Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power Factor Testing
Power Factor Testing
Uploaded by
Mohamed AhmiedCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Insulation Coordination FundamentalsDocument62 pagesInsulation Coordination FundamentalsSiddarthan AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Fixed Stars in AstrologyDocument319 pagesThe Use of Fixed Stars in AstrologyANTHONY WRITER90% (30)
- Theoretical DistributionsDocument7 pagesTheoretical Distributionskritishah550% (2)
- 2461452d Usen Insulation Brochure WDocument12 pages2461452d Usen Insulation Brochure WAnonymous u0wETydF100% (1)
- ACTS125K PLUS Application Notes5Document4 pagesACTS125K PLUS Application Notes5mohsinNo ratings yet
- Safety First - The Crucial Tests of IEC 61439 For Electrical Distribution Boards - LinkedInDocument4 pagesSafety First - The Crucial Tests of IEC 61439 For Electrical Distribution Boards - LinkedInTikanand DewooNo ratings yet
- Log Book W2 - B081910075Document7 pagesLog Book W2 - B081910075Hidan HaidaeNo ratings yet
- Delta4000 PDFDocument7 pagesDelta4000 PDFmk008No ratings yet
- Resistencia AislamientoDocument8 pagesResistencia AislamientoJack DuffNo ratings yet
- In Service Inspection and Testing of Electrical Equipment The Insulation TestDocument3 pagesIn Service Inspection and Testing of Electrical Equipment The Insulation TestBalasoobramaniam CarooppunnenNo ratings yet
- Basic Insulation TestingDocument2 pagesBasic Insulation TestingGabriel Zenarosa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- قيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلDocument7 pagesقيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلMohamedHussein MohamedHusseinNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Voltage - Staying Safe Using High Voltage Test Equipment PDFDocument3 pagesDangerous Voltage - Staying Safe Using High Voltage Test Equipment PDFIsrael JosueNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Insulation-Test Trends - MeggerDocument7 pagesInterpreting Insulation-Test Trends - MeggerJustine Joshua Dagondon100% (1)
- Ichveps2017-Condition Monitoring Metal Clad Switchgear - KHDocument24 pagesIchveps2017-Condition Monitoring Metal Clad Switchgear - KHbmwr1100s_055542No ratings yet
- Insulator Testing of AC Generator WindingDocument4 pagesInsulator Testing of AC Generator WindingAnurag Pritam SahuNo ratings yet
- Breaker Timing - ZensolDocument20 pagesBreaker Timing - ZensolIsmail Azad100% (1)
- Voltage Dependencies of Power Factor in Rotating Machinery InsulationDocument5 pagesVoltage Dependencies of Power Factor in Rotating Machinery InsulationAnonymous kuSnz0kl1No ratings yet
- Surge Arrestor TestingDocument31 pagesSurge Arrestor TestingAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Ee 04 946Document21 pagesEe 04 946Carlos FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Component Tests: Insulation Test SystemDocument12 pagesComponent Tests: Insulation Test System1382aceNo ratings yet
- Off-Line Insulation Testing and Diagnosis of HV MachinesDocument4 pagesOff-Line Insulation Testing and Diagnosis of HV MachinesnaveenNo ratings yet
- Functions and Features of Advanced Hipot Testers: June 18, 2018 by Lee TeschlerDocument4 pagesFunctions and Features of Advanced Hipot Testers: June 18, 2018 by Lee TeschlerVishal ShahNo ratings yet
- Online Offline: Partial Discharge Testing For Cable AssessmentDocument6 pagesOnline Offline: Partial Discharge Testing For Cable AssessmentcubarturNo ratings yet
- Power Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewDocument22 pagesPower Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- Why Test Surge TestingDocument1 pageWhy Test Surge TestingShûbhâm PatilNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Factor Testing Condition BetterDocument4 pagesAssessment: Factor Testing Condition Betterkong shiaw huiNo ratings yet
- Biddl 670065122038Document3 pagesBiddl 670065122038Hamayoun MurtazaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Aging Mechanisms and Diagnostics For Extruded Power CablesDocument6 pagesAn Overview of Aging Mechanisms and Diagnostics For Extruded Power CableschethanNo ratings yet
- 70 120 160 DCTS DS en V15Document4 pages70 120 160 DCTS DS en V15tankopetonNo ratings yet
- Eng 01 ADocument2 pagesEng 01 ARAVINDERANNo ratings yet
- Sample Testing-Equipment-as-per-UL-746Document10 pagesSample Testing-Equipment-as-per-UL-746Aritra DasguptaNo ratings yet
- UT501A User Manual PDFDocument2 pagesUT501A User Manual PDFAlban Abazi100% (1)
- Unit5 HveDocument29 pagesUnit5 Hveview eeehodNo ratings yet
