Professional Documents
Culture Documents
There Are Three Different Process of A River
There Are Three Different Process of A River
Uploaded by
Lewis AspinallOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
There Are Three Different Process of A River
There Are Three Different Process of A River
Uploaded by
Lewis AspinallCopyright:
Available Formats
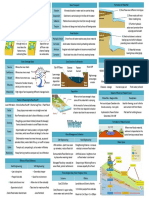
There are three different process of a river.
The first one is
erosion. The second is transportation. The last one is deposition.
Erosion is the wearing a way of rock along the coastline. Destructive
waves are responsible for erosion on the coastline. There are four
types of erosion: Hydraulic action - this is the sheer power of the
waves as they smash against the cliff. Air becomes trapped in the
cracks in the rock and causes the rock to break apart.
Rivers transport material in four main ways: solution, suspension,
saltation, and traction. Solution occurs when minerals are dissolved
in the water and carried along in solution. Suspension is when fine
light material is carried along in the water. Saltation is when small
pebbles and stones are bounced along the river bed. Traction is when
large boulders and rocks are rolled along the river bed.
Flooding
A flood is an overflow of water that submerges land that is usually
dry.
Heavy rainfall is the simplest cause of flooding. When there is too much
rain or it happens too fast, there just isn’t a place for it to go. This can
result in floods like flash flooding.
Broken dams are another cause of flooding. Older infrastructure can fail
when heavy rains come and water levels rise. When dams break, they
unleash torrents of water on unsuspecting households. This is part of what
happened when Hurricane Katrina hit New Orleans in 2005.
Hard engineering is a term used to describe artificial structures that
try to control natural processes, such as erosion, flooding, or
landslides.
Often more effective at preventing flooding than Soft Engineering options
Dams and reservoirs provide oportunity for Hydroelectric power
Job opotunities (e.g in builing artifical levees/dams)
Building flood banks is relatively cheap
Most methods are very expensive
Can harm the environment and destroy wildlife habitats
Building dams can cause flooding upstream and produces methane gas.
Not athetically pleasing (don't look good)
Skilled workers needed to build dams or straighten river channels
Soft engineering is the use of vegetation and natural elements such as
rocks in civil engineering. It is typically applied to reinforce
shorelines and hills to prevent erosion and landslides. In many cases,
soft engineering results in reduced capital and operational costs such
as maintenance.
Sustianable
Relatively cheap (in comparison with hard engineering options)
Afforestation is environmentally friendly
Flood plain zoning uses the land effectively
Requires less maintenance (than hard engineering)
Athetically pleasing
Doesn't harm wildlife habitats
'Do nothing' option is cheap, allows natural floods creating fertile soils
Can be less effective than hard engineering
Takes time (e.g to allow trees to grow)
Comminities may already have build houses so flood plain zoning can't be done.
Land may be valuable for building on rather than leaving for agriculture (Flood plain
zoning)
'Do nothing' option can put lives at risk and doesn't actually reduce the risk of flooding.
You might also like
- Report On Summer Training (July 2019) : Organization: Irrigation Department, Guwahati West Division, UlubariDocument22 pagesReport On Summer Training (July 2019) : Organization: Irrigation Department, Guwahati West Division, UlubariKunal Das75% (4)
- WJEC GCSE Geography A Revision Sheets PDFDocument10 pagesWJEC GCSE Geography A Revision Sheets PDFSandy SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Geo Notes New Curriculum - To Be EditedDocument120 pagesForm 2 Geo Notes New Curriculum - To Be EditedLemarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FloodingDocument5 pagesIntroduction To FloodingJose DíazNo ratings yet
- Computer ProjectDocument17 pagesComputer ProjectNishant MishraNo ratings yet
- Flood MitigationDocument16 pagesFlood MitigationatienzavinamarieNo ratings yet
