Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jan DamesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
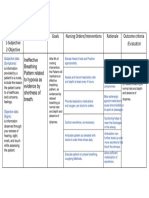
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Acute Respiratory DistressDocument2 pagesAcute Respiratory Distressminaanne100% (3)
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- CAF 1 - Accounting For PartnershipDocument48 pagesCAF 1 - Accounting For PartnershipAhsan Kamran100% (1)
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPie CanapiNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Darunday NCP Rotation 6Document3 pagesDarunday NCP Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Darunday NCP Rotation 6Document3 pagesDarunday NCP Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges Nabua, Camarines Sur College of Health SciencesDocument6 pagesCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges Nabua, Camarines Sur College of Health SciencesDainty LorenNo ratings yet
- Iudmc ActivityDocument10 pagesIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- Valeriano, NCPDocument4 pagesValeriano, NCPVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- NCP Draft PediaDocument9 pagesNCP Draft PediaEmman BarroquilloNo ratings yet
- Dela Peña NCP 3Document2 pagesDela Peña NCP 3Mark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Innefective Airway Clearance NCPDocument4 pagesInnefective Airway Clearance NCPAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Date/Tim e Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues Short Term Goals Short TermDocument4 pagesDate/Tim e Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues Short Term Goals Short TermJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Asthma NCPDocument3 pagesAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4 - NCPDocument15 pagesScenario 4 - NCPVian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfDocument6 pagesNCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfLycah RotoneNo ratings yet
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingDocument2 pagesD. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern (Oxygenation) NCPDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern (Oxygenation) NCPkarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearancerozj0750% (2)
- NursingCrib Com Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument4 pagesNursingCrib Com Nursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaahmed.omer222555No ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP SampleDocument8 pagesNCP SampleKeneth Dave AglibutNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument6 pagesASSESSMENTZerimar Adawe DulnuanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJanella Kyle ParejaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- (SOB) Care PlanDocument1 page(SOB) Care Planshatha faisal100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Case-Study - JenDocument15 pagesNcp-Case-Study - JenJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- (Duty MDH (Ward) Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pages(Duty MDH (Ward) Nursing Care PlanMikaella R. AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Document18 pagesNCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Lyka Shane Pineda AngalaNo ratings yet
- Palileo NCPDocument5 pagesPalileo NCPAeron PalileoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.RDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.Rcen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- ParadigmDocument6 pagesParadigmCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- NCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument10 pagesNCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 Nursing Care PlansDocument15 pagesNCM 118 Nursing Care PlansElle LibalibNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentJohn Glenn BalacanoNo ratings yet
- O Detect Decreased or Adventitious Breath SoundsDocument2 pagesO Detect Decreased or Adventitious Breath SoundsKent JuguilonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaKerks Von Gladiel NapaoNo ratings yet
- THE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeFrom EverandTHE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Advanced Recorder Technique: The Art of Playing the Recorder. Vol. 2: Breathing and SoundFrom EverandAdvanced Recorder Technique: The Art of Playing the Recorder. Vol. 2: Breathing and SoundRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HL-5240 HL-5250DN Mono Laser PrinterDocument4 pagesHL-5240 HL-5250DN Mono Laser PrinterDANIEL CRIADO REDONDONo ratings yet
- W AsiaDocument6 pagesW Asiaapi-213954485No ratings yet
- Art 19 RPCDocument5 pagesArt 19 RPCHappynako Wholesome100% (1)
- Alive Feb 10Document66 pagesAlive Feb 10javed.alam19No ratings yet
- Cognos ResumeDocument4 pagesCognos ResumeAnonymous xMYE0TiNBcNo ratings yet
