Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Single Displacement Reactions
Single Displacement Reactions
Uploaded by
Tiffany Ye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageThis document discusses single displacement reactions, where one element replaces another in a chemical reaction. It introduces the activity series, which arranges elements by their reactivity in single displacement reactions. More reactive elements on the series can displace less reactive elements. The document explains how to use the activity series to predict if single displacement reactions will occur between metals and aqueous compounds, metals and water, or metals and acids. Halogens are also arranged by reactivity on the activity series.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses single displacement reactions, where one element replaces another in a chemical reaction. It introduces the activity series, which arranges elements by their reactivity in single displacement reactions. More reactive elements on the series can displace less reactive elements. The document explains how to use the activity series to predict if single displacement reactions will occur between metals and aqueous compounds, metals and water, or metals and acids. Halogens are also arranged by reactivity on the activity series.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageSingle Displacement Reactions
Single Displacement Reactions
Uploaded by
Tiffany YeThis document discusses single displacement reactions, where one element replaces another in a chemical reaction. It introduces the activity series, which arranges elements by their reactivity in single displacement reactions. More reactive elements on the series can displace less reactive elements. The document explains how to use the activity series to predict if single displacement reactions will occur between metals and aqueous compounds, metals and water, or metals and acids. Halogens are also arranged by reactivity on the activity series.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
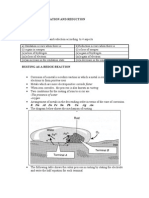
Single Displacement Reactions
Single Displacement
● A reaction by which one element replaces another
● You can figure out if an element will replace another by figuring out which element is more
reactive in the single displacement reaction
○ General equation: AB + C → AC + B
Activity Series - Metals
● Activity series: Elements arranged according to their reactivity in single displacement
○ An elements on the series will displace anything below itself on the series
○ The greater the distance between two elements on the activity series, the more likely
the displacement reaction will occur and the faster it will happen
■ Ex. Iron will displace nickel in a SD reaction, but very slowly
■ Ex. Lithium will displace lead very quickly
○ Hydrogen is highlighted on the activity series because it functions like a metal
○ Silver, platinum and gold are the least reactive on the activity series
Predicting Single Displacement Reactions
● Metal + aqueous ionic compounds
○ Does the reaction Mg(s) + CuSO4 (aq) happen?
○ Check activity series: Mg is higher than Cu, so the reaction will happen
○ Products are solid metal and an aqueous ionic compound
● Metal + water
○ Think of H2O as H+OH-
○ Only lithium to sodium reacts with water
○ Products are always a metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
● Metal + Acid
○ Imagine acids as ionic compounds H+Cl-
○ Products are always hydrogen gas (g) + ionic compound (aq)
Activity Series - Halogens
● Fluorine is most reactive, iodine is the least reactive
○ Can be found in descending reactivity on the periodic table as you go down
You might also like
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument23 pagesChemistry Revision Notesrandom personNo ratings yet
- The Reaction of Metals by Mohammed SulaimanDocument16 pagesThe Reaction of Metals by Mohammed Sulaimanmal7182281No ratings yet
- Summary Notes - Topic 6 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEDocument6 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 6 WJEC (England) Chemistry GCSEReaktivic gaishnikovicNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7: Redox Reactions and The Metal Activity Series OutcomesDocument4 pagesExperiment 7: Redox Reactions and The Metal Activity Series OutcomesSafwan m.tNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 9: The Periodic TableDocument3 pagesCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 9: The Periodic TableKalaiarasu SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions Grade 11Document69 pagesRedox Reactions Grade 11RahulNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument61 pagesChemical ReactionsTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry PDFDocument59 pagesAqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry PDFrosalinaNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionssssDocument28 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionssssCarl OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument51 pagesAqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenGopi SureshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document29 pagesChapter 7Melvin SarsosaNo ratings yet
