Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lomihan
Lomihan
Uploaded by
jimboy faderagao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesThe document contains prayers to Guardian Angel, Hail Mary, and the Apostle's Creed. It begins with a prayer asking the guardian angel for protection and guidance. This is followed by the Hail Mary prayer praising Mary. The document concludes with the Apostle's Creed, which affirms Christian beliefs around God, Jesus Christ, Holy Spirit, church, resurrection of the dead, and eternal life.
Original Description:
Original Title
lomihan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains prayers to Guardian Angel, Hail Mary, and the Apostle's Creed. It begins with a prayer asking the guardian angel for protection and guidance. This is followed by the Hail Mary prayer praising Mary. The document concludes with the Apostle's Creed, which affirms Christian beliefs around God, Jesus Christ, Holy Spirit, church, resurrection of the dead, and eternal life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views12 pagesLomihan
Lomihan
Uploaded by
jimboy faderagaoThe document contains prayers to Guardian Angel, Hail Mary, and the Apostle's Creed. It begins with a prayer asking the guardian angel for protection and guidance. This is followed by the Hail Mary prayer praising Mary. The document concludes with the Apostle's Creed, which affirms Christian beliefs around God, Jesus Christ, Holy Spirit, church, resurrection of the dead, and eternal life.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Guardian Angel Prayer I believe in Jesus Christ, his only Son, our
Angel of God, my guardian dear, Lord,
To whom God's love commits me here, who was conceived by the Holy Spirit
Ever this day, be at my side, and born of the virgin Mary.
To light and guard, He suffered under Pontius Pilate,
Rule and guide. was crucified, died, and was buried;
Amen. he descended to hell.
The third day he rose again from the
Hail Mary dead.
Hail Mary, full of grace, He ascended to heaven
the Lord is with you. and is seated at the right hand of God
Blessed are you among women, the Father almighty.
and blessed is the fruit of your womb, Jesus. From there he will come to judge the
Holy Mary, Mother of God, living and the dead.
pray for us sinners,
I believe in the Holy Spirit,
now and at the hour of our death.
the holy catholic* church,
Amen.
the communion of saints,
the forgiveness of sins,
Apostle’s Creed the resurrection of the body,
I believe in God, the Father almighty, and the life everlasting. Amen.
creator of heaven and earth.
CAM - relative motion between these surfaces is
cam - rotating machine element which gives largely of sliding nature but wear may be
reduced by off-setting the axis of the follower
reciprocating or oscillating motion to another
element known as follower Spherical faced follower - contacting end of
the follower is of spherical shape
- machined to spherical shape in order to
Classification of Follower (surface contact)
reduce stress
Knife Edge Follower - when the contacting
end of the follower has a sharp knife edge Cam with offset follower
- seldom used in practice because the
small area of contacting surface results
in excessive wear
Roller Follower - when the contacting end of
the follower is a roller
- rolling motion takes place between
the contacting surfaces (i.e. the
roller and the cam)
Flat faced or mushroom follower - contacting
end of the follower is a perfectly flat faced
Classification of Cams
According to Motion of the follower Radial or Disc Cam - the follower reciprocates
Reciprocating or translating follower - n the or oscillates in a direction perpendicular to the
follower reciprocates in guides as the cam cam axis
rotates uniformly
Cylindrical Cam - the follower reciprocates or
Oscillating or rotating follower - the uniform oscillates in a direction parallel to the cam
rotary motion of the cam is converted into axis. The follower rides in a groove at its
predetermined oscillatory motion of the cylindrical surface.
follower
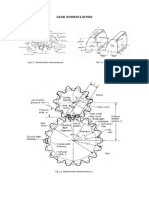
Cam Nomenclature
According to the path of motion of the follower
Radial Follower - the motion of the follower is
along an axis passing through the center of
the cam
Off-set Follower - the motion of the follower is
along an axis away from the axis of the cam
center
Base circle - It is the smallest circle that can Prime circle - It is the smallest circle that can
be drawn to the cam profile be drawn from the center of the cam and
tangent to the pitch curve.
