Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PSobrecorriente
PSobrecorriente
Uploaded by
HugoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PSobrecorriente
PSobrecorriente
Uploaded by
HugoCopyright:
Available Formats
Protección de Sistemas Eléctricos
Maestrı́a en Redes Inteligentes
Klever Quizhpe H.
Universidad de Cuenca
kleber.quizhpe@ucuenca.edu.ec
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 1 / 15
Protección de Sobrecorriente Distancia
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 2 / 15
Principios
The term distance is used for a family of relays that respond to a ratio
of voltage to current and therefore to impedance or component of
impedance .Distance relay may have the following features:
A distance relay has the ability to detect a fault within a pre-set
distance along a transmission line from its location.
Every power line has a resistance and reactive per kilometer
related to its design and construction so its total impedance will
be a function of its length or distance.
A distance relay therefore looks at current and voltage and
compares these two quantities on the basis of Ohm’s law
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 3 / 15
Principios
Consider the simple radial line with distance protection system.These
relays sense local voltage and current and calculate the effective
impedance at that point. This means that the relay requires voltage
and current information
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 4 / 15
Principios
When the protected line becomes faulted, the effective impedance
becomes the impedance from that point to the fault.
Assume balanced three-phase fault at distance d: For internal fault
Vp
at point p: Zp = < ZL . Relay will operate.
I
Vk
For external fault at point k : Zp = > ZL .Relay will not operate
I
V
In general the relay will trip when Zf = < ZL where ZL is the
I
d
impedance at the fault point. For example at point p: Zf p = < ZL
L
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 5 / 15
Principios
Hence the distance relay action is to compare the local voltage with the
local current, i.e. the secondary values of V and I in the voltage and
V
current transformers so as the quantity is the measured impedance
I
Zm where:
V
V T ratio V CT ratio CT ratio
Zm = I
= I = Zf
CT ratio
V T ratio V T ratio
Where Zm is the measured impedance (appears at the relay terminal)
also called the secondary impedance. And Zf is the also called the
primary impedance.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 6 / 15
Tipos de relés de Distancia
In general there are four main types of distance relays:
Impedance relay (Ohms relay)
Admittance relay ( Mho relay)
Reactance relay
Offset Mho relay
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 7 / 15
Tripping characteristics of distance relay
If the relay’s operating boundary is plotted, on an R-X diagram,
its impedance characteristic is a circle with its center at the origin
of the coordinates and its radius will be the setting in ohms
The relay will operate for all values less than its setting i.e. is for
all points within the circle.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 8 / 15
Tripping characteristics of distance relay
The impedance relay does not consider the phase angle between
the voltage and current applied to it.
The relay operates for all impedance values that are less than its
setting (all the values inside the circle).
It restrain for all values (points) outside the circle.
The reach of the distance relay is that distance from the
relaying point to the point of fault. The reach is usually refers as
the relay setting and can be as a distance (m), or as a primary or
secondary impedance.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 9 / 15
Advantage of distance relay
Provide backup protection easily.
Eliminates the pilot channel.
Distance protection is available for both phase and ground faults.
Step distance protection combines instantaneous and time delay
tripping.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 10 / 15
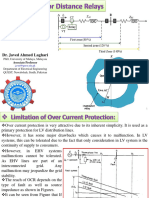
Zones of protection
Due to the tolerance in the circuit components, the measuring accuracy cannot be perfect so it is usual to
set the relay at the local point A at 80 % of the secondary impedance of AB. This is referred as zone 1 or
stage A1 setting.
The remaining 20 % of AB is protected by changing the setting of the relay to reach 50 % into zone BC
(zone 2 or stage A2). Stage A2 is usually set at 0.3 s time. For system reliability (failure of relay A will
cause failure of stage A1 and stageA2), another distance relay is added for backup protection. This
separate relay should have a reach of 20 % into CD and called zone 3 or stage A3 which has a time delay
of 0.6 s.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 11 / 15
Zones of protection
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 12 / 15
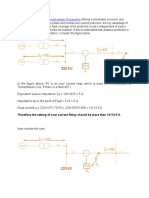
Ejemplo 1
Para la lı́nea de subtransmisión de 66 KV que se indica en la figura,
determinar el seteo de la zona 1 para un relé de distancia (Impedancia
primaria).
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 13 / 15
Ejemplo 2
Determinar los seteos de un relé de distancia en la linea AB de la
figura. El ángulo de la impedancia para cda lı́nea es de 75°. La longitud
de la lı́nea es de 80 Km. El relé de distancia en la barra A esta
alimentado por un TC de relación 200:5 y un TP de 345Kv/220KV Y :
120V/69V Y. Determine los seteos de la zona 1 y 2 de los relés.
