Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1
Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1
Uploaded by
Lloyd Christian PorlajeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1
Lesson No.6.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Friction.may2023-1
Uploaded by
Lloyd Christian PorlajeCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson No.
6: FRICTION: Static and Kinetic
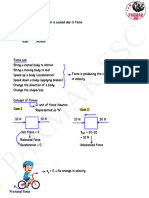
Force of Friction – when an object is in motion either on a surface or in a viscous medium such as air or water, there is
resistance to the motion because the object interacts with its surroundings.
A. Friction: It refers to the actual forces that are exerted to oppose motion. It is a contact resistance exerted by one body
upon a second body when the second body tends to move past the first body.
B. Kinds of Friction:
1. Sliding Friction – It is the frictional resistance an object in motion experiences.
2. Rolling Friction – It is the resistance to motion caused usually by deformation.
3. Fluid Friction – It is a friction encountered by a solid when it moves in a liquid gas.
Example: 1. Resistance moving object on water. 2. Resistance of air on a moving car or airplane.
C. Two Types of Force of Sliding Friction:
1. Force of Static Friction (Fs): It is the type of friction that acts when there is no relative motion between an object
and the surface, or is the starting force must overcome to be set on motion.
Application: Object at rest
Fs ≤ UsN
Analysis of Force of Static Friction
Let Fs max = 30N
a. Fs = 0, if there is no force parallel to the plane. c. The object is about to move or motion is impending.
W F = 30N
Us Fs = - 30N
N Fs = 0
b. The object is still in equilibrium. d. The object will move because the applied force F
F = 30N exceeded the maximum force of static friction.
F = 30N
Fs = - 30N
Us Fs = - 30N
Fs max = Us N
2. Force of Kinetic Friction (Fk): It is the type of friction that acts when an object slides over a surface, or is the force
to maintain in uniform motion.
(Application Moving Objects)
W
Fk = UkN
F
Note: Us > Uk
Uk N Fk
D. Formulas:
U = Ff , U k = Fk , Us = Fs
N N N
Where:
U = coefficient of friction, Us = coefficient of static friction, Uk = coefficient of kinetic friction
Ff = frictional force (it is a contact parallel between two objects that opposes the motion of the body, or
opposite direction of the force F a motion), the frictional resisting force
W = weight of an object
N = resultant normal force (opposite direction of the weight)
Three Cases in Solving Coefficient of Friction U:
Case I: The force F is parallel to the horizontal line. Case II: The force F is applied at an angle θ above the horizontal
N Illustration:
Illustration: F Ff_ = F a. Push F N Motion b. Pull N F
U= θ
N W θ
U Ff
W
U W Ff U W Ff
U= f =F _ F Cos θ__ F _ F Cos θ__
U= f =
N W + F Sin θ N W – F Sin θ
Case III: The force F is at Inclined plane (Friction on Inclined Plane).
Angle of Repose: It is the Angle of inclination at which the object will slide by itself in uniform motion.
Illustration: Motion N
Ff U U = Ff_ = Sin θ = Tan θ
N Cos θ
θ
θ W
You might also like
- Presence of Scabies As A Health DeficitDocument4 pagesPresence of Scabies As A Health DeficitLemuel Glenn Bautista100% (9)
- Physics Grade 12 Revision VERY IMPORTANTDocument261 pagesPhysics Grade 12 Revision VERY IMPORTANTSafoora0% (1)
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument43 pagesNewton's Laws of Motioncooking50% (2)
- LowCam Solutions Guide English34Document7 pagesLowCam Solutions Guide English34gerguselNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Newton's Laws of MotionDocument79 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Newton's Laws of MotionMadhav LohchabNo ratings yet
- 2022 Physical Sciences Revision DocumentDocument174 pages2022 Physical Sciences Revision DocumentThandeka NdlovuNo ratings yet
- Important Terms in FrictionDocument7 pagesImportant Terms in FrictionIrmaNo ratings yet
- 11 Physics Notes 03 Law of MotionDocument55 pages11 Physics Notes 03 Law of MotionLokanath MishraNo ratings yet
- PHYS101 - Laws of MotionDocument53 pagesPHYS101 - Laws of MotionSamuel ArquilloNo ratings yet
- 2 ForcesDocument35 pages2 Forcesschiliza1975No ratings yet
