Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Constitutional Development of India (1773 - 1935)
Constitutional Development of India (1773 - 1935)
Uploaded by
Kartik SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Constitutional Development of India (1773 - 1935)
Constitutional Development of India (1773 - 1935)
Uploaded by
Kartik SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
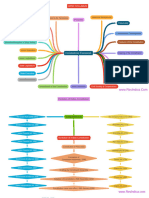
CONSTITUTIONAL DEVELOPMENTS DURING BRITISH RULE (1773 - 1935)
(By IAS PCS Pathshala)
Constitutional Development (1773 - 1935)
Regulating Act of 1773 Pitts India Act of 1784 Charter Act of 1813 Charter Act of 1833 Charter Act of 1853 Government of India Act, Indian Council Act of 1861 Indian Council Act of 1892 Indian Council Act of 1909 Government of India Act, Government of India Act,
1858 (Morley Minto Reforms ) 1919 (Montagu Chelmsford 1935
Reforms )
Governor of Bengal = GG of Distinguished between EIC monopoly over trade in GG of Bengal = GG of India Executive & Legislative GG of India = Viceroy (1st - Decentralisation began. Increase the number non Morley - SOS ; Minto - Viceroy Montagu - SOS; Chelmsford - All India Federation was
Bengal. (1st - Warren Hasting) political and commercial India ended, except trade with (1st - Lord William Bentick) functions of the GG were Lord Canning) of cial member in provincial & Viceroy provisioned for but not created
functions of the Company China and the trade in tea. separated. Legislative powers of Bombay central legislative councils. For the 1st time, Direct since criteria not met.
1st step taken by British to and Madras were restored. But, of cial majority remained. elections were introduced for British had declared 2 years (Princely states did not join it)
control EIC affairs. the Legislative Councils. ago that Introduction of
Viceroy allowed to nominate responsible government was Federal, Concurrent &
Recognised Political & Indians into his expanded its objective. Provincial list created.
Administrative functions of council as non of cial Residuary powers to Viceroy.
EIC for 1st time members.
Abolished Dyarchy at
Act Prohibited servants of First Indians nominated: Raja provincial level. Replaced with
Company from accepting of Benaras, Maharaja of Provincial autonomy.
bribes/doing private trade. Patiala, Sir Dinakar Rao
Dyarchy introduced at the
Centre. Federal subjects
divided into reserved &
transferred.
Council of India (made in
1858) was abolished
Govemors of Bombay, Madras Established a system of EIC was to retain the It attempted to introduced a 6 new members to Legislative Ended the system of Dual New legislative councils were An indirect method of election Increased size of councils Central and Provincial Lists
made subordinate to double government with Court possession of territories and system of open competition Council, 4 members were Government. A new of ce opened in Bengal(1862), to Central/Provincial Councils considerably. For CLC it went produced for the 1st time.
Governor of Bengal of Directors & Board of the revenue for 20 years more for selection of civil servants. appointed by Provisional “Secretary of State" was NWFP(1866) and allowed. from 16 to 60.
Control. (but asserted sovereignty of Governments of Bengal, created. It had complete Punjab(1897) 3 members (of 6) in Viceroy’s
the British Crown over the Bombay, Madras and Agra. authority and control over Indians allowed (1st time) to EC to be Indians.
Board of Control to manage lndian territories) Known as Indian(Central) Indian administration. Viceroy /Governors Executive
political affair. Legislative Council Council.
Secretary of State - member
Court of Directors to manage of the British Cabinet. 1st Indian in Viceroy EC was
commercial affairs Satyendra Prasad
A 15-member advisory body For CLC, of cial maioritv
named Council of India" was present. For PLC, non-of cial
created. SOS was its majorities permitted.
chairman.
SC established in Calcutta British Govt was given 1 lakh rupees for education. Ended EIC's functions as a Legislative council functioned Abolished EIC and transferred Viceroy allowed to make rules Increased functions of Enlarged functions of councils Dyarchy (scheme of Dual Bicameralism introduced In
with 1 CJ and 3 Judge. supreme control over commercial body. Only as a mini-Parliament & all powers to the British and orders for convenient legislative councils. Allowed to at both levels Governance) was introduced 6/11 provinces
company's affairs and administrative functions adopted the same process as Crown. transaction of business in discuss budget, address Ex: Supplementary Questions. in Provinces. Federal Court opened under it
Court of Directors made to administration remained British Parliament council. questions to the executive Resolutions of the Budget. in 1937.
report on revenue, civil and Reserved List were
military affairs In India administered by Governor+
Executive Council (law and
order, nance, land revenue,
irrigation).
