Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Bronchitis 2
What Is Bronchitis 2
Uploaded by
lea jumawanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Secret of 2Document21 pagesThe Secret of 2Anekk Sadh100% (18)
- Abraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsDocument2 pagesAbraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsSahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- RespDocument23 pagesRespAyessa D. RosalitaNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument11 pagesBronchitisRenuka Sivaram100% (2)
- Problem in OxygenationDocument11 pagesProblem in OxygenationNikky Rossel FloresNo ratings yet
- List of Diseases of The Respiratory System: Central Sleep ApneaDocument4 pagesList of Diseases of The Respiratory System: Central Sleep ApneaPaola ParkerNo ratings yet
- Walang Pamagat Na DokumentoDocument3 pagesWalang Pamagat Na Dokumentobenedict cruz DevianaNo ratings yet
- نيومومياDocument1 pageنيومومياMohamed AlsaabNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 FinalDocument2 pagesNCM 118 FinalAddah, Dhenaraiza H.No ratings yet
- LP TBCDocument15 pagesLP TBCFitri fitNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesBronchitis Pa Tho PhysiologyHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical Nursingpinoy HubNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyBrunhild BangayanNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument2 pagesBronchitisАнастасия ПащенкоNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument40 pagesBronchitisJAMES NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Vs BronchiolitisDocument52 pagesBronchitis Vs BronchiolitisUngku Hajar Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Jzdinglasan@bpsu - Edu.ph: Joben Zamora Dinglasan Bs Psych - 1ADocument4 pagesJzdinglasan@bpsu - Edu.ph: Joben Zamora Dinglasan Bs Psych - 1ACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 9Document9 pagesPneumonia 9Samba SukanyaNo ratings yet
- 50 DiseasesDocument44 pages50 DiseasesJewenson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Why It Happens?: BronchiectasisDocument2 pagesWhy It Happens?: BronchiectasisRejoy ObinaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesWeek 1 Respiratory SystemCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Respi PathophysioDocument31 pagesRespi PathophysioIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesLESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemRin HxHNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- Case Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Document14 pagesCase Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Pathology Assignment 1Document2 pagesPathology Assignment 1areebafarooq820No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document16 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Target Organs: LungsDocument3 pagesTarget Organs: LungsMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Asuahan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan PneumoniaDocument15 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Asuahan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan PneumoniaIka Ulya Cahyani PutriNo ratings yet
- Drugs RespiratoryDocument15 pagesDrugs RespiratoryLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesSchematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaanGel1115No ratings yet
- COPDDocument52 pagesCOPDSoySauceNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- Case Study For BronchiectasisDocument7 pagesCase Study For BronchiectasisGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- BSN-3 M6bcdDocument26 pagesBSN-3 M6bcdZel Natulla MoranoNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON BroncitisDocument24 pagesLesson Plan ON Broncitisvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Activity-11-Respiratory-System - PERALTADocument3 pagesActivity-11-Respiratory-System - PERALTACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Respiratory System 2Document76 pagesPathology of The Respiratory System 2Fabian ChapimaNo ratings yet
- Perofrmance Task in Science: Renzo Anjelo Sison Mr. Wilson Vicente T. Gomez Grade 9 Bonicfacio ADocument17 pagesPerofrmance Task in Science: Renzo Anjelo Sison Mr. Wilson Vicente T. Gomez Grade 9 Bonicfacio AAnjelo SisonNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis HandoutDocument5 pagesAcute Bronchitis HandoutDianne LegionNo ratings yet
- Blank 5Document23 pagesBlank 5Mariya EudoraNo ratings yet
- Disease: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument4 pagesDisease: Community Acquired PneumoniaJo Traven AzueloNo ratings yet