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation Testingnutchai2538100% (1)
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingHARISH ROHANNo ratings yet
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingMan Minh SangNo ratings yet
- Tieu Chuan Viet Nam 1234Document24 pagesTieu Chuan Viet Nam 1234Man Minh SangNo ratings yet
- Secondary Substation Transformers Test Application Data Standard TestsDocument2 pagesSecondary Substation Transformers Test Application Data Standard TestsMarcelo Rueda MartínezNo ratings yet
- We Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsDocument8 pagesWe Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsShamil NiftaliyevNo ratings yet
- Final Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsDocument6 pagesFinal Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsJoseph ChamiNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFDocument7 pagesAstm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFJose Maria Castillo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Article Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUDocument6 pagesArticle Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUarnenylundNo ratings yet
- High Volume Armature Testing: Lance Straughn Slaughter CompanyDocument10 pagesHigh Volume Armature Testing: Lance Straughn Slaughter Companyronald allan liviocoNo ratings yet
- Insulation Coordination of HV Lines Resumo Alargado - Linhas Aereas - Final PDFDocument6 pagesInsulation Coordination of HV Lines Resumo Alargado - Linhas Aereas - Final PDFEdward Baleke SsekulimaNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFDocument6 pages10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFbelayneh ayichewNo ratings yet
- Test Equipment 101 - The Basics of Electrical TestingDocument31 pagesTest Equipment 101 - The Basics of Electrical TestingSas BetroNo ratings yet
- Individual Temperature Compensation 42 47Document6 pagesIndividual Temperature Compensation 42 47ivicaNo ratings yet
- Medium-Voltage Circuit Breaker Maintenance: Special FeatureDocument2 pagesMedium-Voltage Circuit Breaker Maintenance: Special FeatureSing Yew LamNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Voltage Transformer TestingDocument7 pagesCapacitive Voltage Transformer TestingSaeedAhmedKhan100% (1)
- HV Reinforced Insulation IntroDocument10 pagesHV Reinforced Insulation IntroMark BatulanNo ratings yet
- Insulation Tests For Assessment Rotating Electrical MachineryDocument10 pagesInsulation Tests For Assessment Rotating Electrical Machineryidontlikeebooks100% (1)
- Baker 2012Document8 pagesBaker 2012JONATHAN MORALESNo ratings yet
- ART-Paper WP en V01 PDFDocument13 pagesART-Paper WP en V01 PDFAnonymous V6y1QL6hn100% (1)
- Hi Pot 160 KVDocument4 pagesHi Pot 160 KVRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Svcet: Μsec (Called 1/50 Μsec Wave)Document4 pagesSvcet: Μsec (Called 1/50 Μsec Wave)Indongo EliaserNo ratings yet
- An Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationDocument9 pagesAn Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationMonthly ImogenNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Insulation TestingDocument6 pagesThe Basics of Insulation TestingNoel RazaNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gawedar Okstate 0664D 14871.pdf JsessionidDocument87 pagesGawedar Okstate 0664D 14871.pdf JsessionidMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Expl SW Chapter 05 STP Part IDocument65 pagesExpl SW Chapter 05 STP Part IMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Vol2 ConstructionDocument14 pagesVol2 ConstructionMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- B1CreationofIntegratedofIndustrialSecuritywiththeuseofModern - KMMS Aug 04 2015 0023Document7 pagesB1CreationofIntegratedofIndustrialSecuritywiththeuseofModern - KMMS Aug 04 2015 0023Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Paper 20Document4 pagesPaper 20Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 42111-42144 - 04 Heat Shrinkable Termination Kit For XLPE PVC Insulated CU Cable 0.4kv - 002Document15 pages42111-42144 - 04 Heat Shrinkable Termination Kit For XLPE PVC Insulated CU Cable 0.4kv - 002Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- IS IEC 61730 1 SolarDocument22 pagesIS IEC 61730 1 SolarMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Insulator Pin For Line Post Type InsulatorDocument10 pagesInsulator Pin For Line Post Type InsulatorMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 40211-40412 - 663011 Pre-Molded Straight Joint Kit For XLPE Insulated Cable - 002Document17 