- PHYS101 Laws of MotionDocument53 pagesPHYS101 Laws of MotionCoolman TatsuNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - ForceDocument34 pagesCh3 - ForceALIF SYAKIR SATARNo ratings yet
- Phy10t3fce&nslm PDFDocument54 pagesPhy10t3fce&nslm PDFRyan Jhay YangNo ratings yet
- A.2.1 ForcesDocument51 pagesA.2.1 ForceszmedendoNo ratings yet
- Chap5 Apply Newton Laws-1Document38 pagesChap5 Apply Newton Laws-1Tuấn Nghĩa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Newton's Laws of Motion PDFDocument79 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Newton's Laws of Motion PDFAbhay mane100% (2)
- Lesson No.7.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Work.may2023-1Document1 pageLesson No.7.Lecture - Physics For Engineers - Work.may2023-1Lloyd Christian PorlajeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics in Two DimensionsDocument105 pagesDynamics in Two DimensionsBoldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- 10 - Work-Energy Methods 19-20Document72 pages10 - Work-Energy Methods 19-20Basel HeshamNo ratings yet
- GE 253 Week 4 Lecture SlidesDocument11 pagesGE 253 Week 4 Lecture SlidesmanishnarayanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Forces and MotionDocument74 pagesChapter 4 Forces and Motiondaua abdouNo ratings yet
- Inclined PlanesDocument7 pagesInclined PlanesBradley ChisolmNo ratings yet
- Friction: K.V. SilcharDocument10 pagesFriction: K.V. SilcharMichael BentonNo ratings yet
- 2.3 WORK and ENERGY PDFDocument60 pages2.3 WORK and ENERGY PDFsanad boshehNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 03 Dynamics: ForceDocument11 pagesChapter # 03 Dynamics: ForceIlyas KhanNo ratings yet
- PHYS 211 6.STATIC 1ST CONDITION MergedDocument36 pagesPHYS 211 6.STATIC 1ST CONDITION MergedLEENo ratings yet
- First Condition of Equilibrium (Fce)Document22 pagesFirst Condition of Equilibrium (Fce)Miggy IsbertoNo ratings yet
- 2.4 WORK and ENERGY-2014Document48 pages2.4 WORK and ENERGY-2014Norfu PINo ratings yet
- Work, Energy and PowerDocument71 pagesWork, Energy and PowerSaurav DuttNo ratings yet
- Sph4u Energy Amp Momentum Unit 2 Notes 1Document36 pagesSph4u Energy Amp Momentum Unit 2 Notes 1hNo ratings yet
- Friction (Updated Notes) - 1-1 - 1631894795Document5 pagesFriction (Updated Notes) - 1-1 - 1631894795Godwin NgenoNo ratings yet
- Midterm Physics ReviewerDocument3 pagesMidterm Physics Reviewerryanabenise.fallera-21No ratings yet
- Physics Katete Grade 10Document68 pagesPhysics Katete Grade 10joshua witika100% (1)
- Force and Motion: Newton'S Laws of MotionDocument23 pagesForce and Motion: Newton'S Laws of Motionelle samsonNo ratings yet
- Work, Enrgy & PowerDocument8 pagesWork, Enrgy & PowerJohannesNo ratings yet
- Special "Extended Time" ExamsDocument16 pagesSpecial "Extended Time" ExamsazureusNo ratings yet
- Physical Science GR 12 - Work, Energy and Power - Theory - FullDocument7 pagesPhysical Science GR 12 - Work, Energy and Power - Theory - Fullthabotomoledi1No ratings yet
- Work, Energy and Power: Quick RevisionDocument22 pagesWork, Energy and Power: Quick Revisionhhgxc GhvNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsDocument8 pagesLaws of Motion: Inertia. The Inertia of A Body Is Related To What We Can Think of As The Amount of Matter It ContainsEduard Benjamin LauronNo ratings yet
- PHYS101 Lesson 2 Dynamics Part 2 - PDFDocument21 pagesPHYS101 Lesson 2 Dynamics Part 2 - PDFYour SageNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument11 pagesWork Energy and PowerKunal RaikarNo ratings yet
- Friction: Tec 114: Basic MechanicsDocument4 pagesFriction: Tec 114: Basic MechanicsGodwin NgenoNo ratings yet
- Tsunamî ? Physics Lecture 2 Force and Laws of Motion English PDFDocument7 pagesTsunamî ? Physics Lecture 2 Force and Laws of Motion English PDFdineshNo ratings yet
- FrictionDocument10 pagesFrictionSaileen FernandesNo ratings yet
- 4 Work and Energy OswDocument95 pages4 Work and Energy OswOoi Soo WeiNo ratings yet
- IJSO Part-17Document1 pageIJSO Part-17SadguruNo ratings yet
- Physics Friction ModuleDocument7 pagesPhysics Friction ModuleFRANCES VISAYANo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument8 pagesLaws of MotionmadhusudanmarthaNo ratings yet
- Topic - Work, Power and EnergyDocument12 pagesTopic - Work, Power and Energysaikat dasNo ratings yet
- I Sci 28 Friction On An InclineDocument2 pagesI Sci 28 Friction On An InclineZian Jolo CatacutanNo ratings yet