Transferred list were
administered through
Provincial legislature +
Governor. (LSG, Health,
Education)
EIC’s territories were called Christian missionaries It was the nal step for Introduced an open Called Act for the Good Recognized the "Portfolio Act also known as "Father of Bicameralism & Direct
“British possessions in India” permitted to preach religion in centralization in British India competition system for civil Government of India. system" where a person in his Communal Electorate”. It Elections introduced.
India servants. Civil Services were department could give nal introduced separate
opened to Indians. orders on behalf of the entire electorates for Muslims. Indian Legislative Council
council became Council of State(RS)
& Legislative Assembly (LS).
Majority In both Houses
chosen by direct election.
Empowered Viceroy to issue Extended system of Extended separate electorate
ordinances w/o concurrence communal electorates to by giving it to depressed
of the legislative council Sikhs, Indian Christians, classes(SC)
during an emergency. Life of Anglo-Indians and Europeans
ordinances 6 months
Increased franchise. Given on Increased franchise. Given
the basis of property tax/ to10% of population.
education
Of ce of "High Commissioner RBI was established under it.
for India" was created in
London. It was given some
functions of SOS
Central Public Service Federal, Provincial and Joint
Commission was opened In Public Service Commissions
1926 for recruiting civil made.
servant.
Appointed a statutory
commission to report on the
Act after 10 years (Simon
Commission)
YouTube - https://www.youtube.com/c/IASPCSPathshala
Telegram - https://t.me/iaspcspathshala
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
fi
You might also like
- Secret Masonic Handshake and OthersDocument13 pagesSecret Masonic Handshake and Othersapi-2671960194% (18)
- TED Talk-Our Dangerous Obsession With Perfectionism Is Getting Worse (Thomas Curran)Document3 pagesTED Talk-Our Dangerous Obsession With Perfectionism Is Getting Worse (Thomas Curran)CARYS BROWN0% (1)
- Polity Imp Topics SYNOPSISDocument15 pagesPolity Imp Topics SYNOPSISG SinghNo ratings yet
- Constitution SummaryDocument130 pagesConstitution SummaryANJANEYULUNo ratings yet
- The Government of India Act, 1858Document3 pagesThe Government of India Act, 1858Sana MNo ratings yet
- History ActsDocument1 pageHistory ActsVishnoo PrathapNo ratings yet
- Polity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS PathshalaDocument7 pagesPolity Repeated Themes & Repeated Topics 2013 2022 IAS PCS Pathshalaekta rawatNo ratings yet
- AP White Paper On Bifurcation IssuesDocument32 pagesAP White Paper On Bifurcation IssuesharishsairamNo ratings yet
- Dristi Reservation in IndiaDocument6 pagesDristi Reservation in IndiarahulNo ratings yet
- RRP 2021 Medieval History Ready ReckonerDocument32 pagesRRP 2021 Medieval History Ready Reckonerhaha kumarNo ratings yet
- List of GovernorsDocument2 pagesList of Governorsnewcontrol testNo ratings yet
- Hand and Seal: JSPSC-Statutory-Appoint: Prez - 62 Yrs - Report: GovernrDocument4 pagesHand and Seal: JSPSC-Statutory-Appoint: Prez - 62 Yrs - Report: Governrpratik100% (1)
- Government of India Act 1858 PDFDocument2 pagesGovernment of India Act 1858 PDFjaivik_ce7584No ratings yet
- List of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaDocument17 pagesList of Governor General and Viceroy in IndiaRavi Kumar Agrahari100% (1)
- 100+ Cases ConstitutionDocument102 pages100+ Cases ConstitutionSourabh K100% (1)
- Medieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHDocument50 pagesMedieval History With Important Facts BY KRISHVamshi Krishna Acharya100% (1)
- Polity Mains RRP 2021Document93 pagesPolity Mains RRP 2021ajay laxman nirmalNo ratings yet
- (MR) Polity by Abhilash MR Sir (MR)Document14 pages(MR) Polity by Abhilash MR Sir (MR)sandarbh12345No ratings yet
- Polity (English) One LinerDocument102 pagesPolity (English) One LinercharanNo ratings yet
- Types of Majorities Used in The Indian ParliamentDocument4 pagesTypes of Majorities Used in The Indian ParliamentAshi SNo ratings yet
- Constitutional BodiesDocument2 pagesConstitutional BodiesGaurav NaharNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity: The 42nd Amendment Act (1976) Is Known As Mini-Constitution'Document20 pagesIndian Polity: The 42nd Amendment Act (1976) Is Known As Mini-Constitution'Balaji vNo ratings yet
