eet3Dan ChapsNo ratings yet
- Aec Report Exp 3 SJDDocument5 pagesAec Report Exp 3 SJDSubbham jyoti DashNo ratings yet
- Design A BJT As AmplifierDocument23 pagesDesign A BJT As AmplifierSamer SeifNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Transistor Bias Circuits-1Document49 pagesLecture 2 - Transistor Bias Circuits-1MeesixNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document26 pagesLecture 5s231060031-5No ratings yet
- Lecture 2.5 Transistor ApplicationsDocument4 pagesLecture 2.5 Transistor ApplicationsAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Analog Fault DerivationDocument89 pagesAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNo ratings yet
- 315 AssignmentDocument13 pages315 AssignmentAbraham sheriffNo ratings yet
- s3 LabDocument54 pagess3 LabVishal bijiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PDFDocument39 pagesChapter 4 PDFAdel AtawiNo ratings yet
- 20EE10094 - Surendra Reddy Gaddam - Lab Report - Expt 1Document18 pages20EE10094 - Surendra Reddy Gaddam - Lab Report - Expt 1SSSSSSSSSSSSNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument156 pagesUnit IrevathianuNo ratings yet
- CH 05Document40 pagesCH 05miathegirl9No ratings yet
- Transistor Biasing and Stabilization: Lesson - 1Document57 pagesTransistor Biasing and Stabilization: Lesson - 1Naseer Mohammed100% (1)
- Unit3 3ph TRF Mubatanhema SlidesDocument59 pagesUnit3 3ph TRF Mubatanhema Slideseljay2422No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Transistors BJT Part IIDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Transistors BJT Part IIdoubleagent93No ratings yet
- ADEC - Lab 3Document14 pagesADEC - Lab 3syed furqan javedNo ratings yet
- EDC - Unit 3 FinalDocument118 pagesEDC - Unit 3 FinalDr UmapathyNo ratings yet
- Transistor DC Biasing 1Document38 pagesTransistor DC Biasing 1farhan jalaludinNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : Electronic Devices Conventional Current Version Seventh Edition FloydDocument63 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : Electronic Devices Conventional Current Version Seventh Edition Floydحافظ حمزہ اعوانNo ratings yet
- AEC NotesDocument271 pagesAEC Notes1DS19EC726- Pankaj Ashok M.No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Lecture 13Document34 pagesElectronic Devices Lecture 13bodzzaa21No ratings yet
- BJT AC DC & MultistageDocument42 pagesBJT AC DC & MultistageJose EspinoNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: DC AnalysisDocument5 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: DC Analysishemanshu_abbey100% (2)
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5Alwani IzzatiNo ratings yet
- American International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesDocument5 pagesAmerican International University-Bangladesh: Electronic DevicesAnamNo ratings yet
- Regulated DC Power Supply Lab AssignmentDocument17 pagesRegulated DC Power Supply Lab AssignmentSebastien Paul100% (1)
- Voltage-Divider Bias Experiment ReadingDocument3 pagesVoltage-Divider Bias Experiment ReadingFaisal SulemaniNo ratings yet
- Ic 2Document30 pagesIc 2Radhie NoahNo ratings yet
- 3 AC AmplificationDocument58 pages3 AC AmplificationAnthony BeltranNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument18 pagesProblemsShrutJainNo ratings yet
- Salam Lababidi Yorgo Daoud Circuit ProjectDocument10 pagesSalam Lababidi Yorgo Daoud Circuit Projectyorgodaoud360No ratings yet
- Voltech Samplequestions 2023batchDocument3 pagesVoltech Samplequestions 2023batchMCKV INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING 1999No ratings yet
- Design of Rogowski Coil With IntegratorDocument32 pagesDesign of Rogowski Coil With Integratorourbobby100% (1)
- Module 4 - Symmetrical Components and Sequence NetworksDocument42 pagesModule 4 - Symmetrical Components and Sequence NetworksferrerfillmoreNo ratings yet
- BJT DC Bias - 2023Document22 pagesBJT DC Bias - 2023Samer SeifNo ratings yet
- Laboratory No. 4Document19 pagesLaboratory No. 4Elizabeth Mei AiharaNo ratings yet
- Bias Transistor1Document46 pagesBias Transistor1angel larasatiNo ratings yet
- Circuits and Electronic Devices: Lecture NoDocument19 pagesCircuits and Electronic Devices: Lecture NoBilal BhattiNo ratings yet