- Types OF CHEMICAL REACTION 2020Document26 pagesTypes OF CHEMICAL REACTION 2020dyron francoNo ratings yet
- Chem Chap 1Document41 pagesChem Chap 1rekha.sat29No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 8 Redox Reactions-1Document60 pagesClass 11 Chapter 8 Redox Reactions-1sibaranjandash2007No ratings yet
- Chem1 Module8Document23 pagesChem1 Module8carlgavinsletartigasNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of MetalsDocument3 pagesBehaviour of MetalsPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis Summary IGCSEDocument1 pageElectrolysis Summary IGCSEeriotacidNo ratings yet
- L5 Chemical ReactionDocument2 pagesL5 Chemical ReactionRain AllejeNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Lecture 16 - Group 1 ElementsDocument12 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Lecture 16 - Group 1 Elementsnazzlor08No ratings yet
- RedoxDocument41 pagesRedoxxedali1912No ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument6 pagesElectricityPraveenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Oxidation and Reduction: - The Presence of Water - OxygenDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Oxidation and Reduction: - The Presence of Water - OxygenzahariffNo ratings yet
- IOC Chemical-ReactionsDocument37 pagesIOC Chemical-ReactionsUwe JasmiraNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument26 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsAshanna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Quiz NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Quiz Noteschisomamadi81No ratings yet
- Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryDocument49 pagesRedox Reactions & ElectrochemistryNatish JaglanNo ratings yet
- Activity SeriesDocument7 pagesActivity SeriesAhmedSaad647No ratings yet
- RedoxDocument41 pagesRedoxNauval ZidnyNo ratings yet
- REACTIVITY SERIES FULL CompleteDocument6 pagesREACTIVITY SERIES FULL CompleteSanbir SaadNo ratings yet
- Single ReplacementDocument3 pagesSingle ReplacementJeianne Decerie MiguelNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Types of Chemical Reactions ObjectiveDocument3 pagesExperiment 4 Types of Chemical Reactions Objectiveفهد سعيد ال مطره الغامديNo ratings yet
- FE ChemDocument9 pagesFE Chembendadick cloneNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument12 pagesChemistry Notesmsaadp0903No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Types Ofchemical ReactionsDocument22 pagesGrade 8 Types Ofchemical ReactionsreddypoulomiNo ratings yet
- FE ChemDocument9 pagesFE Chembendadick cloneNo ratings yet
- Summary Notes For The Prediotic TableDocument11 pagesSummary Notes For The Prediotic TableBeast ShahirHandsomeNo ratings yet
- DMS 1 - Reactions in Aqueous - SolutionDocument20 pagesDMS 1 - Reactions in Aqueous - Solutionsuhiermai3No ratings yet
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - S - N1 MechanismDocument29 pagesNucleophilic Substitution Reactions - S - N1 MechanismTurgid gamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04mauDocument24 pagesChapter 04maunoor awshanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3.04: Particles and Chemical Equation 2Document17 pagesUnit - 3.04: Particles and Chemical Equation 2Ayman HassanNo ratings yet
- Single Replacement Lab As Inquiry BasedDocument4 pagesSingle Replacement Lab As Inquiry Basedapi-239437010No ratings yet
- Displacement ReactionDocument3 pagesDisplacement ReactionShariq KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ChemDocument7 pagesChapter 4 Chemkrishna darjiNo ratings yet
- Aqueous SolutionsDocument24 pagesAqueous Solutionsyutaro tanakaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Document22 pagesChemical Reactions: John A. Schreifels Chemistry 211-Notes 1Hayan LeeNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicDocument60 pagesClass XI Chemistry Unit-8 Redox Reactions: TopicBaljit Singh100% (1)
- Chemical EquationsDocument75 pagesChemical EquationsbagoljoannahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution: SolutionsDocument24 pagesChapter Four: Reactions in Aqueous Solution: SolutionsPaulAngeloPascuaNo ratings yet
- Reactivity Series-DisplacementDocument16 pagesReactivity Series-Displacementmeganekokun kawaiiNo ratings yet
- Regolith Geochemistry & Mineralogy: Mehrooz F AspandiarDocument53 pagesRegolith Geochemistry & Mineralogy: Mehrooz F AspandiarChinox LokooNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Summary SheetDocument4 pagesChemical Reaction Summary SheetTiffany YeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document58 pagesChapter 12maysunNo ratings yet
- 3.2. Electrolytic ProcessesDocument5 pages3.2. Electrolytic ProcessesHumna RazzaqNo ratings yet
- SinglereplacementrxnlabDocument3 pagesSinglereplacementrxnlabapi-239309345No ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecule and Chemical ReactionDocument5 pagesAtoms, Molecule and Chemical ReactionSolomon BinutuNo ratings yet
- Single & Double ReactionsDocument4 pagesSingle & Double ReactionsMCHNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of MetalsDocument7 pagesChemical Properties of MetalsDAKSH GREAD DPSN-STDNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsDocument80 pagesRedox ReactionsShashwatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)