Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Teaching Listening-1
Teaching Listening-1
Uploaded by
Carlos SanchezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Teaching Listening-1
Teaching Listening-1
Uploaded by
Carlos SanchezCopyright:
Available Formats
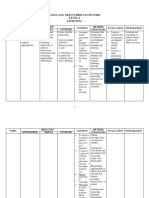
A HISTORICAL SKETCH Myths and Misconceptions about Teaching
Listening Listening comprehension Is an interactive process
Spotlight in 1970s - TPR and Natural Listening is a "passive" skill is the psychomotor as the brain acts on the
Approach. Listening is a "one-way" process process of reciving impulses, bringing to
Vandergrif 2013 Listening is an individual process waves through the ear bear a number of
A good listener in L1 is a good listener in L2. Listening skills are acquired subconsciously and transmittting nerve different cognitive and
Flowerdew - students just "absorb" them impulses to the brain. affective mechanisms.
Strategies are needed to improve listening Listening equals comprehension
Listening and speaking should be taught
separately
Andrea Nayeli Medina Palafox
Nadia Montserrat Corona Muñoz
Listening is an active Through listening, we internalize linguistic information, without which we could
no produce language.
Joshua Jiménez Carro
Andrea Cano process
Eva Magali Vega Nava
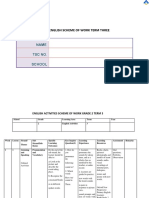
1. Decaring auditory
sounds (raw speech)
Tasks for assessing listening: 2. Determining the
Distinguish between similars function of the speech
(I can go/ I can´t go) event
By Ss's responses 3. Activating schemata
(What time is it?) 4. Assigning literal
Selective tasks meanings.
(Verbal information)
Extensive activities
Assessment (dialogues) 5. Assigning intended
Unplanned, spontaneous, meaning
unconsciously judged by T 6. Determining the
Test demand for shoet- or long-
Deliberated, term memory.
conventionalized 7. Retaining essential Monologues
feedback, planned. information or meanings
1. Planned
2. Spontaneus
Listening
comprehension
*Begining level, Assessing
processess
*Intermediate level and
*Advanced level
listening in the
learners;
each may contain
classroom
botom-up, top-down and
Begining level
interactive excercises.
Types of Dialogues
1. Interpersonal
listeners:
Botom Up= Goal: Listening
spoken 2. Transactional
for Normal Sentence World
Order. language
Top-down= Goal:Listening
for Normal Sentence World
Teaching
Intermediate level
Order.
Interactive
Listening
listeners:
Botom Up= Goal:
Exercises=Following
Directions. techniques Clustering
Advanced level
Recognizing Fast Speech
Begining- Redundancy
Listening
Forms
listeners: Reduced forms
Botom Up= Goal: Identify
Top-down= Goal: Listen to
Identify the Speaker or the
Advanced Performance
Specific Points of Topic. variables
Information. Interactive Exercises:
Top-down= Goal: Find the Listen to Confirm Your
Main Idea of a Lecture Expectations.
Segment.
Interactive Exercises: Use
Incoming Details to
Determine the Accuracy of What makes
Predictions about Content. Include:
1. A focus on listening
listening difficult?
Principles for
Colloquial
2. Stimulating language
techniques Rate of Delivery
3. Authentic language teaching Stress, Rhythm,
and Intonation
and context
listening skills Types of Micro- and Interaction
4. Pre-, While classroom macro skills
and Post-
Listening listening
techniques
performance
Micro-skills
Interactive A top-down approach.
Those activities
By: which interaction -Retain chunks of language of different lengths
5. Check Reactive
Doing Ss - T / T - Ss are -Discriminate among the distintive sound of english
listening 7. Buttom-up Brief choral or implicited
Choosing comprehension individual drills -Recognize reduced forms of words
and top-down
Answering
6. Encourage the activities -distinguish word boundaries
Modeling MACRO
development of Recognize:
-Process speech a different rades of delivery
strategies Extensive -cohesive device
in spoken discourse -process pauses
Intensive Long activities -Communicative functions
-detect sentence constitues
Focusing on like dialogues -Infer situations using real-world
knowledge. recognize a particular meaning
components or lectures -Predict outcomes, infer links
between events, deduce causes
of discourse and effects, and detect such
Selective relations as main idea, supporting
idea.