Trace point - It is a reference point on the
follower and is used to generate the pitch Lift or stroke. It is the maximum travel of the
curve follower from its lowest position to the
topmost position
Pressure angle - It is the angle between the
direction of the follower motion and a normal Motions of the follower
to the pitch curve. - Uniform Velocity
- Simple Harmonic Motion
Pitch point - It is a point on the pitch curve - Uniform Acceleration and Retardation
having the maximum pressure angle. - Cycloidal Motion
Pitch circle - It is a circle drawn from the
centre of the cam through the pitch points.
Pitch curve - It is the curve generated by the
trace point as the follower moves relative to
the cam.
GEAR TRAIN Addendum - amount of tooth that sticks out
above the pitch circle
Rolling Cylinder - simplest way of transferring Common tangent - both curves at the contact
rotary motion from one shaft to another point
- External Set Common normal (Axis of Transmission)
- Internal Set - Line of action
Torque Rotation (mt) - reciprocal of the - Perpendicular to the common tangent
angular velocity (mv) - string s of both involutes, colinear
Gearset - a device to exchange torque for Length of action (z) - line of action between
velocity points of beginning and leaving contact
Pitch Point - contact point between the Arc of action - distance along the pitch circle
cylinders with the mesh
Cycloid - used as a tooth from watches and Arc of approach and Recess - angles
clocks, most other gears use involute curve subtended by these points and the line of
centers
INVOLUTE TOOTH FORM
Involute - curve generated by unwrapping a PRESSURE ANGLE - angle between the axis
taut string from a cylinder (evolute) of transmission and the direction of velocity at
- String is always tangent to cylinder pitch point
- Center of curvature of the involute is Ripple - variation in the output velocity
always at point of tangency Backlash - clearance between the mating
Base circle - cylinders which string are teeth measured at the pitch circle
unwrapped - ( tooth thickness - tooth space width)
Standard values of pressure angle Addendum circle - circle drawn at the top of
- 14.5 , 20, 25, with 20 being commonly the teeth
used and now 14.5 being obsolete Dedendum circle - circle drawn at the bottom
Antibacklash gears - two back-to-back gears of the teeth, root circle
on the same shaft that is fixed to take up the Circular Pitch - distance measured from the
backlash circumference of the pitch circle from a point
American Gear Manufacturers Association of one tooth to the corresponding point on the
(AGMA) - define the standard for gear design next tooth
and manufacture Diametral Pitch - ratio of number of teeth to
- 3 as lowest precision and 16 highest the pitch circle diameter in millimetres
Module - ratio of the pitch circle diameter in
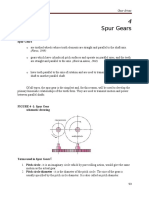
GEAR NOMENCLATURE millimeters to the number of teeth
Pitch circle - imaginary circle which by pure Clearance - radial distance from the top of the
rolling action tooth to the bottom of the tooth
Pitch circle diameter - diameter of pitch circle Clearance circle - A circle passing through the
Pitch point - common point of contact top of the meshing gear
between two pitch circle Total Depth - radial distance between the
Pitch surface - surface of rolling disc addendum and the dedendum circles
pressure angle - angle between the common Working Depth - radial distance from the
to normal to two gear teeth addendum circle to the clearance circle
Addendum - pitch circle to the top of the tooth Tooth Thickness - width of the tooth
Dedendum - pitch rifle to bottom of the tooth measured along the pitch circle
Backlash - difference between the tooth Arc of recess - portion of the path of contact
space and the tooth thickness from the pitch point to the end of the
Face of tooth - surface of the gear tooth engagement of a pair of teeth
above the pitch surface Profile-shifted gears - involute shape with
Flank of tooth - surface of the gear tooth longer addendum on the pinion and a shorter
