Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vector Algebra Solutions
Vector Algebra Solutions
Uploaded by
ReshmiRaiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- How To Calculate Drum Nip LoadDocument1 pageHow To Calculate Drum Nip Loadsushil kumar100% (2)
- SymmetryDocument60 pagesSymmetryDeepak TholiaNo ratings yet
- Dad S TheoremDocument17 pagesDad S TheoremyvazzocaanhdvpmlfmNo ratings yet
- InequalityDocument2 pagesInequalityRijul SainiNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument2 pagesAbcdnguyenthedanNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Quadratic Equation: Exercise # 1Document5 pagesSolutions - Quadratic Equation: Exercise # 1Dhruv AsodariaNo ratings yet
- Senior Maths 2a SolutionsDocument91 pagesSenior Maths 2a Solutionsakrammohammed786000No ratings yet
- Aljdaa Alslmi Tmarin Mhlola 1 1Document4 pagesAljdaa Alslmi Tmarin Mhlola 1 1wahbi yassineNo ratings yet
- Solution: ProblemDocument2 pagesSolution: ProblemĐặng KhánhNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex11dDocument2 pagesAlevelsb p1 Ex11dKeerthy verNo ratings yet
- Iia Iib Vsaq SolDocument41 pagesIia Iib Vsaq Solyashwanth padakandlaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Mechanical Engg. Examination, 2010: 4 Marks For NeatnessDocument2 pagesBachelor of Mechanical Engg. Examination, 2010: 4 Marks For Neatnessrony RkNo ratings yet
- 1b. Vectors - AnswersDocument2 pages1b. Vectors - AnswersDojeNo ratings yet
- Vectors Imp Questions Paper 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesVectors Imp Questions Paper 2 Solutionschaynitt30No ratings yet
- Conditional of Trigonometric IndentitiesDocument2 pagesConditional of Trigonometric IndentitiesJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- Radicales 1bc SolDocument6 pagesRadicales 1bc SolISABELNo ratings yet
- Shortlist Jbmo 2016 v7-1Document27 pagesShortlist Jbmo 2016 v7-1Lyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Math Question BankDocument4 pagesMath Question BankPramit Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Solutions Basic Level DPPDocument12 pagesQuadratic Equations Solutions Basic Level DPPAnkit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4kchaurasia868No ratings yet
- 1 Chapter Test (Vector) SolutionsDocument2 pages1 Chapter Test (Vector) Solutionsyashanshi20721No ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2020 Chapter Wise Tests: C B A C B A XDocument2 pagesJEE Mains 2020 Chapter Wise Tests: C B A C B A XMadhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Determinants 4.2 Sol PDFDocument7 pages12 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Determinants 4.2 Sol PDFJijish RANo ratings yet
- Chapter Review 7Document14 pagesChapter Review 7nasehaNo ratings yet
- Determinants 5 PDFDocument5 pagesDeterminants 5 PDFzaid khanNo ratings yet
- Inequality12 UnknownAuthorDocument1 pageInequality12 UnknownAuthorHai LeNo ratings yet
- CBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP13Document12 pagesCBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP13studyshivansh.17No ratings yet
- A Practice Set 1Document5 pagesA Practice Set 1aNo ratings yet
- SOT DPP 1 To 7 SolutionsDocument14 pagesSOT DPP 1 To 7 SolutionsSainath ChawaliNo ratings yet
- Welq T Mvaviy Mwyz - 11K Aa VQ: M RBKXJ Cixÿv Bs-02Document1 pageWelq T Mvaviy Mwyz - 11K Aa VQ: M RBKXJ Cixÿv Bs-02Murat MuratNo ratings yet
- QE and Complex Numbers DPPDocument9 pagesQE and Complex Numbers DPPsatishmhbdNo ratings yet
- ChÖÔng Xi: NhaÄn DaÏn G Tam GiaÙcDocument17 pagesChÖÔng Xi: NhaÄn DaÏn G Tam GiaÙcnessạ_chaos_knightNo ratings yet
- 08 Class Algebra AssgDocument7 pages08 Class Algebra AssgAnitaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fraction Formulas and ExpressionsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Fraction Formulas and ExpressionspocasallyNo ratings yet
- Important Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Document2 pagesImportant Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Tayyabah ShahNo ratings yet
- 10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFDocument11 pages10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFAntonio Torres PeñaNo ratings yet
