Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Torsion Problems
Torsion Problems
Uploaded by
Sudeep magarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Torsion Problems
Torsion Problems
Uploaded by
Sudeep magarCopyright:
Available Formats
ER GOPINATH CHAPAGAIN MOB NO : 9857072792
WHATTSAPP : 9867792792
CHAPTER 7
TORSION PROBLEMS
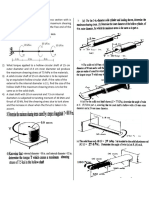
1) The solid circular section of a shaft has 60 mm diameter. When a twisting moment of 5
KN-m is applied on the section. Find the shear stress induced at points a, b and c which is
at a distance of 30mm, 15mm and 0m from the center of circle along the radius. Also draw
a sketch showing distribution of shear stress. Discuss about the results.
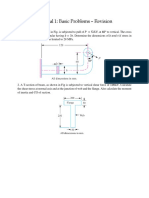
2) A 1.5 mm long, solid shaft with circular section of 50mm diameter is fixed at one end
and is subjected to a twisting moment of 2 KN-m. Determine maximum shear stress and
angle of twist induced in the shaft. Take modulus of rigidity of shaft material as 80 Gpa.
3) A 1 m long wire is hung in vertical position and a disc is attached at the bottom end.
Diameter of wire is 2 mm. Material of wire has yield stress in shear of 150 Mpa. Determine
the angle through which the disc can be rotated so that the wire does not yield. Take G =
80GPa.
4) A 2 meters long hollow cylinder shaft has 80 mm outer diameter and 10 mm wall
thickness. When the torsional load on the shaft is 6 KN-m, determine 1) maximum shear
stress induced and 2) angle of twist. Also draw the distribution of shear stress in the wall
of the shaft. Take G as 80 Gpa.
5) A brass solid circular shaft of diameter 40 mm is 1.0 m long. Determine 1) torsional
strength and 2) torsional rigidity. Take the modulus of rigidity of shaft material as 40 Gpa.
6) A solid shaft rotating at 500 rpm transmits 30 KW. Maximum torque is 20% more than
the mean torque. Material of shaft has the allowable shear stress 65 Mpa and modulus of
rigidity 81 Gpa. Angle of twist in the shaft should not exceed 1° in 1 meter length.
Determine the diameter of shaft.
7) A hollow shaft is subjected to a torque 8 KN-m. The angle of twist in the shaft is to be
limited to 1.7° in a length equal to twenty times the outer diameter. Taking the inner
diameter to outer diameter ratio as 0.7, determine, i) inner diameter and outer diameter and
il) maximum shear stress induced. Take the modulus of rigidity for the shaft material as 80
Gpa.
8) A hollow shaft with inner diameter to outer diameter ratio of 0.8 is to transmit a torque
of 2500 N-m. Taking the allowable shear stress for the shaft material as 45 Mpa and the
limiting angle of twist in 2 meters length of shaft as 1.5°, determine the inner and outer
diameters of the shaft. Take G = 81 KN/mm2
9) A 60 mm diameter shaft is subjected to the torques at various sections as shown in fig
Determine (i) Total angle of twist and (ii) Maximum shear stress induced in each portion.
Take G = 0.8 x 105 Mpa.
ER GOPINATH CHAPAGAIN MOB NO : 9857072792
WHATTSAPP : 9867702792
10) Compare the mass of solid shaft with that of hollow shall of same length, when they
are made of same material and are to transmit same power at same speed. The outer
diameter of hollow shaft is 1.4 times its inner diameter. Maximum shear stresses induced
in both cases are equal.
11) A solid shaft is to transmit 192 KW at 450 rpm. Taking the allowable shear stress for
the shaft material as 70 Mpa, find the diameter of the solid shaft. What percentage of saving
in weight would be obtained, if this shaft were to be replaced by a hollow shaft, whose
internal diameter is 0.8 times its external diameter. The length, material, power to be
transmitted and speed are equal in both cases. Torsional strength of both solid and hollow
shafts should be equal.
12) A solid shaft of 60 mm diameter is to be replaced by a hollow shaft of same length. The
outer diameter of hollow shaft is same as that of solid shaft. If the angle of twist per unit
torsional moment is same in both cases, determine the inner diameter of the hollow shaft.
Take the modulus of rigidity of the hollow shaft to be three times that of solid shaft.
13) A solid shaft of 50 mm diameter is to be replaced by a hollow shaft. Determine the
diameters of hollow shaft, so that the same torsional strength is maintained. Inner diameter
of the hollow shaft is 0.7 times its outer diameter. Determine the torque carrying capacities
of the both solid and hollow shafts, when (i) both shafts are made of steel and have equal
maximum shear stresses induced (il) solid shaft is made of steel and hollow shaft is made
of aluminum. Take the allowable shear stresses for steel and aluminum as ζs= 100 Mpa and
ζAl, = 60 Mpa.