- Selection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterDocument5 pagesSelection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterYuvrajsinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Bizhub c281 c221 c221s Spec Sheet enDocument2 pagesBizhub c281 c221 c221s Spec Sheet enSuraj Acharya SurajNo ratings yet
- 3210 HT 21-12-2023 SPLDocument1 page3210 HT 21-12-2023 SPLVishnu Vardhan ANo ratings yet
- LI Junhao - CVDocument1 pageLI Junhao - CVJunhao LINo ratings yet
- Ads 7865Document35 pagesAds 7865Parasaram SrinivasNo ratings yet
- EMC Standard PDFDocument58 pagesEMC Standard PDFSongkran Pisanupoj0% (1)
- Python Assignment For Absolute BeginnersDocument5 pagesPython Assignment For Absolute BeginnersAmeya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Penlon A-200 SP Circle Absorber - User Manual PDFDocument40 pagesPenlon A-200 SP Circle Absorber - User Manual PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Plant Design TemplateDocument13 pagesPlant Design TemplateRishabhGupta 2k20umba32No ratings yet
- Future Prospects of Duck Production in Asia PDFDocument14 pagesFuture Prospects of Duck Production in Asia PDFridzwanmsNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Quiz Answer Key With NotesDocument13 pagesHands-On Quiz Answer Key With NotesRosen AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Bobie Rose DDocument8 pagesBobie Rose DApril Dawn DaepNo ratings yet
- EContent 3 2024 02 28 06 43 20 CAPITALGAINdocx 2024 02 20 11 29 41Document22 pagesEContent 3 2024 02 28 06 43 20 CAPITALGAINdocx 2024 02 20 11 29 41solanki YashNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Gaining A Competitive AdvantageDocument22 pagesHuman Resource Management Gaining A Competitive AdvantagelinhNo ratings yet
- Abap TablesDocument753 pagesAbap TablesHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lieberose Solar Park - Presentation-WorkedDocument43 pagesLieberose Solar Park - Presentation-WorkedNeetu RajaramanNo ratings yet
- Proceed FormulationsDocument18 pagesProceed FormulationssudhirchughNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document14 pagesCH 8Ajay Kumar GangulyNo ratings yet
- Elections in The Internet AgeDocument30 pagesElections in The Internet AgeMaricel P. GopitaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Debt and Leasing: Debagus SubagjaDocument12 pagesIntermediate Debt and Leasing: Debagus SubagjaDebagus SubagjaNo ratings yet
- Pending Payments: Issuance Work Permit For 2 Year Outside The Country - SkillDocument1 pagePending Payments: Issuance Work Permit For 2 Year Outside The Country - SkillHasnain proNo ratings yet
- Guindaste Liebherr LR 1250Document24 pagesGuindaste Liebherr LR 1250Ronaldo MachadoNo ratings yet
- (Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403Document4 pages(Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403longnguyenNo ratings yet
- Case Hansson Private LabelDocument15 pagesCase Hansson Private Labelpaul57% (7)
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jan DamesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jan DamesCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Scientific Nursing
Cues Objectives Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Rationale Interventions
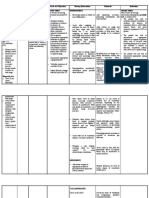
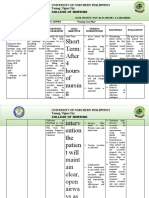
Subjective: Ineffective Common to many After 8 hours of 1. Establish It allows you to After 8 hours of
“Sige kasi Airway pulmonary nursing rapport with understand your nursing
iton an Clearance related diseases intervention, pt and SO patient and SO's intervention,
paginubo ni patient will be feelings and
to increased is bronchospasm patient was able
baby nga able to: communicate
mayda ba production of that reduces the well with them. to:
plema ngan secretions caliber of the maintain
hin nagkukuri small bronchi and airway 2. Assess airway Maintaining maintain
hiya pag may cause patency with for patency. patent airway is airway
hinga”, as difficulty in breath sounds always the first patency with
verbalized. breathing, stasis clear/clearing priority, breath sounds
“Maiha adto demonstrate especially in
of secretions, and clear/clearing
na iya behaviors to cases like trauma,
infection. improve acute evidence by
paginubo kay
han syahan airway neurological normal breath
nagpa check- clearance decompensation, sounds,
up kami ngan 3. Assess or cardiac arrest. normal rate
katapos gin respirations. and depth of
resetahan hiya Note quality, A change in the
respirations,
hin antibiotic rate, pattern, usual respiration
may mean and normal
na co- depth, flaring
amoxiclav tas respiratory O2 saturation
of nostrils,
waray man dyspnea on compromise. An
demonstrate
kaupay asya exertion, increase in
respiratory rate behaviors to
gin pa admit evidence of
na hiya didi,”, and rhythm may improve
splinting, use
as verbalized be a airway
of accessory
“Dida han nag muscles, and compensatory clearance
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
iinubo hiya, position for response to
nagkukuri na breathing. airway GOALS WERE
ak pag pakaon obstruction. MET.