pages40211-40412 - 663011 Pre-Molded Straight Joint Kit For XLPE Insulated Cable - 002Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 11.5KW Solar System With ACDocument2 pages11.5KW Solar System With ACMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Refinerry Techincal ProjectDocument11 pagesRefinerry Techincal ProjectMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Ratings Guide: Seventeenth EditionDocument56 pagesElectric Power Ratings Guide: Seventeenth EditionMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 2 ELVAC RTU in Cable Network I Ring Main Unit I Secondary SubstationDocument8 pages2 ELVAC RTU in Cable Network I Ring Main Unit I Secondary SubstationMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Energies 15 06418Document20 pagesEnergies 15 06418Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Iec 60027letter Symbols To Be Used in Electrical TechnologyDocument16 pagesIec 60027letter Symbols To Be Used in Electrical TechnologyMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 1649753618cable Magnetic Field Evalution Cal Fact Sheet Web 1 pdf1649753618Document2 pages1649753618cable Magnetic Field Evalution Cal Fact Sheet Web 1 pdf1649753618Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 42221-42422 - 66kv-30kv-11kv Heat Shrinkable Outdoor Termination Kit For XLPE Insulated CableDocument17 pages42221-42422 - 66kv-30kv-11kv Heat Shrinkable Outdoor Termination Kit For XLPE Insulated CableMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Promat Energy - Solar Brochure - EnglishDocument2 pagesPromat Energy - Solar Brochure - EnglishMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Minimum Equipment Efficiency Standards: Port of StocktonDocument6 pagesAppendix C Minimum Equipment Efficiency Standards: Port of StocktonMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 200KW Solar System-Technician ParametersDocument10 pages200KW Solar System-Technician ParametersMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document49 pagesChap 2Malak BattahNo ratings yet
- Anastazya Forde CV..Document1 pageAnastazya Forde CV..anastazya fordeNo ratings yet
- 1735 KVA (1388 KW) Mitsubishi PDFDocument1 page1735 KVA (1388 KW) Mitsubishi PDFMd. Harunor RashidNo ratings yet
- Engaging Generation ZDocument9 pagesEngaging Generation Zghoster33No ratings yet
- Applied Ergonomics: Nora Balfe, Sarah Sharples, John R. WilsonDocument13 pagesApplied Ergonomics: Nora Balfe, Sarah Sharples, John R. WilsonDian Palupi RestuputriNo ratings yet
- Iv STD ScienceDocument2 pagesIv STD SciencePradeepNo ratings yet
- Kobayashi ManualDocument27 pagesKobayashi ManualAnonymous utXYfMAXNo ratings yet
- 8th LA Midterms Study GuideDocument12 pages8th LA Midterms Study GuideIts AbbiNo ratings yet
- DQ 1 Week 8Document6 pagesDQ 1 Week 8LeeginaNo ratings yet
- Android-Based Classroom Monitoring System For Teacher Using QR Code TechnologyDocument12 pagesAndroid-Based Classroom Monitoring System For Teacher Using QR Code TechnologyAkmad Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- CFD Modeling of Spontaneous Heating in A Large-Scale Coal ChamberDocument8 pagesCFD Modeling of Spontaneous Heating in A Large-Scale Coal ChamberdenichezNo ratings yet
- Mole RatioDocument2 pagesMole Ratioariansofia1031No ratings yet
- Saarthi - Excel AssignmentDocument17 pagesSaarthi - Excel AssignmentBHUMIT KATARIANo ratings yet
- M-2. Theories of MotivationDocument15 pagesM-2. Theories of MotivationumerNo ratings yet
- First CryDocument4 pagesFirst CrysamikshaNo ratings yet
- Mayr Origins of Feedback ControlDocument11 pagesMayr Origins of Feedback ControlBenjamín Peña Pérez100% (1)
- Correspondence Between My Friend, The Late Gordon T. "Gordy" Pratt, and Chicago Tribune Reporter Lisa Black and Editor Peter Hernon (Sept/Oct 2009)Document8 pagesCorrespondence Between My Friend, The Late Gordon T. "Gordy" Pratt, and Chicago Tribune Reporter Lisa Black and Editor Peter Hernon (Sept/Oct 2009)Peter M. HeimlichNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Pressure TIME: 15 Min: NAME: CLASSDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 - Pressure TIME: 15 Min: NAME: CLASSNur'Afifah Serip MohamadNo ratings yet
- TVL 12 Carpentry NC II w4 6 Types of Wood JointsDocument19 pagesTVL 12 Carpentry NC II w4 6 Types of Wood JointsBenjamin Paner100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Musol SolventDocument15 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Musol SolventHưng Lê TrungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Builders & Construction Co. (Phil.), Inc.: Quality Control ProgramDocument22 pagesDynamic Builders & Construction Co. (Phil.), Inc.: Quality Control ProgramMae Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hef 4516 BTDocument10 pagesHef 4516 BTAdam SchwemleinNo ratings yet
