Professional Documents
Culture Documents
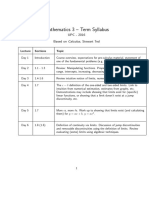
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
Uploaded by
Isra MehmoodCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ubd Fractions PlanDocument9 pagesUbd Fractions Planapi-437407548100% (1)
- Year 10 Mathematics CurriculumDocument2 pagesYear 10 Mathematics CurriculumJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- NumberDocument2 pagesNumberKaif AliNo ratings yet
- MELCs MATHEMATICSDocument19 pagesMELCs MATHEMATICSNiel Marc TomasNo ratings yet
- G 12 AddmaDocument2 pagesG 12 AddmaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Aw Math Unit01Document64 pagesAw Math Unit01Daoud KhanNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion: Topics Objectives No. of Hours Percentage Allocation No. of Items Knowledge UnderstandingDocument2 pagesRatio and Proportion: Topics Objectives No. of Hours Percentage Allocation No. of Items Knowledge Understanding심제이크No ratings yet
- Year 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous ListsDocument4 pagesYear 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous Listslyang1No ratings yet
- MTH JSS 3 SchemeDocument1 pageMTH JSS 3 SchemePatrick Chukwunonso A.No ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Document3 pagesYear 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Hannah LeeNo ratings yet
- mATH 7Document9 pagesmATH 7Joecel De Guzman TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionDocument5 pagesYear 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesDocument2 pagesUnit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesyitagesNo ratings yet
- Most Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Document14 pagesMost Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Mary Jane De YroNo ratings yet
- January: Yearly Teaching Plan 2008 Mathematics Form 1 Month Week Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesJanuary: Yearly Teaching Plan 2008 Mathematics Form 1 Month Week Chapter Learning ObjectivesOliver DeanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4 Math ModeDocument38 pagesModule 3 and 4 Math ModeMHARFE MICAROZNo ratings yet
- SILABUSDocument10 pagesSILABUSMichelle KirstenNo ratings yet
- m3 SyllabusDocument3 pagesm3 SyllabusQari MushtaqNo ratings yet
- RPT Form 1 (BI) MATEMATIK DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Form 1 (BI) MATEMATIK DLPCaroline JetanNo ratings yet
- RPT Matematik Ting 1 DLP 2024Document19 pagesRPT Matematik Ting 1 DLP 2024Noor Hafidzah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Maths JhsDocument6 pagesMaths JhsAtampuri JonahNo ratings yet
- 4 Grade (US) or Year 5 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document33 pages4 Grade (US) or Year 5 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!RPNo ratings yet
- Extended 3rdDocument4 pagesExtended 3rdapi-422996788No ratings yet
- CSC102 - Discrete Structure - COURSE - HANDBOOK - FALL 2021Document6 pagesCSC102 - Discrete Structure - COURSE - HANDBOOK - FALL 2021dj_fr3akNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 7Document7 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 7Khim Stephannie VillarinNo ratings yet
- Subject Group OverviewDocument38 pagesSubject Group OverviewProf. David G.No ratings yet
- Year 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsDocument4 pagesYear 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science High School - Bicol Region CampusDocument4 pagesPhilippine Science High School - Bicol Region CampusNeon ZNo ratings yet
- MELCS Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesMELCS Pre CalculusLiedi Brigette100% (4)
- Class 10 - MathsDocument4 pagesClass 10 - MathsAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- K To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSDocument12 pagesK To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSV.G. Lopez AspirinNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Math 6 q2Document3 pagesCurriculum Map - Math 6 q2Dhevy LibanNo ratings yet
- G 10 AddmaDocument5 pagesG 10 AddmaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Unit 6 Scope and SequenceDocument10 pagesGrade 3 Unit 6 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics XIDocument7 pagesMathematics XIDhanalakshmi ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- EMSAT Math Syllabus 2021Document41 pagesEMSAT Math Syllabus 2021Sou Al KazzazNo ratings yet
