Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dna Report g8
Dna Report g8
Uploaded by
Rhain HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- First Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadDocument2,144 pagesFirst Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadAyub SadiqNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsayesheedattaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument12 pagesNucleotidesIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- xxxxxxxx2023 MAR SBB 1208 NucleotidesDocument13 pagesxxxxxxxx2023 MAR SBB 1208 NucleotidesmechellesibandaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesBiomoleculesrajan.11proNo ratings yet
- L1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentDocument29 pagesL1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument18 pagesTutorialTurky TurkyNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Chapter 4 - DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Chapter 4 - DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesischelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument35 pagesNucleic AcidCheelsy P. ButronNo ratings yet
- Adenine: ThymineDocument1 pageAdenine: ThymineFrancis Joule Aberia TrigueNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Research in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Document27 pagesResearch in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Kim GoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidsRex Blanco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesNucleic AcidsAshley Margareth BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Chemical Basis of Heredity: Study Guide For Module No.Document13 pagesChapter 3: Chemical Basis of Heredity: Study Guide For Module No.REGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesLevels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDianne Joy LeybaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1102 Course WorkDocument5 pagesBio 1102 Course WorkkasingabalyaandrewNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesMarie WrightNo ratings yet
- Biological Function and Chemical Nature of AdenineDocument1 pageBiological Function and Chemical Nature of Adeninerianashah7629No ratings yet
- L2 CytoDocument16 pagesL2 CytoDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 5th LectureDocument24 pagesBIO 001 5th LectureBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDocument4 pagesNucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- Nucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesDocument5 pagesNucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesLuis Felipe Mera GrandasNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous BasesDocument6 pagesNitrogenous BasesMaak Ali AnsariNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Molecules of HeredDocument82 pagesMolecules of HeredTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE BYU MEDICAL WITHUSDocument5 pagesBIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE BYU MEDICAL WITHUSMohammad Kashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18Document18 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18ADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesStructure of Nucleic Acidsplayandhavefun23No ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Document9 pagesDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Clinical Pathology CH 8 Metabolism NotesDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Clinical Pathology CH 8 Metabolism Notesshubhm008No ratings yet
- 2.2 Cell ContructionDocument25 pages2.2 Cell ContructionDesyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleotidesvitro4No ratings yet
- Nucleotides: Cabal, Noreen A. BSPSY 3-3 Group 2Document9 pagesNucleotides: Cabal, Noreen A. BSPSY 3-3 Group 2Reen CabalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument67 pagesNucleic AcidHeddy MyoiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material - Dna and RnaDocument32 pagesGenetic Material - Dna and Rnaapi-217439283No ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering Class 6Document3 pagesBiochemical Engineering Class 6Vittal PiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- JERRY-MAE D. TA-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesJERRY-MAE D. TA-WPS OfficeJerry-mae Dela Cruz TantiadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document9 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesNucleic AcidsДмитрий МатвеевNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDocument14 pagesGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Grade 12Document1 pageChemistry Notes Grade 12Hitman KillerNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23Document3 pages3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23SiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- From My Students Most of AllDocument147 pagesFrom My Students Most of AllRamin HamzaNo ratings yet
- Nuceic AcidsDocument124 pagesNuceic AcidsMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument2 pagesStructure of DNAGuilbert ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Bc120 Spring 2023 Lecture 1Document8 pagesNucleic Acids Bc120 Spring 2023 Lecture 1mmmhh788mNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet
Dna Report g8
Dna Report g8
Uploaded by
Rhain HernandezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dna Report g8
Dna Report g8
Uploaded by
Rhain HernandezCopyright:
Available Formats
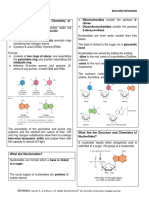
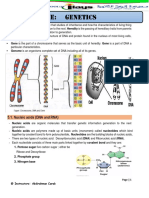
THE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF DNA
DNA
- A DNA molecule consists of two long polynucleotide chains composed of four types of nucleotide
subunits. Each of the chain is known as a DNA chain or DNA strand. Hydrogen bonds between the bse
portion of the nucleotide
POLYNUCLEOTIDE
- are linear bipolymers that are composed of several nucleotide monomers with covalent bonds in a
chain. Each strand of a polynucleotide consists of an alternative sugar and phospate group
HYDROGEN BONDED BASE PAIRS
- the hydrogen bonding between complementary bases holds the two strands of DNA together
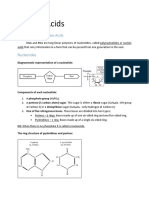
DNA is made up of four building blocks called nucleotides
The bases may either be ADENINE (A), GUANINE (G), CYTOSINE ©, or THYMINE (T)
ADENINE (A)
- a compound which is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic acids. A purine derivative, it is
paired with thymine in double-stranded DNA.
- In humans, there is approximately 30% adenine.
- is said to be one of the most essential organic molecules for life.
GUANINE (G)
- is one of the four constituent bases of nucleic acids. A purine derivative, it is paired with cytosine in
double-stranded DNA.
- Guanine contains amine and ketone, functional groups.
- It is a type of purine.
CYTOSINE
- Cytosine plays an essential role in forming base pairs by bonding with guanine and forming the
genetic code found in both DNA and RNA.
- cytosine is full of nitrogen atoms (it has three). It also has one ring of carbon, which makes it a
pyrimidine. A purine, on the other hand, has two rings of carbon.
THYMINE
- A chemical compound that is used to make one of the building blocks of DNA. It is a type of
pyrimidine.
- DNA uses this because thymine has a higher resistance to photochemical mutation and makes the
genetic code more durable.
