Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gen Chem 2
Gen Chem 2
Uploaded by
Trisha Camille MacarioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Science 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesScience 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryHelma Jabello AriolaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledRann ValleNo ratings yet
- Is The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateDocument5 pagesIs The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateJerica BautNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Document2 pages3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Ainon SalendabNo ratings yet
- (WEEK 1) (Chemistry) Preparatory Learning ActivityDocument6 pages(WEEK 1) (Chemistry) Preparatory Learning Activity12 STEM Kyla Jean TantoyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 1Document27 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 1Kate PedritaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Biochemistry Guided Notes Student VersionDocument12 pagesUnit 2: Biochemistry Guided Notes Student VersionRahsaan BurksNo ratings yet
- Semifinals GenchemDocument4 pagesSemifinals GenchemDave julius CericoNo ratings yet
- Day14 - Gen. Chem 2 - SASDocument6 pagesDay14 - Gen. Chem 2 - SASBilly PestañoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem Long Quiz (Q1 - 2nd Sem)Document4 pagesGen. Chem Long Quiz (Q1 - 2nd Sem)Grophel MesaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - LAS 1 HANDOUTDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - LAS 1 HANDOUTMark RazNo ratings yet
- Midterm GEN CHEM 2 TEST QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesMidterm GEN CHEM 2 TEST QUESTIONSMark Cesar VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesDocument20 pagesGenchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesMathew LlabresNo ratings yet
- Second Monthly Exam-Ma'am MoniqueDocument22 pagesSecond Monthly Exam-Ma'am MoniqueMonique Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Test Ngss ChemistryDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Test Ngss Chemistryapi-664258676No ratings yet
- Learning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesLearning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of Matterrhiantics_kram11No ratings yet
- Day3 Gen.-Chem-2 SASDocument6 pagesDay3 Gen.-Chem-2 SASsierra.johnfrancis123No ratings yet
- Nicky - Phases of Matter Webquest WorksheetDocument5 pagesNicky - Phases of Matter Webquest Worksheetapi-443024841100% (1)
- 2015MatterTest ADocument7 pages2015MatterTest Aguneetgill30No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 KMTDocument6 pagesActivity Sheet 1 KMT9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- (PHYSCI) Quarterly ExaminationDocument2 pages(PHYSCI) Quarterly ExaminationTLGA Emmanuel PotoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYDocument3 pagesPhysical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - AnsDocument8 pages2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - Anslmmlm0505No ratings yet
- Matter QuizDocument5 pagesMatter QuizduhyanNo ratings yet
- Activity sHEETS Q4Document5 pagesActivity sHEETS Q4Jim Alvarez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Document16 pagesGen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Edgardo RoperezNo ratings yet
- A LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Document5 pagesA LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Lexi MasseyNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM2 6thUEDocument4 pagesGENCHEM2 6thUEMea-Ann OscianasNo ratings yet
- Matter Webquest!: Now Let's Get Started On Matter!Document4 pagesMatter Webquest!: Now Let's Get Started On Matter!Brody Woolery100% (1)
- Sum 1, Phy SciDocument3 pagesSum 1, Phy SciJeclyn Filipinas100% (1)
- Gen Chem 2 Week-1Document9 pagesGen Chem 2 Week-1Saige RedNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDrew MalubagNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1 - RemovedDocument14 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1 - RemovedorevillojhnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyCatherine JeaneNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory QuizDocument1 pageCollision Theory QuizMaricel YamatNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade and Section: - ScoreDocument4 pagesName: - Grade and Section: - ScoreJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 1 (Gen Chem 1)Document4 pagesWorksheet No. 1 (Gen Chem 1)Rivamonte, Claire S.No ratings yet
- Final Exam PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument3 pagesFinal Exam PHYSICAL SCIENCEarniel catubigNo ratings yet
- Education Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Document8 pagesEducation Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Lama AldailamiNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictDocument2 pagesModule 1.3: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictJAYNAROSE IBAYAN100% (1)