- Learning Area: Numbers and Operations: Topic 1: Rational Numbers Learning Standards Notes Performance Level/ DescriptorDocument19 pagesLearning Area: Numbers and Operations: Topic 1: Rational Numbers Learning Standards Notes Performance Level/ DescriptorkhaireyahNo ratings yet
- Maths G10e U1Document10 pagesMaths G10e U1api-429688581No ratings yet
- Subject Area Myp Level Time Stateprovincial Area of Myp Vertical and HorizontalDocument12 pagesSubject Area Myp Level Time Stateprovincial Area of Myp Vertical and HorizontalRITA CHANDRANNo ratings yet
- OASMATH7 THDocument3 pagesOASMATH7 THkalebg100No ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- RPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPSarina ShariffNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Mathematics Grade 8Document4 pagesCurriculum Map: Mathematics Grade 8imliving tothefullestNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument29 pagesStatisticsseenubarman12No ratings yet
- 2024 GR 09 MathsDocument2 pages2024 GR 09 MathsLerato GraceNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Document4 pagesYear 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Mahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- RS VIII 3 MathematicsDocument11 pagesRS VIII 3 Mathematicsbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Document14 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Karthiga MohanNo ratings yet
- 2019 After Exam ChecklistDocument3 pages2019 After Exam Checklistkuanyo yoNo ratings yet
- Infant Jesus Academy: Course SyllabusDocument9 pagesInfant Jesus Academy: Course SyllabusJhem VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21Document10 pagesICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21AkashNo ratings yet
- Maths - Syllabus - Grades 10 PDFDocument28 pagesMaths - Syllabus - Grades 10 PDFAmanuel Aklilu100% (1)
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDocument6 pagesGrade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDev MauniNo ratings yet
- RPT KSSM MT T2 Versi Bi 2022Document23 pagesRPT KSSM MT T2 Versi Bi 2022nad ziraNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Document4 pagesGrade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Greg WalkerNo ratings yet
- Junior High School Department: S Ern City CollegeDocument17 pagesJunior High School Department: S Ern City CollegeJoseph Cayetano MuñezNo ratings yet
- Westmead International School: Excellence ǁ Leadership ǁ Innovation ǁ Service WWW - Westmead-Is - Edu.phDocument7 pagesWestmead International School: Excellence ǁ Leadership ǁ Innovation ǁ Service WWW - Westmead-Is - Edu.phRonnie Roldan Ascaño Jr.No ratings yet
- (CS-603 - Computer Graphics) Practical FileDocument6 pages(CS-603 - Computer Graphics) Practical FileParth ViraniNo ratings yet
- Vectors (Tools For Physics) : Chapter 3, Part IDocument14 pagesVectors (Tools For Physics) : Chapter 3, Part IAdian Zahy ArdanaNo ratings yet
- dx dy = r dθ dr.: ExampleDocument7 pagesdx dy = r dθ dr.: Exampleemoh1No ratings yet
- January 2012 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEDocument20 pagesJanuary 2012 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEStevenstrange001 CattyNo ratings yet
- Jee Maths StrategyDocument8 pagesJee Maths Strategyarpitsharma2103No ratings yet
- MIKE ZERO: Creating 2D Bathymetries: Bathymetry Editor & Mesh GeneratorDocument44 pagesMIKE ZERO: Creating 2D Bathymetries: Bathymetry Editor & Mesh GeneratorJordo's CrüeNo ratings yet
- Prime Divisor TrigonometryDocument8 pagesPrime Divisor Trigonometryfake emailNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematical Programming IE406: Dr. Ted RalphsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Mathematical Programming IE406: Dr. Ted RalphsGustavo G Borzellino CNo ratings yet
- R. Piergallini - Covering MovesDocument17 pagesR. Piergallini - Covering MovesJupweNo ratings yet
- 1 Motion at A Circle Problems PDFDocument1 page1 Motion at A Circle Problems PDFZuza PodleśnaNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Ncert Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3 3Document6 pagesByjus Com Ncert Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3 3LEELADHAR XIANo ratings yet
- Two Remarkable Ortho-Homological TrianglesDocument11 pagesTwo Remarkable Ortho-Homological TrianglesIlieCraciun100% (1)
- Mathprog3 HW U07 2Document4 pagesMathprog3 HW U07 2Anil HNo ratings yet
- Well Design, by CompanyDocument39 pagesWell Design, by Companyاحمد عبد الحسين جولانNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 II Plan & Elevation ENHANCEDocument53 pagesChapter 17 II Plan & Elevation ENHANCEChekgu RaihanNo ratings yet
- Tangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationDocument18 pagesTangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationHanuman VermaNo ratings yet
- Dip StrikeDocument5 pagesDip StrikeWajid HussainNo ratings yet
- Cajori F.-A History of Mathematics (1894) PDFDocument516 pagesCajori F.-A History of Mathematics (1894) PDFGaro Ohanoglu100% (2)
- SMK Desa Mahkota Maths T P2 TrialDocument4 pagesSMK Desa Mahkota Maths T P2 Trialorchid3No ratings yet
- Differential Equation-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesDifferential Equation-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2007 May P1 QPDocument16 pages2007 May P1 QPsahar quadriNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Math Power StandardsDocument5 pages6th Grade Math Power Standardsapi-263833433No ratings yet
- LAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Document16 pagesLAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Miel GaboniNo ratings yet
- Maths RevisionDocument3 pagesMaths RevisionGANESHNo ratings yet
- First Option Second Option Third Option Fourth Option Answe R DescriptionDocument35 pagesFirst Option Second Option Third Option Fourth Option Answe R DescriptionHaftu EbuyNo ratings yet
- Area of Rectangles: Grade 3 Geometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesArea of Rectangles: Grade 3 Geometry WorksheetClaudine Manuel LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Sub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetDocument2 pagesSub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetKilaparthi KeertikaNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument53 pagesForce Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Bode Phase GainDocument4 pagesBode Phase GainagrothendieckNo ratings yet
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
Uploaded by
Isra MehmoodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
KS4+Curriculum+Overview+ (F) + +2022.23
Uploaded by
Isra MehmoodCopyright:
Available Formats
Mathematics Curriculum Overview – KS4 (Foundation): 2022/2023
Expand products of two binomials
Unit 14 – Factorise quadratic expressions of the form x 2+ bx+ c
Year 10: Module 0 – Fundamentals of Number Quadratics
(2 weeks) Solve quadratic equations of the form x 2+ bx+ c=0 by factorising
Understand fraction notation, recognising when fractions are equivalent
Develop proofs using quadratic expressions
Fundamentals Find fractions of a quantity
of Number 1 – Convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers
Fractions Apply the four rules of number to fractions Year 10: Module 3 – Number
Understand higher powers; know how to find these, and corresponding roots,
Understand the equivalence of fractions, decimals, percentages including through approximation or using a calculator when necessary
Fundamentals Unit 1 – Indices
Convert between fractions, decimals, percentages Know the difference between decimal approximation and exact values of roots
of Number 2 – Around 3 and Standard
Increase and decrease by a given percentage Derive, understand and use the rules of indices with integer values
Fractions, weeks total Form
Express one number as a percentage of another, including percentage changes Convert between standard form numbers and ordinary numbers
Decimals and (2 weeks)
Calculate and solve problems with reverse percentages Perform calculations involving standard form, with and without a calculator
Percentages
Unit 2 – Know the difference between simple and compound interest
Apply the four operations to negative numbers Geometric Solve problems involving simple and compound interest
Fundamentals
Apply BIDMAS with operations in Brackets Change Solve other problems involving repeated change, such as depreciation
of Number 3 –
Be able to round to a given number of decimal places (1 week) Solve problems involving growth and decay
Negative
Be able to recognise square numbers and recall their square roots
Numbers Recognise and use ratio notation, equivalent ratios and be able to simplify ratios
Use a calculator for complex calculations including roots
Compare ratios to fractions, decimals and percentages
Share quantities in a given ratio
Year 10: Module 1 – Linear Algebra Find missing values in the context of ratio problems
Recognise and describe arithmetic and geometric sequences Unit 3 – Ratio Solve simple ratio and proportion problems e.g. recipes