- RespdiseasesDocument1 pageRespdiseasesPatricia MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Asthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FunctionDocument8 pagesRespiratory FunctionMohammad AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 PTDocument12 pagesLec 3 PTBassam AlgalalyNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- By DPS StudentsDocument10 pagesBy DPS StudentszarakonhaiNo ratings yet
- Article About CaughDocument8 pagesArticle About CaughNour AlhazzaaNo ratings yet
- Etiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The ListDocument3 pagesEtiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The Listselam kalayuNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PDFDocument2 pagesPneumonia PDFlorreaNo ratings yet
- Ast 2Document17 pagesAst 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Asthm 2Document34 pagesAsthm 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Active Cycle of Breathing TechniquesDocument6 pagesActive Cycle of Breathing Techniqueskarl24No ratings yet
- LungsDocument18 pagesLungsMaritess JacintoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System1Document5 pagesRespiratory System1Ombati StephenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoDocument19 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoKen BaxNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument31 pagesRespiratory Disorderssharlinecatuday08No ratings yet
- Seminar 3 (Recovered)Document134 pagesSeminar 3 (Recovered)saranya amuNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandBronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- BARAHAMADocument51 pagesBARAHAMAlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive System AssessmentDocument12 pagesMale & Female Reproductive System Assessmentlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cephalovelvic DisproportionDocument9 pagesCephalovelvic Disproportionlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- JAMALULDocument10 pagesJAMALULlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Depression CareDocument16 pagesPostpartum Depression Carelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesPneumothorax-WPS Officelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RLE Checklists (SHORT)Document78 pagesRLE Checklists (SHORT)lea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Infectious DeseasesDocument16 pagesInfectious Deseaseslea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Herniancm-116Document19 pagesHiatal Herniancm-116lea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Kiding PTB TBDocument20 pagesKiding PTB TBlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Buddhism FinaleDocument5 pagesBuddhism Finalelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RLE SKILLS CHECKLIST 2023 - HandwashingDocument2 pagesRLE SKILLS CHECKLIST 2023 - Handwashinglea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cna Making An Occupied BedDocument3 pagesCna Making An Occupied Bedlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study RleDocument25 pagesCase Study Rlelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - DDocument13 pagesTension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - Dlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument2 pagesRandomlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade Case PresentationDocument3 pagesCardiac Tamponade Case Presentationlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3.2 Batu Saluran KemihDocument64 pages3.1.3.2 Batu Saluran Kemihwinda musliraNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us - Siae Alfo Plus User Manual PDFDocument110 pagesDocslide - Us - Siae Alfo Plus User Manual PDFh2ck3rNo ratings yet
- Signed Off Understanding Culture11 q1 m2 Defining Culture and Politics v3 RemovedDocument24 pagesSigned Off Understanding Culture11 q1 m2 Defining Culture and Politics v3 Removedrhaybien vinluanNo ratings yet
- Treating Straw For Animal FeedingDocument36 pagesTreating Straw For Animal FeedingHybrid BurtonNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Recruitment and Selection Process at Big BazarDocument41 pagesA Project Report ON Recruitment and Selection Process at Big BazarGurusaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Law - Insider - Edison Nation Inc - Separation Agreement and Release - Filed - 11 06 2019 - ContractDocument9 pagesLaw - Insider - Edison Nation Inc - Separation Agreement and Release - Filed - 11 06 2019 - ContractNavrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Description: P Ack AgeDocument3 pagesDescription: P Ack AgeAlexandru CioponeaNo ratings yet
- IELTS SPEAKING - WorkDocument3 pagesIELTS SPEAKING - WorkQuỳnh Anh Nguyễn HồNo ratings yet
- Vishwa Patel FIFA 20215041Document10 pagesVishwa Patel FIFA 20215041Vishwa PatelNo ratings yet
- Step 7 Err Code125936644Document37 pagesStep 7 Err Code125936644mohammadNo ratings yet