below the pitch surface one the gear
Top land - surface of the top of the tooth Contact ratio - average number of teeth in
Face Width - width of the gear tooth contact at any time
measured parallel to its axis Highest Point of single-tooth-contact (HPTSC)
Profile - curve formed by the face and flank of - When load is applied at lower position
the tooth on the tooth rather than its tip
Fillet radius - radius that connects the root
circle to the profile of the tooth GEAR TYPES
Path of contact - path traced by the point of Spur Gear - teeth are parallel to the axis of
contact of two teeth from the beginning to the gear
end of engagement - Simplest and least expensive gear
Arc of contact - e path traced by a point on - Can only be meshed if parallel
the pitch circle from the beginning to the end
of engagement
Arc of approach - portion of the path of
contact from the beginning of the
engagement to the pitch point
Helical Gears - teeth are at a helix angle
- Two crossed helical gears can be
meshed Worms and Worm Gear - only one tooth
- Axes are parallel wrapped continuously around its
- More expensive, quieter than spur circumference
- Can be meshed with a special worm
gear (or worm wheel)
- Ratio = 1 / n of teeth of worm gear
Single Enveloping - worm gear teeth wrapped
around the worm
Herringbone Gear - formed by two helical Double Enveloping - wrap the worm around
gears with same diameter and pitch the gear, resulting in hourglass-shaped
- Often cut on the same gear blank
- Much expensive than helical gears
- No thrust bearing needed
- Tend to use in large, high power
applications
Rack and Pinion - linear gear
- Teeth are trapezoid, true involutes
- Meshes with the pinion
- main application is linear motion
conversion
Efficiency - input/output power expressed in
percent
Bevel Gear Idlers - sing of overall ratio which is affected
- teeth are parallel to the axis of the gear, by intermediate gears
straight bevel gear Compound Gear Train - is one in which at
- teeth are angled with respect to the axis, least one shaft carries more than one gear
spiral bevel gear Nonreverted compound train - input and
- cone axes and apices must intersect in output shafts are not coincident
both cases Reverted compound train - output shaft
- must be replaced in pairs, not concentric with the input shaft
universally interchangeable Planetary train - two-DOF device
Hypoid Gear - used if gears are nonparallel
and nonintersecting
- based on rolling hyperboloids
- tooth form is not involute
Hypoid - contraction of hyperboloid
Noncircular Gear - rolling centrodes of
grashoff double crank
- velocity ratio is not constant
- used in machineries
Gear Train - collection of two or more
meshing gears
FLEXIBLE CONNECTORS Double belt - two thickness of leather are
- used when distance between the driving glued together, flesh side to flesh side
and driven shaft is too great Initial tension - tightness with which it is
stretched being such that there is a tension or
Belts - used to connect shafts as much as 30 pull
ft apart Quarter Turn Belt - belt which connects two
- made of leather, rubber , woven fabrics nonintersecting shaft at right angles with each
and requires pulleys other
Ropes - made of Manila, hemp, cotton or wire Tight and Loose pulleys - used for throwing
in section, required either grooved pulleys or machinery into and out of gear
drums V-belts - type of belting which become
- used for connecting shafts up to 100 ft popular in recent years
and operate at 600 fpm sheave - portion of single grooved pulley
Chains - composed of links or bars Multiple rope or english system - simpler of
- used for connecting shafts which are the two and consist of independent ropes
less than 15ft apart running side by side
Band - used as a general term to denote all American system or continuous - one rope is
kinds of flexible connectors wound around the driving and driven pulleys
Open belt - pulleys turn in the same direction several times
crossed belt - pulleys turn in opposite Drum - cord does not merely pass over a
direction pulley but is made fast to it at one end