- FooooodsDocument3 pagesFooooodslock_jaw30No ratings yet
- Fluvial ErosionDocument20 pagesFluvial ErosionPARAN, DIOSCURANo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit DPPMDocument25 pages2nd Unit DPPMJyothi GNo ratings yet
- Flood: What Is A Flood?Document6 pagesFlood: What Is A Flood?jose ismaelNo ratings yet
- Hilly LandslideDocument16 pagesHilly LandslideSafeer AbroNo ratings yet
- Hydrosphere NotesDocument10 pagesHydrosphere Notesmatthewsc2013No ratings yet
- Causes of FloodsDocument2 pagesCauses of FloodsAwais MinhasNo ratings yet
- Floods and DeltasDocument18 pagesFloods and DeltasThe Equinox DudeNo ratings yet
- Flood ControlDocument5 pagesFlood ControlPip Johnson100% (1)
- Floods Information and Comprehension ActivityDocument7 pagesFloods Information and Comprehension ActivityMeliza LauNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 SWCE PDFDocument20 pagesUnit 5 SWCE PDFsoma sundaramNo ratings yet
- Natural CalamitiesDocument29 pagesNatural CalamitiesvinayaroraknpNo ratings yet
- Suggestions To Solve World Big FloodDocument4 pagesSuggestions To Solve World Big FloodPei Fen KuanNo ratings yet
- Floods!: Sean O'Reilly 9H Geography Mr. Nelson Floods Due: Last Lesson of Week 9 Term 3Document12 pagesFloods!: Sean O'Reilly 9H Geography Mr. Nelson Floods Due: Last Lesson of Week 9 Term 3Sean O'ReillyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6.4 FLOODingDocument48 pagesChapter 6.4 FLOODingMichelle Calera Bocboc100% (1)
- ProjectDocument14 pagesProjectTammamNo ratings yet
- Coastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)Document55 pagesCoastal Landforms Class 8 (2022-2023)As 54bdNo ratings yet
- Pcom FloodingDocument2 pagesPcom FloodingJoyce Ann MasalongaNo ratings yet
- Activity No 3Document5 pagesActivity No 3Aljondear RamosNo ratings yet
- EST Report 51Document13 pagesEST Report 51Rohit GadekarNo ratings yet
- Vsa Geo Project 2020Document13 pagesVsa Geo Project 2020rashmimehNo ratings yet
- Dean's Group (Envi Sci)Document9 pagesDean's Group (Envi Sci)Dean Mark AnacioNo ratings yet
- Application of Retaining Wall in The Control of Flooding and Gully ErosionDocument4 pagesApplication of Retaining Wall in The Control of Flooding and Gully Erosiontsitsi bizaNo ratings yet
- Mass Wasting NotesDocument17 pagesMass Wasting Notesopulithe0% (1)
- Geography Class NotesDocument9 pagesGeography Class Notesanikshajignesh22No ratings yet
- Module 8 (Exogenic Processes)Document11 pagesModule 8 (Exogenic Processes)Cyrel Jay RosalitaNo ratings yet
- Geography Assignment: Department of Geography B. Borooah CollegeDocument16 pagesGeography Assignment: Department of Geography B. Borooah CollegeNeha Mishra100% (2)
- Lu2 - Physical Environmental Characteristics and Components 2021Document43 pagesLu2 - Physical Environmental Characteristics and Components 2021NeehaNo ratings yet
- I. Hard and Soft EngineeringDocument25 pagesI. Hard and Soft EngineeringDomingo Brioso Gamis IIINo ratings yet
- Science Notes 10Document1 pageScience Notes 10John SmithNo ratings yet
- Full Essay of LanslideDocument5 pagesFull Essay of LanslideHijab Sang Ratu100% (1)
- Soil Errosion'Document24 pagesSoil Errosion'prathaNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion: Land UseDocument5 pagesSoil Erosion: Land UseSyakirah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Deforestation: LandslideDocument3 pagesDeforestation: LandslideKrezel Kaye Calawigan BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- River EngineeringDocument23 pagesRiver EngineeringPinky Rose Alfaro GreganaNo ratings yet
- Essay About LandslideDocument1 pageEssay About LandslideabastillashannahbelleNo ratings yet
- Watershed Management and Engineering InterventionsDocument5 pagesWatershed Management and Engineering InterventionsLovely Rucel Collado VillafuerteNo ratings yet
- fld 1Document1 pagefld 1bikramorigaonNo ratings yet
- Natural HazardsDocument28 pagesNatural Hazardsswastika_singhNo ratings yet
- 13 14 Hard Vs Soft Card Sort CompleteDocument1 page13 14 Hard Vs Soft Card Sort Completeapi-336814146No ratings yet
- Dredging and Flood RiskDocument2 pagesDredging and Flood RiskJustin SharpeNo ratings yet
- EVS Floods 2Document8 pagesEVS Floods 2Ajay DevganNo ratings yet
- UK Environment Agency: Dredging and Flood RiskDocument2 pagesUK Environment Agency: Dredging and Flood RisktoobaziNo ratings yet