- Crossword Puzzle: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document2 pagesCrossword Puzzle: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Iia - Properties of Water StudentDocument4 pagesIia - Properties of Water Studentapi-423322065No ratings yet
- PT Science 7 1stDocument3 pagesPT Science 7 1stSherene Frances BasilioNo ratings yet
- Situation Separation TechniqueDocument4 pagesSituation Separation Techniqueranulfo mayolNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocument4 pagesCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- ADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1Document23 pagesADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1EDGAR RIVERANo ratings yet
- Midterm Genchem2Document5 pagesMidterm Genchem2MONTEALTO ALDRICH FAJARDONo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Week 1-8 PDFDocument29 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Week 1-8 PDFDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- LP1 Gen. Chemistry 2 3rd Quarter SY2022-2023 CheckedDocument17 pagesLP1 Gen. Chemistry 2 3rd Quarter SY2022-2023 CheckedLady mistressNo ratings yet
- GenChem 1 - Worksheet 1 3Document8 pagesGenChem 1 - Worksheet 1 3Keith Laurence Lalisan CaliaoNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes WorksheetAndrew ChenNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document1 page© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - 1Document4 pagesScience 6 - 1Celina Grace VergaraNo ratings yet
- LP2 GenChem2Document10 pagesLP2 GenChem2Jaypee ViñassNo ratings yet
- Capiz National High School SUMMATIVE TEST in Science 7 Unit 1 (Module 2)Document1 pageCapiz National High School SUMMATIVE TEST in Science 7 Unit 1 (Module 2)Laysa FalsisNo ratings yet
- 3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudDocument4 pages3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudCarl Anthony Lague Pahuyo100% (1)
- Name 3Document2 pagesName 3marylou austriaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1Document2 pagesGen Bio 1Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document1 pageScience 7Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document2 pagesScience 10Trisha Camille Macario100% (2)
- Grade 6Document2 pagesGrade 6Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- ChemPlusChem - 2020 - Pilgrim - Metal Organic Frameworks and Metal Organic Cages A PerspectiveDocument16 pagesChemPlusChem - 2020 - Pilgrim - Metal Organic Frameworks and Metal Organic Cages A PerspectiveRahaf AljboriNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter Three Extra Practice Problemsleaveme07No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab ReportDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer Lab Reportkabo busanangNo ratings yet
- XII Reagents and Mechanism LDADocument21 pagesXII Reagents and Mechanism LDAAmey PatneNo ratings yet
- Nature of MaterialsDocument20 pagesNature of MaterialsBALBIDO John LesterNo ratings yet
- Design Practices - DrumsDocument32 pagesDesign Practices - Drumsagarwalashwin32100% (2)
- Unit 4 Chemistry NotesDocument72 pagesUnit 4 Chemistry NotesRabiatNo ratings yet
- In Vivo Metallic Biomaterials and Surface Modification: Takao HanawaDocument7 pagesIn Vivo Metallic Biomaterials and Surface Modification: Takao HanawaGabriel Vazquez VegaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer PDFDocument240 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer PDFAdJi Abdillah KharismaNo ratings yet
- ĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóDocument7 pagesĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóTrung Bùi QuốcNo ratings yet
- 2-Stage Reliq CycleDocument2 pages2-Stage Reliq Cycleravi rayNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2004 Paper 1 Level 5-7Document32 pagesKS3 Science 2004 Paper 1 Level 5-7wok20902No ratings yet
- MOISTURE - The Second Most Destructive Lubricant Contaminate, and Its Effects On Bearing LifeDocument4 pagesMOISTURE - The Second Most Destructive Lubricant Contaminate, and Its Effects On Bearing LifeAnonymous F2TxS3YoaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreDocument10 pagesInstitute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreMUmairQrNo ratings yet
- GrapheneDocument37 pagesGrapheneNazia AslamNo ratings yet
- Water Fired Absorption Chillers WFC SeriesDocument16 pagesWater Fired Absorption Chillers WFC SeriesUmut Sinan ÇetinbaşNo ratings yet
- PH Control Kel. 5 4a S1Document21 pagesPH Control Kel. 5 4a S1zahrah nadhirah kaniaNo ratings yet
- Theory of RadiationsDocument18 pagesTheory of RadiationsApoorva BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Colloidal Aggregation in Chiral Bacterial BathsDocument13 pagesUnconventional Colloidal Aggregation in Chiral Bacterial BathsakhilvarNo ratings yet