Single belt - single thickness of leather are Wire Rope - suitable for transmission of large
fastened end to end power to great distances
Chains - frequently used as connectors Renold Inverted Tooth Chain - by Hans
between parallel axes Renold
Sprockets - wheels over which chain runs - consist of peculiar form with straight
bearing edges that runs over sprocket
Classification of Chains wheels
1. Hosting Chains Morse Rocker-Joint Chain - eliminates the
Coil Chain - most common form of sliding friction of rivets
hoisting chain, consist oval links
Stud-link chain - will not kink or tangle
so easily as coil chain
2. Conveyor CHain - detachable or hook-joint
type, closed-end pintle type
- sprocket teeth is largely empirical
3. Power Transmission Chain
Block Chain - chains of block type are
used
Roller Chain
Silent Chain - used when maximum
quietness is desired and it is necessary to
transmit heavier lods
Chain Length
You might also like
- The Language of Our Dna Scalar EnergyDocument5 pagesThe Language of Our Dna Scalar EnergyNat Silva100% (1)
- Gear NomenclatureDocument41 pagesGear NomenclatureViswanathan SrkNo ratings yet
- MD Liki HahaDocument1 pageMD Liki HahaJohn ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Mael FinalsDocument9 pagesMael FinalsAtzu YuNo ratings yet
- Machine FinalDocument1 pageMachine FinalLhorene Morhiel CatahanNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements ReviewerDocument4 pagesMachine Elements ReviewerJohn Carlo Balucio LlaveNo ratings yet
- Mael RemDocument5 pagesMael Remfortress139No ratings yet
- Ephrem Zeleke: Prepared byDocument44 pagesEphrem Zeleke: Prepared bysamuel mechNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument9 pagesGearsMark CruzNo ratings yet
- Gear Terms and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesGear Terms and DefinitionsAaron_Liu_1555No ratings yet
- Spur GearDocument73 pagesSpur GearhaymanotNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument5 pagesGearsSagar. K. MNo ratings yet
- Gear LecturDocument50 pagesGear LecturMuralikrishnan GM100% (1)
- Module 4 GearsDocument73 pagesModule 4 GearsDheeraj PNo ratings yet
- GearDocument31 pagesGearshah jalpaNo ratings yet
- GearDocument26 pagesGearRadhika GandhiNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument70 pagesGearsJayesh NayakantiNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission Systems: Prepared by Dr.A.Vinoth JebarajDocument148 pagesDesign of Transmission Systems: Prepared by Dr.A.Vinoth Jebarajrishi raja RajaNo ratings yet
- Gear Geometry & Profile TheoryDocument24 pagesGear Geometry & Profile Theoryansh1983100% (2)
- Gears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekDocument20 pagesGears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekSujai BaskarNo ratings yet
- Gears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekDocument20 pagesGears Nomenclature: by Feedback by Comments 1 MahekSujai BaskarNo ratings yet
- Spurs GearDocument16 pagesSpurs GearAshenafi KenaNo ratings yet
- ME324 Lecture5Document66 pagesME324 Lecture5Jam Maica TuboNo ratings yet
- Involute Spur GearDocument7 pagesInvolute Spur GeardhimanrayatNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSDocument6 pagesModule 3 PDF File SPUR GEARSAdolfo KayeNo ratings yet
- Module IV: Gears and Gear TrainsDocument38 pagesModule IV: Gears and Gear TrainsSuraj VinayNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument2 pagesREVIEWERfortress139No ratings yet
- GearsDocument5 pagesGearsAllaine BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Cam & Follower: Prof. Sumit Kumar Assistant Professor NIETM, NagpurDocument18 pagesCam & Follower: Prof. Sumit Kumar Assistant Professor NIETM, NagpurSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Plate 3Document5 pagesPlate 3shaunmedina0006No ratings yet
- Definition of Spur Gear - A Gearwheel With Teeth Projecting Parallel To The Wheel's Axis. Nomenclature of Spur GearDocument6 pagesDefinition of Spur Gear - A Gearwheel With Teeth Projecting Parallel To The Wheel's Axis. Nomenclature of Spur GearMichael Angelo ComediaNo ratings yet
