Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Back Bonding
Back Bonding
Uploaded by
Shashwat Pal0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 page1. BH3 does not exist as a stable molecule because it forms dimers (B2H6) to remove electron deficiency, while BF3 is stabilized through pi back bonding.
2. The ease of hydrolysis for boron trihalides increases in the order BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 due to the increasing ability of the heavier halides to accept electrons through back bonding and form coordinate bonds.
3. The B-F bond length is shortest in BF3 compared to its complexes with NH3 and N(CH3)3 due to pi back bonding not being present in pure BF3.
Original Description:
Original Title
10. back bonding
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. BH3 does not exist as a stable molecule because it forms dimers (B2H6) to remove electron deficiency, while BF3 is stabilized through pi back bonding.
2. The ease of hydrolysis for boron trihalides increases in the order BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 due to the increasing ability of the heavier halides to accept electrons through back bonding and form coordinate bonds.
3. The B-F bond length is shortest in BF3 compared to its complexes with NH3 and N(CH3)3 due to pi back bonding not being present in pure BF3.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views1 pageBack Bonding
Back Bonding
Uploaded by
Shashwat Pal1. BH3 does not exist as a stable molecule because it forms dimers (B2H6) to remove electron deficiency, while BF3 is stabilized through pi back bonding.
2. The ease of hydrolysis for boron trihalides increases in the order BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3 due to the increasing ability of the heavier halides to accept electrons through back bonding and form coordinate bonds.
3. The B-F bond length is shortest in BF3 compared to its complexes with NH3 and N(CH3)3 due to pi back bonding not being present in pure BF3.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
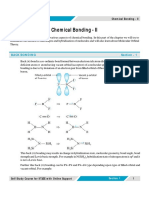
BACK BONDING
ASSIGNMENT - 10
1. BF3 exists but BH3 does not. Why explain?
2. Arrange the following boron trihalides in the increasing order of their ease of hydrolysis. Also give the
reason for the same.
BF3, BCl3, BBr3
3. In which of the following compounds B – F bond length is shortest ?
(A) BF4– (B) BF3 NH3 (C) BF3 (D) BF3 N(CH3)3
4. Which of the following statement is false for trisilylamine ?
(A) Three sp2 orbitals are used for bonding, giving a plane triangular structure.
(B) The lone pair of electrons occupy a p-orbital at right angles to the plane triangle and this overlaps with
empty p–orbitals on each of the three silicon atoms resulting in bonding.
(C) The N–Si bond length is shorter than the expected N–Si bond length.
(D) It is a weaker Lewis base than trimethyl amine.
5. Which of the following statement is correct for the 1 : 1 complex of trimethyl amine and boron tri fluoride?
(A) The B - F bond length in the complex is longer than that of in BF3.
(B) The N is pyramidal with sp3 hybridisation and B is planar with sp2 hybridisation.
(C) The coordination geometry of N and B both are tetrahedral with sp3 hybridisation each.
(D) (A) and (C) both.
Answer Key
1. BF3 molecule being electron deficient gets stabilised through P – Pback bonding. where as BH3 removes
its electron deficiency through dimerisation and thus exists as B2H6.
2. BF3 < BCl3 < BBr3
Electron acceptor strength of boron halides on the basis of back bonding is BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3 Hydrolysis
takes place through coordinate bond formation, easier the coordinate bond formation greater is the extent
of hydrolysis.