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 14 / 15
Trabajo en clase
Ejercicios protección de distancia
Klever Quizhpe H. (UC) Short title 15 / 15
You might also like
- Unit-2-Distance & Differential ProtectionDocument167 pagesUnit-2-Distance & Differential Protectionsubbu2051100% (2)
- Horm 4Document6 pagesHorm 4suchandrar100% (2)
- C57 (1) .12.34-2004 ErrataDocument2 pagesC57 (1) .12.34-2004 Erratamagdy522100% (1)
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- High Pass 145Document7 pagesHigh Pass 145ebasaytunoNo ratings yet
- 7 - Distance ProtectionDocument81 pages7 - Distance ProtectionSarthak Vats100% (1)
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocument12 pagesRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2- relay types -and characterstics con'tDocument54 pagesChapter 2- relay types -and characterstics con'tNamee BekeleNo ratings yet
- 13th LectureDocument73 pages13th LectureNaveed RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Capacitave Sensing ChapterDocument33 pagesCapacitave Sensing ChapterGNNo ratings yet
- RLC Laboratory CircuitDocument9 pagesRLC Laboratory CircuitGhiță SfîraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitDocument5 pagesExperiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitAhmed SalehNo ratings yet
- Aaheli Maity EmtDocument18 pagesAaheli Maity EmtSreyan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- A Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Document50 pagesA Arte Da Eletronica 3oedicao (1) (0101-0150)Baba GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- Non-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 ADocument6 pagesNon-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 AyethweNo ratings yet
- Protecting Ieds With Deviation of Power Frequency: Transmission and DistributionDocument3 pagesProtecting Ieds With Deviation of Power Frequency: Transmission and DistributionGangaDhar100% (1)
- Branch: Computer Science Engineering Topic: Multivibrators and 555 TimerDocument32 pagesBranch: Computer Science Engineering Topic: Multivibrators and 555 TimerfjygfjygNo ratings yet
- 06 Distance ProtectionDocument20 pages06 Distance ProtectionArliel John Garbo100% (1)
- Miller Sweep CircuitDocument9 pagesMiller Sweep CircuitAiza GhanchiNo ratings yet
- Reduced Distance RelayingDocument12 pagesReduced Distance Relayingmmorgenwaine9No ratings yet
- RLC CircuitDocument9 pagesRLC CircuitHemangee PurohitNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and Uses of CapacitorsDocument6 pagesCapacitance and Uses of CapacitorsyogocNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay TheoryDocument54 pagesDistance Relay TheoryTun tun linNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection 2Document56 pagesPower System Protection 2Ahmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Analog NotesDocument54 pagesAnalog NotesSiddharth KumarNo ratings yet
- 01M Equivalent CircuitDocument43 pages01M Equivalent Circuitবিবেক রত্নNo ratings yet
- PSobrecorriente PDFDocument32 pagesPSobrecorriente PDFSebas TenesacaNo ratings yet
- Web - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1Document6 pagesWeb - Itu.edu - TR Yumakk Downloads Lab Notes Distance Protection v1sunitharajababuNo ratings yet
- ALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"Document39 pagesALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"api-19788618No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Protection SystemDocument97 pagesChapter 3 - Protection SystemSyafiq MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dr. Samsul Haimi Dahlan Emc/Fkee/UthmDocument193 pagesPrepared by Dr. Samsul Haimi Dahlan Emc/Fkee/UthmDanielNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument34 pagesRC CircuitsFaiz ShbNo ratings yet
- NA Exp6-RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesNA Exp6-RL RC CircuitakshithadharmasothNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 AC Measurents RC A RL Ckts 210330Document7 pagesExperiment 4 AC Measurents RC A RL Ckts 210330MK MillyNo ratings yet
- Distance Relay Interview Questions With AnswersDocument3 pagesDistance Relay Interview Questions With Answersprabakaran79No ratings yet
- Medium Lines, ABCD Cons With ProblemsDocument31 pagesMedium Lines, ABCD Cons With ProblemsAreyan HaqueNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 15-LabsDocument63 pagesPower Electronics 15-LabsKrishna v.mNo ratings yet
- VSWR LabDocument5 pagesVSWR LabKrishna Prasad PheluNo ratings yet
- Ece V Microwaves and Radar 10ec54 SolutionDocument77 pagesEce V Microwaves and Radar 10ec54 SolutionmansourvcxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document8 pagesLecture 2Mustafa Khider100% (1)
- Understanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V VDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Attenuators and Compensation: R R V R V R R R V Vnithinjose4uNo ratings yet
- Distribution Automation Handbook: Section 8.15 Impedance-Based Fault LocationDocument24 pagesDistribution Automation Handbook: Section 8.15 Impedance-Based Fault Locationronald_chan_2No ratings yet