- Ngec5 ModuleDocument133 pagesNgec5 ModuleTheodore GrandeNo ratings yet
- Prachi Uniqueness of Human BeingDocument19 pagesPrachi Uniqueness of Human BeingasifanisNo ratings yet
- MID 039 - CID 0167 - FMI 12: TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesMID 039 - CID 0167 - FMI 12: TroubleshootingNerminTurkenceNo ratings yet
- About Pratham Education Foundation About Pratham Education FoundationDocument3 pagesAbout Pratham Education Foundation About Pratham Education FoundationsoumyalambaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.2 Root and Mitosis in An Onion CellDocument3 pagesActivity 4.2 Root and Mitosis in An Onion CellPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Fake News Detection Using NLPDocument9 pagesFake News Detection Using NLPIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
Power Factor Testing
Power Factor Testing
Uploaded by
Mohamed AhmiedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Factor Testing
Power Factor Testing
Uploaded by
Mohamed AhmiedCopyright:
Available Formats
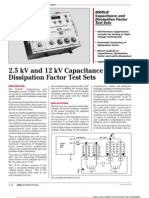
POWER FACTOR TESTING
Educational Series: Why Test?
Why Perform Power Factor Testing? What are the Test Procedures?
Most failures of electrical equipment are Once the equipment is taken out of
the result of a breakdown in the insulation service, an AC voltage at or below the
system. Power factor testing is an normal rating is placed on the equipment
effective way to detect defective electrical conductors. At the same time, the
equipment insulation. Power factor is the dielectric losses to ground are measured.
ratio of the capacitive or ‘charging’ current After correcting the field measurements to
(measured in volt-amperes) to resistive or standard conditions, the test results are What are the Advantages?
‘leakage’ current (measured in watts). It is then compared to guides which list proper
a means of measuring insulation integrity values for specific types of equipment and Power factor tests can detect the presence
since the smaller the power factor, the insulations. These guides are contained in of “poor” insulation even if there is a layer
better the insulator. an extensive data library compiled by of “good” insulation in series. However, DC
testing thousands of similar types of tests usually show a high insulation
Insulation may be deteriorating, however, equipment in the field and at the factory. resistance under this condition.
the equipment may not fail for some time.
Although this condition represents a If an abnormal condition is indicated, a At a given voltage, the charging current
serious hazard, if deteriorated insulation is number of special tests may be used to and the dielectric loss increase as the
detected before failure, it can often be localize the problem. These include hot quantity of insulation increases. However,
reconditioned rather than being replaced. guard tests, hot collar tests, ungrounded the power factor ratio remains the same no
This allows corrective action to be taken specimen tests, cross check tests, oil tests, matter how much insulation is present.
during a planned outage before extensive and dielectric loss tests on wood This makes it possible to establish
members. simplified test values for particular types
equipment damage results from insulation
of insulation.
failure. What Types of Equipment are
Tested? Power factor testing provides a measure
Power factor testing also makes it
and evaluation of the overall condition of
possible to detect equipment insulation
The most frequent applications of power medium and high voltage AC apparatus
problems without making an internal
factor testing include medium and high insulation under simulated normal-
visual inspection. The result is a
voltage transformers and circuit breakers. frequency operating conditions. This is
significant decrease in maintenance cost
Other equipment such as bushings, independent of the duration of the test. DC
and downtime. Power factor testing is one
reclosers, switches, cables, capacitors, tests not only require more time, they also
of the best testing techniques for lightning arrestors, liquid insulation, do not simulate normal insulation operating
predictive and preventive maintenance. potheads, rotating machinery, and conditions. Furthermore, the results are
voltage regulators may also be power affected by the duration of the test.
factor tested.