By scanning
Key words Responsive -Distinguish between literal and
look forward iimplied meanings.
Demanding -Use facial, kinesic, body language,
Nonverbal cues to for specific
and other nonverbal clues to
responses to decipher meanings.
meaning Ss info.
-Develop and use a battery of
listening strategies: detecting key
Activate background words, the meaning of words from
context, apelling for help etc.
information
You might also like
- Explicit Teaching Grade 1Document45 pagesExplicit Teaching Grade 1Divine Grace Samortin95% (22)
- Learning To Sing: A Transformative Approach to Vocal Performance and InstructionFrom EverandLearning To Sing: A Transformative Approach to Vocal Performance and InstructionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Dance and Sexuality (Lynne) PDFDocument31 pagesDance and Sexuality (Lynne) PDFLuis Ángel Bejarano Maluquish100% (2)
- Ela Service Learning Lesson Plan 1Document3 pagesEla Service Learning Lesson Plan 1api-490377001No ratings yet
- Article Buddy User ManualDocument6 pagesArticle Buddy User ManualWrestling AddictionNo ratings yet
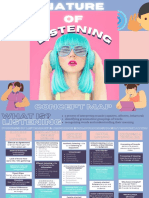
- Nature of ListeningDocument29 pagesNature of ListeningIrin JardineroNo ratings yet
- Verbotonal MethodDocument23 pagesVerbotonal MethodScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Methods Historical Context Teacher's Role Student's Role Ability Class Advantages Disadvantages Brown's Principles Grammar TranslationDocument5 pagesMethods Historical Context Teacher's Role Student's Role Ability Class Advantages Disadvantages Brown's Principles Grammar TranslationLuigi OliNo ratings yet
- BROCHUREDocument2 pagesBROCHUREAvielle SalvatureNo ratings yet
- Task Title: Observation Task 5: Literacy Software / Web-Based ProgramsDocument3 pagesTask Title: Observation Task 5: Literacy Software / Web-Based Programsapi-296835930No ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Listening and Reading: Prepared by Kinsley NG Sen Fa, Segi College Penang, Program DECEDocument23 pagesLesson 4: Listening and Reading: Prepared by Kinsley NG Sen Fa, Segi College Penang, Program DECEKinsley Ng Sen FaNo ratings yet
- Dillard D ModulefiveassignmentDocument3 pagesDillard D Modulefiveassignmentapi-643705176No ratings yet
- As17 Teaching and Assessment of The Macro SkillsDocument9 pagesAs17 Teaching and Assessment of The Macro SkillsJane ButalidNo ratings yet
- 8 Profile Profile Profile Profile ProfileDocument9 pages8 Profile Profile Profile Profile ProfileDeborahCordeiroNo ratings yet
- Week 11 Models of ListeningDocument3 pagesWeek 11 Models of ListeningChing ServandoNo ratings yet
- Mapa Conceptual Listening 2Document1 pageMapa Conceptual Listening 2Eréndira CovixNo ratings yet
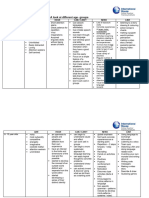
- A Look at 4 Different Age GroupsDocument4 pagesA Look at 4 Different Age GroupsluisNo ratings yet
- Teaching of ListeningDocument107 pagesTeaching of ListeningAre KushiNo ratings yet
- Listening Presentation 1Document9 pagesListening Presentation 1KROSDEVIL505No ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument2 pagesConcept MapGeraldine FloresNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 Curriculum Guide - Language ArtsDocument111 pagesGrade 4 Curriculum Guide - Language ArtsJazminie OsborneNo ratings yet
- Teaching Listening and SpeakingDocument17 pagesTeaching Listening and SpeakingHarry Engelo Anthony PaalaNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics Mind MapDocument1 pagePsycholinguistics Mind MapScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Working Memory and Auditory Processing in School-Age ChildrenDocument15 pagesWorking Memory and Auditory Processing in School-Age ChildrenvviraaNo ratings yet