- this is required to store all the data for life to function
- DNA uses thymine instead of uracil
You might also like
- First Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadDocument2,144 pagesFirst Aid Revised (Easiest Edition On Earth) @mueen - AhmadAyub SadiqNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument16 pagesNucleic AcidsayesheedattaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDDocument30 pagesBiochemistry of NUCLEIC ACIDZayan HaiderNo ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument12 pagesNucleotidesIlac Tristan BernardoNo ratings yet
- xxxxxxxx2023 MAR SBB 1208 NucleotidesDocument13 pagesxxxxxxxx2023 MAR SBB 1208 NucleotidesmechellesibandaNo ratings yet
- BiomoleculesDocument7 pagesBiomoleculesrajan.11proNo ratings yet
- L1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentDocument29 pagesL1+2 - Nucleic Acids and Structure StudentHaris KhokharNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument18 pagesTutorialTurky TurkyNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Chapter 4 - DNA, RNA and Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY Chapter 4 - DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesischelsea AlexandriaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument35 pagesNucleic AcidCheelsy P. ButronNo ratings yet
- Adenine: ThymineDocument1 pageAdenine: ThymineFrancis Joule Aberia TrigueNo ratings yet
- Genetic MaterialDocument62 pagesGenetic MaterialFaris ShamimNo ratings yet
- Research in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Document27 pagesResearch in Lecture "All About Nucleic Acid": Bicol University College of Nursing Legazpi City 2015-2016Kim GoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesNucleic AcidsRex Blanco NuñezNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesStructure of Nucleic AcidsHanz Glitzer MosquedaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument4 pagesNucleic AcidsAshley Margareth BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Chemical Basis of Heredity: Study Guide For Module No.Document13 pagesChapter 3: Chemical Basis of Heredity: Study Guide For Module No.REGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Nucleic AcidDocument33 pagesStructure and Function of Nucleic AcidLaiba FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - MBDocument31 pagesChapter 3 - MBMustee TeferaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesLevels of Structure in Nucleic AcidsDianne Joy LeybaNo ratings yet
- Bio 1102 Course WorkDocument5 pagesBio 1102 Course WorkkasingabalyaandrewNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesDocument3 pagesNucleic Acid: 1. Nitrogenous BasesMarie WrightNo ratings yet
- Biological Function and Chemical Nature of AdenineDocument1 pageBiological Function and Chemical Nature of Adeninerianashah7629No ratings yet
- L2 CytoDocument16 pagesL2 CytoDea Marienila CuberoNo ratings yet
- BIO 001 5th LectureDocument24 pagesBIO 001 5th LectureBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDocument4 pagesNucleic Acid: Biochem ReviewerDaine MarconNo ratings yet
- Nucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesDocument5 pagesNucleobase: Nucleobases, Also Known As Nitrogenous BasesLuis Felipe Mera GrandasNo ratings yet
- Nitrogenous BasesDocument6 pagesNitrogenous BasesMaak Ali AnsariNo ratings yet
- Karthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFDocument45 pagesKarthikeya XII-A Chemistry Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudiNo ratings yet
- Molecules of HeredDocument82 pagesMolecules of HeredTri Hiu AmborowatiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- BIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE BYU MEDICAL WITHUSDocument5 pagesBIOMOLECULAR STRUCTURE BYU MEDICAL WITHUSMohammad Kashif KhanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18Document18 pagesNucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis 2017-18ADEEL AHMADNo ratings yet
- Structure of Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesStructure of Nucleic Acidsplayandhavefun23No ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenDocument1 pageDeoxyribonucleic Acid (: ListenCristiaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Document9 pagesDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Clinical Pathology CH 8 Metabolism NotesDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Clinical Pathology CH 8 Metabolism Notesshubhm008No ratings yet
- 2.2 Cell ContructionDocument25 pages2.2 Cell ContructionDesyNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- NucleotidesDocument4 pagesNucleotidesvitro4No ratings yet
- Nucleotides: Cabal, Noreen A. BSPSY 3-3 Group 2Document9 pagesNucleotides: Cabal, Noreen A. BSPSY 3-3 Group 2Reen CabalNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument67 pagesNucleic AcidHeddy MyoiNo ratings yet
- Genetic Material - Dna and RnaDocument32 pagesGenetic Material - Dna and Rnaapi-217439283No ratings yet
- Biochemical Engineering Class 6Document3 pagesBiochemical Engineering Class 6Vittal PiseNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five GeneticsDocument28 pagesChapter Five GeneticsYahya AbdiwahabNo ratings yet
- JERRY-MAE D. TA-WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesJERRY-MAE D. TA-WPS OfficeJerry-mae Dela Cruz TantiadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDocument33 pagesChapter 8. Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsSofeaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 5Document9 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 5Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesNucleic AcidsДмитрий МатвеевNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid MetabolismDocument41 pagesNucleic Acid MetabolismPavani AkkalaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiDocument14 pagesGenetic Control: By. Yasmine HadiastrianiYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Grade 12Document1 pageChemistry Notes Grade 12Hitman KillerNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23Document3 pages3.5. Nucleic Acids 22-23SiNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- From My Students Most of AllDocument147 pagesFrom My Students Most of AllRamin HamzaNo ratings yet
- Nuceic AcidsDocument124 pagesNuceic AcidsMohammed HasnatNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNADocument2 pagesStructure of DNAGuilbert ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Bc120 Spring 2023 Lecture 1Document8 pagesNucleic Acids Bc120 Spring 2023 Lecture 1mmmhh788mNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology for Students: A College Level Study Guide for Life Science and Allied Health MajorsNo ratings yet