- Jiang Et Al 2024 Sustainable Aerobic Allylic C H Bond Oxidation With Heterogeneous Iron CatalystDocument10 pagesJiang Et Al 2024 Sustainable Aerobic Allylic C H Bond Oxidation With Heterogeneous Iron CatalystSaliya Ranashigha BandaraNo ratings yet
- PH3256 Physics For Information Science 1Document7 pagesPH3256 Physics For Information Science 1mohd.shakil5682No ratings yet
- ABSOGER Atmosphere Controlled, Nitrogen GeneratorDocument4 pagesABSOGER Atmosphere Controlled, Nitrogen GeneratorRaja Pathamuthu.GNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 HWDocument14 pagesTopic 10 HWIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersDocument15 pages2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersonnoezNo ratings yet
- Intern ReportDocument46 pagesIntern ReportAbhishek LambaNo ratings yet
- 12JPCM01 Answer KeyDocument13 pages12JPCM01 Answer Keyaachathyaa0032No ratings yet
- Chemistry - CH 2 - Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesChemistry - CH 2 - Atomic StructureHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument47 pagesElectrochemistryUtshav paudelNo ratings yet
- Contavan BA: Preliminary LeafletDocument3 pagesContavan BA: Preliminary Leafletmazhar naveedNo ratings yet
- 1B Energy Gap of LED Using Newton RingsDocument4 pages1B Energy Gap of LED Using Newton RingsRufaNo ratings yet
Gen Chem 2
Gen Chem 2
Uploaded by
Trisha Camille MacarioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gen Chem 2
Gen Chem 2
Uploaded by
Trisha Camille MacarioCopyright:
Available Formats
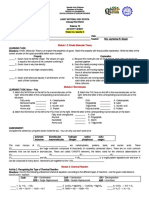
St. Peter’s College Test II. Supplementation: Supply the following with the correct answers.
Choose your
Sabayle St., Iligan City answer from the word bank and write it on the space provided.
Telephone No. (063) 222-2660 local 113
Email Address: spcbed18@gmail.com gen. chem. 1 Supercritical
A.Y: 2022 – 2023 Prelim Exam Dispersion force solution Le Chatelier’s Critical pressure
March 16-17, 2023 fluids
BASIC EDUCATION DEPARTMENT Intermolecular
4 x-ray diffraction Hydrogen bond 6
forces
Name: _________________________________ Score: _____/50
Ion-dipole force Non-volatile Water cohesive
Grade & Section: _________________________
Aqueous
General Instruction: Use ballpen in writing your answer. 1 ERASURE = -1 Hydrogen force Henry’s Law viscosity hydrogen
solution
Test I. Multiple Choice:
1. Kinetic Molecular Theory is used to explain the __________ of __________.
a. behavior, particles c. speed, particles A. Identification.
b. behavior, matter d. speed, matter __________1. Holds the particles of liquid and solid close together.
2. Juan observed the ice as it melts on the table. He wondered what happened __________2. A much stronger bond than a normal dipole-dipole bond.
to the movement of the particles present on the ice. Which of the following __________3. Force that occurs when ionic compound is mixed with a polar compound.
concepts can help Juan?
a. The movement of the particles become slower as phase change __________4. Type of force present in all molecules.
happens. __________5. The strongest intermolecular force in pure substances.
b. The movement of the particles become slower because there are spaces
between particles. __________6. Resistance of a liquid to flow.
c. The movement of the particles become faster because the temperature __________7. An attraction between the molecules in the liquid.
of the ice changes sufficiently as phase change happens.
d. The movement of the particles become faster because the particles in ice __________8. Liquids that do not vaporize easily.
is faster than the particles in water. __________9. Fluids have characteristics of both the liquid and the gas.
3. Based on the KMT, what happens to the kinetic energy of the particles as __________10. Pressure where the critical point transition occurs.
temperature increases?
__________11. How many hydrogen bonds can a water molecule form?
a. KE increases c. KE remains the same
b. KE decreases d. KE is constant __________12. A solution where water is the solvent.
4. Which of the following is TRUE about the properties of solids? __________13. The relationship associating gas pressure and solubility.
a. Molecules are not held rigidly in position. __________14. Universal solvent.
b. Many solids are characterized by long-range order; that is, the molecules
are arranged in regular configurations in three dimensions. __________15. The goal of this method is to determine the distance between the
c. There is even less empty space in a liquid than in a solid. layers of atoms.
d. Solids are almost incompressible and possess definite shape and volume
5. Which of the following is NOT true about the properties of liquids?
a. Liquids are incompressible
b. The molecules in liquid can move past one another freely
c. Liquid can flow, can be poured, and assumes the shape of its container
d. In a liquid, the molecules are so close together that there is very little
empty space.