ha iya pero 4. Note for
yana nag balik changes in
na an iya gana HR and Increased work of
pag kaon”, as temperature. breathing can lead
verbalized to tachycardia and
hypertension.
Objective: Retained
Productive secretions or
cough atelectasis may be
Crackles upon a sign of an
inspiration existing infection
Pale lips or inflammatory
With process
wheezing manifested by a
fever or increased
5. Note cough temperature.
for efficacy
and Coughing is a
productivity. mechanism for
clearing
secretions. An
ineffective cough
compromises
airway clearance
and prevents
mucus from being
expelled.
Respiratory
muscle fatigue,
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
severe
bronchospasm, or
thick and
tenacious
secretions are
6. Use pulse possible causes of
oximetry to ineffective cough.
monitor
oxygen Pulse oximetry is
saturation; used to detect
assess arterial changes in
blood gases oxygenation.
(ABGs). Oxygen
saturation should
be maintained at
90% or greater.
Alteration in
ABGS may result
in increased
pulmonary
7. Place the secretions and
patient in a respiratory
semi fowler’s fatigue.
position or
elevate head. Upright position
limits abdominal
contents from
pushing upward
and inhibiting
lung expansion.
This position
promotes better
8. Monitor for
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
the risk of lung expansion
aspiration. and improved air
exchange.
Should they
aspirate on their
secretions this
will put them at a
significantly
increased risk for
aspiration
9. Administer pneumonia,
medications, which would
as ordered: further impair gas
a. Salbutamo exchange and
l 1 neb respiratory
q8H failure.
b. Budesonid
e 1 neb Nebulizer
q12H treatment may be
c. Ceftriaxon administered
e 840 mg to help loosen the
as IV drip mucus in your
to run for lungs and help
30 breathe better.
minutes Antibiotic
treatment may be
given, as well.
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Scientific Nursing
Cues Objectives Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Rationale Interventions
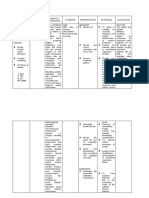
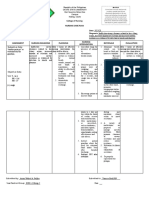
Subjective: Impaired gas Lung function After 8 hours of 1. Establish It allows you to After 8 hours of
“Sige kasi exchange related abnormalities nursing rapport understand your nursing
iton an to related to both at rest and intervention, patient and SO's intervention,
paginubo ni patient will be feelings and
alveolar-capillary during exercise patient was able
baby nga able to: communicate well
mayda ba gas diffusion are frequently with them. to:
plema ngan imbalance observed in Show signs of
hin nagkukuri patients with improved gas 2. Assess Rapid and Show signs of
hiya pag exchange respiratory shallow breathing improved gas
chronic
hinga”, as show rate, depth, patterns and
respiratory exchange as
verbalized. improved and effort, hypoventilation
disease. including the evidenced by
“Maiha adto status of affect gas
use of oxygen
na iya breathing. exchange
accessory saturation
paginubo kay
han syahan SO will: muscles, nasal within normal
nagpa check- verbalize flaring, and range,
up kami ngan understanding abnormal absence or
katapos gin health breathing
diminished
resetahan hiya teachings in patterns.