- AP PQ BQ x: α θ β α θ β cos 1 cos cos = − −Document3 pagesAP PQ BQ x: α θ β α θ β cos 1 cos cos = − −sudhansh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: (Aq) (Aq) (S)Document3 pagesLab Report: (Aq) (Aq) (S)finaNo ratings yet
- Regional Mathematics Olympiad - 2015: Centre - DelhiDocument5 pagesRegional Mathematics Olympiad - 2015: Centre - DelhiRajkumar MajjiNo ratings yet
- Expansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesDocument5 pagesExpansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesghanshyamtewaniNo ratings yet
- Expansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesDocument5 pagesExpansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesghanshyamtewaniNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot × @JEE - Tests) 02 RA - (Vector-3D-02) - SolDocument6 pages(@bohring - Bot × @JEE - Tests) 02 RA - (Vector-3D-02) - SolRishi JangidNo ratings yet
- VECTORDocument2 pagesVECTORSoubhadra MahantiNo ratings yet
- Inequality11 TranQuocAnhDocument2 pagesInequality11 TranQuocAnhHai LeNo ratings yet
- Maths DPP SolutionDocument6 pagesMaths DPP SolutionYash OstwalNo ratings yet
- 6ei 110105 SDHC Trig ReviewDocument8 pages6ei 110105 SDHC Trig ReviewCarolyn Copeland LangNo ratings yet
- QE Determinant & Matrices SOLUTION FOR DROPPER PDFDocument37 pagesQE Determinant & Matrices SOLUTION FOR DROPPER PDFRaahiNo ratings yet
- A Special Class of InequalitiesDocument10 pagesA Special Class of InequalitiesVũ Tiến GiápNo ratings yet
- LOG TRI QB SolDocument34 pagesLOG TRI QB SolRahul JainNo ratings yet
- ТРИГОНОМЕТРИЯ ФОРМУЛИ помощDocument1 pageТРИГОНОМЕТРИЯ ФОРМУЛИ помощkrisrumenov007No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation - DPP 01 (Extra DPP) - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Document3 pagesQuadratic Equation - DPP 01 (Extra DPP) - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024prashantyadavpky07No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem NotesDocument5 pagesPythagorean Theorem NotespeterashNo ratings yet
- Aims Tutorial: (VSAQ)Document9 pagesAims Tutorial: (VSAQ)madhuNo ratings yet
- Vol45 No2 C PDFDocument15 pagesVol45 No2 C PDFJLNo ratings yet
- MS Xii Maths PB3 2023-24Document9 pagesMS Xii Maths PB3 2023-24abhay012abhay3No ratings yet
- 2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsDocument5 pages2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsWinnie SitNo ratings yet
- 10.Document8 pages10.7766xh82xsNo ratings yet
- Sin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsDocument10 pagesSin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsChetnaNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ftre-2023-Sample Paper-Class-Viii-P3-S&mDocument11 pagesFtre-2023-Sample Paper-Class-Viii-P3-S&mReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Scopus Preview - Scopus - International Journal of Membrane Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageScopus Preview - Scopus - International Journal of Membrane Science and TechnologyReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes MCQsReshmiRai100% (1)
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsReshmiRai100% (1)
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data Handling MCQsDocument3 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data Handling MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Hasyanandam December 2022Document52 pagesHasyanandam December 2022ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Application Format For Selection of Chairperson/Members To Child Welfare Committee and Social Worker Members To Juvenile Justice BoardDocument5 pagesApplication Format For Selection of Chairperson/Members To Child Welfare Committee and Social Worker Members To Juvenile Justice BoardReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Answer: Name: Student ID #: Section #: 12 / 14Document2 pagesAnswer: Name: Student ID #: Section #: 12 / 14ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- 4-2 Area Under A CurveDocument8 pages4-2 Area Under A CurveReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- We The Stars If We At..: Spoken EnglishDocument4 pagesWe The Stars If We At..: Spoken EnglishReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Q&A - MNK Payment StructureDocument1 pageQ&A - MNK Payment StructureReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Butter y Mating Optimization: January 2016Document14 pagesButter y Mating Optimization: January 2016ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Columbus Discovered America!Document4 pagesColumbus Discovered America!ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathematics Mind Map enDocument32 pagesIb Mathematics Mind Map enFatito CevallosNo ratings yet