Generate terms of a sequence given a rule (2 weeks) Solve problems using unitary method
Unit 8 – Recognise the link between gradient and proportion
Find a formula for the nth term of a linear and geometric sequences
Sequences Solve problems involving direct proportion in numerical and algebraic contexts
Explain whether a number is a member of a given sequence
(1 week) Solve problems involving inverse proportion in contexts such as speed, distance and
time
Form and solve linear equations in one variable
Unit 9 – Linear Understand and use inequality notation Year 10: Module 4 – 2D Geometry
Equations and Represent inequalities on a number line, and vice versa
Inequalities Form and solve linear inequalities, including where the unknown appears on both Unit 4 – Find missing sides in right-angled triangles using Pythagoras’ Theorem
(1 week) sides and those involving fractions and brackets Pythagoras’ Identify whether a triangle is right-angled by considering the lengths of its sides
Theorem Solve problems with Pythagoras’ Theorem including in practical contexts
Solve problems involving co-ordinates and mid-points of line segments (2 week)
Plot straight line graphs Use angle facts to find missing angles in increasingly complex situations
Unit 10 – Understand the equation of a straight line, interpreting the gradient and intercept Unit 5 – Use angle facts to justify results in simple proofs
Coordinates Find the equation of a straight line given sufficient information Geometric Use the known properties of triangles and quadrilaterals to follow and to derive
and Linear Rearrange formulae where the subject appears only once Reasoning simple proofs in rectilinear figures, including key angle and area facts
Graphs Prove whether two straight lines are parallel (2 week)
(2 weeks) Solve problems with parallel lines
Understand and use bearings; solve problems involving bearings
Construct and interpret graphs of real-life contexts such as: Understand and use the trigonometric ratios sin, cos and tan
Unit 6 –
Unit 11 – Real- o Currency conversion Understand the link between similar triangles and trigonometry
Bearings and
Life Graphs o Temperature conversion Derive and use the exact values of sin θ and cos θ for θ = 00, 300, 450, 600 and 900
Trigonometry
(1 week) o Distance-time graphs Know the exact value of tan θ for θ = 00, 300, 450, 600
(3 weeks)
Interpret the gradient and y-intercept of a straight-line in context Solve problems involving right-angled triangles using Pythagoras’ Theorem and
trigonometry
Year 10: Module 2 – Further Algebra
Year 10: Module 5 – Proportional Reasoning
Unit 12 – Set up and solve (algebraically) two linear simultaneous equations in two variables,
Simultaneous interpreting the solution in context Unit 7 –
Use and apply compound units such as speed, density and pressure
Equations Use linear graphs to estimate values of y for given values of x Compound
Know and apply Density = Mass ÷ Volume
(2 weeks) Use linear graphs to find approximate solutions of simultaneous linear equations Measures
Use and apply compound units in algebraic contexts
Unit 13 – Draw and recognise quadratic graphs (1 week)
Quadratic Use quadratic graphs to find the approximate solution to quadratic equations
Graphs Identify intercepts and the turning points of graphs of quadratic functions
(1 week)
Mathematics Curriculum Overview – KS4 (Foundation): 2022/2023
Year 10: Module 6 – Geometry and Number
Understand decimal place value
Unit 15 – Units Convert between metric units
and Decimals Use the four rules of number with decimals
(1 week) Round numbers to a given number of decimal places or significant figures
Identify and use the terms centre, radius, chord, diameter, circumference, tangent, arc,
Unit 16 – sector and segment
Circles Calculate the area and circumference of a circle
(2 weeks) Calculate the length of an arc of a sector of a circle
Calculate the area of a sector of a circle
Unit 17 – Recognise the vocabulary associated with 3D solids
Working with Construct and interpret plans and elevations of 3D solids
3D Shapes
(1 week)
Calculate the surface area and volume of prisms, cylinders, spheres, cones, pyramids
Compare the surface area and volume of solid shapes
Unit 18 – Form and solve equations related to 3D shapes
Calculations Give answers in terms of if appropriate
with 3D Shapes Understand the limits of accuracy, using inequality notation
(2 weeks) Convert between area and volume units