use of
hin antibiotic appropriate
ways of 3. Assess the Any irregularity accessory
na co-
promoting gas lungs for of breath sounds muscles when
amoxiclav tas
exchange in areas of may disclose the breathing,
waray man
patient and decreased cause of impaired diminished
kaupay asya
importance of ventilation gas exchange.
gin pa admit fatigability,
compliance to and auscultate
na hiya didi,”, and absence
treatment presence of
as verbalized or diminished
adventitious
“Dida han nag
sounds. difficulty of
iinubo hiya,
nagkukuri na breathing
4. Monitor Changes in
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
ak pag pakaon patient’s behavior and show
ha iya pero behavior and mental status can improved
yana nag balik mental status be early signs of status of
na an iya gana for the onset impaired gas
breathing.
pag kaon”, as of exchange.
verbalized restlessness, Verbalize
agitation, understanding
Objective: crying, health
Productive confusion, teachings in
cough and (in the appropriate
Crackles upon late stages) ways of
inspiration extreme
promoting gas
Pale lips lethargy.
With BP, HR, and exchange in
wheezing 5. Monitor for respiratory rate all patient and
alteration in increase with importance of
BP and HR. initial hypoxia
compliance to
and hypercapnia
treatment
Central cyanosis
6. Observe for of tongue and oral GOALS WERE
nail beds, mucosa indicates MET.
cyanosis in severe hypoxia
the skin; and is a medical
especially emergency
note the color
of the tongue
and oral
mucous
Pulse oximetry is
membranes.
a useful tool to
7. Monitor detect changes in
oxygen oxygenation.
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
saturation
continuously,
using a pulse
oximeter.
Increasing PaCO2
8. Note blood and decreasing
gas (ABG) PaO2 are signs of
results as respiratory
available and acidosis and
note changes hypoxemia
Upright or semi-
9. Position Fowler’s position
patient with allows increased
head of the thoracic capacity,
bed elevated, total descent of
in a semi- the diaphragm,
Fowler’s and increased
position (head lung expansion
of the bed at preventing the
45 degrees abdominal
when supine) contents from
as tolerated. crowding.
Ambulation
facilitates lung
expansion,
secretion
clearance and
stimulates deep
breathing.
Nebulizer
10. Administer
treatment may be
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
medications, administered to
as ordered: help loosen the
d. Salbutamo mucus in your
l 1 neb lungs and help
q8H breathe better.
e. Budesonid Antibiotic
e 1 neb treatment may be
q12H given, as well.
f. Ceftriaxon
e 840 mg
as IV drip
to run for
30
minutes
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Scientific Nursing
Cues Objectives Rationale Evaluation
Diagnosis Rationale Interventions
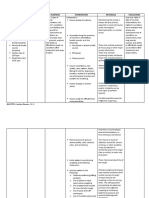
Subjective: Risk for Pneumonia is an After 8 hours of 10. Establish It allows you to After 8 hours of
“Sige kasi infection related infection itself but nursing rapport understand your nursing
iton an to presence of a risk for intervention, patient and SO's intervention,
paginubo ni patient will be feelings and
existing infection infection nursing patient was able
baby nga able to: communicate well
mayda ba diagnosis is with them. to:
plema ngan appropriate as Show signs of
hin nagkukuri untreated worsening or 11. Assess Rapid and Show signs of
hiya pag impending respiratory shallow breathing worsening or
pneumonia can
hinga”, as infections rate, depth, patterns and
progress into a impending
verbalized. display and effort, hypoventilation
secondary including the infections
“Maiha adto improvement affect gas
infection use of display
na iya in infection exchange
or sepsis. evidenced by accessory improvement
paginubo kay
han syahan vital signs and muscles, nasal in infection
nagpa check- physical flaring, and evidenced by
up kami ngan condition abnormal vital signs and
katapos gin breathing
physical
resetahan hiya SO will: patterns.
condition
hin antibiotic verbalize
understanding 12. Assess the Any irregularity SO was able
na co-
on health lungs for of breath sounds to verbalize
amoxiclav tas
teachings areas of may disclose the understanding
waray man
regarding decreased cause of impaired on health
kaupay asya
importance ventilation gas exchange.