- Concerto in C Minor - Johann Christian Bach - CelloDocument24 pagesConcerto in C Minor - Johann Christian Bach - CellojosianeNo ratings yet
- 865 F.2d 1260 Unpublished DispositionDocument25 pages865 F.2d 1260 Unpublished DispositionScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Ip RoutingDocument34 pagesIp RoutingericmscNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0749070421000397Document14 pagesPi Is 0749070421000397Vlady78No ratings yet
- Level 1 - Cambridge Vocab For IELTS, English, Ielts - MemriseDocument3 pagesLevel 1 - Cambridge Vocab For IELTS, English, Ielts - MemrisetunisianouNo ratings yet
- PRM AnswerDocument28 pagesPRM AnswerMinh TrangNo ratings yet
- Derridas Legacies Literature and PhilosophyDocument184 pagesDerridas Legacies Literature and Philosophyinnommable100% (1)
- Ileus - Prof - Bachtiar Murtala (PP) PDFDocument37 pagesIleus - Prof - Bachtiar Murtala (PP) PDFAchmad Rizki AlhasaniNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology 101Document9 pagesDevelopmental Psychology 101Ibov VanizNo ratings yet
- Sarah GarzaDocument1 pageSarah Garzasarah_garza67424No ratings yet
- FIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyDocument2 pagesFIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyAlexMartinNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorder PPT by Shreyasi MittalDocument35 pagesEating Disorder PPT by Shreyasi MittalPrachi gattaniNo ratings yet
- MA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1Document127 pagesMA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1avers990% (1)
- My PastorDocument3 pagesMy PastorPastor Emma MukisaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory - Course Outline 2021Document4 pagesGame Theory - Course Outline 2021Mayank RanjanNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFDocument1 pageTransfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFnohe992127No ratings yet
- Module 3 Literature ActivitiesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Literature ActivitiesAlexis Joy P. DangoNo ratings yet
- Le 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaDocument122 pagesLe 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaGiorgio FerracinNo ratings yet
What Is Bronchitis 2
What Is Bronchitis 2
Uploaded by
lea jumawanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Bronchitis 2
What Is Bronchitis 2
Uploaded by
lea jumawanCopyright:
Available Formats
What is bronchitis?
Definition
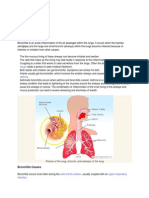
Bronchitis is inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi),the air passage between
the nose and the lungs. More specifically, bronchitis is when the lining of the bronchial tubes
becomes inflamed or infected. Bronchitis is caused by viruses, bacteria, and other particles that
irritate bronchial tubes.
TYPES OF BEONCHITIS
Acute bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a shorter illness that commonly follows a cold or viral infection, such as the
flu Acute bronchitis usually lasts a few days or weeks.
Chronic bronchitis
Chronic bronchitis is characterized by a persistent mucus-producing cough on most days of the
month three months of a year fort to successive years and absence of a secondary cause of the
cough.
Pathophysiology
Due to E/F
Microorganism enter into the respiratory tract by inhalation
Widespread inflammation occurs
Thin mucus lining of the bronchi can become irritated and swollen
Cell that makes up this lining may leak fluid and in response to the inflammation
Coughing as a reflex that works to clear secretion from the lungs
Alveolar fluid response
Narrowing of the airways
Ventilation decrease as a secretion thickens
Mucus within the airways produces resistance in small airways and can cause severe ventilation
perfusion imbalance
Bronchitis
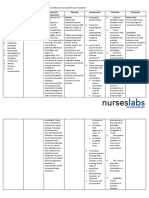
Signs & symptoms of bronchitis
Inflammation or swelling of the bronchi
Coughing
Production of clear, white, yellow, grey, or green mucus (sputum)
Shortness of breath
Wheezing
Fatigue
Fever and chills
Chest pain or discomfort
Blocked or runny nose
Pharmacologic management
Antibiotics – these are effective for bacterial infections, but not for viral infections. They
may also prevent secondary infection.
Cough medicine – one must be careful not to completely suppress the cough, for it is an
important way to bring up mucus and remove irritants from the lungs.
Bronchodilators - these open the bronchial tubes and clear out mucus.
Mucolytics – these thin or loosen mucus in the airways, making it easier to cough up
sputum.
Anti-inflammatory medicines and glucocorticoid steroids – these are for more persistent
symptoms.
Pulmonary rehabilitation program – this includes work with a respiratory therapist to help
breathing.
