Professional Documents
Culture Documents
فحص الراس والرقبة
فحص الراس والرقبة
Uploaded by
Hiba AhmedOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
فحص الراس والرقبة
فحص الراس والرقبة
Uploaded by
Hiba AhmedCopyright:
Available Formats
Head & Neck
Bones:
The facial skeleton is composed of: mandible; maxilla; nasal;
palatine; lacrimal; vomer; zygoma; bones.
The cranial skeleton includes: frontal; temporal; parietal; occipital
bones.
Triangles of the Neck
Ant. & Post. -
Sternocleidomastoid M. – action,
relations – triangles
relations – Maj. Vessels
relations – Deep L. N.
The sternocleidomastoid muscle overlies the carotid sheath. The carotid sheath lies
lateral to the larynx. This sheath contains the common carotid artery, the internal jugular
vein, and the vagus nerve.
Important structures in the neck:
- Larynx – thy. & cric. Cart. - sites , details
- Thyroid G.
- Salivary Gs.
- Cervical L. N. – In details:
➔
+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
++++
Notes about Lymphadenopathy :-
➔ Lymphadenopathy is either Generalized or local – each is either due to
infection or malignancy [primary or secondary], other causes are rare like
autoimmune dis., storage dis.
➔ Examination of lymph nodes involves inspection and palpation.
Inflammation of the overlying skin and associated pain usually implies an
infective aetiology, whereas malignant lymphadenopathy is usually non-
tender.
➔ Determine the position, size, shape, consistency, mobility, tenderness
and whether it is an isolated lymph node or whether several coalesce. For the
Cervical & Axillary nodes, it is often helpful to relax overlying muscles during
their examination.
➔ It has been estimated that the neck contains more than 75 L. N. on each
side.
These are grouped in superficial & deep - longitudinal & circular L.N.s
➢ Sites:
Bruise = contusion = ecchymosis = كدمة
Abrasion = scratch = erosion = سحجة
Bad Body Odour
Main Causes of Bad Body Odour:
• Poor personal hygiene / Excessive sweating
• Extreme old age
• Major mental illness
• Alcohol or drug misuse
• Physical disability preventing normal hygiene
Bad Smell:
1. Halitosis (bad breath) is caused by decomposing food wedged between
the teeth, gingivitis, stomatitis, atrophic rhinitis and tumours of nasal
passages.
2. Tobacco, Alcohol
3. Foetor Hepaticus: ‘ammonia’ like smell in patients with liver failure.
4. Acetone like smell as in diabetic ketoacidosis or starvation
5. Uraemic foetor: fishy like smell as in uraemia
6. putrid or fetid smell of chronic anaerobic suppuration due to
bronchiectasis or lung abscess
7. foul-smelling belching in patients with gastric outlet obstruction
Characteristic features
Many disorders have characteristic facial or body features, which may aid
in early correct diagnosis, which is called ‘Spot Diagnosis’ like:
Acromegaly, Cushing syndrome, Down’s syndrome (trisomy 21),
Achondroplasia,
Examination of the Mouth
Always inspect the mouth with a good light and use a spatula.
■ Inspect the external appearance of the lips.
■ Retract the lips to see the buccal mucosa.
■ Push the cheek outwards to see the buccal side of the gum.
■ Push the tongue away from the inside of the gum and the floor of the
mouth.
■ Push the tongue to one side to see the lateral aspect of its posterior
third.
■ Depress the tongue to look at the fauces, tonsils and pharynx.
➔ Always remember to palpate the structures in the mouth bimanually, one
finger
inside and one outside.
➔ Always wear a glove [for protection from possible contagious lesions]
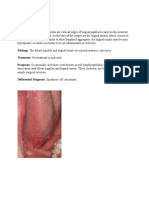
Abnormal Tongue Findings
• Tremor of the Tongue: can be due to anxiety, thyrotoxicosis,
delirium tremens or parkinson. [Fasciculation (irregular twitching of the tongue)
occurs in lower motor neurone disorders, e.g. motor neurone disease].