- Chap1 Lect3Document7 pagesChap1 Lect3Ibraheem MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Microwave Engineering - MeasurementsDocument12 pagesMicrowave Engineering - MeasurementshariprasathpremNo ratings yet
- ELEC4611-24 Exp 1Document10 pagesELEC4611-24 Exp 1qumg3hsNo ratings yet
- TCs TPsDocument29 pagesTCs TPsChino JordanNo ratings yet
- AIM/OBJECTIVE-Determination of Steady State Response of R - L, R-C and R-L-C Circuit and Calculation of Impedance and Power FactorDocument9 pagesAIM/OBJECTIVE-Determination of Steady State Response of R - L, R-C and R-L-C Circuit and Calculation of Impedance and Power FactorSoumyarup Basu100% (1)
- Me 005Document25 pagesMe 005Pratheesh S KumarNo ratings yet
- Lic LabDocument15 pagesLic Labpratik kumarNo ratings yet
- Cs AmplifierDocument129 pagesCs AmplifierjisooNo ratings yet
- ,,,,CNT Lab ReportDocument13 pages,,,,CNT Lab ReportHosea MuchiriNo ratings yet
- TLRF-AU 2 MarksDocument15 pagesTLRF-AU 2 MarksTECH FROM ASHNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADocument155 pagesPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNo ratings yet
- A. Wound Type:: 1. What Are The Types of CT? Example?Document8 pagesA. Wound Type:: 1. What Are The Types of CT? Example?deltavijayakumarNo ratings yet
- LINEREV ProtectionDocument92 pagesLINEREV Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (2)
- 9 Capacitor Charging and DischargingDocument2 pages9 Capacitor Charging and DischargingMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier (Oscillator) : Pattanan Amatanon EE1A3Document6 pagesOperational Amplifier (Oscillator) : Pattanan Amatanon EE1A3pamatanonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 26 PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet 26 PDFVijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Control Solutions For Enhanced Resilience of Modern Power-Electronic-Interfaced Distribution SystemsDocument15 pagesAdvanced Control Solutions For Enhanced Resilience of Modern Power-Electronic-Interfaced Distribution Systemsndaryanto 92No ratings yet
- Module-5 Extra Material (Power Converters)Document69 pagesModule-5 Extra Material (Power Converters)NamiraNo ratings yet
- Westinghouse: Coupling Capacitor Potential DevicesDocument8 pagesWestinghouse: Coupling Capacitor Potential DevicesRick JordanNo ratings yet
- Retarder 2Document9 pagesRetarder 2James FlawrenceNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection - Part 08Document16 pagesPower System Protection - Part 08Rahul MandalNo ratings yet
- Powerwave 5755.00Document1 pagePowerwave 5755.00Punky HeroNo ratings yet
- X10 SeriesDocument3 pagesX10 SeriesDương ThânNo ratings yet
- Omron E2A Series: Extended Ranged DC 3-Wire Proximity SensorsDocument1 pageOmron E2A Series: Extended Ranged DC 3-Wire Proximity SensorsjosebezerraoliveiraNo ratings yet
- EE012 - Differential Current Protection of Transformer Using Arduino With Voice AlertDocument6 pagesEE012 - Differential Current Protection of Transformer Using Arduino With Voice AlertMahammad MuneerNo ratings yet
- Aec BitsDocument9 pagesAec BitsComrade Venkata HarshaNo ratings yet
- 3 +220+KV+single+core+ PDFDocument10 pages3 +220+KV+single+core+ PDFعريب صالح الروسانNo ratings yet
- LCR Meter Project ReportDocument12 pagesLCR Meter Project ReportDarshan Sonawane100% (1)
- Service Manual: LT-26WX84Document95 pagesService Manual: LT-26WX84phuoclocNo ratings yet
- 850T5 - 1983 - Serie1 Schema ElettricoDocument1 page850T5 - 1983 - Serie1 Schema ElettricoEugy AlexNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric CurrentDocument22 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric CurrentAnurag Tiwari100% (1)
- Thermal RadiationDocument4 pagesThermal RadiationMustafidzul MustaphaNo ratings yet
- MC33926 PDFDocument25 pagesMC33926 PDFKACH1234No ratings yet
- EMMI Lab PDFDocument31 pagesEMMI Lab PDFSarithareddy AvuluriNo ratings yet
- Door Locks ElectricalDocument107 pagesDoor Locks ElectricalRepuesto GeneralNo ratings yet
- Phase Shifting TransformersDocument6 pagesPhase Shifting TransformersWaldemar ZiomekNo ratings yet
- Manual 5520Document420 pagesManual 5520Manuel Morales CubillanaNo ratings yet
- Audio Note Japan KondoDocument23 pagesAudio Note Japan KondoBranislav MihajlovicNo ratings yet
- A High Voltage Programmable Ramp Generator: Articles You May Be Interested inDocument6 pagesA High Voltage Programmable Ramp Generator: Articles You May Be Interested inali esmaeelniaNo ratings yet
- Relay Replacement ScheduleDocument1 pageRelay Replacement Schedulekrcdewanew100% (1)
- PSS 166LR W5X Elbow ConnectorDocument2 pagesPSS 166LR W5X Elbow ConnectorSamMooreNo ratings yet
- 28521-871.01.10-B (MSB Design Descri..)Document9 pages28521-871.01.10-B (MSB Design Descri..)Kukuh WidodoNo ratings yet
- C3EE43822HDocument17 pagesC3EE43822HAnnisa TurrahmahNo ratings yet
- Transformers Stray LossDocument34 pagesTransformers Stray LossPop GabrielNo ratings yet