- For More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IDocument4 pagesFor More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - Il8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Matlab Code - 2D Structured and Unstructred MeshDocument12 pagesMatlab Code - 2D Structured and Unstructred MeshAbhiyan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Prism P.U. Science College: A B ABDocument2 pagesPrism P.U. Science College: A B ABChinmay SultanpuriNo ratings yet
- สถิตย์ศาสตร์วิศวะกรรม จุฬาDocument136 pagesสถิตย์ศาสตร์วิศวะกรรม จุฬาKru Boss Suddee100% (1)
- Differentiation and IntegrationDocument16 pagesDifferentiation and Integrationazmat18No ratings yet
- Linear Relationships Math NotesDocument32 pagesLinear Relationships Math NotesWeb Books100% (1)
- Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and The Unit CellDocument6 pagesEarth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and The Unit CellMukesh BohraNo ratings yet
- Allcomic 1914Document80 pagesAllcomic 1914waeNo ratings yet
- P3 Turunan Fungsi AljabarDocument27 pagesP3 Turunan Fungsi AljabarChaiRun AveiroNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q2 Week 5Document3 pagesMath 10 Q2 Week 5Ken FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Caucasus MO 2022Document2 pagesCaucasus MO 2022Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- ST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamDocument13 pagesST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamTommy UwuuwuNo ratings yet
- Altair Hyperworks Hypermesh 7 Basic Training Tutorial Day2Document153 pagesAltair Hyperworks Hypermesh 7 Basic Training Tutorial Day2Madhan Babu100% (1)
- Clipping Using Homogeneous CoordinatesDocument7 pagesClipping Using Homogeneous CoordinateshendersonNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics and Spiritual DimensionsDocument16 pagesVedic Mathematics and Spiritual Dimensionsgerom100% (1)
- Question Paper Paper 1R June 2014 PDFDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper Paper 1R June 2014 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Pchapter 1Document3 pagesPchapter 1Burak OrsNo ratings yet
- Math7 2Document19 pagesMath7 2Jerry DNo ratings yet
- 1 To 35 PDFDocument67 pages1 To 35 PDFSanthoshsir VadhyarNo ratings yet
- MELC Grade 10 1st To 4thDocument8 pagesMELC Grade 10 1st To 4thJoey De LunaNo ratings yet
- TechDraft 7 - 8-Module 5bDocument20 pagesTechDraft 7 - 8-Module 5bLeoben GalimaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14Document8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14api-245300570No ratings yet
- Researches in The Lunar Theory Author(s) : G. W. Hill Source: American Journal of Mathematics, 1878, Vol. 1, No. 1 (1878), Pp. 5-26 Published By: The Johns Hopkins University PressDocument23 pagesResearches in The Lunar Theory Author(s) : G. W. Hill Source: American Journal of Mathematics, 1878, Vol. 1, No. 1 (1878), Pp. 5-26 Published By: The Johns Hopkins University PresskommallNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3Jen AmundsenNo ratings yet
- Maths CirclesDocument28 pagesMaths CirclesAdhi AdhiNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Ccss Mig Unit 4 Draft - 9!23!13Document9 pagesAlg 2 Ccss Mig Unit 4 Draft - 9!23!13rcarteagaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDocument34 pagesProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
Vector Algebra Solutions
Vector Algebra Solutions
Uploaded by
ReshmiRaiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Vector Algebra Solutions
Vector Algebra Solutions
Uploaded by
ReshmiRaiCopyright:
Available Formats
JEE Mains 2020 Total Marks
80
Chapter wise Tests
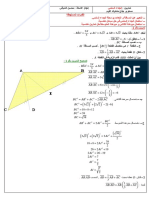
1. (c) c +a c + a − 2b
BE = OE − OB = −b =
R = P + Q + 2 PQ cos
2 2 2
Similarly, 2 2 and
a + b − 2c
CF =
( 7 Q) = P + Q + 2 PQ cos 60
2 2 2
2 .