Power factor tests provide a benchmark
Power factor testing is used as a factory which may be compared over periods of
test and in the field for acceptance testing, time in an organized manner and are used
preventive maintenance, and emergency to identify any trends on apparatus
diagnostic testing. insulation. It provides a more complete
picture of overall insulation conditions.
Used in conjunction with capacitance and
AC resistance, it provides comprehensive
data on the condition of the insulation.
VertivCo.com | Vertiv - Electrical Reliability Services, 1-877-468-6384
© 2017 Vertiv Co. All rights reserved. Vertiv and the Vertiv logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Vertiv Co. All other names and logos referred to are trade names, trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. While every precaution has been
taken to ensure accuracy and completeness herein, Vertiv Co. assumes no responsibility, and disclaims all liability, for damages resulting from use of this information or for any errors or omissions. Specifications are subject to change without notice.
YT-02-08 (R6/17) 1
You might also like
- Insulation Coordination FundamentalsDocument62 pagesInsulation Coordination FundamentalsSiddarthan AnnamalaiNo ratings yet
- The Use of Fixed Stars in AstrologyDocument319 pagesThe Use of Fixed Stars in AstrologyANTHONY WRITER90% (30)
- Theoretical DistributionsDocument7 pagesTheoretical Distributionskritishah550% (2)
- 2461452d Usen Insulation Brochure WDocument12 pages2461452d Usen Insulation Brochure WAnonymous u0wETydF100% (1)
- ACTS125K PLUS Application Notes5Document4 pagesACTS125K PLUS Application Notes5mohsinNo ratings yet
- Safety First - The Crucial Tests of IEC 61439 For Electrical Distribution Boards - LinkedInDocument4 pagesSafety First - The Crucial Tests of IEC 61439 For Electrical Distribution Boards - LinkedInTikanand DewooNo ratings yet
- Log Book W2 - B081910075Document7 pagesLog Book W2 - B081910075Hidan HaidaeNo ratings yet
- Delta4000 PDFDocument7 pagesDelta4000 PDFmk008No ratings yet
- Resistencia AislamientoDocument8 pagesResistencia AislamientoJack DuffNo ratings yet
- In Service Inspection and Testing of Electrical Equipment The Insulation TestDocument3 pagesIn Service Inspection and Testing of Electrical Equipment The Insulation TestBalasoobramaniam CarooppunnenNo ratings yet
- Basic Insulation TestingDocument2 pagesBasic Insulation TestingGabriel Zenarosa LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- قيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلDocument7 pagesقيم التوترات المستمرة لقياس مقاومة العزلMohamedHussein MohamedHusseinNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Voltage - Staying Safe Using High Voltage Test Equipment PDFDocument3 pagesDangerous Voltage - Staying Safe Using High Voltage Test Equipment PDFIsrael JosueNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Insulation-Test Trends - MeggerDocument7 pagesInterpreting Insulation-Test Trends - MeggerJustine Joshua Dagondon100% (1)
- Ichveps2017-Condition Monitoring Metal Clad Switchgear - KHDocument24 pagesIchveps2017-Condition Monitoring Metal Clad Switchgear - KHbmwr1100s_055542No ratings yet
- Insulator Testing of AC Generator WindingDocument4 pagesInsulator Testing of AC Generator WindingAnurag Pritam SahuNo ratings yet
- Breaker Timing - ZensolDocument20 pagesBreaker Timing - ZensolIsmail Azad100% (1)
- Voltage Dependencies of Power Factor in Rotating Machinery InsulationDocument5 pagesVoltage Dependencies of Power Factor in Rotating Machinery InsulationAnonymous kuSnz0kl1No ratings yet
- Surge Arrestor TestingDocument31 pagesSurge Arrestor TestingAdetunji TaiwoNo ratings yet
- Ee 04 946Document21 pagesEe 04 946Carlos FigueiredoNo ratings yet
- Component Tests: Insulation Test SystemDocument12 pagesComponent Tests: Insulation Test System1382aceNo ratings yet
- Off-Line Insulation Testing and Diagnosis of HV MachinesDocument4 pagesOff-Line Insulation Testing and Diagnosis of HV MachinesnaveenNo ratings yet