gin pa admit teachings
and how to and auscultate
na hiya didi,”, regarding
prevent presence of
as verbalized importance
infection adventitious
“Dida han nag
sounds. and how to
iinubo hiya,
nagkukuri na prevent
13. Monitor Changes in
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
ak pag pakaon patient’s behavior and infection
ha iya pero behavior and mental status can
yana nag balik mental status be early signs of GOALS WERE
na an iya gana for the onset impaired gas MET.
pag kaon”, as of exchange.
verbalized restlessness,
agitation,
Objective: crying,
Productive confusion,
cough and (in the
Crackles upon late stages)
inspiration extreme
Pale lips lethargy.
With Dropping blood
wheezing 14. Monitor for pressure,
worsening hypothermia
signs of or hyperthermia,
infection elevated heart
rate, and
tachypnea are
signs of sepsis
that require
immediate
attention.
15. Assess lab An elevated white
values. blood count is
indicative of
infection. This is
an expected
finding with
pneumonia, but
should not
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
continue to rise
with treatment. If
sepsis is
suspected, a blood
culture can be
obtained.
16. Consider
sources of Any inserted lines
infection. such as IVs,
urinary catheters,
feedings tubes,
suction tubing, or
ventilation tubes
are potential
sources of
infection.
Remove
unnecessary lines
as soon as
possible. Surgical
incisions and any
skin breakdown
should be
monitored for
redness, warmth,
17. Encourage drainage, or odor
fluid intake that signals an
and nutrition. infection.
Hydration is vital
to prevent
dehydration and
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
supports
homeostasis.
Fluids help the
kidneys filter and
flush waste
products
preventing renal
and urinary
infections.
Encouraging oral
fluids will
18. Promote skin mobilize
integrity. respiratory
secretions. Proper
nutrition
promotes energy
and supports the
immune system.
The skin is the
body’s first
barrier against
infection. Skin
breakdown allows
pathogens to enter
the body. If a
patient is
immobile they
must be
11. Administer repositioned
medications, every 2 hours to
as ordered: maintain skin
g. Salbutamo
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
l 1 neb integrity. Keep
q8H skin clean and dry
h. Budesonid through frequent
e 1 neb perineal care or
q12H linen changes.
i. Ceftriaxon
e 840 mg Nebulizer
as IV drip treatment may be
to run for administered to
30 help loosen the
minutes mucus in your
lungs and help
breathe better.
Antibiotic
treatment may be
given, as well.
Dames, Jan Remedios B – Clinical Group D | Nursing Care Plan
You might also like
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternReichelle Perlas62% (13)
- Acute Respiratory DistressDocument2 pagesAcute Respiratory Distressminaanne100% (3)
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument8 pagesCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- CAF 1 - Accounting For PartnershipDocument48 pagesCAF 1 - Accounting For PartnershipAhsan Kamran100% (1)
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledPie CanapiNo ratings yet
- Data NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoDocument3 pagesData NSG Diagnosis Goals & Outcomes NSG Interventions Rationale Evaluation O: StoClaudineNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- Darunday NCP Rotation 6Document3 pagesDarunday NCP Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Darunday NCP Rotation 6Document3 pagesDarunday NCP Rotation 6Ezra Miguel DarundayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Outcome Intervention Rationale EvaluationMarivic Yuson MalagarNo ratings yet
- Camarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges Nabua, Camarines Sur College of Health SciencesDocument6 pagesCamarines Sur Polytechnic Colleges Nabua, Camarines Sur College of Health SciencesDainty LorenNo ratings yet
- Iudmc ActivityDocument10 pagesIudmc ActivityJeraldine GumpalNo ratings yet
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- Valeriano, NCPDocument4 pagesValeriano, NCPVALERIANO TRISHANo ratings yet
- NCP Draft PediaDocument9 pagesNCP Draft PediaEmman BarroquilloNo ratings yet