- DinaTsagariJaya 2016 7AssessingListening HandbookOfSecondLanguDocument16 pagesDinaTsagariJaya 2016 7AssessingListening HandbookOfSecondLangua01794115No ratings yet
- Typology of Children With Special NeedsDocument1 pageTypology of Children With Special NeedsKryselle DianopraNo ratings yet
- Methologi ES Proponen TS Approach Design ProcedureDocument6 pagesMethologi ES Proponen TS Approach Design ProcedureG-yan Dungan MamuyacNo ratings yet
- 4 170502181330 PDFDocument9 pages4 170502181330 PDFRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument9 pagesListening SkillsRawand AwniNo ratings yet
- Differences in Auditory ProcessingDocument6 pagesDifferences in Auditory ProcessingRubens RibeiroNo ratings yet
- TNLP Teacher's Book 2Document10 pagesTNLP Teacher's Book 2roberto abel santaella hinojosaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document14 pagesPresentation 1sadia mushtaqNo ratings yet
- Teaching To ListenDocument34 pagesTeaching To ListenArlenne M FernandezNo ratings yet
- Theory/Approach/Method Proponent and Year PublishedDocument2 pagesTheory/Approach/Method Proponent and Year PublishedDanizelle Kaye Cadocoy BernardoNo ratings yet
- Purcom NotesDocument2 pagesPurcom NotesPeaches PHNo ratings yet
- Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesListening SkillsPrince RathoreNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Issues in ListenigDocument23 pages6.1 Issues in ListenigIffat BasirNo ratings yet
- Songs: PsychologicalDocument3 pagesSongs: PsychologicalPaloma Perez UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Infography Argente CarlosDocument2 pagesInfography Argente Carloscarlos argenteNo ratings yet
- Ultra HandoutsDocument3 pagesUltra HandoutsArmina GuiamalonNo ratings yet
- Grade 1: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument5 pagesGrade 1: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayEvan Maagad LutchaNo ratings yet
- BCSS Sec Unit 1 Listening and Speaking SkillsDocument16 pagesBCSS Sec Unit 1 Listening and Speaking Skillsjiny benNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Neurological and Cognitive ConsiderationsDocument29 pagesGroup 2 - Neurological and Cognitive ConsiderationsluzNo ratings yet
- Pre-Kindergarten & Transitional Kindergarten: Developing Early LearnersDocument17 pagesPre-Kindergarten & Transitional Kindergarten: Developing Early LearnersMTee DNo ratings yet
- ListeningDocument13 pagesListeningErwin Maverick VelascoNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Listening PDFDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Listening PDFJHANELLE MAE PALAFOXNo ratings yet
- Competence: Communicative Language TeachingDocument2 pagesCompetence: Communicative Language TeachingEVAPLNo ratings yet
- Phonology and Additional Language Learners - JVDL 16Document6 pagesPhonology and Additional Language Learners - JVDL 16Signup LettersNo ratings yet
- IV TERM - LESSON PLAN 2 - UNIT 08 - 3rd GRADE - QUINTANADocument5 pagesIV TERM - LESSON PLAN 2 - UNIT 08 - 3rd GRADE - QUINTANARuth Violeta Ore RojasNo ratings yet
- English Grade 2Document18 pagesEnglish Grade 2Omyjayd KeNo ratings yet
- Signs of Attentive/Active ListeningDocument2 pagesSigns of Attentive/Active Listeningsol cityNo ratings yet
- Early Language Acquisition: Cracking The Speech CodeDocument13 pagesEarly Language Acquisition: Cracking The Speech CodeYanpinginbkkNo ratings yet
- The Listening-Speaking ConnectionDocument3 pagesThe Listening-Speaking ConnectionRubens RibeiroNo ratings yet
- L1 - Listening StrategiesDocument14 pagesL1 - Listening StrategiesodsonstorageNo ratings yet
- Methods L1 Vocabulary Grammar PracticeDocument6 pagesMethods L1 Vocabulary Grammar PracticeSonya BladeNo ratings yet
- HEARING DISABILITY TriptychDocument3 pagesHEARING DISABILITY TriptychScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Power English BrochureDocument8 pagesPower English BrochureJay PadhNo ratings yet