7 Q = P + Q + PQ P + PQ − 6 Q = 0
2 2 2 2
Now, AD + BE + CF
P + 3 PQ − 2 PQ − 6 Q = 0
2 2
b + c − 2a c + a − 2 b a + b − 2c
= + + =0
2 2 2
P(P + 3Q) − 2Q(P + 3Q) = 0
.
5. (c)
(P − 2Q)(P + 3Q) = 0 If x be the position vector of B, then a divides AB in the ratio
P − 2Q = 0 or P + 3Q = 0 2 : 3.
P 2 x + 3(a + 2 b )
=2 a=
P − 2 Q = 0 Q 2+3
From .
2. (b) 5 a − 3 a − 6 b = 2 x x = a − 3 b.
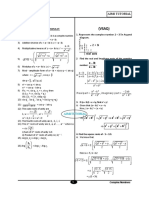
R cos = 6 cos 0 + 2 2 cos(180 o − B) + 5 cos 270 o 6. (c)
a .b = aa cos 120
,
| a | =| b | = a (say)
a2
−8 = − a=4
2
(Negative sign does not occur in moduli).
7. (c)
OA = P1 i, CB = − P1 i, OB = − P1 i + Pj
Let
R cos = 6 − 2 2 cos B …..(i)
R sin = 6 sin 0 + 2 2 sin(180 − B) + 5 sin 270
o o
R sin = 2 2 sin B − 5 …..(ii)
From (i) and (ii),
R 2 = 36 + 8 cos 2 B − 24 2 cos B + 8 sin2 B + 25 − 20 2 sin B
= 61 + 8(cos 2 B + sin2 B) − 24 2 cos B − 20 2 sin B OB . j (− P1i + Pj) . j 1
= cos 60 =
ABC is a right angled isosceles triangle OB P12 + P 2 2
i.e., B = C = 45
2 P = P 2 + P12 P1 = P 3
1 1
= 61 + 8 (1) − 24 2 − 20 2
R2 2 2 = 25 | OB | = P 2 + P12 = P 2 + 3 P 2 = 2 P.
R =5 . 8. (a)
3. (a) It is obvious.
Resultant vector 9. (c)
= (2i + 4 j − 5 k) + (i + 2 j + 3 k) = 3i + 6 j − 2k
| a b | = 1 | sin | = 1 sin = 1 =
3i + 6 j − 2k 1 2.
= = (3 i + 6 j − 2 k)
Unit vector 9 + 36 + 4 7
. 10. (a)
4. (a) (a − b) (a + b) = a a − b a + a b − b b
b +c b + c − 2a = a b − b a = a b + a b = 2(a b).
AD = OD − OA = −a =
2 2 , 11. (d)
(where O is the origin for reference) ab 1
= (2i + k).
| a b| 5
Unit vector is equal to
12. (c)
i j k
ab = 3 2 − 1 = −5 i + 3 j − 9 k.
12 5 − 5
IN ASSOCIATION WITH JEEMAIN.GURU
JEE Mains 2020 Total Marks
80
Chapter wise Tests
−5 i + 3 j − 9 k The vector equation of a plane through the line of intersection
ab = .
