Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Taxonomy Notes
Taxonomy Notes
Uploaded by
M A R I O NOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Taxonomy Notes
Taxonomy Notes
Uploaded by
M A R I O NCopyright:
Available Formats
Content Page
A taxon is a group of organisms that share a common characteristic and are classified together in a
hierarchical system of classification, such as species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, and
kingdom.
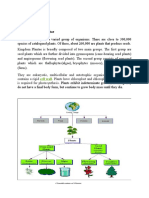
The five kingdom system flow diagram classifies organisms into five kingdoms: Monera, Protista,
Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. Monera includes bacteria and cyanobacteria; Protista includes
protozoa, algae, and slime molds; Fungi includes fungi and yeasts; Plantae includes plants; and
Animalia includes animals.
Viruses are not part of the current classification system because they are not living organisms. They
lack many of the characteristics of life, such as the ability to grow, reproduce, and metabolize
without a host cell.
The seven taxa, from largest to smallest, are: kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and
species.
Binomial nomenclature is a system of naming and classifying organisms using two Latinized names:
the genus and species. The genus name is capitalized, and the species name is lowercase. For
example, Homo sapiens is the binomial name for humans. Binomial nomenclature allows for a
unique and standardized way to identify and classify organisms based on their physical and genetic
characteristics.
Handout
The five kingdom system is a way of classifying living organisms based on their characteristics and
evolutionary relationships. Here's an overview of each kingdom and some examples of organisms
found in each:
Monera: This kingdom includes unicellular prokaryotic organisms, such as bacteria and
cyanobacteria. These organisms are typically very small, and many are found in soil, water, or living
in or on other organisms.
Protista: This kingdom includes unicellular eukaryotic organisms, such as protozoa, algae, and slime
molds. These organisms are found in a variety of environments, from freshwater to soil to the ocean.
Fungi: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms, such as mushrooms, yeasts, and
molds. Fungi play important roles in decomposing dead plant and animal matter, as well as in the
production of food and medicines.
Plantae: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are capable of
photosynthesis, such as trees, grasses, and flowers. Plants are important producers of oxygen and
play a critical role in the global carbon cycle.
Animalia: This kingdom includes multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic and
mobile, such as insects, fish, birds, and mammals. Animals play important roles in food webs and
ecosystems, as well as in human culture and society.
It's worth noting that the five kingdom system is now considered outdated and has been replaced by
more complex and nuanced classification systems, but it still provides a useful starting point for
understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
You might also like
- Blueprint For God Power Workbook - FinalDocument46 pagesBlueprint For God Power Workbook - FinalMali100% (2)
- Biology Now 2nd Edition Houtman Test BankDocument21 pagesBiology Now 2nd Edition Houtman Test Bankashleebernardgikfndpcxw100% (18)
- Phylogenetic Relationships Between The Three KingdomsDocument5 pagesPhylogenetic Relationships Between The Three Kingdomsibadullah shah100% (1)
- Meinig Beholding EyeDocument9 pagesMeinig Beholding EyeNatalie YatesNo ratings yet
- Intro 19Document26 pagesIntro 19Amola Mostafa100% (2)
- Green Education ModuleDocument124 pagesGreen Education ModuleCatherine S. Baldismo100% (2)
- Introduction To Environmental ScienceDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Environmental ScienceEljhon Satsat100% (1)
- Chapter-2 (Biology)Document24 pagesChapter-2 (Biology)pramod peterNo ratings yet
- 5 Kingdom of LifeDocument12 pages5 Kingdom of LifeDivyanshu AggarwalNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument8 pagesScienceCold CoockiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Biology)Document12 pagesChapter 2 (Biology)MahendraKumarNo ratings yet