3. C 4. B 5. D
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding - IIDocument43 pagesChemical Bonding - IIAnonymous BnZrzImmC9No ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - II: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeDocument43 pagesChemical Bonding - II: Join Our Telegram Channel: @airjeeVallabhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - IIDocument43 pagesChemical Bonding - IIGodzilla EarthNo ratings yet
- P Block Nurture 9 16Document8 pagesP Block Nurture 9 16Tanishka MahajanNo ratings yet
- 86.7.1 Boron Trihalides 195Document21 pages86.7.1 Boron Trihalides 195laythNo ratings yet
- P Block (English)Document207 pagesP Block (English)Aditya YadavNo ratings yet
- 23 OctDocument2 pages23 OctsarahNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document11 pagesAssignment 5Asma SohailNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: One or More Than One Answer Type QuestionsDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding: One or More Than One Answer Type Questionssree anugraphicsNo ratings yet
- Boron FamilyDocument20 pagesBoron FamilyP. PARIS KATHERINE REBECCAH BCMBC2019No ratings yet
- 3 2PPDocument3 pages3 2PPSandeep ChallaNo ratings yet
- P-Block (Group 13 To 14) NM Solution (-1) Chem PDFDocument31 pagesP-Block (Group 13 To 14) NM Solution (-1) Chem PDFChauhan RonakNo ratings yet
- Chemcial Bonding Advanced Problems-2024Document6 pagesChemcial Bonding Advanced Problems-2024gummadavellikoushikNo ratings yet
- Test Paper - 1 - Main - For Final ExamDocument7 pagesTest Paper - 1 - Main - For Final ExamritvikpradeepNo ratings yet
- 11.chemical BondingDocument10 pages11.chemical BondingAtif KhanNo ratings yet
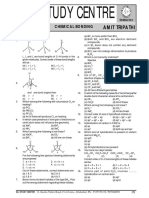
- Sai Study Centre: Amit TripathiDocument16 pagesSai Study Centre: Amit Tripathiphineasferb000% (1)
- Test ReviewDocument3 pagesTest ReviewgraceNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Revision DPP 2024Document4 pagesChemical Bonding - Revision DPP 2024Soham GhodkhandeNo ratings yet
- CBO-3 TH E FHxs4gaDocument14 pagesCBO-3 TH E FHxs4gaHimanshu ThalorNo ratings yet
- 4.chemical Bonding - Molecular Structure AK 2 (2018-19)Document12 pages4.chemical Bonding - Molecular Structure AK 2 (2018-19)Tarun RaoNo ratings yet
- Practice Quiz CH 4Document6 pagesPractice Quiz CH 4KahfiantoroNo ratings yet
- 3 2PPDocument3 pages3 2PPSandeep ChallaNo ratings yet
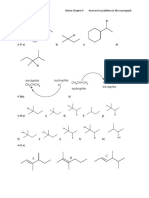
- Chem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The CoursepackDocument7 pagesChem 221 Bruice Chapter 4 Answers To Problems in The CoursepackParham ElahiNo ratings yet
- Xi Iit Chemistry-Chemical Bonding (Bond Parameters & Dipolemoment) CW - 6 Bond Length and Bond Angle ComparisionDocument8 pagesXi Iit Chemistry-Chemical Bonding (Bond Parameters & Dipolemoment) CW - 6 Bond Length and Bond Angle ComparisionVVK XI B SIVABALAKUMARAN SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructurenamratanimiNo ratings yet
- Chem241 - Exp 3Document12 pagesChem241 - Exp 3Noor AbdulqaderNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument22 pagesInorganic ChemistryuniquestarNo ratings yet
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Back BondingDocument10 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: Section (A) : Back BondingwanderedNo ratings yet
- HL Bonding Questions 2Document4 pagesHL Bonding Questions 2ehodariNo ratings yet
- Ms Teams Chemical Bonding We 2 Ans KeyDocument4 pagesMs Teams Chemical Bonding We 2 Ans KeyArsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingYanti FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 28 - Elemental Boron Chemistry: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonDocument10 pagesLecture 28 - Elemental Boron Chemistry: 2P32 - Principles of Inorganic Chemistry Dr. M. PilkingtonFatma SöğütNo ratings yet
- BoranesDocument32 pagesBoranessaumya satyarthyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4th Edition Burdge Solutions ManualDocument32 pagesChemistry 4th Edition Burdge Solutions Manualacrania.dekle.z2kajy100% (30)
- DPP - 3Document3 pagesDPP - 3Imran NazishNo ratings yet
- FBF FPF: Inorganic Chemistry QUIZ # 03 Time: 10 MinDocument4 pagesFBF FPF: Inorganic Chemistry QUIZ # 03 Time: 10 Minhoney1002No ratings yet
- Pbde PaperDocument4 pagesPbde PaperAlexSNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th Objective (In)Document6 pagesCHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th Objective (In)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry WorksheetDocument5 pagesChemistry Worksheet987f7gjvt7No ratings yet
- Boron & Carbon Family: Chapter Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesBoron & Carbon Family: Chapter Practice ProblemsAyush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Electron Deficient MoleculesDocument3 pagesElectron Deficient MoleculesshahawisshahawisNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Substitution PDFDocument13 pagesAromatic Substitution PDFNesha VincentNo ratings yet
- DPT-29 Che&zoo Neet 03.02.24Document12 pagesDPT-29 Che&zoo Neet 03.02.24pinnaacleclasses salemNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem - 01 - Back BondingDocument8 pagesPractice Problem - 01 - Back Bondingwtaker69No ratings yet
- Reaction IntermediateDocument18 pagesReaction IntermediateManaswini P100% (1)
- Blue Angels Global School: Subject: Chemistry Class: - Xi Date: 1.12.2021Document4 pagesBlue Angels Global School: Subject: Chemistry Class: - Xi Date: 1.12.2021Praveen SinghNo ratings yet