- 06 GearsDocument22 pages06 GearsTeaching ClubNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Gears and Gear TrainsDocument93 pagesChapter 4-Gears and Gear TrainssahilrajpootasusNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Gears 1Document10 pagesModule 6 Gears 1RioNo ratings yet
- 012 - Gear TheoryDocument38 pages012 - Gear TheoryC. RonaldNo ratings yet
- Machine Elements Spur GearDocument7 pagesMachine Elements Spur GearJAVIER, Reinnier Jhiro C.No ratings yet
- Group 3 (Gears)Document52 pagesGroup 3 (Gears)CherrydhelNo ratings yet
- Mael TransesDocument4 pagesMael TransesERICKA MAE CANTOSNo ratings yet
- Gears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Document8 pagesGears: Looking For GATE Preparation Material? Join & Get Here Now!Akash SoniNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsgauravthamanNo ratings yet
- Helicalgear 170104101849Document9 pagesHelicalgear 170104101849ChiragSMishra0% (1)
- Introduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Mechanisms: 7 GearsDezert EagleNo ratings yet
- Lecture Design of Spur GearDocument97 pagesLecture Design of Spur GearOwais Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Line of Action or Pressure Line: The Force, Which The Driving Tooth Exerts at Point of Contact of The TwoDocument2 pagesLine of Action or Pressure Line: The Force, Which The Driving Tooth Exerts at Point of Contact of The TwoMari MuthuNo ratings yet
- Gear Terminology: Pitch Circle: Addendum Circle: Dedendum Circle: ClearanceDocument11 pagesGear Terminology: Pitch Circle: Addendum Circle: Dedendum Circle: ClearanceFawad HassanNo ratings yet
- Gears Design MD2Document52 pagesGears Design MD2Faizan MohyuddinNo ratings yet
- DVGDocument53 pagesDVGbalajigandhirajanNo ratings yet
- Gears - General: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignDocument229 pagesGears - General: Shigley's Mechanical Engineering DesignbasitNo ratings yet
- Spur Gears: Pre-University Engineering Sciences Yr 2Document20 pagesSpur Gears: Pre-University Engineering Sciences Yr 2Jordan BrownNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Gear, Contact Ratio, InterferenceDocument52 pagesGroup 1 Gear, Contact Ratio, InterferenceAnthony FajardoNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument3 pagesGearsNuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9-SPUR GEARS AND GEAR TRAINSDocument64 pagesChapter 9-SPUR GEARS AND GEAR TRAINSMohammed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- BEH 41103 Chapt 1Document14 pagesBEH 41103 Chapt 1Fairoz UsuNo ratings yet
- 4SPURDocument12 pages4SPURNeil RubsNo ratings yet
- Unit IVDocument70 pagesUnit IVMugilNo ratings yet
- Gears PDFDocument45 pagesGears PDFSanmukh ShindeNo ratings yet
- GearsDocument45 pagesGearsSomendra Brijesh Pandey100% (1)
- Metrology, Gear MeasurementDocument44 pagesMetrology, Gear MeasurementPiu Kundu100% (23)
- Mixers VS Kneading MachineDocument3 pagesMixers VS Kneading Machinejimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- Dough Is An Essential Ingredient in BakingDocument1 pageDough Is An Essential Ingredient in Bakingjimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- Design For Solar Hybrid Mobile Multipurpose Cold SDocument1 pageDesign For Solar Hybrid Mobile Multipurpose Cold Sjimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- Narrative (SPES)Document2 pagesNarrative (SPES)jimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Waste CompactoDocument6 pagesDesign and Development of Waste Compactojimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- RRL IpiprintDocument6 pagesRRL Ipiprintjimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- HAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHADocument5 pagesHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAHAjimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- DC and Ac Act1Document2 pagesDC and Ac Act1jimboy faderagaoNo ratings yet
- Energy and Exergy Analysis of Solar Power Tower PlantsDocument10 pagesEnergy and Exergy Analysis of Solar Power Tower PlantsBranislavPetrovicNo ratings yet