• Macroglossia (enlargement of the tongue) may occur in acromegaly,
amyloidosis or tumour infiltration.
• Oral thrush = White patches that may be scraped off the tongue are due
to the fungal yeast, Candida. Common causes include inhaled steroids,
immune deficiency, e.g. HIV and terminal illness.
• Glossitis is a smooth reddened tongue due to atrophy of the papillae. It
is common in alcoholics, in nutritional deficiencies of iron, folate and
vitamin B12, and in 30% of patients with coeliac disease. Glossitis may
cause a burning sensation over the tongue but usually a painful tongue is
a symptom of anxiety or depression.
• Leukoplakia is a thickened white patch that cannot be scraped off the
tongue. It may be premalignant.
You might also like
- BS en Iso 11064-3-2000 - (2019-10-09 - 04-01-15 PM)Document48 pagesBS en Iso 11064-3-2000 - (2019-10-09 - 04-01-15 PM)SHAILENDRA100% (4)
- Er63419 Rev101 140628Document329 pagesEr63419 Rev101 140628Roman BeránekNo ratings yet
- Pemicu 1 GI: Mustika Rukmana 405130182 Kel 1Document69 pagesPemicu 1 GI: Mustika Rukmana 405130182 Kel 1tikaNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of Heent & LgsDocument34 pagesPhysical Examination of Heent & Lgstsehay asratNo ratings yet
- 1.1a The Normal Oral Mucosa PDF-2Document18 pages1.1a The Normal Oral Mucosa PDF-2marianaffernandes10No ratings yet
- Ent History Taking and Examination-1Document16 pagesEnt History Taking and Examination-1Jyotirmayee100% (5)
- SalivaryDocument26 pagesSalivaryMustafa AliNo ratings yet
- University of Jordan Dentistry 2016: Ibrahim ShawaqfehDocument21 pagesUniversity of Jordan Dentistry 2016: Ibrahim ShawaqfehHanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- Internal DiseasesDocument409 pagesInternal DiseasesPatrick Igbinoba - MFNo ratings yet
- Cleft Lip & Cleft Palate FinalDocument39 pagesCleft Lip & Cleft Palate FinalHARINI LAKSHMI TUMULURINo ratings yet
- GROUP 1 - Inspection, Palpation, Simple Sentences.Document22 pagesGROUP 1 - Inspection, Palpation, Simple Sentences.Andrea Estefania Apolo LomasNo ratings yet
- Folliate PappilaeDocument9 pagesFolliate PappilaeEga Muhamad YusufNo ratings yet
- General Patient Examination and Differential DiagnosisDocument37 pagesGeneral Patient Examination and Differential DiagnosisDr Ortho HaddiwalaNo ratings yet
- Constricting Force: SuspensionDocument33 pagesConstricting Force: SuspensionMAHFUZ ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment Lesson 1Document44 pagesHealth Assessment Lesson 1Bernice EbbiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination 2022-2023Document39 pagesClinical Examination 2022-2023نورالهدى حسام عليNo ratings yet
- Fissured TongueDocument31 pagesFissured Tonguenuratiqah_jasmiadNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mouth & PharynxDocument79 pagesAssessment of Mouth & PharynxMUHAMMAD SALMANNo ratings yet
- Hair, Face, Nose, Neck, Skin, and NailsDocument4 pagesHair, Face, Nose, Neck, Skin, and NailsZJ GarcianoNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve InjuryDocument3 pagesCranial Nerve InjuryCabdi Kaafi Maxamad CumarNo ratings yet
- General Survey by DR ADBDocument34 pagesGeneral Survey by DR ADBRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- ENT Urgencies / Emergencies in Primary CareDocument55 pagesENT Urgencies / Emergencies in Primary CareDr_Aan_ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances ofDocument93 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances ofChampak PaulNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Examination SchemeDocument3 pagesThyroid Examination SchemeUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- 2 Normal Oral Cavity Findings and Variants of NormalDocument6 pages2 Normal Oral Cavity Findings and Variants of NormalalbaablyNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam Internal FINALDocument27 pagesPhysical Exam Internal FINALMohammad AlrefaiNo ratings yet