Nursing management
1. Assess the condition of patient.
2. Assess the vital signs.
3. Provide comfortable position.
4. Change the position periodically.
5. Maintain personal hygiene.
6. Use pulse oximetry & suction.
7. Deep breathing exercise learn to patient.
8. Refer to physiotherapist(if need).
9. Provide oxygen according to physician order.
10. Provide psychological support to patient.
11. Provide knowledge about chronic bronchitis.
12. Administer medication according to physician order.
Bronchodilators, antibiotics, mucolytics.
You might also like
- The Secret of 2Document21 pagesThe Secret of 2Anekk Sadh100% (18)
- Abraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsDocument2 pagesAbraham-Hicks 2001-2009 Collection 56CDsSahl H JamsheerNo ratings yet
- RespDocument23 pagesRespAyessa D. RosalitaNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument11 pagesBronchitisRenuka Sivaram100% (2)
- Problem in OxygenationDocument11 pagesProblem in OxygenationNikky Rossel FloresNo ratings yet
- List of Diseases of The Respiratory System: Central Sleep ApneaDocument4 pagesList of Diseases of The Respiratory System: Central Sleep ApneaPaola ParkerNo ratings yet
- Walang Pamagat Na DokumentoDocument3 pagesWalang Pamagat Na Dokumentobenedict cruz DevianaNo ratings yet
- نيومومياDocument1 pageنيومومياMohamed AlsaabNo ratings yet
- NCM 118 FinalDocument2 pagesNCM 118 FinalAddah, Dhenaraiza H.No ratings yet
- LP TBCDocument15 pagesLP TBCFitri fitNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 pagesBronchitis Pa Tho PhysiologyHemant KumarNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical NursingDocument9 pagesIsabela State University: Republic of The Philippines San Fabian, Echague, Isabela Activity 2 Medical-Surgical Nursingpinoy HubNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY Acute BronchitisFrancine kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesBronchiectasis PathophysiologyBrunhild BangayanNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument2 pagesBronchitisАнастасия ПащенкоNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument40 pagesBronchitisJAMES NYIRENDANo ratings yet
- Bronchitis Vs BronchiolitisDocument52 pagesBronchitis Vs BronchiolitisUngku Hajar Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Jzdinglasan@bpsu - Edu.ph: Joben Zamora Dinglasan Bs Psych - 1ADocument4 pagesJzdinglasan@bpsu - Edu.ph: Joben Zamora Dinglasan Bs Psych - 1ACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia 9Document9 pagesPneumonia 9Samba SukanyaNo ratings yet
- 50 DiseasesDocument44 pages50 DiseasesJewenson SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Why It Happens?: BronchiectasisDocument2 pagesWhy It Happens?: BronchiectasisRejoy ObinaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesWeek 1 Respiratory SystemCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Respi PathophysioDocument31 pagesRespi PathophysioIsmael JaaniNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument22 pagesLESSON 1.3-Common Diseases and Disorders of The Respiratory SystemRin HxHNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument15 pagesBronchitisAakanksha vaishnav100% (1)
- Case Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Document14 pagesCase Study: Submitted By: Jane Arian Berzabal Nbb2Jane Arian BerzabalNo ratings yet
- Pathology Assignment 1Document2 pagesPathology Assignment 1areebafarooq820No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document16 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Kimberly Abella CabreraNo ratings yet
- Target Organs: LungsDocument3 pagesTarget Organs: LungsMae Arra Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Asuahan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan PneumoniaDocument15 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Asuahan Keperawatan Pada Klien Dengan PneumoniaIka Ulya Cahyani PutriNo ratings yet
- Drugs RespiratoryDocument15 pagesDrugs RespiratoryLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaDocument11 pagesSchematic Diagram OF BronchopneumoniaanGel1115No ratings yet
- COPDDocument52 pagesCOPDSoySauceNo ratings yet