Total: 32 Weeks Teaching
*Content in italics covered in the Year 9 Scheme of Work
Mathematics Curriculum Overview – KS4 (Foundation): 2022/2023
Unit 23 – Translate a shape by a given vector
Transformation Reflect a shape in a line, including on coordinate axes
s Rotate a shape about a centre, including on coordinate axes
Year 11: Module 0 – Fundamentals of Number
(1 week) Identify the transformation carried out by comparing an object and image
Understand fraction notation, recognising when fractions are equivalent Unit 24 –
Enlarge shapes from a given centre, with and without coordinate grids
Fundamentals Find fractions of a quantity Similarity and
Understand that the corresponding angles of similar shapes are equal
of Number 1 – Convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers Enlargement
Solve problems involving similar triangles
Fractions Apply the four rules of number to fractions (1 week)
Use rulers, protractors and pairs of compasses accurately
Understand the equivalence of fractions, decimals, percentages Around 2 Use the standard ruler and compass constructions for: perpendicular bisector of a line
Fundamentals Convert between fractions, decimals, percentages weeks total segment; constructing a perpendicular to a given line at a given point; bisecting a
of Number 2 – Increase and decrease by a given percentage Unit 25 – given angle
Fractions, Express one number as a percentage of another, including percentage changes Congruence, Understand and use the perpendicular distance from a point to a line as the shortest
Decimals and Calculate and solve problems with reverse percentages Constructions distance to the line
Percentages and Loci (2 Construct triangles and quadrilaterals from given information
weeks) Apply ruler and compass constructions to construct figures
Identify the loci of points and use these to solve real-world problems
Year 11: Module 1 – Probability Recognise congruent triangles
Prove pairs of triangles are congruent using SSS, ASA, AAS and RHS
Use the language associated with probability
Unit 19 -
Find the probability of a single event when there are equally likely events
Fundamentals
of Probability
Convert between different forms of probability – fractions, decimals, percentages Year 11: Module 0 – Fundamentals of Algebra
Know that P(Not A) = 1 – P(A) Form and solve linear equations in one variable
(1 week)
Solve equations from probability problems Form and solve linear inequalities, including where the unknown appears on both
Understand what is meant by relative frequency Fundamentals
Unit 20 – sides and those involving fractions and brackets Around 1 week
Understand why relative frequency is sometimes used as an estimate for probability of Algebra –
Theoretical Find the equation of a straight line given sufficient information total
Compare theoretical probability with result obtained by experiments Linear
and Rearrange formulae where the subject appears only once
Use Venn diagrams and two-way tables to solve probability problems Algebra
Experimental Understand higher powers; know how to find these, and corresponding roots,
Construct Venn diagrams and two-way tables to solve probability problems including through approximation or using a calculator when necessary
Probability
Use the addition law for probability, understanding when events are mutually
(1 week)
exclusive
Systematically list sample spaces
Unit 21 – Use the product rule for counting
Combined Year 11: Module 3 – Algebraic Reasoning
Understand the multiplication rule for independent and dependent events
Events Use tree diagrams to solve probability problems Formulate simple formulae from real-world situations
(1 week) Construct tree diagrams to solve probability problems Unit 26 – Simplify more complex algebraic expressions, including powers multiplied over a
Algebraic single bracket
Reasoning Use reasoning to show whether two expressions are equivalent
Year 11: Module 0 – Fundamentals of Geometry (1 week) Use the identity symbol
Develop and critique simple mathematical arguments
Find the area and perimeter of quadrilaterals, triangles and rectilinear figures Interpret the gradient of a straight line graph as a rate of change
Fundamentals Find the area and perimeter of simple, 2D composite shapes Unit 27 – Understand that X is inversely proportional to Y is equivalent to X is proportional to
of Geometry 1 Formulate and solve equations using area and perimeter rules Algebraic 1/Y