- P PPPPPPPPPPP ! P "!PPP P!P P !P!"PP "P P#P " PP P$%P PP "&P'" PP" " !P#P PP P (!P"PPPP) PP"PP!P PPPP &P'"P PP P! PP PP!P&PDocument4 pagesP PPPPPPPPPPP ! P "!PPP P!P P !P!"PP "P P#P " PP P$%P PP "&P'" PP" " !P#P PP P (!P"PPPP) PP"PP!P PPPP &P'"P PP P! PP PP!P&PRaina Abad AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification: Name Anuj Class 11Document19 pagesBiological Classification: Name Anuj Class 11Anuj MorNo ratings yet
- Clasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesDocument16 pagesClasificacion de Los Seres Vivos en InglesPamelaMelissaManriqueGraosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Taxonomy: DiversityDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Taxonomy: DiversityRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Linnaeuss System of ClassificationDocument33 pagesLinnaeuss System of Classificationheartyjune.ortizo0610No ratings yet
- Five Kingdom SystemDocument8 pagesFive Kingdom SystemsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Biological Classification - WatermarkDocument22 pagesChapter - 2 Biological Classification - WatermarkLE X KRISHNANo ratings yet
- TOXONOMYDocument42 pagesTOXONOMYNanami MumuzunoNo ratings yet
- Sample OnlyDocument6 pagesSample OnlySeb LlaveNo ratings yet
- Beta Monic Ai-MonicaiDocument6 pagesBeta Monic Ai-MonicaiJAYAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Classifying Living OrganismsDocument54 pagesClassifying Living Organismstiya.bakugo.katsuki01No ratings yet
- "Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings WhichDocument11 pages"Biodiversity" Is A Concise Form of "Biological Diversity" and Was Biodiversity Is The Occurrence of Diverse or Varied Forms of Living Beings Whichbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Plant KingdomDocument9 pagesPlant KingdomsanaullahNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument5 pagesAnimal KingdomEstrella RamosNo ratings yet
- 5 Kingdoms of Living ThingsDocument1 page5 Kingdoms of Living ThingssandrakristikNo ratings yet
- Fungus - WikipediaDocument167 pagesFungus - WikipediaReynaldo RafaelNo ratings yet
- BIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION pp1Document17 pagesBIODIVERSITY AND CLASSIFICATION pp1Mpilwenhle KuneneNo ratings yet
- Define Zoology: Ornithology% (&) % ,%& (%Document4 pagesDefine Zoology: Ornithology% (&) % ,%& (%Belle MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Fungus: 1 EtymologyDocument28 pagesFungus: 1 EtymologyJohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 (Biology) PDFDocument12 pagesChapter-2 (Biology) PDFSHIVANSHI SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Portfolio EnglishDocument1 pagePortfolio EnglishLío GamesNo ratings yet
- 03 TaxonomyDocument11 pages03 TaxonomythinkiitNo ratings yet
- Classification - Taxonomy ReadingDocument7 pagesClassification - Taxonomy Readingapi-262368188No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-2 Class 11Document6 pagesChapter 1-2 Class 11Maitreyee NirgunNo ratings yet
- JoannaDocument4 pagesJoannapfaxawaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - BiodiversityDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - BiodiversityShah SaqibNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document31 pagesPresentation 1Soo Ming Huey 明慧No ratings yet
- Ben Ladin A. Datuman BS Med - Tech.-1Document4 pagesBen Ladin A. Datuman BS Med - Tech.-1Gap UnoNo ratings yet
- Ben Ladin A. Datuman BS Med - Tech.-1Document4 pagesBen Ladin A. Datuman BS Med - Tech.-1Gap UnoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document16 pagesCH 1exercisestartNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity Classification of OrganismsDocument18 pagesBiodiversity Classification of OrganismsFoong Tze HingNo ratings yet
- Microbes in The Biological World: Ahmad Masood Department of Botany H.D. Jain College, Ara (V.K.S. University, Ara)Document18 pagesMicrobes in The Biological World: Ahmad Masood Department of Botany H.D. Jain College, Ara (V.K.S. University, Ara)Fah RukhNo ratings yet
- Ke BiologyDocument13 pagesKe Biologybhupendrapawar279No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document5 pagesChapter 3Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- Oraganism and Its EnvironmentsDocument7 pagesOraganism and Its EnvironmentsKim AlvarezNo ratings yet
- UploadDocument20 pagesUploadKashish RajNo ratings yet
- The Five Kingdom ClassificationDocument2 pagesThe Five Kingdom ClassificationAbishan6 Khulal6No ratings yet
- CH 2Document13 pagesCH 2Debabrata DashNo ratings yet
- Five Kingdom SystemDocument4 pagesFive Kingdom SystemG.Y AcademyNo ratings yet