- L2 - Listening SkillsDocument7 pagesL2 - Listening Skillscejix87209No ratings yet
- Listening As A Lifelong Learning Skill-What, Why, and How: October 2018Document7 pagesListening As A Lifelong Learning Skill-What, Why, and How: October 2018imranvdp306c2No ratings yet
- Participant's Number: 19060115710097 Name: Aditiya Firmansyah, S.Pd.IDocument1 pageParticipant's Number: 19060115710097 Name: Aditiya Firmansyah, S.Pd.Iteuku aditiyaNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Good ListenerDocument26 pagesHow To Be A Good ListenerHarmanjit Dhillon100% (1)
- Chapter 6 ListeningDocument3 pagesChapter 6 ListeningChelsea NacinoNo ratings yet
- 1) HearingDocument2 pages1) HearingRemar Jhon YambaNo ratings yet
- Model Sentence: He's Just Left.: Subj + Have' (For 3Document6 pagesModel Sentence: He's Just Left.: Subj + Have' (For 3Dmitriy DoroshenkoNo ratings yet
- The Stereotyped Versus The Empowered TheDocument45 pagesThe Stereotyped Versus The Empowered ThePortia du BelmontNo ratings yet
- An Account of The Structure of Chinese Characters Under 300 Primary FormsDocument231 pagesAn Account of The Structure of Chinese Characters Under 300 Primary Formsneferisa100% (2)
- BRM Research ProjectDocument37 pagesBRM Research ProjectTanvi Thukral100% (1)
- Essay Writing Mechanics Nutri MonthDocument3 pagesEssay Writing Mechanics Nutri MonthMyka Andrea Panganiban GarciaNo ratings yet
- Mla Worksheet-220Document3 pagesMla Worksheet-220api-289656014100% (1)
- Rizal in DapitanDocument8 pagesRizal in DapitanPearl Garland Mendia100% (1)
- Rapport, Probing, NegotiationDocument49 pagesRapport, Probing, NegotiationyakarimNo ratings yet
- Valerie Domanski Resume 2022 LDTCDocument2 pagesValerie Domanski Resume 2022 LDTCapi-377293252No ratings yet
- ISE II - Independent Listening - CA2 (Big City)Document7 pagesISE II - Independent Listening - CA2 (Big City)cataleayNo ratings yet
- Kisi-Kisi Kompre YayankDocument45 pagesKisi-Kisi Kompre YayankGusti JihadNo ratings yet
- How It Works - MYMOVEDocument9 pagesHow It Works - MYMOVEJubaerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Outline JBDocument3 pagesLesson Outline JBapi-241811643No ratings yet
- Bilingual CountryDocument14 pagesBilingual CountryMariana AnencovNo ratings yet
- Mediation IntroductionDocument3 pagesMediation IntroductionAlexandra Cortés de la CruzNo ratings yet
- Reflection Essay 1 English 1301Document3 pagesReflection Essay 1 English 1301api-579831401No ratings yet
- Grade 11-Humanities and Social Sciences DAY Time Subjects TeachersDocument8 pagesGrade 11-Humanities and Social Sciences DAY Time Subjects TeachersHoney Lin LptNo ratings yet
- Reading SkillsDocument4 pagesReading SkillsDebrah NavajjahNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics Networks PDFDocument2 pagesFiber Optics Networks PDFJulieNo ratings yet
- 1 First Insight Into Business CorrespondenceDocument21 pages1 First Insight Into Business CorrespondenceNabilah Nur SalmaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Buying Behavior and Maslow Hierarchy of NeedsDocument31 pagesConsumer Buying Behavior and Maslow Hierarchy of NeedsBharat Bhushan Singh SinghNo ratings yet
- Technology and GlobalizationDocument5 pagesTechnology and GlobalizationKhalid T MohadNo ratings yet
- Edwards-Online Weekly Log Updated 2Document3 pagesEdwards-Online Weekly Log Updated 2Guyan GordonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan G9Document3 pagesLesson Plan G9TaTa AcusarNo ratings yet
- Communication in The Presence of Noise PDFDocument2 pagesCommunication in The Presence of Noise PDFSashaNo ratings yet
- IV Quadrant EContent DevelopmentDocument14 pagesIV Quadrant EContent DevelopmentrituchakravartyNo ratings yet