B. Fill in the blanks. Test IV. Giving Meaning: Define the following terms briefly and concisely.
1. Matter is made of __________ that are constantly in motion. This
1. Solvent vs. Solute
energy in __________ is called __________.
2. The amount of __________ energy in a substance is related to its __________.
3. There is space between __________. The amount of space in between 2. Dilute Solution vs. Concentrated Solution
particles are related to the substances __________ of matter.
4. Phase changes happen when the __________ of the substance changes
3. Aqueous solution vs. Non-aqueous Solution
sufficiently.
5. __________ occurs when most of the molecules don’t have ___ ___ ___ to overcome
their _________ attraction. 4. Miscible Substances vs. Immiscible Substances
Test III. True or False: Read the statements carefully. Write FACT if the statement is true. If
false, change the underlined word/phrase to make the statement true. 5. Saturated vs. Unsaturated vs. Supersaturated
_______1. Weak intermolecular forces have high vapor pressure.
_______2. The rate of evaporation is equal to the rate of condensation.
_______3. When a liquid reaches the boiling point there is enough energy for molecules
in the interior to break free and enter the vaporization state.
_______4. Increasing temperature of a liquid increases the vapor pressure.
_______5. Evaporation is the direct transition from the solid to the gas state.
_______6. Particles in a solution are visible to the naked eye.
_______7. Dilute solution has more amount of solute than solvent.
_______8. Mixture of alcohol and water is an example of miscible substances.
_______9. Adding heat to a boiling liquid does not increase the temperature above the
boiling point.
_______10. Concentration is the maximum amount of a substance that will dissolve in a
given amount of solvent at a specified temperature.
You might also like
- Science 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesScience 10 LAS 4.1.1 The Kinetic Molecular TheoryHelma Jabello AriolaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledRann ValleNo ratings yet
- Is The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateDocument5 pagesIs The Transition of A Substance Directly From The Solid To The Gas State, Without Passing Through The Liquid StateJerica BautNo ratings yet
- 3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Document2 pages3RD QUARTER GEN CHem2Ainon SalendabNo ratings yet
- (WEEK 1) (Chemistry) Preparatory Learning ActivityDocument6 pages(WEEK 1) (Chemistry) Preparatory Learning Activity12 STEM Kyla Jean TantoyNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Module 1Document27 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Module 1Kate PedritaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Biochemistry Guided Notes Student VersionDocument12 pagesUnit 2: Biochemistry Guided Notes Student VersionRahsaan BurksNo ratings yet
- Semifinals GenchemDocument4 pagesSemifinals GenchemDave julius CericoNo ratings yet
- Day14 - Gen. Chem 2 - SASDocument6 pagesDay14 - Gen. Chem 2 - SASBilly PestañoNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet General Chemistry 2 (Q2 - Wks. 1-2) Kinetic Molecular TheoryJeffrey YumangNo ratings yet
- Gen. Chem Long Quiz (Q1 - 2nd Sem)Document4 pagesGen. Chem Long Quiz (Q1 - 2nd Sem)Grophel MesaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 - LAS 1 HANDOUTDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 - LAS 1 HANDOUTMark RazNo ratings yet
- Midterm GEN CHEM 2 TEST QUESTIONSDocument4 pagesMidterm GEN CHEM 2 TEST QUESTIONSMark Cesar VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesDocument20 pagesGenchem 2 Module 1 - Kinetic Molecular Model & Intermolecular ForcesMathew LlabresNo ratings yet
- Second Monthly Exam-Ma'am MoniqueDocument22 pagesSecond Monthly Exam-Ma'am MoniqueMonique Joy ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Test Ngss ChemistryDocument4 pagesUnit 4 Test Ngss Chemistryapi-664258676No ratings yet
- Learning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of MatterDocument7 pagesLearning: Formation of Elements in The Universe and Properties of Matterrhiantics_kram11No ratings yet
- Day3 Gen.-Chem-2 SASDocument6 pagesDay3 Gen.-Chem-2 SASsierra.johnfrancis123No ratings yet
- Nicky - Phases of Matter Webquest WorksheetDocument5 pagesNicky - Phases of Matter Webquest Worksheetapi-443024841100% (1)