– Area and Find missing sides in right-angled triangles using Pythagoras’ Theorem Proportion Recognise and interpret graphs that illustrate direct and inverse proportion
Perimeter Identify whether a triangle is right-angled by considering the lengths of its sides (1 week) Construct and interpret equations that describe direct and inverse proportion
Solve problems with Pythagoras’ Theorem including in practical contexts Around 2
Find unknown angles in geometrical figures involving square, rectangle, weeks total
Fundamentals
parallelogram, rhombus, trapezium and triangle
of Geometry 2
Identify the different types of angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal Year 11: Module 4 – Statistics
– Solving Construct simple charts for ungrouped data
such as corresponding angles, alternate angles and co-interior angles
Angle Calculate the mean, median and mode and range of ungrouped data
Understand and use the sum of the exterior angles of a polygon
Problems Unit 28 – Basic Find the modal class of grouped data
Solve problems involving the angles and number of sides in a regular polygon
Statistics Estimate the mean, median and range of grouped data
(1 week) Make comparisons between sets of data using summary statistics
Year 11: Module 2 – Geometrical Reasoning Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of different measures used in statistics
Understand what is meant by an outlier
Unit 22 – Represent a two-dimensional vector as a column vector
Vectors Add and subtract vectors Know the difference between a sample and a population
Unit 29 –
(1 week) Multiply a vector by a scalar Understand different types of sampling
Sampling
Find the sizes of groups in a stratified sample
(1 week)
Discuss the reliability of different types of sample
Mathematics Curriculum Overview – KS4 (Foundation): 2022/2023
Choose the most appropriate pictorial representation for a particular set of data
Unit 30 –
Recognise when graphs and charts can be misleading
Representing
Choose the most appropriate measures for representation of a set of data
Data
Interpret and construct graphs for time series data
(1 week)
Identify trends from time series graphs
Plot and use scatter graphs to identify correlation
Unit 31 – Understand that correlation does not imply causality
Scatter Graphs Draw (by eye) lines of best fit
(1 week) Interpolate and extrapolate to make estimates, knowing the limitations of this
Identify outliers on a scatter graph
Total: 19 Weeks Teaching
You might also like
- Ubd Fractions PlanDocument9 pagesUbd Fractions Planapi-437407548100% (1)
- Year 10 Mathematics CurriculumDocument2 pagesYear 10 Mathematics CurriculumJoel OkohNo ratings yet
- NumberDocument2 pagesNumberKaif AliNo ratings yet
- MELCs MATHEMATICSDocument19 pagesMELCs MATHEMATICSNiel Marc TomasNo ratings yet
- G 12 AddmaDocument2 pagesG 12 AddmaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Aw Math Unit01Document64 pagesAw Math Unit01Daoud KhanNo ratings yet
- Ratio and Proportion: Topics Objectives No. of Hours Percentage Allocation No. of Items Knowledge UnderstandingDocument2 pagesRatio and Proportion: Topics Objectives No. of Hours Percentage Allocation No. of Items Knowledge Understanding심제이크No ratings yet
- Year 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous ListsDocument4 pagesYear 8 EOY Revision Topics - Includes All Previous Listslyang1No ratings yet
- MTH JSS 3 SchemeDocument1 pageMTH JSS 3 SchemePatrick Chukwunonso A.No ratings yet
- Year 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Document3 pagesYear 11 Maths Methods Term 2 2023 V2Hannah LeeNo ratings yet
- mATH 7Document9 pagesmATH 7Joecel De Guzman TorrefrancaNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionDocument5 pagesYear 7 Plan - Australian Curriculum: Mathematics: Implementation Year: School Name: Year Level DescriptionLi NguyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesDocument2 pagesUnit 7: Classification and Definition of Common Solid ShapesyitagesNo ratings yet
- Most Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Document14 pagesMost Essential Learning Module in Mathematics 2020Mary Jane De YroNo ratings yet
- January: Yearly Teaching Plan 2008 Mathematics Form 1 Month Week Chapter Learning ObjectivesDocument4 pagesJanuary: Yearly Teaching Plan 2008 Mathematics Form 1 Month Week Chapter Learning ObjectivesOliver DeanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 and 4 Math ModeDocument38 pagesModule 3 and 4 Math ModeMHARFE MICAROZNo ratings yet