- Dela Peña NCP 3Document2 pagesDela Peña NCP 3Mark Teofilo Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Innefective Airway Clearance NCPDocument4 pagesInnefective Airway Clearance NCPAllen Vincent Cauton TulaganNo ratings yet
- NCPPDocument11 pagesNCPPAngelo Miguel MuñozNo ratings yet
- Date/Tim e Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues Short Term Goals Short TermDocument4 pagesDate/Tim e Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goals and Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues Short Term Goals Short TermJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnos Is Backgro Und Knowled Ge Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention and Rationale EvaluationSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Breathing PatternPRINCESS KOBAYASHINo ratings yet
- Asthma NCPDocument3 pagesAsthma NCPjaijai magbanuaNo ratings yet
- Scenario 4 - NCPDocument15 pagesScenario 4 - NCPVian RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan in Pedia Ward: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharlynne AraojoNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument5 pagesNCP 1 AND SOAPIE 1) Ineffective Breathing PatternMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NCP SciDocument3 pagesNCP SciJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- NCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfDocument6 pagesNCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfLycah RotoneNo ratings yet
- D. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingDocument2 pagesD. Nursing Care Plan: Impaired Gas Exchange Related To Altered Oxygen Supply As Evidenced by Difficulty in BreathingReinette LastrillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivecammel ramos100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan: Ineffective Airway ClearanceNeil AlviarNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern (Oxygenation) NCPDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern (Oxygenation) NCPkarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPRyan John Bito-onNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway Clearancerozj0750% (2)
- NursingCrib Com Nursing Care Plan Bronchial AsthmaDocument4 pagesNursingCrib Com Nursing Care Plan Bronchial Asthmaahmed.omer222555No ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument7 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- NCP SampleDocument8 pagesNCP SampleKeneth Dave AglibutNo ratings yet
- ASSESSMENTDocument6 pagesASSESSMENTZerimar Adawe DulnuanNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPJanella Kyle ParejaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- (SOB) Care PlanDocument1 page(SOB) Care Planshatha faisal100% (1)
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPMae Denn LabordoNo ratings yet
- Requirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaDocument7 pagesRequirement in NCM 312: Presented By: Chloie Marie C. Rosalejos Submitted To: Ma. Lynn C. ParambitaChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Case-Study - JenDocument15 pagesNcp-Case-Study - JenJennifer AlamonNo ratings yet
- (Duty MDH (Ward) Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pages(Duty MDH (Ward) Nursing Care PlanMikaella R. AcenaNo ratings yet
- NCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Document18 pagesNCP FDAR DS of Covid 19Lyka Shane Pineda AngalaNo ratings yet
- Palileo NCPDocument5 pagesPalileo NCPAeron PalileoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.RDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: St. Anthony's College San Jose, Antique Nursing Department NAME:R.D.Rcen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceJet BautistaNo ratings yet
- ParadigmDocument6 pagesParadigmCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing ActualDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing ActualArian May Marcos100% (1)
- Trixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2DDocument6 pagesTrixie Ann C. Salasibar BSN 2B-2Dann camposNo ratings yet
- NCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument10 pagesNCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 Nursing Care PlansDocument15 pagesNCM 118 Nursing Care PlansElle LibalibNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale Evaluation IndependentJohn Glenn BalacanoNo ratings yet