- Functions and Features of Advanced Hipot Testers: June 18, 2018 by Lee TeschlerDocument4 pagesFunctions and Features of Advanced Hipot Testers: June 18, 2018 by Lee TeschlerVishal ShahNo ratings yet
- Online Offline: Partial Discharge Testing For Cable AssessmentDocument6 pagesOnline Offline: Partial Discharge Testing For Cable AssessmentcubarturNo ratings yet
- Power Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewDocument22 pagesPower Cable Testing and Diagnostics OverviewanuragpugaliaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- High Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusDocument29 pagesHigh Voltage Testing of Electrical ApparatusNRCM EEENo ratings yet
- Why Test Surge TestingDocument1 pageWhy Test Surge TestingShûbhâm PatilNo ratings yet
- Assessment: Factor Testing Condition BetterDocument4 pagesAssessment: Factor Testing Condition Betterkong shiaw huiNo ratings yet
- Biddl 670065122038Document3 pagesBiddl 670065122038Hamayoun MurtazaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Aging Mechanisms and Diagnostics For Extruded Power CablesDocument6 pagesAn Overview of Aging Mechanisms and Diagnostics For Extruded Power CableschethanNo ratings yet
- 70 120 160 DCTS DS en V15Document4 pages70 120 160 DCTS DS en V15tankopetonNo ratings yet
- Eng 01 ADocument2 pagesEng 01 ARAVINDERANNo ratings yet
- Sample Testing-Equipment-as-per-UL-746Document10 pagesSample Testing-Equipment-as-per-UL-746Aritra DasguptaNo ratings yet
- UT501A User Manual PDFDocument2 pagesUT501A User Manual PDFAlban Abazi100% (1)
- Unit5 HveDocument29 pagesUnit5 Hveview eeehodNo ratings yet
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation Testingnutchai2538100% (1)
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingHARISH ROHANNo ratings yet
- Megger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingDocument24 pagesMegger - The Complete Guide To Electrical Insulation TestingMan Minh SangNo ratings yet
- Tieu Chuan Viet Nam 1234Document24 pagesTieu Chuan Viet Nam 1234Man Minh SangNo ratings yet
- Secondary Substation Transformers Test Application Data Standard TestsDocument2 pagesSecondary Substation Transformers Test Application Data Standard TestsMarcelo Rueda MartínezNo ratings yet
- We Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsDocument8 pagesWe Can Classify Test Failure Modes in Power Transformers Accord Ing To Transform Er Com Po NentsShamil NiftaliyevNo ratings yet
- Final Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsDocument6 pagesFinal Version - Impulse Testing and Insulation Deterioration in Electric MotorsJoseph ChamiNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFDocument7 pagesAstm D 1169 Metodo para Resistividad PDFJose Maria Castillo HernandezNo ratings yet
- Article Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUDocument6 pagesArticle Testing The State of High Voltage Insulation Hummel ENUarnenylundNo ratings yet
- High Volume Armature Testing: Lance Straughn Slaughter CompanyDocument10 pagesHigh Volume Armature Testing: Lance Straughn Slaughter Companyronald allan liviocoNo ratings yet
- Insulation Coordination of HV Lines Resumo Alargado - Linhas Aereas - Final PDFDocument6 pagesInsulation Coordination of HV Lines Resumo Alargado - Linhas Aereas - Final PDFEdward Baleke SsekulimaNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFDocument6 pages10 11648 J Epes 20180705 12 PDFbelayneh ayichewNo ratings yet
- Test Equipment 101 - The Basics of Electrical TestingDocument31 pagesTest Equipment 101 - The Basics of Electrical TestingSas BetroNo ratings yet
- Individual Temperature Compensation 42 47Document6 pagesIndividual Temperature Compensation 42 47ivicaNo ratings yet
- Medium-Voltage Circuit Breaker Maintenance: Special FeatureDocument2 pagesMedium-Voltage Circuit Breaker Maintenance: Special FeatureSing Yew LamNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Voltage Transformer TestingDocument7 pagesCapacitive Voltage Transformer TestingSaeedAhmedKhan100% (1)