- SILABUSDocument10 pagesSILABUSMichelle KirstenNo ratings yet
- m3 SyllabusDocument3 pagesm3 SyllabusQari MushtaqNo ratings yet
- RPT Form 1 (BI) MATEMATIK DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Form 1 (BI) MATEMATIK DLPCaroline JetanNo ratings yet
- RPT Matematik Ting 1 DLP 2024Document19 pagesRPT Matematik Ting 1 DLP 2024Noor Hafidzah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Maths JhsDocument6 pagesMaths JhsAtampuri JonahNo ratings yet
- 4 Grade (US) or Year 5 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document33 pages4 Grade (US) or Year 5 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!RPNo ratings yet
- Extended 3rdDocument4 pagesExtended 3rdapi-422996788No ratings yet
- CSC102 - Discrete Structure - COURSE - HANDBOOK - FALL 2021Document6 pagesCSC102 - Discrete Structure - COURSE - HANDBOOK - FALL 2021dj_fr3akNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Grade 7Document7 pagesCurriculum Map Grade 7Khim Stephannie VillarinNo ratings yet
- Subject Group OverviewDocument38 pagesSubject Group OverviewProf. David G.No ratings yet
- Year 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsDocument4 pagesYear 8 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan MathsMahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Science High School - Bicol Region CampusDocument4 pagesPhilippine Science High School - Bicol Region CampusNeon ZNo ratings yet
- MELCS Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesMELCS Pre CalculusLiedi Brigette100% (4)
- Class 10 - MathsDocument4 pagesClass 10 - MathsAlok RanjanNo ratings yet
- K To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSDocument12 pagesK To 12 MELC Mathematics JHSV.G. Lopez AspirinNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map - Math 6 q2Document3 pagesCurriculum Map - Math 6 q2Dhevy LibanNo ratings yet
- G 10 AddmaDocument5 pagesG 10 AddmaJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Unit 6 Scope and SequenceDocument10 pagesGrade 3 Unit 6 Scope and SequencereemaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics XIDocument7 pagesMathematics XIDhanalakshmi ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- EMSAT Math Syllabus 2021Document41 pagesEMSAT Math Syllabus 2021Sou Al KazzazNo ratings yet
- Learning Area: Numbers and Operations: Topic 1: Rational Numbers Learning Standards Notes Performance Level/ DescriptorDocument19 pagesLearning Area: Numbers and Operations: Topic 1: Rational Numbers Learning Standards Notes Performance Level/ DescriptorkhaireyahNo ratings yet
- Maths G10e U1Document10 pagesMaths G10e U1api-429688581No ratings yet
- Subject Area Myp Level Time Stateprovincial Area of Myp Vertical and HorizontalDocument12 pagesSubject Area Myp Level Time Stateprovincial Area of Myp Vertical and HorizontalRITA CHANDRANNo ratings yet
- OASMATH7 THDocument3 pagesOASMATH7 THkalebg100No ratings yet
- 2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Document32 pages2 Grade (US) or Year 3 (UK) : A Full Month of Real Life Problem Solving!Jwan DelawiNo ratings yet
- RPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPDocument17 pagesRPT Math f1 2023 2024 DLPSarina ShariffNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map: Mathematics Grade 8Document4 pagesCurriculum Map: Mathematics Grade 8imliving tothefullestNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument29 pagesStatisticsseenubarman12No ratings yet
- 2024 GR 09 MathsDocument2 pages2024 GR 09 MathsLerato GraceNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Document4 pagesYear 9 Lower Secondary Long Term Plan Maths (Annual Plan)Mahamed AbusnenaNo ratings yet
- RS VIII 3 MathematicsDocument11 pagesRS VIII 3 Mathematicsbhaskar51178No ratings yet
- RPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Document14 pagesRPT Mathematics Year 6 9DLP 2021Karthiga MohanNo ratings yet
- 2019 After Exam ChecklistDocument3 pages2019 After Exam Checklistkuanyo yoNo ratings yet
- Infant Jesus Academy: Course SyllabusDocument9 pagesInfant Jesus Academy: Course SyllabusJhem VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21Document10 pagesICSE Class 7 Maths Reduced Syllabus 2020 21AkashNo ratings yet
- Maths - Syllabus - Grades 10 PDFDocument28 pagesMaths - Syllabus - Grades 10 PDFAmanuel Aklilu100% (1)
- 0606 Teaching PlanDocument9 pages0606 Teaching PlanKyle ZhangNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDocument6 pagesGrade 5 Math Scopeand Sequence GuideDev MauniNo ratings yet
