Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Absorption Assimilation 1 Min
Absorption Assimilation 1 Min
Uploaded by
DhwityOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Absorption Assimilation 1 Min
Absorption Assimilation 1 Min
Uploaded by
DhwityCopyright:
Available Formats
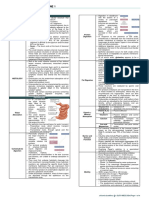
Absorption & Assimilation
Absorption Assimilation
• Process of absorption of end • Process of synthesis of
products of digestion into the blood macromolecules from simple
or lymph from intestinal mucosa absorbed molecules
• Occurs by active, passive • Helps in cell growth, development &
or facilitated transport mechanisms new cell production
Duodenum
• First section of small intestine
• Connects to pyloric sphincter of
the stomach
• Bile & pancreatic juices mix with
chyme
Jejunum
• Middle section of small intestine
• Primary site of nutrient
absorption & is 3 ft in length
Ileum Small Intestine
• Terminal section of small • 10 ft convoluted tube-like
intestine structure
• Empties into large intestine • Mesentery surrounds it & anchors
• Completes remaining nutrient it in place
absorption & is 6 ft in length • Special cells help absorb nutrients
from intestinal lining to
bloodstream
Absorptive Area
• Huge surface area due to presence • Villi: Digested food particles pass
of mucosal folds, villi, and microvilli. from lumen of intestine to blood
capillaries or lacteal.
villi
• Amino acids & monosaccharides
enter blood capillary network.
• Larger molecules of digested fat
Crypt Microvilli
enter lacteal & are emptied into
Enterocyte lymphatic system.
• Villi & microvilli are exposed to
• Water & fatty acids are absorbed
lumen.
by osmosis & diffusion.
• Microvilli: Creates brush-like border
that increases rate of nutrient • Glucose, amino acids & minerals
absorption. are absorbed by active transport.
You might also like
- The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument31 pagesThe Gastrointestinal SystemEen AliNo ratings yet
- Quiz BankDocument722 pagesQuiz BankMouniraNo ratings yet
- Med Terminology in A Flash - CardioDocument66 pagesMed Terminology in A Flash - CardiobencleeseNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of DigestionDocument3 pagesMechanism of DigestionDev BhutamwarNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Membrane DigestionDocument43 pages3.4 Membrane DigestionSurvin KandhariNo ratings yet
- 3 4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food andDocument8 pages3 4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food andCASSENDREA CHAI CHEN YI MoeNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationDocument9 pages3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationFrank ZachNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationDocument9 pages3.4 Process of Absorption and Transportation of Digested Food and DefecationYu Xuan ChongNo ratings yet
- Histology of Small Intestine For 2nd Year Mbbs (By DR Sundus)Document21 pagesHistology of Small Intestine For 2nd Year Mbbs (By DR Sundus)Mudassar RoomiNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument45 pagesDigestionAADHINo ratings yet
- 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodDocument15 pages6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodEdina ZayaniNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine 1Document4 pagesSmall Intestine 1Ha Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi USUS HALUSDocument28 pagesFisiologi USUS HALUSSarah AmaniNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q4 - Week 1 - Absorption-n-AssimilationDocument44 pagesG8 Science Q4 - Week 1 - Absorption-n-AssimilationLeyannNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q4 Week 1 Absorption N AssimilationDocument44 pagesG8 Science Q4 Week 1 Absorption N AssimilationdarontolentinoNo ratings yet
- Villi and AbsorptionDocument9 pagesVilli and AbsorptionShehbaaz SinghNo ratings yet
- Organs Associated With The Digestive TractDocument41 pagesOrgans Associated With The Digestive TractCenen de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 11 Structure of Small IntestineDocument12 pages11 Structure of Small IntestineFranchesca Rosabel BudimanNo ratings yet
- Updated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and DigestionDocument40 pagesUpdated - CHAPTER 3 Nutrition and Digestiondeela decemberNo ratings yet