- Alsharhan - Study DeskDocument1 pageAlsharhan - Study DeskNayef FtouniNo ratings yet
- In-And Ga-Based Inorganic Double Perovskites With Direct Bandgaps For Photovoltaic ApplicationDocument6 pagesIn-And Ga-Based Inorganic Double Perovskites With Direct Bandgaps For Photovoltaic Applicationa s m mosabbirNo ratings yet
- History of The Periodic TableDocument25 pagesHistory of The Periodic TableLeah Jane MalinaoNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Linear Momentum: - Newton's Second Law of Motion For A System IsDocument30 pagesConservation of Linear Momentum: - Newton's Second Law of Motion For A System IsOmer AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 3-Pile Cap Design Example Using ASDIP FOUNDATION SoftwareDocument7 pages3-Pile Cap Design Example Using ASDIP FOUNDATION SoftwareKrishna SodhaNo ratings yet
- AccessoriesDocument4 pagesAccessoriesCristhian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkDocument23 pages2.2 Heat Transfer in Steelwork Protected and Unprotected SteelworkMahbub AlamNo ratings yet
- CentspotDocument2 pagesCentspotvicky khanNo ratings yet
- A Reliable Single-Phase Bipolar Buck-Boost Direct PWM AC-AC Converter With Continuous Input/ Output CurrentsDocument12 pagesA Reliable Single-Phase Bipolar Buck-Boost Direct PWM AC-AC Converter With Continuous Input/ Output CurrentsDar JahangeerNo ratings yet
- 11 12 Automatic Tension Control BTS VFDDocument2 pages11 12 Automatic Tension Control BTS VFDGioj MejNo ratings yet
- Circles?: How ManyDocument18 pagesCircles?: How ManyGabriel medinaNo ratings yet
- 3583.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.01 - Tutorial - 05 - Excavation of An NATM TunnelDocument14 pages3583.PLAXIS - 2D - CEV22.01 - Tutorial - 05 - Excavation of An NATM TunnelPhalgun MoturuNo ratings yet
- Exercise PDFDocument16 pagesExercise PDFThenaisieNo ratings yet
- 3GBA282270 ADF M2bax 280smg 4Document2 pages3GBA282270 ADF M2bax 280smg 4chmatias3No ratings yet
- Abu Zaria 100 Level Physics Courses - FlashLearnersDocument7 pagesAbu Zaria 100 Level Physics Courses - FlashLearnersSamuelNo ratings yet
- 30GSC KDK For GT ProjectDocument1 page30GSC KDK For GT ProjectTejo WahonoNo ratings yet
- Intent of AMC 2. Equipment Information 3. Hydraulics Checklist 4. Transmission Checklist 5. Electrical and C&I Checklist 6. Overall Machine ChecklistDocument13 pagesIntent of AMC 2. Equipment Information 3. Hydraulics Checklist 4. Transmission Checklist 5. Electrical and C&I Checklist 6. Overall Machine Checklistsufiyanahmed1611No ratings yet
- TSE 10 ManualDocument100 pagesTSE 10 Manualmmason.verschurenNo ratings yet
- AP C Mech 1. Unit 1. Kinematics One Dimensional Motion Part 2Document11 pagesAP C Mech 1. Unit 1. Kinematics One Dimensional Motion Part 2moonidiveNo ratings yet
- Vector Drive - Troubleshooting Guide: Haas Technical DocumentationDocument7 pagesVector Drive - Troubleshooting Guide: Haas Technical DocumentationViruzeNo ratings yet
- Lab Experiment 3 - Flow Through PipesDocument8 pagesLab Experiment 3 - Flow Through PipesLance HernandezNo ratings yet
- MA02 June 2022Document28 pagesMA02 June 2022Vedant DasNo ratings yet
- Pages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector DiagramDocument2 pagesPages From 5054 - w15 - QP - 21-9 - Chapter Kinematic and Vector Diagramlelon ongNo ratings yet
- Apparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputDocument5 pagesApparatus:: AIM: Acquire The Knowledge of Output Devices Like CRO and DSO For Observing OutputAdwait BorikarNo ratings yet
- Electricalpower Engineering Exam Study GuideDocument35 pagesElectricalpower Engineering Exam Study GuideCharaf BelNo ratings yet
- Definition in The Quantum Efficiency MeasurementDocument2 pagesDefinition in The Quantum Efficiency MeasurementSaifulIslamNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Products: Technical BrochureDocument50 pagesLow Voltage Products: Technical BrochureabbdealerNo ratings yet
- F 1080 - 93 R98 Rjewodatotnsotg - PDFDocument2 pagesF 1080 - 93 R98 Rjewodatotnsotg - PDFJuanNo ratings yet