- Step Forward in Plant Taxonomy Book (Final)Document113 pagesStep Forward in Plant Taxonomy Book (Final)DoctorQariNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument209 pagesBiologyammugolu07No ratings yet
- MCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of BacteriaDocument35 pagesMCP 201 - The Kingdom Protista, Classification and Nomenclature of Bacteriachinecheremstephanie2022No ratings yet
- DocumentDocument20 pagesDocumentMohammad Daniyal SidiquieNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity and Classification 1Document33 pagesBiodiversity and Classification 1api-202349222No ratings yet
- Kingdoms in The Taxonomy of OrganismsDocument48 pagesKingdoms in The Taxonomy of OrganismsRomella Faye Bituin TabordaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity: The Origin of SpeciesDocument19 pagesBiodiversity: The Origin of Speciesnasrin banuNo ratings yet
- Monophyletic: Group) - This Fungal Group Is Distinct From The Structurally SimilarDocument4 pagesMonophyletic: Group) - This Fungal Group Is Distinct From The Structurally SimilarAce DanielNo ratings yet
- f4 Bio FolioDocument4 pagesf4 Bio FolioFoong Tze HingNo ratings yet
- 3-Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument5 pages3-Taxonomy and Classificationgaragegreat26No ratings yet
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Iological LassificationDocument13 pages© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Iological LassificationKM_ArunNo ratings yet
- Soil OrganismsDocument4 pagesSoil Organismstibau4No ratings yet
- Animals, Plants, and EcosystemsDocument27 pagesAnimals, Plants, and EcosystemsseulshNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument54 pagesBiological ClassificationAyesha MahboobNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Evo BioDocument8 pagesReviewer in Evo BioMichaela ParalejasNo ratings yet
- Biodanza: Poética Del Encuentro (Verónica Toro y Raúl Terrén)Document10 pagesBiodanza: Poética Del Encuentro (Verónica Toro y Raúl Terrén)Carlos Moisés MogollónNo ratings yet
- Botany SummaryDocument6 pagesBotany SummaryKristiooyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life 1Document5 pagesChapter 4 - Carbon and The Molecular Diversity of Life 1Hezron BarnabasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Biology of Animals - Evolutionary and Functional MorphologyDocument250 pagesRespiratory Biology of Animals - Evolutionary and Functional Morphologyraulmoscoso3No ratings yet
- Origin of LifeDocument13 pagesOrigin of LifeUbaid GurmaniNo ratings yet
- Branches of ScienceDocument6 pagesBranches of ScienceRishel TubogNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Upper Primary Science Section1&2Document30 pagesSyllabus Upper Primary Science Section1&2Ruvy Jean Codilla-FerrerNo ratings yet
- Imat Test Specification 2018 PDFDocument18 pagesImat Test Specification 2018 PDFPhương NghiNo ratings yet
- Branches of Biology QuizDocument2 pagesBranches of Biology QuizRetxed LeifNo ratings yet
- Soul PurposeDocument3 pagesSoul PurposeEd CrivelloNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Respect For Nature: WWW - Umweltethik.atDocument19 pagesThe Ethics of Respect For Nature: WWW - Umweltethik.atKarla BožićNo ratings yet
- 10 Characteristics of LifeDocument5 pages10 Characteristics of LifeDaryl YohNo ratings yet
- The Alien InvasionDocument14 pagesThe Alien InvasionincroyablNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 3 Q2 LAMP v3 PDFDocument10 pagesSCIENCE 3 Q2 LAMP v3 PDFRezaline Bongcaras CelsoNo ratings yet
- Writing Answer KeyDocument24 pagesWriting Answer KeyDon JohnNo ratings yet
- 4A-Discussion ForumDocument3 pages4A-Discussion ForumVincentus BinNo ratings yet
- The Reincarnation of Edgar CaseyDocument87 pagesThe Reincarnation of Edgar CaseySalvador C. Vilches86% (7)
- Science Year 5: Work Sample PortfolioDocument30 pagesScience Year 5: Work Sample Portfolioallan.manaloto23No ratings yet
- 2nd Q Lesson 2 Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeDocument15 pages2nd Q Lesson 2 Unifying Themes in The Study of LifeEvangeline Agtarap100% (4)
- BIO002 - Introductory Biology Lecture 1 AY2017-2018Document12 pagesBIO002 - Introductory Biology Lecture 1 AY2017-2018feviola tNo ratings yet
- Architecture Can Elevate Human SpiritDocument1 pageArchitecture Can Elevate Human Spiritwafa rafiaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper On Cell DiversityDocument5 pagesTerm Paper On Cell Diversitydhjiiorif100% (1)
- Your Life As Planet EarthDocument301 pagesYour Life As Planet EarthAbdelwahab Gomaa100% (1)