- Q4 - Week 1PTDocument58 pagesQ4 - Week 1PTrebeccaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 28 Human Nutrition (Absorption)Document25 pagesLife Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 28 Human Nutrition (Absorption)191012tvsNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and AbsorptionDocument18 pages6.1 Digestion and AbsorptionStacey Deo MakoyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document26 pagesChapter 4Rayonesh RayanaNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Lesson 6Document13 pagesHuman Nutrition Lesson 6SUNDARI SIVASANKARNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Bio F4Document51 pagesChapter 9 Bio F4Vinieysha LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Anatomi EmbriologiDocument61 pagesAnatomi EmbriologiAanisah Ikbaar SayyidahNo ratings yet
- Structure of Intestinal VilliDocument14 pagesStructure of Intestinal VilliM B DNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Renal SystemsDocument108 pagesDigestive and Renal SystemsMenalqueNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Made by Veena MamDocument93 pagesLife Processes: Made by Veena MamAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Kimia KedokteranDocument67 pagesKimia KedokteranPutriNo ratings yet
- BBT221 Lec 16,17 - Digestive SystemDocument32 pagesBBT221 Lec 16,17 - Digestive Systemiamraiyan123No ratings yet
- Histology of StomachDocument19 pagesHistology of StomachBig BossNo ratings yet
- 2022 L5 - Cell MembraneDocument36 pages2022 L5 - Cell MembraneTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Nutrients, Digestive System and Excretory SystemDocument27 pagesUnit 2: Nutrients, Digestive System and Excretory Systemapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesDigestive SystemMJMadlangbayanNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Traktus DigestivusDocument39 pagesFisiologi Traktus DigestivusdrhendyjuniorNo ratings yet
- 4.histology of The Digestive SystemDocument43 pages4.histology of The Digestive Systemokoti.omutanyi22No ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption PDFDocument8 pages6.1 Digestion and Absorption PDFAdam AzzehNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 2Document71 pagesDigestive System 2dmutethia68No ratings yet
- G9 Biology Extension Manual 01 Digestion 2021 AnsDocument4 pagesG9 Biology Extension Manual 01 Digestion 2021 AnsBen WongNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument69 pagesDigestive SystemAdriane Basa100% (1)
- 6.1 U4 Villi Increase The Surface Area of Epithelium Over Which Absorption Is Carried OutDocument9 pages6.1 U4 Villi Increase The Surface Area of Epithelium Over Which Absorption Is Carried Outrh 077No ratings yet
- Ruminants and Rodents: Biology Form 4:nutritionDocument30 pagesRuminants and Rodents: Biology Form 4:nutritionAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument78 pagesDigestive SystemBerrak AydınNo ratings yet
- CHP 7 - Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesCHP 7 - Digestive SystemAliha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Divyasparshi: Healer Suresh NagarsekarDocument35 pagesDivyasparshi: Healer Suresh Nagarsekarprashant borgeNo ratings yet
- Digestive System 1Document33 pagesDigestive System 1Ashley JibrielleNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and AbsorptionDocument37 pages6.1 Digestion and AbsorptionmeerabNo ratings yet
- HANDOUTS Finals CH 16Document31 pagesHANDOUTS Finals CH 16hii385156No ratings yet
- Anatomy: Chapter 75: Gastrointestinal InfectionsDocument8 pagesAnatomy: Chapter 75: Gastrointestinal InfectionsTrisha Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesChapter 2 - Digestive SystemDale TelgenhoffNo ratings yet
- Struktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanDocument133 pagesStruktur Dan Fungsi Sistem PenghadamanStephanie Ming FunNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyDocument55 pagesSmall Intestine: DR Raghuveer ChoudharyPhysiology by Dr RaghuveerNo ratings yet
- Salivary GlandDocument65 pagesSalivary GlandSagal Nur100% (1)
- Lecture - Biology of Farm Animals - .1Document56 pagesLecture - Biology of Farm Animals - .1kdcypbv5c2No ratings yet
- Problem 3 GI Tract Group 13Document159 pagesProblem 3 GI Tract Group 13Alicia TjinNo ratings yet