- Neurology NotesDocument31 pagesNeurology NotesArif Setyawan75% (4)
- Assessing Head, Face and NeckDocument112 pagesAssessing Head, Face and NeckHyacinth Jane Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- StomatitisDocument44 pagesStomatitisNessa Layos Morillo100% (1)
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Drhpsingh Additional ProfessorDocument44 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis Media: Drhpsingh Additional ProfessorIndieNo ratings yet
- Head, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNDocument44 pagesHead, Mouth, Nose, Throat, Neck and Regional Lymph Nodes: Kristin Clephane, MSN, RN, CPNMike100% (1)
- Physical Examination Head Neck Chest Breast and AbdomenDocument116 pagesPhysical Examination Head Neck Chest Breast and AbdomenSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Foreign BodiesDocument14 pagesForeign BodiesRadinal IrwinsyahNo ratings yet
- Semiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidDocument59 pagesSemiology Lecture 4. Facies, Neck, ThyroidmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology I Final ReviewDocument373 pagesOral Pathology I Final ReviewAlex ChangNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Palatal SwellingsDocument90 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Palatal SwellingsAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKA100% (1)
- Deviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatDocument83 pagesDeviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Frail Elderly Client: A. Skin, Hair, and NailsDocument11 pagesAssessment of The Frail Elderly Client: A. Skin, Hair, and Nailsshannon c. lewisNo ratings yet
- Newborn Physical AssessmentDocument7 pagesNewborn Physical AssessmentFady Jehad Zaben100% (1)
- Diseases of Oral Cavity FinalDocument117 pagesDiseases of Oral Cavity FinalRamanujam SridharNo ratings yet
- Catetan BergunaDocument22 pagesCatetan BergunamellvinNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances - Dr. Nermine El BaheyDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances - Dr. Nermine El BaheyMOHAMED AMINNo ratings yet
- 10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatDocument25 pages10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatArka Ogeh100% (1)
- Presentation On Cogenital Anomalies of Respiratory TractDocument89 pagesPresentation On Cogenital Anomalies of Respiratory Tractmaggykariuki002No ratings yet
- Surgery: General ExamintionDocument6 pagesSurgery: General Examintionapi-3829364No ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Injuries: Oral Complications of H and N Radiation TherapyDocument5 pagesPhysical and Chemical Injuries: Oral Complications of H and N Radiation TherapynewmexicoomfsNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document27 pagesGroup 3api-643588876No ratings yet
- Examination of Cranial Nerves: .Abducent 6 - Trochlear, 4 .Occulomotor, 3Document21 pagesExamination of Cranial Nerves: .Abducent 6 - Trochlear, 4 .Occulomotor, 3Shauki AliNo ratings yet
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument16 pagesAcute Otitis Mediaadrianne18sNo ratings yet
- Thaslima. OMFSDocument33 pagesThaslima. OMFSDr Dennis jebaraj - Basic to Pro dentistryNo ratings yet
- Head Neck-Pharynx Larynx Thyroid GlandDocument8 pagesHead Neck-Pharynx Larynx Thyroid GlandMe MyselfNo ratings yet
- Asphyxial Deaths: DR Sagal Omar Anatomical PathologistDocument30 pagesAsphyxial Deaths: DR Sagal Omar Anatomical PathologistMaxamed AadanNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument6 pagesPhysical AssessmentDonna Flor NabuaNo ratings yet
- H.A Rle 11-14Document48 pagesH.A Rle 11-14Aira AndradaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 1Document36 pagesLecture No 1Pawan balesara PkNo ratings yet
- Oral Surgery: Components of Medical HistoryDocument9 pagesOral Surgery: Components of Medical Historyمرتضى محمد فاضل جرجوكNo ratings yet