- 2015MatterTest ADocument7 pages2015MatterTest Aguneetgill30No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet 1 KMTDocument6 pagesActivity Sheet 1 KMT9Wezen Jowelyn Mae G. TabuzoNo ratings yet
- (PHYSCI) Quarterly ExaminationDocument2 pages(PHYSCI) Quarterly ExaminationTLGA Emmanuel PotoyNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYDocument3 pagesPhysical Science 11th ABM HUMSS - NOKEYOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - AnsDocument8 pages2324 - F3 - Sci Exam - Final (Roi) - Anslmmlm0505No ratings yet
- Matter QuizDocument5 pagesMatter QuizduhyanNo ratings yet
- Activity sHEETS Q4Document5 pagesActivity sHEETS Q4Jim Alvarez RomeroNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Document16 pagesGen Chem2 Module 1 (Q2)Edgardo RoperezNo ratings yet
- A LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Document5 pagesA LITTLE CHEMISTRY Chapter 2-1 and 2-2Lexi MasseyNo ratings yet
- GENCHEM2 6thUEDocument4 pagesGENCHEM2 6thUEMea-Ann OscianasNo ratings yet
- Matter Webquest!: Now Let's Get Started On Matter!Document4 pagesMatter Webquest!: Now Let's Get Started On Matter!Brody Woolery100% (1)
- Sum 1, Phy SciDocument3 pagesSum 1, Phy SciJeclyn Filipinas100% (1)
- Gen Chem 2 Week-1Document9 pagesGen Chem 2 Week-1Saige RedNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDrew MalubagNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1 - RemovedDocument14 pagesGen Chem 2 Q2 Module 1 - RemovedorevillojhnNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Solutions WS Part I - VocabularyCatherine JeaneNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory QuizDocument1 pageCollision Theory QuizMaricel YamatNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade and Section: - ScoreDocument4 pagesName: - Grade and Section: - ScoreJulie PedregosaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet No. 1 (Gen Chem 1)Document4 pagesWorksheet No. 1 (Gen Chem 1)Rivamonte, Claire S.No ratings yet
- Final Exam PHYSICAL SCIENCEDocument3 pagesFinal Exam PHYSICAL SCIENCEarniel catubigNo ratings yet
- Education Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Document8 pagesEducation Gate International School 2: Name: - Grade: 6Lama AldailamiNo ratings yet
- Module 1.3: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictDocument2 pagesModule 1.3: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Lagay National High School Calauag West DistrictJAYNAROSE IBAYAN100% (1)
- Crossword Puzzle: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document2 pagesCrossword Puzzle: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Iia - Properties of Water StudentDocument4 pagesIia - Properties of Water Studentapi-423322065No ratings yet
- PT Science 7 1stDocument3 pagesPT Science 7 1stSherene Frances BasilioNo ratings yet
- Situation Separation TechniqueDocument4 pagesSituation Separation Techniqueranulfo mayolNo ratings yet
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocument4 pagesCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNo ratings yet
- ADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1Document23 pagesADM GEN - CHEMISTRY 2 Lesson 1EDGAR RIVERANo ratings yet
- Midterm Genchem2Document5 pagesMidterm Genchem2MONTEALTO ALDRICH FAJARDONo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Week 1-8 PDFDocument29 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Week 1-8 PDFDarey ApostolNo ratings yet
- LP1 Gen. Chemistry 2 3rd Quarter SY2022-2023 CheckedDocument17 pagesLP1 Gen. Chemistry 2 3rd Quarter SY2022-2023 CheckedLady mistressNo ratings yet
- GenChem 1 - Worksheet 1 3Document8 pagesGenChem 1 - Worksheet 1 3Keith Laurence Lalisan CaliaoNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes WorksheetDocument4 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes WorksheetAndrew ChenNo ratings yet
- © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document1 page© 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Kaung Myat SanNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - 1Document4 pagesScience 6 - 1Celina Grace VergaraNo ratings yet
- LP2 GenChem2Document10 pagesLP2 GenChem2Jaypee ViñassNo ratings yet
- Capiz National High School SUMMATIVE TEST in Science 7 Unit 1 (Module 2)Document1 pageCapiz National High School SUMMATIVE TEST in Science 7 Unit 1 (Module 2)Laysa FalsisNo ratings yet