- FRICTION Unit 5 PDFDocument15 pagesFRICTION Unit 5 PDFSurulivelrajantNo ratings yet
- Midterm Physics ReviewerDocument4 pagesMidterm Physics Reviewerj1mmygamin9No ratings yet
- 05 Work EnergyDocument60 pages05 Work EnergyAshwin KushwahaNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Sec 2Document21 pagesCH 6 Sec 2FWGANo ratings yet
- Work, Power and Energy Notes - ShayanDocument18 pagesWork, Power and Energy Notes - ShayanShayan FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of Rigid BodyDocument45 pagesEquilibrium of Rigid BodyHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Engineering Science: Dynamics (Newton's Second Law, Force, Inertia)Document39 pagesEngineering Science: Dynamics (Newton's Second Law, Force, Inertia)DRAGON LAMNo ratings yet
- Physics Lecture Notes: 1.3 ForcesDocument10 pagesPhysics Lecture Notes: 1.3 Forcesben10uziNo ratings yet
- Exercise CONTEXT CLUESDocument2 pagesExercise CONTEXT CLUESSri MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Pro Tip Catalogue 4 07Document28 pagesPro Tip Catalogue 4 07notengofffNo ratings yet
- 9-10-2014 CWMA CNG-LNG Presentation 2014 (246 Pages)Document246 pages9-10-2014 CWMA CNG-LNG Presentation 2014 (246 Pages)kkaranagNo ratings yet
- ST315A Kiln Temperature ControllerDocument2 pagesST315A Kiln Temperature ControllerDave WalkerNo ratings yet
- Cliping & Clamping of DiodesDocument19 pagesCliping & Clamping of DiodesashutoshvashistNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: DEGALAN® LP 64/12Document2 pagesData Sheet: DEGALAN® LP 64/12Akhtar aliNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power PlantDocument50 pagesThermal Power PlantQasim KhalidNo ratings yet
- notes-on-miasms-heredity-and-nosodes-9788131910702Document13 pagesnotes-on-miasms-heredity-and-nosodes-9788131910702innahifi111No ratings yet
- Aviation Security Assignment 3Document5 pagesAviation Security Assignment 3Yousef Al HashemiNo ratings yet
- Kilmanun 2023 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1153 012037Document9 pagesKilmanun 2023 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 1153 012037rburhansyah4625No ratings yet
- Attendance ApplicationDocument1 pageAttendance Applicationgeniousbond007No ratings yet
- Roald Amundsen and The South PoleDocument11 pagesRoald Amundsen and The South PoleRhonda BushNo ratings yet
- (SOSC1960) (2012) (S) Quiz - jqj28 97890Document3 pages(SOSC1960) (2012) (S) Quiz - jqj28 97890alex61937No ratings yet
- DLL Mapeh-1 Q1 W3Document5 pagesDLL Mapeh-1 Q1 W3Melody FullerNo ratings yet
- Tower Crane SketchDocument20 pagesTower Crane SketchShafiqNo ratings yet
- Physics Problem Set S y 2020 21Document3 pagesPhysics Problem Set S y 2020 21GeeklyGamer 02No ratings yet
- Inoculating Techniques LabDocument5 pagesInoculating Techniques LabJerome LisingNo ratings yet
- RP 30 2 Selection and Use of Measurement InstrumentDocument212 pagesRP 30 2 Selection and Use of Measurement Instrumentmohammed el erianNo ratings yet
- FIR Design MintedDocument6 pagesFIR Design MintedGajendra PaikraNo ratings yet
- Problems of Dyeing Polyester With Disperse DyesDocument1 pageProblems of Dyeing Polyester With Disperse DyesrashidtexNo ratings yet
- API Vol 2Document220 pagesAPI Vol 2Mosam ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Isye6501 Office Hour Fa22 Week10 MonDocument8 pagesIsye6501 Office Hour Fa22 Week10 MonXuan KuangNo ratings yet
- Hidden FiguresDocument3 pagesHidden FiguresDrnNo ratings yet
- Cells Concept MapDocument1 pageCells Concept MapprameetaNo ratings yet
- A Survey of Field Applications of Gel Treatments For Water ShutoffDocument11 pagesA Survey of Field Applications of Gel Treatments For Water ShutoffBình TrầnNo ratings yet
- Rayleigh-Bénard Convection in A Horizontal Layer of Porous Medium Saturated With A Thermally Radiating Dielectric FluidDocument10 pagesRayleigh-Bénard Convection in A Horizontal Layer of Porous Medium Saturated With A Thermally Radiating Dielectric FluidIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Brosur - High Cap Tri-Seal SeriesDocument12 pagesBrosur - High Cap Tri-Seal Seriesjoko.maryanto.82No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Operation Winter 2019 Question PaperDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Operation Winter 2019 Question PaperMitesh ThakurNo ratings yet