- Physiology of DigetionDocument22 pagesPhysiology of DigetionMadhavarao MaddisettyNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument7 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionShahil Aftab HussainNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology NotesDocument28 pagesHuman Physiology NotesZaraNo ratings yet
- The Histology of The Small IntestineDocument31 pagesThe Histology of The Small IntestineMartha Orendu Oche AttahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 1Document37 pagesBiochemistry 1Odongo TonnyNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument1 pageHuman Digestive SystemDhwityNo ratings yet
- Yaclass - In-Mind Map Lesson Science CBSE Class 7Document2 pagesYaclass - In-Mind Map Lesson Science CBSE Class 7DhwityNo ratings yet
- .In-Commercial Use of Micro-OrganismDocument2 pages.In-Commercial Use of Micro-OrganismDhwityNo ratings yet
- .In-Medicinal Use of Micro-OrganismDocument2 pages.In-Medicinal Use of Micro-OrganismDhwityNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection, Lab Report GuideDocument5 pagesHeart Dissection, Lab Report GuideJohn OsborneNo ratings yet
- Physiology & Pathophysiology - 2000Document4,648 pagesPhysiology & Pathophysiology - 2000tcabanilNo ratings yet
- Endo 3 Notes PDFDocument9 pagesEndo 3 Notes PDFDilNo ratings yet
- Exc 9 Act 6Document5 pagesExc 9 Act 6Nabila Putri Dinda A.No ratings yet
- Eye and Ear HistologyDocument96 pagesEye and Ear HistologyErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MD100% (1)
- Approach To Jaundice PatientDocument24 pagesApproach To Jaundice Patientabela_amuluNo ratings yet
- GI NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageGI NeurotransmittersMaryam FadahNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3Document2 pagesQuiz 3Abdalrahman AhmedNo ratings yet
- Liver FunctionDocument24 pagesLiver FunctionramireddyNo ratings yet
- Braak Et Al. - 2004 - Stages in The Development of Parkinson's Disease-Related PathologyDocument14 pagesBraak Et Al. - 2004 - Stages in The Development of Parkinson's Disease-Related PathologyAleja ToPaNo ratings yet
- ECG Course - Introduction To ECGDocument54 pagesECG Course - Introduction To ECGPD-A UB 2017No ratings yet
- Week 5: Endocrinology: I. Pituitary ControlDocument26 pagesWeek 5: Endocrinology: I. Pituitary ControlBenjamin NgNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi Dialisis DR Ratih Tri KD MAJUDocument56 pagesPenyakit Ginjal Kronik Dan Indikasi Dialisis DR Ratih Tri KD MAJUFitriana WijayatiNo ratings yet
- Head Neck Brain BDC ExportDocument4 pagesHead Neck Brain BDC ExportYvetal GardeNo ratings yet
- Pale Lights Cheat Sheet - Chapter 25Document11 pagesPale Lights Cheat Sheet - Chapter 25firsttenorNo ratings yet
- Bio Final Assignment 7Document5 pagesBio Final Assignment 7Lorena Centeno SantosNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument126 pagesLymphatic SystemChris Deinielle Marcoleta SumaoangNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Rouviere's Sulcus-Aspects of Incorporating This Valuable Sign For Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument3 pages2018 - Rouviere's Sulcus-Aspects of Incorporating This Valuable Sign For Laparoscopic CholecystectomyBattousaih1No ratings yet
- 1 Medical-PräsentDocument84 pages1 Medical-PräsentpurplefokNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Exercise 1 Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesModule 4 Exercise 1 Cardiovascular SystemWalid BacundoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Endocrine SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 9 - Endocrine SystemrishellemaepilonesNo ratings yet
- Guppy Brain Atlas SmallerDocument4 pagesGuppy Brain Atlas Smallerapi-394354061No ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus SMF/ Bagian Ilmu Bedah (Short Case 1)Document59 pagesLaporan Kasus SMF/ Bagian Ilmu Bedah (Short Case 1)Roby Aditya SuryaNo ratings yet
- Hashimoto EncephalopathyDocument37 pagesHashimoto EncephalopathyIbrahim IbrahimNo ratings yet
- OralcholecystographyDocument13 pagesOralcholecystographySuman PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Chapt 27 Ap2Document5 pagesChapt 27 Ap2candybio83No ratings yet
- Dyspepsia and Homeopathic TreatmentDocument62 pagesDyspepsia and Homeopathic Treatmentdrmsupriya100% (1)
- 652302BSCNDocument2 pages652302BSCNjames9122000aNo ratings yet