- 3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudDocument4 pages3rd SUMMATIVE TEST Final Na JudCarl Anthony Lague Pahuyo100% (1)
- Name 3Document2 pagesName 3marylou austriaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1Document2 pagesGen Bio 1Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- Science 7Document1 pageScience 7Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document2 pagesScience 10Trisha Camille Macario100% (2)
- Grade 6Document2 pagesGrade 6Trisha Camille MacarioNo ratings yet
- ChemPlusChem - 2020 - Pilgrim - Metal Organic Frameworks and Metal Organic Cages A PerspectiveDocument16 pagesChemPlusChem - 2020 - Pilgrim - Metal Organic Frameworks and Metal Organic Cages A PerspectiveRahaf AljboriNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three Extra Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChapter Three Extra Practice Problemsleaveme07No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lab ReportDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer Lab Reportkabo busanangNo ratings yet
- XII Reagents and Mechanism LDADocument21 pagesXII Reagents and Mechanism LDAAmey PatneNo ratings yet
- Nature of MaterialsDocument20 pagesNature of MaterialsBALBIDO John LesterNo ratings yet
- Design Practices - DrumsDocument32 pagesDesign Practices - Drumsagarwalashwin32100% (2)
- Unit 4 Chemistry NotesDocument72 pagesUnit 4 Chemistry NotesRabiatNo ratings yet
- In Vivo Metallic Biomaterials and Surface Modification: Takao HanawaDocument7 pagesIn Vivo Metallic Biomaterials and Surface Modification: Takao HanawaGabriel Vazquez VegaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer PDFDocument240 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer PDFAdJi Abdillah KharismaNo ratings yet
- ĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóDocument7 pagesĐỒ THỊ logP hđồ thị môi chất lạnh đóTrung Bùi QuốcNo ratings yet
- 2-Stage Reliq CycleDocument2 pages2-Stage Reliq Cycleravi rayNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science 2004 Paper 1 Level 5-7Document32 pagesKS3 Science 2004 Paper 1 Level 5-7wok20902No ratings yet
- MOISTURE - The Second Most Destructive Lubricant Contaminate, and Its Effects On Bearing LifeDocument4 pagesMOISTURE - The Second Most Destructive Lubricant Contaminate, and Its Effects On Bearing LifeAnonymous F2TxS3YoaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreDocument10 pagesInstitute of Metallurgy and Materials Engineering Faculty of Chemical and Materials Engineering University of The Punjab LahoreMUmairQrNo ratings yet
- GrapheneDocument37 pagesGrapheneNazia AslamNo ratings yet
- Water Fired Absorption Chillers WFC SeriesDocument16 pagesWater Fired Absorption Chillers WFC SeriesUmut Sinan ÇetinbaşNo ratings yet
- PH Control Kel. 5 4a S1Document21 pagesPH Control Kel. 5 4a S1zahrah nadhirah kaniaNo ratings yet
- Theory of RadiationsDocument18 pagesTheory of RadiationsApoorva BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Unconventional Colloidal Aggregation in Chiral Bacterial BathsDocument13 pagesUnconventional Colloidal Aggregation in Chiral Bacterial BathsakhilvarNo ratings yet
- Jiang Et Al 2024 Sustainable Aerobic Allylic C H Bond Oxidation With Heterogeneous Iron CatalystDocument10 pagesJiang Et Al 2024 Sustainable Aerobic Allylic C H Bond Oxidation With Heterogeneous Iron CatalystSaliya Ranashigha BandaraNo ratings yet
- PH3256 Physics For Information Science 1Document7 pagesPH3256 Physics For Information Science 1mohd.shakil5682No ratings yet
- ABSOGER Atmosphere Controlled, Nitrogen GeneratorDocument4 pagesABSOGER Atmosphere Controlled, Nitrogen GeneratorRaja Pathamuthu.GNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 HWDocument14 pagesTopic 10 HWIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersDocument15 pages2011 H2 Chem SRJC Prelim Paper 2 Suggested AnswersonnoezNo ratings yet
- Intern ReportDocument46 pagesIntern ReportAbhishek LambaNo ratings yet
- 12JPCM01 Answer KeyDocument13 pages12JPCM01 Answer Keyaachathyaa0032No ratings yet
- Chemistry - CH 2 - Atomic StructureDocument7 pagesChemistry - CH 2 - Atomic StructureHassan RiazNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument47 pagesElectrochemistryUtshav paudelNo ratings yet
- Contavan BA: Preliminary LeafletDocument3 pagesContavan BA: Preliminary Leafletmazhar naveedNo ratings yet
- 1B Energy Gap of LED Using Newton RingsDocument4 pages1B Energy Gap of LED Using Newton RingsRufaNo ratings yet