14) A solid shaft has 50 mm diameter. Determine the inner and outer diameters of a hollow
shaft such that it's area of cross section is same as that of solid shaft. The inner diameter of
hollow shaft is 0.8 times its outer diameter. Compare the torsional strengths and torsional
stiffnesses of solid shaft and hollow shaft. Length and material are same in both cases
15) A hollow shaft has inner diameter to outer diameter ratio of 3: 5. Compare the torque
carrying capacity of hollow shaft with that of solid shaft. Both shafts have same material,
equal masses and are subjected to equal maximum shear stresses.
16) A 60 mm diameter solid brass shaft is to be replaced by a hollow steel shaft. The outer
diameter of hollow shaft is equal to the diameter of solid shaft. Considering length, angle
of twist and torque transmitted to be equal in both cases, determine the inner diameter of
the hollow shaft. Modulus of rigidity of steel is twice that of brass.
You might also like
- Risky Drinking and Alcohol Use Disorder - Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateDocument12 pagesRisky Drinking and Alcohol Use Disorder - Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, Course, Assessment, and Diagnosis - UpToDateqerat88No ratings yet
- Me8593 Iq R17Document4 pagesMe8593 Iq R17Vaideesh LJNo ratings yet
- QP Pe Series 2Document2 pagesQP Pe Series 2AADARS M SNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BIGDocument3 pagesUnit 3 BIGVasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- SM Mid3 Model QuestionsDocument3 pagesSM Mid3 Model QuestionsSaitama BackupNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Unit 3 Question Bank: Jansons Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Unit 3 Question Bank: Jansons Institute of TechnologyVasanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements 1,2Document35 pagesMachine Elements 1,2Joseph OpinionNo ratings yet
- G For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of TheDocument6 pagesG For The Material Is 82 GN/m2. If The I-Section Is Replaced by A T-Section Made of Theክበር ተመስጌንNo ratings yet
- MODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDocument3 pagesMODEL QUESTION PAPER Mechanical VibrationsDarani PriyaNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument4 pagesDocumentjayakumarNo ratings yet
- Sheet2 MachineDesign1Document2 pagesSheet2 MachineDesign1محمد معوضNo ratings yet
- Sub. TMMD Tutorial 1: TheoriesDocument2 pagesSub. TMMD Tutorial 1: TheoriesPurvesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Spring WorksheetDocument4 pagesSpring WorksheetYonas BelaynehNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 1Melvin Shady PereiraNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3Document2 pagesWorksheet 3Yonas BelaynehNo ratings yet
- 3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)Document9 pages3-1 DMM1 (Nov 2009 Regular)micmechNo ratings yet
- DME Assignment 1Document2 pagesDME Assignment 1sumikannuNo ratings yet
- Cross Section: Ø 120 MM, T 6 MM Material: Steel G 81 000 N/MMDocument3 pagesCross Section: Ø 120 MM, T 6 MM Material: Steel G 81 000 N/MMEyoatem TeferiNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesAssignment QuestionskhanNo ratings yet
- Roll Number: Tiet, Engineering Auxiliary Exam, 21 February 2018 Course: Machine Design (UME 408/504/508) Max Marks: 100 Time: 03 HoursDocument2 pagesRoll Number: Tiet, Engineering Auxiliary Exam, 21 February 2018 Course: Machine Design (UME 408/504/508) Max Marks: 100 Time: 03 Hoursvasu jamwalNo ratings yet
- Me2254 SM QBDocument15 pagesMe2254 SM QBhodvmkvecautoNo ratings yet
- PMD ModelDocument8 pagesPMD ModelDamodara SatyaDeva MadhukarNo ratings yet
- Me1302 DmeDocument4 pagesMe1302 DmesumikannuNo ratings yet
- MD Tut PDFDocument6 pagesMD Tut PDFNelsan PatelNo ratings yet
- Me 331Document5 pagesMe 331arumugam_rNo ratings yet
- 12ME5DCDM2Document3 pages12ME5DCDM2Abhyudaya SinghNo ratings yet
- ME-323 Threaded-Members 42423Document48 pagesME-323 Threaded-Members 42423Jam Maica TuboNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Numericals DMEDocument3 pagesQuestion Bank Numericals DMEVanessa SmithNo ratings yet
- Internal Test 1Document3 pagesInternal Test 1Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Dme - Ii (17me64) : Assignement 01Document3 pagesDme - Ii (17me64) : Assignement 01NAVEEN H ENo ratings yet
- gupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9Document3 pagesgupta PG - No:176) Exercise 9mahendra babu mekalaNo ratings yet
