Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & Definitions
OCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & Definitions
Uploaded by
Temi BalogunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & Definitions
OCR A Chemistry A-Level - Chapter 9 - Enthalpy - Keywords & Definitions
Uploaded by
Temi BalogunCopyright:
Available Formats
Keywords Definitions
Activiation energy The minimum energy required for a reaction to take place.
Average Bond Enthalpy The energy required to break one mole of gaseous bonds.
Actual bond enthalpies may differ from the average as the
average bond enthalpy considers a particular bond in a
range of molecules.
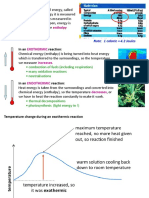
Endothermic reaction A reaction which takes in energy (ΔH is positive). More
energy is required to break bonds than is released by
making bonds
Exothermic reaction A reaction which gives out energy (ΔH is negative). More
energy is released by bond making than is used in bond
breaking.
Enthalpy (H) A value that represents the heat content of a system.
Enthalpy Change (ΔH) The change in the heat content of a system during a
reaction. This can be determined from experimental results
using q = mcΔT (where q is the heat change of the
surroundings, m is the mass of the surroundings, c is the
specific heat capacity and ΔT is the change in
temperature).
Enthalpy Change of Combustion (ΔcH) The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a
substance is completely combusted.
Enthalpy Change of Formation (ΔfH) The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of a
compound is formed from its elements.
Enthalpy Change of Neutralisation (ΔneutH) The enthalpy change that takes place when one mole of
water is formed from a neutralisation reaction.
Enthalpy Change of Reaction (ΔrH) The enthalpy change that is associated with a particular
chemical equation.
Enthalpy Profile Diagram Shows the difference in the enthalpy of reactants and
products as well as the activation energy of a reaction.
Hess’ Law The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the
route it takes.
Standard Conditions a pressure of 100 kPa and a temperature of 298K.
Standard State The physical state (s, l, g, aq) of a substance under
standard conditions.
You might also like
- Soil Resistivity ReportDocument10 pagesSoil Resistivity ReportALEX BNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Chemical EnergeticsDocument42 pagesChapter 6 Chemical Energeticsgajenrao100% (1)
- BS 1042.1.3 PDFDocument22 pagesBS 1042.1.3 PDFChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Definitions Topic 3.2.1 Enthalpy Changes OCR A Chemistry A LevelDocument1 pageDefinitions Topic 3.2.1 Enthalpy Changes OCR A Chemistry A LevelCHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Notes On Physical ChemistryDocument1 pageNotes On Physical Chemistryfletcherberryheath2006No ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument6 pagesChemical EnergeticsNelsonNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument57 pagesEnergeticsTannia SammyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5.1: Chapter 5: Energetics - GlossaryDocument4 pagesWorksheet 5.1: Chapter 5: Energetics - GlossaryBrandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- Sign Convention: ΔW = positiveDocument4 pagesSign Convention: ΔW = positiveprernashaluNo ratings yet
- AS CHM 11 Energetics Notes PDFDocument34 pagesAS CHM 11 Energetics Notes PDFBasitKhan100% (1)
- 1.4 EnergeticsDocument14 pages1.4 EnergeticsBhPO2023No ratings yet
- CHE 1000 Lecture Notes - ThermochemistryDocument39 pagesCHE 1000 Lecture Notes - ThermochemistryNathan MulunguNo ratings yet
- 8 Energetics Notes PDFDocument27 pages8 Energetics Notes PDFMustufa Feroz100% (1)
- Energetics: To Entropy On Next Page To Spontaneous Reactions On Next PageDocument2 pagesEnergetics: To Entropy On Next Page To Spontaneous Reactions On Next PageaurennosNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 Lecture Note On Thermo Chemical KineticsDocument24 pagesCHM 101 Lecture Note On Thermo Chemical Kineticsekanadefestus007100% (1)
- Enthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy Changes and Hess CyclesMoon KimNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 Enthalpy ChangesDocument9 pages3.2.1 Enthalpy ChangesSofia YNo ratings yet
- Chm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedDocument68 pagesChm271 - Chapter 2 Thermochemistry - UpdatedNurfarhanah AsyknNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4mehrunnisaqaisar111No ratings yet