Unit vector along 115 of the planes r.(i + 3 j − k) = 0 and r.( j + 2k) =0 can be written
13. (b) as
A vector perpendicular to the plane determined by the points (r.(i + 3 j − k)) + (r.( j + 2k)) = 0 .....(i)
P(1, − 1, 2); Q(2, 0, − 1) R(0, 2, 1)
and is given by This passes through 2i + j − k
QR PR (−2i + 2 j + 2k) (−i + 3 j − k) (2i + j − k).(i + 3 j − k) + (2i + j − k).( j + 2k) = 0
2i + j + k 2i + j + k
= = . or (2 + 3 + 1) + (0 + 1 − 2) = 0 = 6
4 +1 +1 6
Put the value of in (i) we get
Therefore, unit vector
14. (a)
r.(i + 9 j + 11k) = 0 , which is the required plane.
[a b b c c a] = (a b). [(b c ) (c a)]
= (a b). ([b c a] c − [b c c ] a) = (a b). ([b c a] c − 0)
= [b c a][a b c ] = [a b c ][a b c ] = 4.4 = 16.
15. (d)
[i k j] + [k j i] + [j k i] = [i k j] + [i k j] − [i k j] = [i k j] = −1
.
16. (a)
(a b) c = (a . c ) b − (b . c ) a
= (3 + 2 + 4)(2i + j − k) − (2 − 2 − 2)(3i − j + 2k)
= 18i + 9 j − 9 k + 6i − 2 j + 4 k = 24 i + 7 j − 5 k .
17. (a)
The plane is 2 x − y + z = 4 and the line is
x −1 y − 2 z +1
= =
1 −1 1
2 +1 +1 4 2 2 2 2
sin = = = = sin−1
3 3
6 3 18 .
18. (c)
It is obvious.
19. (b)
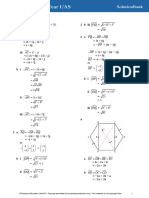
Let be the angle made by n with z-axis.
1
l = cos 45 o = ,
Then direction cosines of n are 2
1
m = cos 60 o =
2 and n = cos .
2
1 1
2
l 2 + m 2 + n 2 = 1 + + n2 = 1
2 2
1 1
n2 = n=
4 2, [ is acute, n = cos 0 ]
| n|= 8 n =| n | (li + m j + nk)
We have ,
1 1 1
n = 8 i + j + k
2 2 2 = 4 2i + 4 j + 4 k
( 2 ,−1, 1)
The required plane passes through the point having
position vector a = 2 i − j + k .
r. n = a. n
So, its vector equation is (r − a ).n = 0 or
r.(4 2i + 4 j + 4 k) = ( 2 i − j + k).(4 2i + 4 j + 4 k)
r. ( 2 i + j + k) = 2
.
20. (a)
IN ASSOCIATION WITH JEEMAIN.GURU
You might also like
- How To Calculate Drum Nip LoadDocument1 pageHow To Calculate Drum Nip Loadsushil kumar100% (2)
- SymmetryDocument60 pagesSymmetryDeepak TholiaNo ratings yet
- Dad S TheoremDocument17 pagesDad S TheoremyvazzocaanhdvpmlfmNo ratings yet
- InequalityDocument2 pagesInequalityRijul SainiNo ratings yet
- AbcdDocument2 pagesAbcdnguyenthedanNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Quadratic Equation: Exercise # 1Document5 pagesSolutions - Quadratic Equation: Exercise # 1Dhruv AsodariaNo ratings yet
- Senior Maths 2a SolutionsDocument91 pagesSenior Maths 2a Solutionsakrammohammed786000No ratings yet
- Aljdaa Alslmi Tmarin Mhlola 1 1Document4 pagesAljdaa Alslmi Tmarin Mhlola 1 1wahbi yassineNo ratings yet
- Solution: ProblemDocument2 pagesSolution: ProblemĐặng KhánhNo ratings yet
- Alevelsb p1 Ex11dDocument2 pagesAlevelsb p1 Ex11dKeerthy verNo ratings yet
- Iia Iib Vsaq SolDocument41 pagesIia Iib Vsaq Solyashwanth padakandlaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Mechanical Engg. Examination, 2010: 4 Marks For NeatnessDocument2 pagesBachelor of Mechanical Engg. Examination, 2010: 4 Marks For Neatnessrony RkNo ratings yet
- 1b. Vectors - AnswersDocument2 pages1b. Vectors - AnswersDojeNo ratings yet
- Vectors Imp Questions Paper 2 SolutionsDocument4 pagesVectors Imp Questions Paper 2 Solutionschaynitt30No ratings yet
- Conditional of Trigonometric IndentitiesDocument2 pagesConditional of Trigonometric IndentitiesJaishree RamNo ratings yet
- Radicales 1bc SolDocument6 pagesRadicales 1bc SolISABELNo ratings yet