- HV Reinforced Insulation IntroDocument10 pagesHV Reinforced Insulation IntroMark BatulanNo ratings yet
- Insulation Tests For Assessment Rotating Electrical MachineryDocument10 pagesInsulation Tests For Assessment Rotating Electrical Machineryidontlikeebooks100% (1)
- Baker 2012Document8 pagesBaker 2012JONATHAN MORALESNo ratings yet
- ART-Paper WP en V01 PDFDocument13 pagesART-Paper WP en V01 PDFAnonymous V6y1QL6hn100% (1)
- Hi Pot 160 KVDocument4 pagesHi Pot 160 KVRodrigoNo ratings yet
- Svcet: Μsec (Called 1/50 Μsec Wave)Document4 pagesSvcet: Μsec (Called 1/50 Μsec Wave)Indongo EliaserNo ratings yet
- An Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationDocument9 pagesAn Online Technique For Monitoring The InsulationMonthly ImogenNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Insulation TestingDocument6 pagesThe Basics of Insulation TestingNoel RazaNo ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5From EverandAnalog Dialogue Volume 46, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Gawedar Okstate 0664D 14871.pdf JsessionidDocument87 pagesGawedar Okstate 0664D 14871.pdf JsessionidMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Expl SW Chapter 05 STP Part IDocument65 pagesExpl SW Chapter 05 STP Part IMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Vol2 ConstructionDocument14 pagesVol2 ConstructionMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- B1CreationofIntegratedofIndustrialSecuritywiththeuseofModern - KMMS Aug 04 2015 0023Document7 pagesB1CreationofIntegratedofIndustrialSecuritywiththeuseofModern - KMMS Aug 04 2015 0023Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Paper 20Document4 pagesPaper 20Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 42111-42144 - 04 Heat Shrinkable Termination Kit For XLPE PVC Insulated CU Cable 0.4kv - 002Document15 pages42111-42144 - 04 Heat Shrinkable Termination Kit For XLPE PVC Insulated CU Cable 0.4kv - 002Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- IS IEC 61730 1 SolarDocument22 pagesIS IEC 61730 1 SolarMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Insulator Pin For Line Post Type InsulatorDocument10 pagesInsulator Pin For Line Post Type InsulatorMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 40211-40412 - 663011 Pre-Molded Straight Joint Kit For XLPE Insulated Cable - 002Document17 pages40211-40412 - 663011 Pre-Molded Straight Joint Kit For XLPE Insulated Cable - 002Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 11.5KW Solar System With ACDocument2 pages11.5KW Solar System With ACMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Refinerry Techincal ProjectDocument11 pagesRefinerry Techincal ProjectMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Electric Power Ratings Guide: Seventeenth EditionDocument56 pagesElectric Power Ratings Guide: Seventeenth EditionMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 2 ELVAC RTU in Cable Network I Ring Main Unit I Secondary SubstationDocument8 pages2 ELVAC RTU in Cable Network I Ring Main Unit I Secondary SubstationMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Energies 15 06418Document20 pagesEnergies 15 06418Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Iec 60027letter Symbols To Be Used in Electrical TechnologyDocument16 pagesIec 60027letter Symbols To Be Used in Electrical TechnologyMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 1649753618cable Magnetic Field Evalution Cal Fact Sheet Web 1 pdf1649753618Document2 pages1649753618cable Magnetic Field Evalution Cal Fact Sheet Web 1 pdf1649753618Mohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 42221-42422 - 66kv-30kv-11kv Heat Shrinkable Outdoor Termination Kit For XLPE Insulated CableDocument17 pages42221-42422 - 66kv-30kv-11kv Heat Shrinkable Outdoor Termination Kit For XLPE Insulated CableMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Promat Energy - Solar Brochure - EnglishDocument2 pagesPromat Energy - Solar Brochure - EnglishMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Appendix C Minimum Equipment Efficiency Standards: Port of StocktonDocument6 pagesAppendix C Minimum Equipment Efficiency Standards: Port of StocktonMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- 200KW Solar System-Technician ParametersDocument10 pages200KW Solar System-Technician ParametersMohamed AhmiedNo ratings yet