- Importent NoteDocument54 pagesImportent Notekhaled.s.alformNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExaminationDocument11 pagesClinical ExaminationMavra zNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck PPT 2024Document65 pagesHead and Neck PPT 2024lallsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - Health AssessmentDocument10 pagesChapter 14 - Health Assessmentannoja selvaNo ratings yet
- OHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideFrom EverandOHNS--Otolaryngology; Head and Neck surgery: pocket field guideNo ratings yet
- ფიზიკა 7 - მოსწავლის წიგნიDocument219 pagesფიზიკა 7 - მოსწავლის წიგნიBeso ChargeishviliNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisDocument10 pagesAnalysis and Modelling of CFT Members Moment Curvature AnalysisMahdi ValaeeNo ratings yet
- BlueridgemountnsDocument37 pagesBlueridgemountnsကဗ်ာရည္းစားNo ratings yet
- 3 Ijrerd-A128 PDFDocument6 pages3 Ijrerd-A128 PDFRathod NileshNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesCirculatory Systemsmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument50 pagesUntitledKatrina F JonesNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Embedded SystemsDocument6 pagesAssignment: Embedded SystemsSudarshanNo ratings yet
- Conflict Resolution A Study of King Solomon's PrinciplesDocument22 pagesConflict Resolution A Study of King Solomon's Principlescupidgal99No ratings yet
- Oishi GroupDocument20 pagesOishi GroupCamilleJoyceAdrianoNo ratings yet
- Argus Field Service Kit User Guide PDFDocument4 pagesArgus Field Service Kit User Guide PDFBeneDict Ben DNo ratings yet
- Revision From DRDocument11 pagesRevision From DRMahmoud GamalNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia of Popular Science (Steven N.shore)Document353 pagesEncyclopaedia of Popular Science (Steven N.shore)Muhammad Ali HaiderNo ratings yet
- Surface and Hoisting Equipment Critical Area Fully Item NDT Inspection Disassembled On Location InspectionDocument4 pagesSurface and Hoisting Equipment Critical Area Fully Item NDT Inspection Disassembled On Location Inspectioncmrig74No ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Tax:: GST IntroductionDocument12 pagesDirect and Indirect Tax:: GST IntroductionDdaksh KumarNo ratings yet
- PIX MR CatalogueDocument60 pagesPIX MR CatalogueAmir SofyanNo ratings yet
- DAILY REPORT (29/01/2015) Project: BK-TNG Wellhead Platform Item: Fabrication of Pressure VesselDocument20 pagesDAILY REPORT (29/01/2015) Project: BK-TNG Wellhead Platform Item: Fabrication of Pressure VesselVanvien LeNo ratings yet
- Makino STL Cam PDFDocument98 pagesMakino STL Cam PDFberri23No ratings yet
- Mini ProjectDocument12 pagesMini ProjectHima Bindu PambalaNo ratings yet
- Arni DivisionDocument42 pagesArni DivisionAO VandavasiNo ratings yet
- Design of Storm Sewer MeterDocument2 pagesDesign of Storm Sewer MeterrachanaNo ratings yet
- 09 02ChapGereDocument12 pages09 02ChapGereAfoldo100% (1)
- Urine Examination# DivyaDocument69 pagesUrine Examination# DivyaMedicine 0786No ratings yet
- Wheel of The YearDocument7 pagesWheel of The YearFabricioFernandezNo ratings yet
- Theory of Chemical BondingDocument36 pagesTheory of Chemical BondingI Putu Adi Surya MahardikaNo ratings yet
- Kumon Mathematics Progress Tracker Levels C To O PDFDocument2 pagesKumon Mathematics Progress Tracker Levels C To O PDFcharmradeekNo ratings yet
- MNRE 29 Jun 2021 PPA ExtensionDocument1 pageMNRE 29 Jun 2021 PPA Extensionharsha kunturNo ratings yet
- Antimony Leaching From Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Used For Bottled Drinking WaterDocument6 pagesAntimony Leaching From Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Used For Bottled Drinking WaterjesicagabrNo ratings yet
- MingCha Product Guide 2004Document20 pagesMingCha Product Guide 2004Leo CL KwanNo ratings yet