- Shortlist Jbmo 2016 v7-1Document27 pagesShortlist Jbmo 2016 v7-1Lyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Math Question BankDocument4 pagesMath Question BankPramit Kumar PalNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations Solutions Basic Level DPPDocument12 pagesQuadratic Equations Solutions Basic Level DPPAnkit RanjanNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4Document4 pagesExercise 4kchaurasia868No ratings yet
- 1 Chapter Test (Vector) SolutionsDocument2 pages1 Chapter Test (Vector) Solutionsyashanshi20721No ratings yet
- JEE Mains 2020 Chapter Wise Tests: C B A C B A XDocument2 pagesJEE Mains 2020 Chapter Wise Tests: C B A C B A XMadhu SudhanNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Determinants 4.2 Sol PDFDocument7 pages12 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Determinants 4.2 Sol PDFJijish RANo ratings yet
- Chapter Review 7Document14 pagesChapter Review 7nasehaNo ratings yet
- Determinants 5 PDFDocument5 pagesDeterminants 5 PDFzaid khanNo ratings yet
- Inequality12 UnknownAuthorDocument1 pageInequality12 UnknownAuthorHai LeNo ratings yet
- CBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP13Document12 pagesCBSE I Succeed Math 12th SP13studyshivansh.17No ratings yet
- A Practice Set 1Document5 pagesA Practice Set 1aNo ratings yet
- SOT DPP 1 To 7 SolutionsDocument14 pagesSOT DPP 1 To 7 SolutionsSainath ChawaliNo ratings yet
- Welq T Mvaviy Mwyz - 11K Aa VQ: M RBKXJ Cixÿv Bs-02Document1 pageWelq T Mvaviy Mwyz - 11K Aa VQ: M RBKXJ Cixÿv Bs-02Murat MuratNo ratings yet
- QE and Complex Numbers DPPDocument9 pagesQE and Complex Numbers DPPsatishmhbdNo ratings yet
- ChÖÔng Xi: NhaÄn DaÏn G Tam GiaÙcDocument17 pagesChÖÔng Xi: NhaÄn DaÏn G Tam GiaÙcnessạ_chaos_knightNo ratings yet
- 08 Class Algebra AssgDocument7 pages08 Class Algebra AssgAnitaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Fraction Formulas and ExpressionsDocument2 pagesAlgebraic Fraction Formulas and ExpressionspocasallyNo ratings yet
- Important Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Document2 pagesImportant Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 2.4Tayyabah ShahNo ratings yet
- 10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFDocument11 pages10 0000@Cms Math CA@Crux@v44@n3@Solutions443 PDFAntonio Torres PeñaNo ratings yet
- AP PQ BQ x: α θ β α θ β cos 1 cos cos = − −Document3 pagesAP PQ BQ x: α θ β α θ β cos 1 cos cos = − −sudhansh kumarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: (Aq) (Aq) (S)Document3 pagesLab Report: (Aq) (Aq) (S)finaNo ratings yet
- Regional Mathematics Olympiad - 2015: Centre - DelhiDocument5 pagesRegional Mathematics Olympiad - 2015: Centre - DelhiRajkumar MajjiNo ratings yet
- Expansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesDocument5 pagesExpansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesghanshyamtewaniNo ratings yet
- Expansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesDocument5 pagesExpansions and Factorisations Allen Thane NotesghanshyamtewaniNo ratings yet
- (@bohring - Bot × @JEE - Tests) 02 RA - (Vector-3D-02) - SolDocument6 pages(@bohring - Bot × @JEE - Tests) 02 RA - (Vector-3D-02) - SolRishi JangidNo ratings yet
- VECTORDocument2 pagesVECTORSoubhadra MahantiNo ratings yet
- Inequality11 TranQuocAnhDocument2 pagesInequality11 TranQuocAnhHai LeNo ratings yet
- Maths DPP SolutionDocument6 pagesMaths DPP SolutionYash OstwalNo ratings yet
- 6ei 110105 SDHC Trig ReviewDocument8 pages6ei 110105 SDHC Trig ReviewCarolyn Copeland LangNo ratings yet