- District Map Odisha: West Bengal JharkhandDocument1 pageDistrict Map Odisha: West Bengal JharkhandSamrat MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Handout On Security Issues Class-5 by Mr. Pavneet SinghDocument4 pagesHandout On Security Issues Class-5 by Mr. Pavneet SinghRahul Kumar DubeyNo ratings yet
- Modern History EvernoteDocument18 pagesModern History EvernoteKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Modern History Revision Notes - IxambeeDocument25 pagesModern History Revision Notes - IxambeeTanish KalraNo ratings yet
- Geography (English) One LinerDocument198 pagesGeography (English) One LinerappuNo ratings yet
- One Liner Case LawDocument4 pagesOne Liner Case LawGautamNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Bodies in IndiaDocument12 pagesConstitutional Bodies in IndiaRishabh SareenNo ratings yet
- Delhi SultanateDocument10 pagesDelhi SultanateTavishee ChessNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity OnelinerDocument5 pagesIndian Polity OnelinerKiran PatilNo ratings yet
- Spectrum Short NotesDocument141 pagesSpectrum Short NotesTANISH BANSALNo ratings yet
- World History Class Notes Avadh OjhaDocument43 pagesWorld History Class Notes Avadh Ojhaas90363450% (2)
- Lexicon Ethics by Raz KR - Compressed PDFDocument333 pagesLexicon Ethics by Raz KR - Compressed PDFBasant Singh100% (1)
- Pradeep Singh EthicsDocument14 pagesPradeep Singh EthicsRahul ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- General Studies Indian PolityDocument28 pagesGeneral Studies Indian Politymadhub_17No ratings yet
- Polity Laxmikant Short NotesDocument120 pagesPolity Laxmikant Short NotesKundanNo ratings yet
- AoS 1781Document16 pagesAoS 1781shuaib12saifiNo ratings yet
- Example Final CompressedDocument39 pagesExample Final CompressedVarun TkNo ratings yet
- Indian Geography Revision SlidesDocument256 pagesIndian Geography Revision SlidesSateesh100% (1)
- Indian National MovemenentDocument28 pagesIndian National Movemenentmakkala shireeshaNo ratings yet
- Rjs Previous Year Paper 2013-18-3 2Document130 pagesRjs Previous Year Paper 2013-18-3 2Jayvardhan singhNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of HRV Parameter Based Deep Neural NetworkDocument4 pagesPerformance Evaluation of HRV Parameter Based Deep Neural NetworkInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- IkshvakusDocument27 pagesIkshvakusAnil KondaNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument25 pagesIndian PolitySharad GuptaNo ratings yet
- Modern Indian History Notes by Ias - Network-1Document138 pagesModern Indian History Notes by Ias - Network-1Tej S. Gurjar100% (1)
- Power Notes For PolityDocument8 pagesPower Notes For PolitypaaritoshNo ratings yet
- L IV E: Indian PolityDocument111 pagesL IV E: Indian PolityALLU SRISAINo ratings yet
- Cyber Crime Synopsis PDFDocument6 pagesCyber Crime Synopsis PDFAmanNo ratings yet
- History-Complete Study NoteDocument48 pagesHistory-Complete Study NoteRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- GOI Acts Table SummaryDocument8 pagesGOI Acts Table Summaryvxpzfs29rhNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Full PDF EM PDFDocument127 pagesIndian Polity Full PDF EM PDFnitshya samNo ratings yet
- Government of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TrainingDocument17 pagesGovernment of Tamilnadu: Department of Employment and TraininglokeshNo ratings yet
- L2 PPT Brief History of Constitutional Developments 2 1670967075Document79 pagesL2 PPT Brief History of Constitutional Developments 2 1670967075legendx4406No ratings yet
- Part 1Document8 pagesPart 1thesatyamjha09No ratings yet
- INSIGHTS ON INDIAN POLITY Kano 1689416005Document12 pagesINSIGHTS ON INDIAN POLITY Kano 1689416005Sayeda MazumderNo ratings yet
- Making of Constitution Important Acts Constitutional Land Mark Important ProvisionsDocument5 pagesMaking of Constitution Important Acts Constitutional Land Mark Important ProvisionsMushini NagabhushanNo ratings yet
- Laxmikant HDocument2 pagesLaxmikant Hkrishna chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- IASbaba Polity Prelims SolutionsDocument67 pagesIASbaba Polity Prelims SolutionsapoorvnigNo ratings yet