- Chem Academy: Exercise - IDocument16 pagesChem Academy: Exercise - IHamit Rana100% (1)
- IIIA Group Elements PDFDocument6 pagesIIIA Group Elements PDFPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Worksheet Chemical BondingDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Worksheet Chemical BondingShashwatNo ratings yet
- WPT Centre Xi Iit Jee Che Key 02-12-23Document2 pagesWPT Centre Xi Iit Jee Che Key 02-12-23Deena chemistNo ratings yet
- Chem 22-23 S3 Exam2Document12 pagesChem 22-23 S3 Exam2LSWNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Single Option Correct:-: Xy Yz Xy y XDocument3 pagesChemical Bonding Single Option Correct:-: Xy Yz Xy y Xdevshah7707No ratings yet
- C. Three Bonds of The Same Length: IB Chemistry HL Topic4 Questions 1Document22 pagesC. Three Bonds of The Same Length: IB Chemistry HL Topic4 Questions 1Sylvia NamandaNo ratings yet
- 3center and 2 Electron BondDocument20 pages3center and 2 Electron BondAmin GNo ratings yet
- CHM 102 - Assigmnent QuestionsDocument2 pagesCHM 102 - Assigmnent Questionsprerana23No ratings yet
- CH 10Document13 pagesCH 10patilamardip0078122No ratings yet
- Amorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesFrom EverandAmorphous Semiconductors: Structural, Optical, and Electronic PropertiesNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb (Part 2)From EverandInorganic Reactions and Methods, The Formation of Bonds to C, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb (Part 2)A. P. HagenNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrom EverandSimulation of Transport in NanodevicesFrançois TriozonNo ratings yet
- 3c04ebd1_691c_43ad_8bc8_2e029dee94ecDocument1 page3c04ebd1_691c_43ad_8bc8_2e029dee94ecShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 003 ????? Lecture Planner Physical Chemistry Varun JEE AdvaDocument1 page003 ????? Lecture Planner Physical Chemistry Varun JEE AdvaShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 002 Set, Relations, Funciton and ITF 01 Class Notes Varun JEEDocument15 pages002 Set, Relations, Funciton and ITF 01 Class Notes Varun JEEShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Mole and Equiv ConceptDocument25 pagesMole and Equiv ConceptShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 2B. Complex Numbers L-ViDocument37 pages2B. Complex Numbers L-ViShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- CM Test 1Document21 pagesCM Test 1Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws Of Motion _ DPP 02 __ Varun JEE Advanced 2024Document3 pagesNewton Laws Of Motion _ DPP 02 __ Varun JEE Advanced 2024Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Newton LawDocument14 pagesNewton LawShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 3B. Progressions L-ViDocument25 pages3B. Progressions L-ViShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Application of Dipole MomentDocument1 pageApplication of Dipole MomentShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- LOGARITHMS L-V and VIDocument15 pagesLOGARITHMS L-V and VIShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- VECTOR 6 - CROSS Product - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics) - 1Document2 pagesVECTOR 6 - CROSS Product - Vikas Agarwal (MT Physics) - 1Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 6.ionic Equilibrium TheoryDocument41 pages6.ionic Equilibrium TheoryShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Percentage Ionic Character Using Dipole MomentDocument1 pageCalculation of Percentage Ionic Character Using Dipole MomentShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- EklavyATS-2023-Full Test 13 - NQT - 2-May 25 - Result SheetDocument8 pagesEklavyATS-2023-Full Test 13 - NQT - 2-May 25 - Result SheetShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- 01b.functions L-ViDocument18 pages01b.functions L-ViShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Review 1D - Without AnswersDocument3 pagesKinematics Review 1D - Without AnswersShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- DPP - 3 - Squence and SeriesDocument4 pagesDPP - 3 - Squence and SeriesShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Class Test-1 - MoleDocument2 pagesClass Test-1 - MoleShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- JEE 10 - Math Test-1Document14 pagesJEE 10 - Math Test-1Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Result 1 Jee AdvncedDocument1 pageResult 1 Jee AdvncedShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- JEE 11 - Advanced Test-1-Paper-2Document26 pagesJEE 11 - Advanced Test-1-Paper-2Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Exercise5Document8 pagesTrigonometry Exercise5Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Exercise6Document4 pagesTrigonometry Exercise6Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- FREEE CHLORINE IN BLEACHING POWDER Assignment-9Document1 pageFREEE CHLORINE IN BLEACHING POWDER Assignment-9Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry DPP1Document3 pagesTrigonometry DPP1Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Exercise2Document12 pagesTrigonometry Exercise2Shashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Dhristi-JEE-Hinglish-W-23-24 - May 14 Adv TestDocument1 pageDhristi-JEE-Hinglish-W-23-24 - May 14 Adv TestShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonomery - Basic ExerciseDocument11 pagesTrigonomery - Basic ExerciseShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Exercise1Document10 pagesTrigonometry Exercise1Shashwat PalNo ratings yet