- QE Determinant & Matrices SOLUTION FOR DROPPER PDFDocument37 pagesQE Determinant & Matrices SOLUTION FOR DROPPER PDFRaahiNo ratings yet
- A Special Class of InequalitiesDocument10 pagesA Special Class of InequalitiesVũ Tiến GiápNo ratings yet
- LOG TRI QB SolDocument34 pagesLOG TRI QB SolRahul JainNo ratings yet
- ТРИГОНОМЕТРИЯ ФОРМУЛИ помощDocument1 pageТРИГОНОМЕТРИЯ ФОРМУЛИ помощkrisrumenov007No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation - DPP 01 (Extra DPP) - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024Document3 pagesQuadratic Equation - DPP 01 (Extra DPP) - JEE Ultimate Crash Course 2.0 2024prashantyadavpky07No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem NotesDocument5 pagesPythagorean Theorem NotespeterashNo ratings yet
- Aims Tutorial: (VSAQ)Document9 pagesAims Tutorial: (VSAQ)madhuNo ratings yet
- Vol45 No2 C PDFDocument15 pagesVol45 No2 C PDFJLNo ratings yet
- MS Xii Maths PB3 2023-24Document9 pagesMS Xii Maths PB3 2023-24abhay012abhay3No ratings yet
- 2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsDocument5 pages2122 S6 Math Pre-Mock Exam Paper 2 - AnsWinnie SitNo ratings yet
- 10.Document8 pages10.7766xh82xsNo ratings yet
- Sin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsDocument10 pagesSin Cos Sin 1 Cos 1: Class - Xii Mathematics Ncert SolutionsChetnaNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYFrom EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Ftre-2023-Sample Paper-Class-Viii-P3-S&mDocument11 pagesFtre-2023-Sample Paper-Class-Viii-P3-S&mReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Scopus Preview - Scopus - International Journal of Membrane Science and TechnologyDocument1 pageScopus Preview - Scopus - International Journal of Membrane Science and TechnologyReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 10 Visualising Solid Shapes MCQsReshmiRai100% (1)
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 4 Practical Geometry MCQsReshmiRai100% (1)
- Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQsDocument2 pagesClass 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data Handling MCQsDocument3 pagesClass 8 Maths Chapter 5 Data Handling MCQsReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Hasyanandam December 2022Document52 pagesHasyanandam December 2022ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Application Format For Selection of Chairperson/Members To Child Welfare Committee and Social Worker Members To Juvenile Justice BoardDocument5 pagesApplication Format For Selection of Chairperson/Members To Child Welfare Committee and Social Worker Members To Juvenile Justice BoardReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Answer: Name: Student ID #: Section #: 12 / 14Document2 pagesAnswer: Name: Student ID #: Section #: 12 / 14ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- 4-2 Area Under A CurveDocument8 pages4-2 Area Under A CurveReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- We The Stars If We At..: Spoken EnglishDocument4 pagesWe The Stars If We At..: Spoken EnglishReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Q&A - MNK Payment StructureDocument1 pageQ&A - MNK Payment StructureReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Butter y Mating Optimization: January 2016Document14 pagesButter y Mating Optimization: January 2016ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Columbus Discovered America!Document4 pagesColumbus Discovered America!ReshmiRaiNo ratings yet