- Energetics 1Document53 pagesEnergetics 1anellebrown299No ratings yet
- Energy Changes PDFDocument4 pagesEnergy Changes PDFMahmudul Hassan ShuvoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 (References)Document10 pagesCHAPTER 8 (References)JeromeNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Energetics and Thermochemistry PDFDocument5 pagesTopic 5 Energetics and Thermochemistry PDFSveta StepanovaNo ratings yet
- 3.2.1 EnthalpyDocument2 pages3.2.1 Enthalpylucy.yasmin06No ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Energy ChangesDocument11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Energy ChangesahmedNo ratings yet
- ACIS EnergeticsDocument58 pagesACIS EnergeticsJeenal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chemical Energetics AssignmentDocument3 pagesChemical Energetics AssignmentGovindi BahadurNo ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument4 pagesEnthalpyanon_47693748No ratings yet
- Chapter One Energenetic (Thermochemistry) : BY: Hana Eva Loren Chemical Regular BDocument9 pagesChapter One Energenetic (Thermochemistry) : BY: Hana Eva Loren Chemical Regular BKaterina limbongNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument12 pagesEnergeticsAliyah HamiltonNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument17 pagesEnthalpy ChangesDoc_Croc100% (1)
- 8-Energetics-NotesDocument27 pages8-Energetics-Noteserror.sutNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Energetics Notes SL and HLDocument5 pagesChemistry Energetics Notes SL and HLNimisha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Notes Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: Thermodynamics Top ConceptsDocument7 pagesChapter Notes Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: Thermodynamics Top ConceptsDivyam TanwarNo ratings yet
- Energetics: Chemical Reactions and Energy ChangesDocument30 pagesEnergetics: Chemical Reactions and Energy ChangesTyrese SmithNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Revision Guide Energetics Aqa 1Document9 pages1.4 Revision Guide Energetics Aqa 1SewarNo ratings yet
- Theme 2 Lecture 6Document17 pagesTheme 2 Lecture 6ntokozocecilia81No ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument4 pagesEnthalpy ChangesRaiyad RezaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Activity SheetDocument15 pagesEnthalpy Activity SheetPrincess Fenix Sabio100% (1)
- Law of ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesLaw of ThermodynamicsaryanrajdavkoylanagarNo ratings yet
- Csec Chemistry 22 - 23 Rates & EnergeticsDocument12 pagesCsec Chemistry 22 - 23 Rates & EnergeticsbessaryanneNo ratings yet
- Energetics PDFDocument6 pagesEnergetics PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument30 pagesEnergy ChangesFaik esen KarasoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05 Energetics TextbookDocument26 pagesChapter 05 Energetics TextbookMirei IidaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 Notes (New)Document12 pagesTopic 4 Notes (New)amenaNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument41 pagesThermochemistryNina CrisantoNo ratings yet
- (H2 CHEM) Chapter 7 - Chemical Energetics (Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics)Document33 pages(H2 CHEM) Chapter 7 - Chemical Energetics (Thermochemistry and Thermodynamics)SevinatorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)Document28 pagesChapter 1 CHM476 (Part 1)PUTRI DAYANA BATRIESYA ABDUL HANIFNo ratings yet
- Chemistry From BBDocument8 pagesChemistry From BBLorenz lingaoNo ratings yet
- BHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy EnergeticsDocument59 pagesBHS CSEC Grade 11 Energy Energeticsabigail allenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Thermochemistry-Exothermic and EndothermicNadine TariganNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 NotesDocument28 pagesUnit 2 NotesMuhammad ZaiNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes NotesDocument20 pagesEnthalpy Changes NotesIGCSE 2k21No ratings yet
- Chemical EnergeticsDocument4 pagesChemical Energeticsdung luongtuanNo ratings yet
- EnergeticsDocument57 pagesEnergeticsEfraim KasinoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical KineticsDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Chemical KineticsAkpa KenechukwuNo ratings yet
- ThermochemistryDocument28 pagesThermochemistryMuhammad Nazif AzmiNo ratings yet