- Full PolityDocument44 pagesFull PolityBalaji vNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Quick Revision Polity 120 Days Upsc Perlims 2021 10pointerDocument8 pagesDay 1 Quick Revision Polity 120 Days Upsc Perlims 2021 10pointerAllindiatestNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Military Law in India: Including the Mutiny Acts and Articles of WarFrom EverandThe Evolution of Military Law in India: Including the Mutiny Acts and Articles of WarNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument1 pageProjectKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Data CAGDocument1 pageBio Data CAGKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- PAXMUN'21 CertificateDocument1 pagePAXMUN'21 CertificateKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reasoning QuestionsDocument62 pagesReasoning QuestionsKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- RealprojectDocument1 pageRealprojectKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Important ArticlesDocument19 pagesImportant ArticlesKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- d63aa017-34ac-4fb8-ac12-946926f4ace4Document115 pagesd63aa017-34ac-4fb8-ac12-946926f4ace4Kartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- f6df1686-dd22-44a9-9164-65f97f594171Document5 pagesf6df1686-dd22-44a9-9164-65f97f594171Kartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Best 500 Vocab Sets 1 To 20 MergedDocument122 pagesBest 500 Vocab Sets 1 To 20 MergedKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2024 Calendar WebDocument20 pages2024 Calendar WebgreenietorbesNo ratings yet
- Schineller JesuitGlossaryDocument40 pagesSchineller JesuitGlossaryKun Mindaugas Malinauskas SJNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment SM.Document6 pagesGroup Assignment SM.Waheed LangahNo ratings yet
- English Grammar ExerciseDocument8 pagesEnglish Grammar ExerciseLeonardo Jr PinedaNo ratings yet
- Rule 138 Sec 4Document2 pagesRule 138 Sec 4Austin Viel Lagman MedinaNo ratings yet
- Candidate List 64CCE 10-09-2018 OAPDocument115 pagesCandidate List 64CCE 10-09-2018 OAPOm PrakashNo ratings yet
- HIC Shelter Data Pack 30 July 2005Document227 pagesHIC Shelter Data Pack 30 July 2005Edi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Analysis BCGDocument21 pagesPortfolio Analysis BCGAnuranjanSinha100% (2)
- The Mughal EmpireDocument4 pagesThe Mughal Empirelock_jaw30No ratings yet
- Sustainable Supermarkets: DiscussionDocument1 pageSustainable Supermarkets: DiscussionЮлія ПапірникNo ratings yet
- Aff. of Witness - Kimberly EstoleroDocument2 pagesAff. of Witness - Kimberly EstoleroSteps RolsNo ratings yet
- Republic v. Science Park of The Philippines 2021Document13 pagesRepublic v. Science Park of The Philippines 2021f919No ratings yet
- By Fr. Michel Rodrigue'sDocument3 pagesBy Fr. Michel Rodrigue'sangel_sagun_1No ratings yet
- 3.teaching Guide Catchup Science Values Grade 7Document3 pages3.teaching Guide Catchup Science Values Grade 7Aires IchonNo ratings yet
- Adverse Claim and SPA Mangaldan PangasinanDocument4 pagesAdverse Claim and SPA Mangaldan PangasinanRichard R. GemotaNo ratings yet
- SEC Primary RegistrationDocument13 pagesSEC Primary RegistrationElreen Pearl AgustinNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Children and Young People With Physical Medical NeedsDocument3 pagesGuidance For Children and Young People With Physical Medical NeedsfionaphimisterNo ratings yet
- Artikel Syekh Ibrahim Musa Sang Inspirator Kebangkitan Oleh Kel.12Document10 pagesArtikel Syekh Ibrahim Musa Sang Inspirator Kebangkitan Oleh Kel.12baskaraNo ratings yet
- Querying and Reporting DataDocument27 pagesQuerying and Reporting DataPortelly JdrNo ratings yet
- Reflective ReportDocument6 pagesReflective ReportZulkifli Che HusinNo ratings yet
- EO-GA-21 Expanding Open Texas COVID-19Document8 pagesEO-GA-21 Expanding Open Texas COVID-19Amber NicoleNo ratings yet
- A 196120 in DirektDocument297 pagesA 196120 in DirektduromihalicNo ratings yet
- Key Challenges Facing Public Sector LeadersDocument6 pagesKey Challenges Facing Public Sector LeadersSifa MtashaNo ratings yet
- VTOL - WikipediaDocument46 pagesVTOL - WikipediaLeng ChaiNo ratings yet
- DX4E 2.4ghz ManualDocument84 pagesDX4E 2.4ghz ManualvayaveNo ratings yet
- Mba Project of WelingkarDocument9 pagesMba Project of WelingkarrakeshNo ratings yet
- 1.0.1.2 Class Activity - Network by Design - ILMDocument3 pages1.0.1.2 Class Activity - Network by Design - ILMLajos HomorNo ratings yet
- No. Branch (Mar 2022) Legal Name Organization Level 4 (1 Mar 2022) Average TE/day, 2019 Average TE/day, 2020 Average TE/day, 2021 (A)Document7 pagesNo. Branch (Mar 2022) Legal Name Organization Level 4 (1 Mar 2022) Average TE/day, 2019 Average TE/day, 2020 Average TE/day, 2021 (A)Irfan JauhariNo ratings yet