- SM Coaching QuestionDocument3 pagesSM Coaching QuestionSelvaraj GNo ratings yet
- Torsion TutorialDocument2 pagesTorsion Tutorialankurshah1986No ratings yet
- SM Model Exam QuestionDocument5 pagesSM Model Exam QuestionAravind PhoenixNo ratings yet
- Dme Question BankDocument4 pagesDme Question BankRavi Patil100% (1)
- MD1 M3 Compiled Ot 1Document67 pagesMD1 M3 Compiled Ot 1Jiuan AndradaNo ratings yet
- 15ME641Document3 pages15ME641Anmol NairNo ratings yet
- COMPRE EXAM Machine Design No ChoicesDocument6 pagesCOMPRE EXAM Machine Design No ChoicesJunalin FabroNo ratings yet
- DMM-1 MID-2 Assignment QuestionsDocument3 pagesDMM-1 MID-2 Assignment Questionsuppada AnilNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- DMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDocument11 pagesDMM - I Question Bank For StudentsDushyanthkumar DasariNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 04Document1 pageAssignment 04Jim BennyNo ratings yet
- DME 1 Question BankDocument5 pagesDME 1 Question BankRahul YedduNo ratings yet
- STL203SDocument6 pagesSTL203SClaudioNo ratings yet
- Dme Assignment 2Document21 pagesDme Assignment 2helloapple1211No ratings yet
- Dme Model QuestionDocument2 pagesDme Model QuestiondharaniventhanNo ratings yet
- DME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)Document7 pagesDME Chapter Three: or (Summer 15)honeyfunnyNo ratings yet
- DMM Question BankDocument2 pagesDMM Question Bankzubair ahmedNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 2Document2 pagesExercise No. 2mariamaber007No ratings yet
- Test On Strength of MaterialDocument9 pagesTest On Strength of MaterialJonathan Green100% (1)
- Assignment No 1 MD-1..Document3 pagesAssignment No 1 MD-1..Yadnyesh TaNo ratings yet
- Dme Lab Sheets Ii Iii IvDocument4 pagesDme Lab Sheets Ii Iii IvA58Vikas UbovejaNo ratings yet
- Automobile Design Rev2015Document6 pagesAutomobile Design Rev2015Rithik Raj RanjuNo ratings yet
- Dme Model 2Document6 pagesDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiNo ratings yet
- 5 6231228562666425264Document2 pages5 6231228562666425264guptabkt18No ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2 Mechanics of Solids (NME-302)Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2 Mechanics of Solids (NME-302)nitin_johriNo ratings yet
- Is, S. Exam-Pa: HA", .201 FSI-P-MCHEDocument9 pagesIs, S. Exam-Pa: HA", .201 FSI-P-MCHESachin KumarNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Assignment 1 of Strength of MaterailDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 of Strength of MaterailSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Semester 2019 FallDocument3 pagesSemester 2019 FallSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Describing An Object1Document5 pagesDescribing An Object1Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- MemorandumDocument1 pageMemorandumSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Semester 2017 SpringDocument5 pagesSemester 2017 SpringSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- THERMODYNAMIC CYCLE Chapter 6Document58 pagesTHERMODYNAMIC CYCLE Chapter 6Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- A Project Proposal To Establish A Hostel in LecDocument8 pagesA Project Proposal To Establish A Hostel in LecSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- ENTROPY1Document43 pagesENTROPY1Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Job Application & Resume (Civil) 1Document4 pagesJob Application & Resume (Civil) 1Sudeep magar100% (1)
- MEETING1Document2 pagesMEETING1Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Sum of Natural Number Using Recursive FunationDocument1 pageSum of Natural Number Using Recursive FunationSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Sum of Digit by Recursive FunctionDocument1 pageSum of Digit by Recursive FunctionSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- MathI (1sty) Dec05Document1 pageMathI (1sty) Dec05Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Raise Power of X To N by Recursive FunctionDocument1 pageRaise Power of X To N by Recursive FunctionSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- To Print Tha Pattern PROGRAMMINGDocument1 pageTo Print Tha Pattern PROGRAMMINGSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Wave Motion (Questions)Document1 pageChapter 2 - Wave Motion (Questions)Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Function Call by ValueDocument1 pageFunction Call by ValueSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Excursion and Study of Various Geological Field FeaturesDocument38 pagesExcursion and Study of Various Geological Field FeaturesSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Geological TourDocument41 pagesGeological TourSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Numerical+solution)Document60 pagesChapter 2 (Numerical+solution)Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Numerical With Old Question 2Document7 pagesChapter 2 - Numerical With Old Question 2Sudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Numerical) GarimaDocument43 pagesChapter 2 (Numerical) GarimaSudeep magarNo ratings yet