- O Detect Decreased or Adventitious Breath SoundsDocument2 pagesO Detect Decreased or Adventitious Breath SoundsKent JuguilonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument19 pagesNursing Process Care Plan For Ineffective Breathing Pattern Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation EvaluationZIANAH JOY FAMYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan Patient: Mrs. K Age: 68 Diagnosis: Community Acquired PneumoniaKerks Von Gladiel NapaoNo ratings yet
- THE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeFrom EverandTHE WATER AND THE BREATH: A guide to using water and breathing towards a stress free and successful lifeNo ratings yet
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Advanced Recorder Technique: The Art of Playing the Recorder. Vol. 2: Breathing and SoundFrom EverandAdvanced Recorder Technique: The Art of Playing the Recorder. Vol. 2: Breathing and SoundRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HL-5240 HL-5250DN Mono Laser PrinterDocument4 pagesHL-5240 HL-5250DN Mono Laser PrinterDANIEL CRIADO REDONDONo ratings yet
- W AsiaDocument6 pagesW Asiaapi-213954485No ratings yet
- Art 19 RPCDocument5 pagesArt 19 RPCHappynako Wholesome100% (1)
- Alive Feb 10Document66 pagesAlive Feb 10javed.alam19No ratings yet
- Cognos ResumeDocument4 pagesCognos ResumeAnonymous xMYE0TiNBcNo ratings yet
- Selection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterDocument5 pagesSelection of High Efficient Passive Soft Switching Regenerative Snubber For DC-DC Boost ConverterYuvrajsinh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Bizhub c281 c221 c221s Spec Sheet enDocument2 pagesBizhub c281 c221 c221s Spec Sheet enSuraj Acharya SurajNo ratings yet
- 3210 HT 21-12-2023 SPLDocument1 page3210 HT 21-12-2023 SPLVishnu Vardhan ANo ratings yet
- LI Junhao - CVDocument1 pageLI Junhao - CVJunhao LINo ratings yet
- Ads 7865Document35 pagesAds 7865Parasaram SrinivasNo ratings yet
- EMC Standard PDFDocument58 pagesEMC Standard PDFSongkran Pisanupoj0% (1)
- Python Assignment For Absolute BeginnersDocument5 pagesPython Assignment For Absolute BeginnersAmeya DikshitNo ratings yet
- Penlon A-200 SP Circle Absorber - User Manual PDFDocument40 pagesPenlon A-200 SP Circle Absorber - User Manual PDFluisNo ratings yet
- Plant Design TemplateDocument13 pagesPlant Design TemplateRishabhGupta 2k20umba32No ratings yet
- Future Prospects of Duck Production in Asia PDFDocument14 pagesFuture Prospects of Duck Production in Asia PDFridzwanmsNo ratings yet
- Hands-On Quiz Answer Key With NotesDocument13 pagesHands-On Quiz Answer Key With NotesRosen AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Bobie Rose DDocument8 pagesBobie Rose DApril Dawn DaepNo ratings yet
- EContent 3 2024 02 28 06 43 20 CAPITALGAINdocx 2024 02 20 11 29 41Document22 pagesEContent 3 2024 02 28 06 43 20 CAPITALGAINdocx 2024 02 20 11 29 41solanki YashNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Gaining A Competitive AdvantageDocument22 pagesHuman Resource Management Gaining A Competitive AdvantagelinhNo ratings yet
- Abap TablesDocument753 pagesAbap TablesHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lieberose Solar Park - Presentation-WorkedDocument43 pagesLieberose Solar Park - Presentation-WorkedNeetu RajaramanNo ratings yet
- Proceed FormulationsDocument18 pagesProceed FormulationssudhirchughNo ratings yet
- CH 8Document14 pagesCH 8Ajay Kumar GangulyNo ratings yet
- Elections in The Internet AgeDocument30 pagesElections in The Internet AgeMaricel P. GopitaNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Debt and Leasing: Debagus SubagjaDocument12 pagesIntermediate Debt and Leasing: Debagus SubagjaDebagus SubagjaNo ratings yet
- Pending Payments: Issuance Work Permit For 2 Year Outside The Country - SkillDocument1 pagePending Payments: Issuance Work Permit For 2 Year Outside The Country - SkillHasnain proNo ratings yet
- Guindaste Liebherr LR 1250Document24 pagesGuindaste Liebherr LR 1250Ronaldo MachadoNo ratings yet
- (Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403Document4 pages(Thaytro - Net) de Thi THPT 2020 Mon Anh de Chinh Thuc Ma de 403longnguyenNo ratings yet
- Case Hansson Private LabelDocument15 pagesCase Hansson Private Labelpaul57% (7)