- Week 007 Module ThermochemistryDocument12 pagesWeek 007 Module ThermochemistryFigh terNo ratings yet
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 11 PlusDocument21 pages11 PlusTemi BalogunNo ratings yet
- Ecology MindmapsDocument3 pagesEcology MindmapsTemi Balogun100% (1)
- Cells, Batteries and Fuel CellsDocument3 pagesCells, Batteries and Fuel CellsTemi BalogunNo ratings yet
- Chem Revision NotesDocument5 pagesChem Revision NotesTemi BalogunNo ratings yet
- (AQA) English Language Paper 1 GuidanceDocument1 page(AQA) English Language Paper 1 GuidanceTemi BalogunNo ratings yet
- ISO224 Reinforced Isolated Amplifier With Single-Ended Input of 12 V and Differential Output of 4 VDocument37 pagesISO224 Reinforced Isolated Amplifier With Single-Ended Input of 12 V and Differential Output of 4 VMattias RahmNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PHY150 Chapter 1Document19 pagesTutorial PHY150 Chapter 1affiqaiman010503No ratings yet
- CBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterDocument2 pagesCBSE Class-12 Physics Quick Revision Notes Chapter-05: Magnetism and MatterabcdNo ratings yet
- Design of Pressure Windows PDFDocument2 pagesDesign of Pressure Windows PDFMoisés SolisNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Calculus - PhysicsDocument27 pagesFinal Exam - Calculus - Physicsarvie montemayorNo ratings yet
- Btech 2 Sem Engineering Mechanics Me 201 2017 18Document2 pagesBtech 2 Sem Engineering Mechanics Me 201 2017 18Ashutosh IndNo ratings yet
- Vocational Training in A 132 KV SubstationDocument69 pagesVocational Training in A 132 KV SubstationRahul SahaNo ratings yet
- LTspice - IV PresentationDocument263 pagesLTspice - IV PresentationrobertNo ratings yet
- Diesel Generator Sets: Standby & Prime: 50Hz & 60 HZ, 230/400V, 277/480V 3-PhDocument3 pagesDiesel Generator Sets: Standby & Prime: 50Hz & 60 HZ, 230/400V, 277/480V 3-PhAsad SharifNo ratings yet
- Norzagaray and Bulacan Clinker Capacity Expansion 7114035 Republic Cement & Building Materials, Inc. Norzagaray, Bulacan Storage TunnelDocument15 pagesNorzagaray and Bulacan Clinker Capacity Expansion 7114035 Republic Cement & Building Materials, Inc. Norzagaray, Bulacan Storage TunnelMos LugtuNo ratings yet
- Physics HelpDocument4 pagesPhysics HelpEiko RiskerNo ratings yet
- 2 - FLDS 385 Chapter 2 Principles of HydraulicsDocument47 pages2 - FLDS 385 Chapter 2 Principles of HydraulicsAvneet MultaniNo ratings yet
- c4 4 Diagrama EelctricoDocument2 pagesc4 4 Diagrama EelctricoEdwin Cruz100% (1)
- PhysicsDocument125 pagesPhysicshamidNo ratings yet
- Focs2 WDocument76 pagesFocs2 WTECNO AYUDANo ratings yet
- Severe Overvoltage During Single-Phase Open PeriodDocument38 pagesSevere Overvoltage During Single-Phase Open PeriodNguyen Xuan TungNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 5 Dynamic Simulations of Electric Machinery: Using MATLAB/SIMULINK:0137237855:..Document5 pagesPage 1 of 5 Dynamic Simulations of Electric Machinery: Using MATLAB/SIMULINK:0137237855:..JorgeMoisesNo ratings yet
- AP3041 Oscilador TV Haier 50yca PDFDocument14 pagesAP3041 Oscilador TV Haier 50yca PDFmaroNo ratings yet
- M1 02QDocument6 pagesM1 02QChryssa EconomouNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components: 1.1. Colour Coding of ResistorDocument84 pagesBasic Electronic Components: 1.1. Colour Coding of ResistorPakistan augustNo ratings yet
- Ge CH 11Document152 pagesGe CH 11Sanju DasNo ratings yet
- Capacitance Pressure TransmitterDocument3 pagesCapacitance Pressure TransmitterRufat SafaraliyevNo ratings yet
- Blackhole Shadow Ray ImagingDocument13 pagesBlackhole Shadow Ray ImagingAMOGH JHANWARNo ratings yet
- VPRS 4300V VPRM5450Document3 pagesVPRS 4300V VPRM5450Tuan MinhNo ratings yet
- 1mrk509075-Men D en Builder S Guide - CombiflexDocument123 pages1mrk509075-Men D en Builder S Guide - CombiflexCarlos RiveraNo ratings yet
- How Much Coal Required To Produce 1 MW Power?: What Is The TPH of A Boiler?Document5 pagesHow Much Coal Required To Produce 1 MW Power?: What Is The TPH of A Boiler?coconut borneoNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT REPORT 4-Verifying Current Divider RuleDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT REPORT 4-Verifying Current Divider RuleOluwamurewa .ANo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Fan Coil Tipo Ducto18000 BtuDocument5 pagesFicha Tecnica Fan Coil Tipo Ducto18000 BtuGiancarlo Reategui GuerraNo ratings yet