- Annals Change FinalDocument92 pagesAnnals Change FinalandriNo ratings yet
- ACOMD2H16Document3 pagesACOMD2H16boss100% (1)
- Jeremy Bentham: Which Promotes The Greatest Good For The Greatest Number of People". Unlike Egoism in WhichDocument3 pagesJeremy Bentham: Which Promotes The Greatest Good For The Greatest Number of People". Unlike Egoism in WhichAnna Michelle MagbanuaNo ratings yet
- Hindus Acknowledge The Law of KarmaDocument3 pagesHindus Acknowledge The Law of KarmaAnil Kumar BNo ratings yet
- Dom Lab ManuelDocument56 pagesDom Lab ManuelMartin De Boras PragashNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Excel WorksheetDocument4 pagesNew Microsoft Excel WorksheetRaheel Neo AhmadNo ratings yet
- Kuliah UmumDocument6 pagesKuliah UmumYosua ardianNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Q1 W3Document20 pagesScience 8 Q1 W3Renz LaraNo ratings yet
- ActivatrDocument10 pagesActivatromr7No ratings yet
- Đáp Án C A The Growth of Bike-Sharing Schemes Around The WorldDocument4 pagesĐáp Án C A The Growth of Bike-Sharing Schemes Around The WorldThu An TranNo ratings yet
- Department of Mahtematics and Statistics University of Jaffna LEVEL 1S (2018/2019) Statistics For Computing I - CSC105S3 Tutorial - 02Document2 pagesDepartment of Mahtematics and Statistics University of Jaffna LEVEL 1S (2018/2019) Statistics For Computing I - CSC105S3 Tutorial - 02Michael JhonshonNo ratings yet
- Pharmacological Screening Methods-QbDocument12 pagesPharmacological Screening Methods-Qbprateeksha100% (1)
- ZTE LTE Throughput KPIsDocument101 pagesZTE LTE Throughput KPIsMehmet Can KahramanNo ratings yet
- Soap Companies Do Battle: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements inDocument7 pagesSoap Companies Do Battle: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements inJohn Carlo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- GCP CarbonBudget 2023 Slides v1.0-2-1Document94 pagesGCP CarbonBudget 2023 Slides v1.0-2-1YULIANTONo ratings yet
- Asphalt MSDSDocument8 pagesAsphalt MSDSJunard M. Lu HapNo ratings yet
- Higher Secondary Level All Posts in Detail Selection Post XI RBEDocument7 pagesHigher Secondary Level All Posts in Detail Selection Post XI RBESaurabh SidanaNo ratings yet
- L2 A2PLUS U1 Basics Grammar VocabularyDocument2 pagesL2 A2PLUS U1 Basics Grammar VocabularyÄÐåm Dris Said100% (1)
- Dror Paley - Principles of Deformity Correction (2002, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg) - 1-100Document100 pagesDror Paley - Principles of Deformity Correction (2002, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg) - 1-100Wilker AraújoNo ratings yet
- The Role of Sociology in Economic and Social DevelopmentDocument4 pagesThe Role of Sociology in Economic and Social DevelopmentAcademic JournalNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document21 pagesCH 08Juan PepeNo ratings yet
- Writing Your ManifestoDocument3 pagesWriting Your ManifestoluamsmarinsNo ratings yet
- Internal Tearing Resistance of Paper: Standard Test Method ForDocument7 pagesInternal Tearing Resistance of Paper: Standard Test Method ForAngel ValladaresNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Regional Economics HooverDocument164 pagesAn Introduction To Regional Economics Hooversfdkhkfjsfnsk njfsnksfnNo ratings yet
- Metroval EnglishDocument6 pagesMetroval EnglishJORGE LUIZ GALVAO BUENO FILHONo ratings yet
- Classification by Depth Distribution of Phytoplankton and ZooplanktonDocument31 pagesClassification by Depth Distribution of Phytoplankton and ZooplanktonKeanu Denzel BolitoNo ratings yet
- NEEDLE ROLLER BEARINGS SKF CatalogDocument84 pagesNEEDLE ROLLER BEARINGS SKF CatalogashtariNo ratings yet
- En DVC 2018 35Document18 pagesEn DVC 2018 35Lina María CañónNo ratings yet
- PPM Brochure AcrulogDocument2 pagesPPM Brochure AcrulogadrianchoingNo ratings yet