- PE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesDocument32 pagesPE1 - Lect 1-PN Junction Diode PrinciplesAbdel-aziz SamiNo ratings yet
- Design DC and Ac Load Lines - Fall 2022Document5 pagesDesign DC and Ac Load Lines - Fall 2022Amera AdilNo ratings yet
- Performance of Cts in PowergridDocument61 pagesPerformance of Cts in PowergridS ManoharNo ratings yet
- Lec1 Single Stage AmpDocument29 pagesLec1 Single Stage AmpA8719No ratings yet
- New Analogue RepDocument4 pagesNew Analogue Repfedley sikoliaNo ratings yet
- PGK 110 HB Baur En-GbDocument3 pagesPGK 110 HB Baur En-GbAlan GallagherNo ratings yet
- BJT NotesDocument110 pagesBJT NotesHardesh Chauhan100% (1)
- BJT Circuits - Basic Electronics GuideDocument55 pagesBJT Circuits - Basic Electronics GuideNenad Stamenović100% (1)
- Transistor As An Amplifier: S BB CCDocument3 pagesTransistor As An Amplifier: S BB CCsreelakshmi.ece eceNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Wa0018.Document10 pagesWa0018.Gatik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of 2N4416 N Channel JFET Single Stage Amplifier For Large Bandwidth and Low Voltage GainDocument9 pagesDesign and Analysis of 2N4416 N Channel JFET Single Stage Amplifier For Large Bandwidth and Low Voltage GainEditor IjasreNo ratings yet
- IRFD120Document7 pagesIRFD120Diego AliasNo ratings yet
- Comp ArchitectureDocument21 pagesComp ArchitectureHariPrasanth GovindarajuNo ratings yet
- Ch. 1 - Semiconductor Diodes SummaryDocument2 pagesCh. 1 - Semiconductor Diodes SummaryJesryniel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Erazo Cristian SCR SimulacionDocument2 pagesErazo Cristian SCR SimulacionCris Choso ErazoNo ratings yet
- Memory OrganizationDocument70 pagesMemory OrganizationrahqansayeedNo ratings yet
- RT Marking Information &LL (Ookoo..p. Packing: TO-252Document2 pagesRT Marking Information &LL (Ookoo..p. Packing: TO-252Marck SolterNo ratings yet
- Module2 PDFDocument16 pagesModule2 PDFSrihari UttanurNo ratings yet
- P50N06Document4 pagesP50N06Rui MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To ElectronicsDocument4 pagesModule 1 Introduction To ElectronicsAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 SPICE Netlist SimulationDocument4 pagesLab 1 SPICE Netlist SimulationDavid TynanNo ratings yet
- Ece TransistorsDocument52 pagesEce TransistorsKalpesh BamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Power MOSFET Electrical CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesPower MOSFET Electrical CharacteristicsMarco FajardoNo ratings yet
- Nte 331Document2 pagesNte 331Cesar Augusto Arriaga ArriagaNo ratings yet
- Photodiode PDFDocument13 pagesPhotodiode PDFRizkyAnandarNo ratings yet
- Inkjet-Printed High Mobility Transparent-Oxide SemiconductorsDocument5 pagesInkjet-Printed High Mobility Transparent-Oxide Semiconductorsjulio perezNo ratings yet
- 2N3055 (NPN), MJ2955 (PNP) Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsDocument3 pages2N3055 (NPN), MJ2955 (PNP) Complementary Silicon Power TransistorsMichaelAngeloDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Threshold Voltage MosfetDocument6 pagesThreshold Voltage MosfetsantoshineepandaNo ratings yet
- Stephen HawkingDocument31 pagesStephen Hawkingmaheshwarivikas1982No ratings yet
- 20N60Document3 pages20N60FlashPTNo ratings yet
- Transistor InfoDocument3 pagesTransistor InfoErantha SampathNo ratings yet
- CMOS Transistor Theory: Thanks To Prof. David HarrisDocument29 pagesCMOS Transistor Theory: Thanks To Prof. David HarrisHarshdeep BhatiaNo ratings yet
- NPCIL Electronics PaperDocument9 pagesNPCIL Electronics Papernetcity143No ratings yet
- 4213 TPS Industrial Thermal BookDocument3 pages4213 TPS Industrial Thermal BookSebastian EspinozaNo ratings yet
- 2007-Behavioural and Electrothermal Modelling of TheDocument4 pages2007-Behavioural and Electrothermal Modelling of TheruanNo ratings yet
- SKKT 132, SKKH 132: Thyristor Bridge, SCR, BridgeDocument5 pagesSKKT 132, SKKH 132: Thyristor Bridge, SCR, BridgeRahim AfghanNo ratings yet
- SPW-Unit II - Notes-Semiconductor DevicesDocument35 pagesSPW-Unit II - Notes-Semiconductor DevicesArnab MitraNo ratings yet