- RPT KSSM MT T2 Versi Bi 2022Document23 pagesRPT KSSM MT T2 Versi Bi 2022nad ziraNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Document4 pagesGrade 7 Mississippi College-And Career-Readiness Standards For Mathematics RCSD Quarter 1Greg WalkerNo ratings yet
- Junior High School Department: S Ern City CollegeDocument17 pagesJunior High School Department: S Ern City CollegeJoseph Cayetano MuñezNo ratings yet
- Westmead International School: Excellence ǁ Leadership ǁ Innovation ǁ Service WWW - Westmead-Is - Edu.phDocument7 pagesWestmead International School: Excellence ǁ Leadership ǁ Innovation ǁ Service WWW - Westmead-Is - Edu.phRonnie Roldan Ascaño Jr.No ratings yet
- (CS-603 - Computer Graphics) Practical FileDocument6 pages(CS-603 - Computer Graphics) Practical FileParth ViraniNo ratings yet
- Vectors (Tools For Physics) : Chapter 3, Part IDocument14 pagesVectors (Tools For Physics) : Chapter 3, Part IAdian Zahy ArdanaNo ratings yet
- dx dy = r dθ dr.: ExampleDocument7 pagesdx dy = r dθ dr.: Exampleemoh1No ratings yet
- January 2012 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEDocument20 pagesJanuary 2012 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEStevenstrange001 CattyNo ratings yet
- Jee Maths StrategyDocument8 pagesJee Maths Strategyarpitsharma2103No ratings yet
- MIKE ZERO: Creating 2D Bathymetries: Bathymetry Editor & Mesh GeneratorDocument44 pagesMIKE ZERO: Creating 2D Bathymetries: Bathymetry Editor & Mesh GeneratorJordo's CrüeNo ratings yet
- Prime Divisor TrigonometryDocument8 pagesPrime Divisor Trigonometryfake emailNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematical Programming IE406: Dr. Ted RalphsDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Mathematical Programming IE406: Dr. Ted RalphsGustavo G Borzellino CNo ratings yet
- R. Piergallini - Covering MovesDocument17 pagesR. Piergallini - Covering MovesJupweNo ratings yet
- 1 Motion at A Circle Problems PDFDocument1 page1 Motion at A Circle Problems PDFZuza PodleśnaNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Ncert Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3 3Document6 pagesByjus Com Ncert Solutions Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3 3LEELADHAR XIANo ratings yet
- Two Remarkable Ortho-Homological TrianglesDocument11 pagesTwo Remarkable Ortho-Homological TrianglesIlieCraciun100% (1)
- Mathprog3 HW U07 2Document4 pagesMathprog3 HW U07 2Anil HNo ratings yet
- Well Design, by CompanyDocument39 pagesWell Design, by Companyاحمد عبد الحسين جولانNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 II Plan & Elevation ENHANCEDocument53 pagesChapter 17 II Plan & Elevation ENHANCEChekgu RaihanNo ratings yet
- Tangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationDocument18 pagesTangents and Normal: IIT JEE (Main) ExaminationHanuman VermaNo ratings yet
- Dip StrikeDocument5 pagesDip StrikeWajid HussainNo ratings yet
- Cajori F.-A History of Mathematics (1894) PDFDocument516 pagesCajori F.-A History of Mathematics (1894) PDFGaro Ohanoglu100% (2)
- SMK Desa Mahkota Maths T P2 TrialDocument4 pagesSMK Desa Mahkota Maths T P2 Trialorchid3No ratings yet
- Differential Equation-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesDifferential Equation-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- 2007 May P1 QPDocument16 pages2007 May P1 QPsahar quadriNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Math Power StandardsDocument5 pages6th Grade Math Power Standardsapi-263833433No ratings yet
- LAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Document16 pagesLAS Q3 Weeks 3 To 4Miel GaboniNo ratings yet
- Maths RevisionDocument3 pagesMaths RevisionGANESHNo ratings yet
- First Option Second Option Third Option Fourth Option Answe R DescriptionDocument35 pagesFirst Option Second Option Third Option Fourth Option Answe R DescriptionHaftu EbuyNo ratings yet
- Area of Rectangles: Grade 3 Geometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesArea of Rectangles: Grade 3 Geometry WorksheetClaudine Manuel LibunaoNo ratings yet
- Sub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetDocument2 pagesSub-Mathematics, Class-Ix Chapter - Linear Equation in Two Variables WorksheetKilaparthi KeertikaNo ratings yet
- Force Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesDocument53 pagesForce Vectors: Cien 3144 Structural Theory 1 Ensc 20043 Statics of Rigid BodiesAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Bode Phase GainDocument4 pagesBode Phase GainagrothendieckNo ratings yet