- Weathering-and-Erosion Practice TestDocument10 pagesWeathering-and-Erosion Practice Testletlhogonologeorge11No ratings yet
- B Ing LM LaporanDocument3 pagesB Ing LM LaporanktraditaNo ratings yet
- Principal Types and Causes: Floods Directive Tide River LakeDocument4 pagesPrincipal Types and Causes: Floods Directive Tide River LakeNeeraj SharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is FloodDocument11 pagesWhat Is FloodMuskan Rathi 5100No ratings yet
- Report FloodDocument1 pageReport FloodWesdiat DwipraptaNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument7 pagesDisaster Managementsyon mongaNo ratings yet
- EsDocument2 pagesEsAlthea LeeNo ratings yet
- Silt TrapDocument5 pagesSilt TrapasyreenhaikalNo ratings yet
- Soil Erosion PDFDocument20 pagesSoil Erosion PDFAja FightingNo ratings yet
- Flood Control and Disaster Management: Causes of FloodsDocument5 pagesFlood Control and Disaster Management: Causes of Floodshassam_subhani5881No ratings yet
- Fema - Living With Dams - P 956Document32 pagesFema - Living With Dams - P 956Abdulmuqtadetr AhmadiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Raj JamariyaNo ratings yet
- Structural DesignDocument52 pagesStructural Designbaig951No ratings yet
- Dams - C5 - Foundation and Abutment PreparationDocument4 pagesDams - C5 - Foundation and Abutment PreparationJohan Vd Merwe SnrNo ratings yet
- Success Story - Semla - Rajkot - GujaratDocument22 pagesSuccess Story - Semla - Rajkot - GujaratJyoti MishraNo ratings yet
- Reservoir StudyDocument121 pagesReservoir Studywatercrunch100% (3)
- Laboratory Test During The Dam ConstructionDocument12 pagesLaboratory Test During The Dam ConstructionTauseef Ahmad0% (1)
- Industrial VisitDocument10 pagesIndustrial VisitBilal Nawaz KiyaniNo ratings yet
- Dam & Reservoir Project - IndiaDocument9 pagesDam & Reservoir Project - IndiaDave Robert HasibuanNo ratings yet
- No Erosion Criterion For Granular Filter PDFDocument7 pagesNo Erosion Criterion For Granular Filter PDFMuhammad IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chimoio Water Supply Project FinalDesignDocument124 pagesChimoio Water Supply Project FinalDesignSunil KammanankadaNo ratings yet
- River Water Quality ManualDocument79 pagesRiver Water Quality ManualIwan M SyariefuddinNo ratings yet
- Gravity Dams Unit-IIDocument44 pagesGravity Dams Unit-IIvixivi6780No ratings yet
- Was The Dam Itself of Sound Design in The Product of Quality ConstructionDocument3 pagesWas The Dam Itself of Sound Design in The Product of Quality ConstructionSama Bsr0% (1)
- Madhucon BrochureDocument19 pagesMadhucon BrochureZoeb MerchantNo ratings yet
- COMPRO Bintang AuroraDocument26 pagesCOMPRO Bintang AurorabintangNo ratings yet
- File 0147 Jeoteknik Ve Enjeksiyon-KKARAKUS-AKOCBAYDocument7 pagesFile 0147 Jeoteknik Ve Enjeksiyon-KKARAKUS-AKOCBAYMuhammadImranShahzadNo ratings yet
- Karl Terzaghi 1Document353 pagesKarl Terzaghi 1W. ANo ratings yet
- Applications of Microorganisms To Geotechnical EngineeringDocument15 pagesApplications of Microorganisms To Geotechnical EngineeringAshokan KelothNo ratings yet
- Lafarge - TA Grinding VRM v1 (Final)Document62 pagesLafarge - TA Grinding VRM v1 (Final)elwathig bakhiet100% (1)
- Perform Irrigation v2Document8 pagesPerform Irrigation v2VanzNo ratings yet
- Raz ls37 Buildingbigdreams CLRDocument11 pagesRaz ls37 Buildingbigdreams CLRapi-221749347No ratings yet
- Prospects of Electricity From Tidal Power in Coastal Regions of BangladeshDocument10 pagesProspects of Electricity From Tidal Power in Coastal Regions of BangladeshAnonymous C9ZNFkrb6No ratings yet
- Hydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsDocument2 pagesHydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsKing BangngayNo ratings yet
- A Study On Construction Challenges of Bridges in The Hilly Areas of TamilnaduDocument29 pagesA Study On Construction Challenges of Bridges in The Hilly Areas of TamilnaduShraman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Stream Restoration Project Planning and DesignDocument36 pagesStream Restoration Project Planning and DesignPK PhilavongNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument6 pagesReportHassan AliNo ratings yet