- Ib Mathematics Mind Map enDocument32 pagesIb Mathematics Mind Map enFatito CevallosNo ratings yet
- For More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - IDocument4 pagesFor More Sample Papers Visit:: Summative Assessment - Il8o8r8d8s8i8v8No ratings yet
- Matlab Code - 2D Structured and Unstructred MeshDocument12 pagesMatlab Code - 2D Structured and Unstructred MeshAbhiyan PaudelNo ratings yet
- Prism P.U. Science College: A B ABDocument2 pagesPrism P.U. Science College: A B ABChinmay SultanpuriNo ratings yet
- สถิตย์ศาสตร์วิศวะกรรม จุฬาDocument136 pagesสถิตย์ศาสตร์วิศวะกรรม จุฬาKru Boss Suddee100% (1)
- Differentiation and IntegrationDocument16 pagesDifferentiation and Integrationazmat18No ratings yet
- Linear Relationships Math NotesDocument32 pagesLinear Relationships Math NotesWeb Books100% (1)
- Earth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and The Unit CellDocument6 pagesEarth Materials Lab 2 - Lattices and The Unit CellMukesh BohraNo ratings yet
- Allcomic 1914Document80 pagesAllcomic 1914waeNo ratings yet
- P3 Turunan Fungsi AljabarDocument27 pagesP3 Turunan Fungsi AljabarChaiRun AveiroNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Q2 Week 5Document3 pagesMath 10 Q2 Week 5Ken FerrolinoNo ratings yet
- Caucasus MO 2022Document2 pagesCaucasus MO 2022Hoàng MinhNo ratings yet
- ST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamDocument13 pagesST - Stephen - Girl - College - F3 Math P1 17 18 Final ExamTommy UwuuwuNo ratings yet
- Altair Hyperworks Hypermesh 7 Basic Training Tutorial Day2Document153 pagesAltair Hyperworks Hypermesh 7 Basic Training Tutorial Day2Madhan Babu100% (1)
- Clipping Using Homogeneous CoordinatesDocument7 pagesClipping Using Homogeneous CoordinateshendersonNo ratings yet
- Vedic Mathematics and Spiritual DimensionsDocument16 pagesVedic Mathematics and Spiritual Dimensionsgerom100% (1)
- Question Paper Paper 1R June 2014 PDFDocument20 pagesQuestion Paper Paper 1R June 2014 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Pchapter 1Document3 pagesPchapter 1Burak OrsNo ratings yet
- Math7 2Document19 pagesMath7 2Jerry DNo ratings yet
- 1 To 35 PDFDocument67 pages1 To 35 PDFSanthoshsir VadhyarNo ratings yet
- MELC Grade 10 1st To 4thDocument8 pagesMELC Grade 10 1st To 4thJoey De LunaNo ratings yet
- TechDraft 7 - 8-Module 5bDocument20 pagesTechDraft 7 - 8-Module 5bLeoben GalimaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14Document8 pagesCalculus Capcity Matrix Second Sememster 13 14api-245300570No ratings yet
- Researches in The Lunar Theory Author(s) : G. W. Hill Source: American Journal of Mathematics, 1878, Vol. 1, No. 1 (1878), Pp. 5-26 Published By: The Johns Hopkins University PressDocument23 pagesResearches in The Lunar Theory Author(s) : G. W. Hill Source: American Journal of Mathematics, 1878, Vol. 1, No. 1 (1878), Pp. 5-26 Published By: The Johns Hopkins University PresskommallNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document9 pagesChapter 3Jen AmundsenNo ratings yet
- Maths CirclesDocument28 pagesMaths CirclesAdhi AdhiNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Ccss Mig Unit 4 Draft - 9!23!13Document9 pagesAlg 2 Ccss Mig Unit 4 Draft - 9!23!13rcarteagaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDocument34 pagesProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengNo ratings yet