- "Bronchitis": Respiratory DisorderDocument40 pages"Bronchitis": Respiratory Disorderaswin379No ratings yet
- Case Study For BronchiectasisDocument7 pagesCase Study For BronchiectasisGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- BSN-3 M6bcdDocument26 pagesBSN-3 M6bcdZel Natulla MoranoNo ratings yet
- What Is Acute BronchitisDocument11 pagesWhat Is Acute BronchitisKerri-DojhnHallNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ON BroncitisDocument24 pagesLesson Plan ON Broncitisvani reddyNo ratings yet
- Activity-11-Respiratory-System - PERALTADocument3 pagesActivity-11-Respiratory-System - PERALTACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Pathology of The Respiratory System 2Document76 pagesPathology of The Respiratory System 2Fabian ChapimaNo ratings yet
- Perofrmance Task in Science: Renzo Anjelo Sison Mr. Wilson Vicente T. Gomez Grade 9 Bonicfacio ADocument17 pagesPerofrmance Task in Science: Renzo Anjelo Sison Mr. Wilson Vicente T. Gomez Grade 9 Bonicfacio AAnjelo SisonNo ratings yet
- Acute Bronchitis HandoutDocument5 pagesAcute Bronchitis HandoutDianne LegionNo ratings yet
- Blank 5Document23 pagesBlank 5Mariya EudoraNo ratings yet
- Disease: Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument4 pagesDisease: Community Acquired PneumoniaJo Traven AzueloNo ratings yet
- RespdiseasesDocument1 pageRespdiseasesPatricia MedeirosNo ratings yet
- Asthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory FunctionDocument8 pagesRespiratory FunctionMohammad AlkhatibNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 PTDocument12 pagesLec 3 PTBassam AlgalalyNo ratings yet
- BronchitisDocument3 pagesBronchitiscorsaruNo ratings yet
- By DPS StudentsDocument10 pagesBy DPS StudentszarakonhaiNo ratings yet
- Article About CaughDocument8 pagesArticle About CaughNour AlhazzaaNo ratings yet
- Etiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The ListDocument3 pagesEtiology: 1. Compare Lobar Pneumonia With Lobular Pneumonia On The Listselam kalayuNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia PDFDocument2 pagesPneumonia PDFlorreaNo ratings yet
- Ast 2Document17 pagesAst 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Asthm 2Document34 pagesAsthm 2AbuAbdullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Active Cycle of Breathing TechniquesDocument6 pagesActive Cycle of Breathing Techniqueskarl24No ratings yet
- LungsDocument18 pagesLungsMaritess JacintoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System1Document5 pagesRespiratory System1Ombati StephenNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoDocument19 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: (NoKen BaxNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument31 pagesRespiratory Disorderssharlinecatuday08No ratings yet
- Seminar 3 (Recovered)Document134 pagesSeminar 3 (Recovered)saranya amuNo ratings yet
- Bronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandBronchiectasis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- BARAHAMADocument51 pagesBARAHAMAlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Male & Female Reproductive System AssessmentDocument12 pagesMale & Female Reproductive System Assessmentlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cephalovelvic DisproportionDocument9 pagesCephalovelvic Disproportionlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- JAMALULDocument10 pagesJAMALULlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Depression CareDocument16 pagesPostpartum Depression Carelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesPneumothorax-WPS Officelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RLE Checklists (SHORT)Document78 pagesRLE Checklists (SHORT)lea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Infectious DeseasesDocument16 pagesInfectious Deseaseslea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Herniancm-116Document19 pagesHiatal Herniancm-116lea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Kiding PTB TBDocument20 pagesKiding PTB TBlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Buddhism FinaleDocument5 pagesBuddhism Finalelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RLE SKILLS CHECKLIST 2023 - HandwashingDocument2 pagesRLE SKILLS CHECKLIST 2023 - Handwashinglea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cna Making An Occupied BedDocument3 pagesCna Making An Occupied Bedlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Case Study RleDocument25 pagesCase Study Rlelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Tension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - DDocument13 pagesTension Pneumoth Orax: Presented By: Juhara, Amroussie M. BSN 3 - Dlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument2 pagesRandomlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Tamponade Case PresentationDocument3 pagesCardiac Tamponade Case Presentationlea jumawanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3.2 Batu Saluran KemihDocument64 pages3.1.3.2 Batu Saluran Kemihwinda musliraNo ratings yet
- Docslide - Us - Siae Alfo Plus User Manual PDFDocument110 pagesDocslide - Us - Siae Alfo Plus User Manual PDFh2ck3rNo ratings yet
- Signed Off Understanding Culture11 q1 m2 Defining Culture and Politics v3 RemovedDocument24 pagesSigned Off Understanding Culture11 q1 m2 Defining Culture and Politics v3 Removedrhaybien vinluanNo ratings yet
- Treating Straw For Animal FeedingDocument36 pagesTreating Straw For Animal FeedingHybrid BurtonNo ratings yet
- A Project Report ON Recruitment and Selection Process at Big BazarDocument41 pagesA Project Report ON Recruitment and Selection Process at Big BazarGurusaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Law - Insider - Edison Nation Inc - Separation Agreement and Release - Filed - 11 06 2019 - ContractDocument9 pagesLaw - Insider - Edison Nation Inc - Separation Agreement and Release - Filed - 11 06 2019 - ContractNavrita KaurNo ratings yet
- Description: P Ack AgeDocument3 pagesDescription: P Ack AgeAlexandru CioponeaNo ratings yet
- IELTS SPEAKING - WorkDocument3 pagesIELTS SPEAKING - WorkQuỳnh Anh Nguyễn HồNo ratings yet
- Vishwa Patel FIFA 20215041Document10 pagesVishwa Patel FIFA 20215041Vishwa PatelNo ratings yet
- Step 7 Err Code125936644Document37 pagesStep 7 Err Code125936644mohammadNo ratings yet
- Concerto in C Minor - Johann Christian Bach - CelloDocument24 pagesConcerto in C Minor - Johann Christian Bach - CellojosianeNo ratings yet
- 865 F.2d 1260 Unpublished DispositionDocument25 pages865 F.2d 1260 Unpublished DispositionScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Ip RoutingDocument34 pagesIp RoutingericmscNo ratings yet
- Pi Is 0749070421000397Document14 pagesPi Is 0749070421000397Vlady78No ratings yet
- Level 1 - Cambridge Vocab For IELTS, English, Ielts - MemriseDocument3 pagesLevel 1 - Cambridge Vocab For IELTS, English, Ielts - MemrisetunisianouNo ratings yet
- PRM AnswerDocument28 pagesPRM AnswerMinh TrangNo ratings yet
- Derridas Legacies Literature and PhilosophyDocument184 pagesDerridas Legacies Literature and Philosophyinnommable100% (1)
- Ileus - Prof - Bachtiar Murtala (PP) PDFDocument37 pagesIleus - Prof - Bachtiar Murtala (PP) PDFAchmad Rizki AlhasaniNo ratings yet
- Developmental Psychology 101Document9 pagesDevelopmental Psychology 101Ibov VanizNo ratings yet
- Sarah GarzaDocument1 pageSarah Garzasarah_garza67424No ratings yet
- FIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyDocument2 pagesFIS Data Integrity: Mr. Sigurd BjelkarøyAlexMartinNo ratings yet
- Eating Disorder PPT by Shreyasi MittalDocument35 pagesEating Disorder PPT by Shreyasi MittalPrachi gattaniNo ratings yet
- MA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1Document127 pagesMA BRKNMS-3007 284376 156-1 v1avers990% (1)
- My PastorDocument3 pagesMy PastorPastor Emma MukisaNo ratings yet
- Game Theory - Course Outline 2021Document4 pagesGame Theory - Course Outline 2021Mayank RanjanNo ratings yet
- Transfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFDocument1 pageTransfusion Reaction Algorithm V 2 FINAL 2016 11 02 PDFnohe992127No ratings yet
- Module 3 Literature ActivitiesDocument3 pagesModule 3 Literature ActivitiesAlexis Joy P. DangoNo ratings yet
- Le 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaDocument122 pagesLe 3000 Sostanze Controverse Che Neways Non UtilizzaGiorgio FerracinNo ratings yet