- Chap 2Document49 pagesChap 2Malak BattahNo ratings yet
- Anastazya Forde CV..Document1 pageAnastazya Forde CV..anastazya fordeNo ratings yet
- 1735 KVA (1388 KW) Mitsubishi PDFDocument1 page1735 KVA (1388 KW) Mitsubishi PDFMd. Harunor RashidNo ratings yet
- Engaging Generation ZDocument9 pagesEngaging Generation Zghoster33No ratings yet
- Applied Ergonomics: Nora Balfe, Sarah Sharples, John R. WilsonDocument13 pagesApplied Ergonomics: Nora Balfe, Sarah Sharples, John R. WilsonDian Palupi RestuputriNo ratings yet
- Iv STD ScienceDocument2 pagesIv STD SciencePradeepNo ratings yet
- Kobayashi ManualDocument27 pagesKobayashi ManualAnonymous utXYfMAXNo ratings yet
- 8th LA Midterms Study GuideDocument12 pages8th LA Midterms Study GuideIts AbbiNo ratings yet
- DQ 1 Week 8Document6 pagesDQ 1 Week 8LeeginaNo ratings yet
- Android-Based Classroom Monitoring System For Teacher Using QR Code TechnologyDocument12 pagesAndroid-Based Classroom Monitoring System For Teacher Using QR Code TechnologyAkmad Ali AbdulNo ratings yet
- CFD Modeling of Spontaneous Heating in A Large-Scale Coal ChamberDocument8 pagesCFD Modeling of Spontaneous Heating in A Large-Scale Coal ChamberdenichezNo ratings yet
- Mole RatioDocument2 pagesMole Ratioariansofia1031No ratings yet
- Saarthi - Excel AssignmentDocument17 pagesSaarthi - Excel AssignmentBHUMIT KATARIANo ratings yet
- M-2. Theories of MotivationDocument15 pagesM-2. Theories of MotivationumerNo ratings yet
- First CryDocument4 pagesFirst CrysamikshaNo ratings yet
- Mayr Origins of Feedback ControlDocument11 pagesMayr Origins of Feedback ControlBenjamín Peña Pérez100% (1)
- Correspondence Between My Friend, The Late Gordon T. "Gordy" Pratt, and Chicago Tribune Reporter Lisa Black and Editor Peter Hernon (Sept/Oct 2009)Document8 pagesCorrespondence Between My Friend, The Late Gordon T. "Gordy" Pratt, and Chicago Tribune Reporter Lisa Black and Editor Peter Hernon (Sept/Oct 2009)Peter M. HeimlichNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 - Pressure TIME: 15 Min: NAME: CLASSDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 - Pressure TIME: 15 Min: NAME: CLASSNur'Afifah Serip MohamadNo ratings yet
- TVL 12 Carpentry NC II w4 6 Types of Wood JointsDocument19 pagesTVL 12 Carpentry NC II w4 6 Types of Wood JointsBenjamin Paner100% (1)
- Safety Data Sheet: Musol SolventDocument15 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Musol SolventHưng Lê TrungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Builders & Construction Co. (Phil.), Inc.: Quality Control ProgramDocument22 pagesDynamic Builders & Construction Co. (Phil.), Inc.: Quality Control ProgramMae Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Hef 4516 BTDocument10 pagesHef 4516 BTAdam SchwemleinNo ratings yet
- Ngec5 ModuleDocument133 pagesNgec5 ModuleTheodore GrandeNo ratings yet
- Prachi Uniqueness of Human BeingDocument19 pagesPrachi Uniqueness of Human BeingasifanisNo ratings yet
- MID 039 - CID 0167 - FMI 12: TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesMID 039 - CID 0167 - FMI 12: TroubleshootingNerminTurkenceNo ratings yet
- About Pratham Education Foundation About Pratham Education FoundationDocument3 pagesAbout Pratham Education Foundation About Pratham Education FoundationsoumyalambaNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.2 Root and Mitosis in An Onion CellDocument3 pagesActivity 4.2 Root and Mitosis in An Onion CellPreiy Julian De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Fake News Detection Using NLPDocument9 pagesFake News Detection Using NLPIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet