Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 viewsSecurity 2
Security 2
Uploaded by
علي الورفليThe document discusses several methods for key management, types of attacks on cryptosystems, and various cryptographic techniques throughout history including the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, polyalphabetic ciphers like the Vigenère cipher, the one-time pad, and transposition methods. It also covers cryptanalysis techniques like frequency analysis that can be used to break certain ciphers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CIS Microsoft 365 Foundations Benchmark v1.5.0Document218 pagesCIS Microsoft 365 Foundations Benchmark v1.5.0md azamNo ratings yet
- SOC Analyst Course Content v3Document16 pagesSOC Analyst Course Content v3Halil YapraklıNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 SWOT Analysis of SHOPEE CompanyDocument4 pagesGROUP 6 SWOT Analysis of SHOPEE CompanyTry Zega100% (1)
- SSL/TLS Under Lock and Key: A Guide to Understanding SSL/TLS CryptographyFrom EverandSSL/TLS Under Lock and Key: A Guide to Understanding SSL/TLS CryptographyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cryptography and Network Security: Xiang-Yang LiDocument43 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Xiang-Yang Linadeem_skNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerDocument39 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerSNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques in Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument46 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques in Cryptography and Network SecurityEswin AngelNo ratings yet
- Cys505 Lecture02Document56 pagesCys505 Lecture02Abdirizak AbokarNo ratings yet
- Ch3 NISDocument37 pagesCh3 NIS410 Sarang JagdaleNo ratings yet
- Vignere Cipher EtcDocument72 pagesVignere Cipher EtcAhsan JameelNo ratings yet
- CNS LabmanualDocument21 pagesCNS LabmanualakiraNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Information and Network SecurityDocument44 pagesCryptography: Information and Network SecurityLeng Hour lengNo ratings yet
- Classical Ciphers: by Mr. Fasee Ullah Cusit PeshawarDocument34 pagesClassical Ciphers: by Mr. Fasee Ullah Cusit PeshawarNewklear HurtedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cryptography: 1.1 PreliminariesDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Cryptography: 1.1 Preliminariesxcekax_net1666No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument53 pagesCryptographySrinivas Likith RavulaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security Pseudo-Random Number: Xiang-Yang LiDocument13 pagesCryptography and Network Security Pseudo-Random Number: Xiang-Yang LishahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document49 pagesLecture 3Opoka John ModiNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: Information System SecurityDocument54 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: Information System SecurityYazanAlomariNo ratings yet
- NW &s Unit-2Document9 pagesNW &s Unit-2Sony ElipeNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument30 pagesClassical Encryption Techniquesextatic11No ratings yet
- Crypto LabDocument17 pagesCrypto LabwaqasbeforwardofficalNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOGRAPHYDocument23 pagesCRYPTOGRAPHYAnnarathna ANo ratings yet
- Traditional Symmetric Key CiphersDocument9 pagesTraditional Symmetric Key CiphersSamsung A30No ratings yet
- COMP202 Complexity of Algorithms Number Theory and Cryptography (See Relevant Sections of Chapter 10 in Goodrich and Tamassia.)Document81 pagesCOMP202 Complexity of Algorithms Number Theory and Cryptography (See Relevant Sections of Chapter 10 in Goodrich and Tamassia.)strokenfilledNo ratings yet
- Describe in Detail The Following Classical Cryptosystems With An Example Shift CipherDocument4 pagesDescribe in Detail The Following Classical Cryptosystems With An Example Shift CipherAneelaMalikNo ratings yet
- Course: Cryptography Code: CS-21123 Branch: M.Tech - IS 1 SemesterDocument28 pagesCourse: Cryptography Code: CS-21123 Branch: M.Tech - IS 1 SemesterManish BarlaNo ratings yet
- Cys535 Lecture02Document56 pagesCys535 Lecture02Waseem LaghariNo ratings yet
- Handout 7 - CryptographyDocument124 pagesHandout 7 - Cryptographyhordes-decker0gNo ratings yet
- Is Lab ManualDocument24 pagesIs Lab ManualAbhilashPadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Lec1 IntroDocument22 pagesLec1 IntroSaikarNo ratings yet
- CITS1003 2 CryptographyDocument51 pagesCITS1003 2 Cryptographytzarin372No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2Rahul BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lab1 PDFDocument12 pagesLab1 PDFKhalil Al-khateebNo ratings yet
- Cryptography - Classical Encryption Techniques Substitution Ciphers - Simplest: ReplaceDocument9 pagesCryptography - Classical Encryption Techniques Substitution Ciphers - Simplest: Replacetharmaraj14No ratings yet
- Cryptology BasicsDocument11 pagesCryptology Basicsbuffet_jobsNo ratings yet
- Course: Cryptography and Network Security Code: CS-16104 Branch: B.Tech - CS 6 SemesterDocument26 pagesCourse: Cryptography and Network Security Code: CS-16104 Branch: B.Tech - CS 6 SemesterManav ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument14 pagesChapter ISreekanth RallapalliNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part-IIIDocument7 pagesUnit-1 - Part-IIIRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Cryptography NotesDocument24 pagesCryptography NotesAsif KoujaganurNo ratings yet
- CSS Lab Manual - PrintDocument45 pagesCSS Lab Manual - PrintXavier TxANo ratings yet
- Worked Example - Scalable Key Cryptography:: The Set of N's As ModuliDocument10 pagesWorked Example - Scalable Key Cryptography:: The Set of N's As ModulighionoiucNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2Jasleen VirdiNo ratings yet
- Cryptology MIS 412Document4 pagesCryptology MIS 412stephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document164 pagesChapter 3Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument10 pages1st LectureAHMED DARAJNo ratings yet
- L 05 Cryptographyandapplications 160825094546Document73 pagesL 05 Cryptographyandapplications 160825094546kavisandeepaniNo ratings yet
- Crypto Techniques VKDocument25 pagesCrypto Techniques VKVikas KNo ratings yet
- Assignment#02.... Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument9 pagesAssignment#02.... Classical Encryption TechniquesAdnan Adnan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Information Security Management - Cryptography: Computer ScienceDocument78 pagesInformation Security Management - Cryptography: Computer ScienceAbhishek Singh DeyolNo ratings yet
- Cryptography PDFDocument42 pagesCryptography PDFShreyaskar Singh100% (2)
- Lecture 9Document86 pagesLecture 9Alhussain DarbiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 E21cseu0021Document5 pagesAssignment 4 E21cseu0021sahilbhanotkNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Symmetric CiphersDocument51 pagesModule 1 Symmetric Ciphersshazia sulthanaNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument36 pagesClassical Encryption TechniquesShashank VenkatNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security MsmeDocument27 pagesCryptography and Network Security Msmesanthosh n prabhuNo ratings yet
- 1 CryptoDocument83 pages1 Cryptomhming1103No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document47 pagesLecture 2Talha MehmoodNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Cryptography ch02Document38 pagesWilliam Stallings Cryptography ch02Suganya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security: Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture Slides by Lawrie BrownDocument39 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture Slides by Lawrie BrownhussainbedsNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Cryptography: Fundamental concepts of Encryption, Milestones, Mega-Trends and sustainable Change in regard to Secret Communications and its NomenclaturaFrom EverandTransformation of Cryptography: Fundamental concepts of Encryption, Milestones, Mega-Trends and sustainable Change in regard to Secret Communications and its NomenclaturaNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNAFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNANo ratings yet
- 300+ (UPDATED) CISSP MCQs and Answers (PDF)Document25 pages300+ (UPDATED) CISSP MCQs and Answers (PDF)Pierre-Marie Diambra0% (1)
- Data Embassy Correction 1Document2 pagesData Embassy Correction 1Donald bhai ModiNo ratings yet
- TIB SpotWebPlay 4.0.2 InstallationManualDocument101 pagesTIB SpotWebPlay 4.0.2 InstallationManualsrgaurNo ratings yet
- The Permutation CipherDocument19 pagesThe Permutation CipherAman HandaNo ratings yet
- Apple Platform Security GuideDocument196 pagesApple Platform Security Guideazm9sNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6Document3 pagesWebinar 6Mark Israel SantosNo ratings yet
- Topics To LearnDocument26 pagesTopics To LearnVidhya MohananNo ratings yet
- Unified Endpoint Management and Security 2022Document5 pagesUnified Endpoint Management and Security 2022Mathieu LEROYNo ratings yet
- Christopher Whyte - Information Warfare in The Age of Cyber ConflictDocument271 pagesChristopher Whyte - Information Warfare in The Age of Cyber ConflictyuryumaoNo ratings yet
- Nis-1 5Document5 pagesNis-1 5comedy loverNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Technical Reference Guide For CMMC v2 - (Public Preview) - 20220304Document280 pagesMicrosoft Technical Reference Guide For CMMC v2 - (Public Preview) - 20220304Malik100% (1)
- Sqli InjectionDocument7 pagesSqli Injectionprem_kumar_kushawahaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Baseline Requirements PolicyDocument3 pagesBluetooth Baseline Requirements PolicyMohamed SihanNo ratings yet
- Adapting To The Cyber Domain: Comparing US and UK Institutional, Legal, and Policy InnovationsDocument40 pagesAdapting To The Cyber Domain: Comparing US and UK Institutional, Legal, and Policy InnovationsHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- How Bitcoin Achieves DecentralizationDocument77 pagesHow Bitcoin Achieves DecentralizationRithvik RajaniNo ratings yet
- Consent Statement - Supplier Accreditation 2019Document4 pagesConsent Statement - Supplier Accreditation 2019Emmanuel Joseph AnggonNo ratings yet
- The Golden Tax Department and Emergence of Goldenspy MalwareDocument26 pagesThe Golden Tax Department and Emergence of Goldenspy MalwarerodrigoduocNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Maze of Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics - Anything ConnectedDocument23 pagesNavigating The Maze of Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics - Anything ConnectedBhuNo ratings yet
- Scientific Paper Alexandru TrifuDocument6 pagesScientific Paper Alexandru TrifuAlexandru TrifuNo ratings yet
- CIS Palo Alto Firewall 10 Benchmark v1.1.0Document210 pagesCIS Palo Alto Firewall 10 Benchmark v1.1.0awaissadiq45No ratings yet
- Request For Proposal Intranet SharePoint Project 1Document40 pagesRequest For Proposal Intranet SharePoint Project 1Rodgers MoondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document31 pagesChapter 3Nithya NairNo ratings yet
- Comp3632 ProtocolsDocument41 pagesComp3632 ProtocolsKavya BalajiNo ratings yet
- HqpassDocument314 pagesHqpassPsic MNo ratings yet
- CSS322Y09S2E01 Midterm Exam AnswersDocument16 pagesCSS322Y09S2E01 Midterm Exam AnswersHassanein Al-hadadNo ratings yet
- Malware AnalysisDocument15 pagesMalware AnalysisJosue OuattaraNo ratings yet
Security 2
Security 2
Uploaded by
علي الورفلي0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views20 pagesThe document discusses several methods for key management, types of attacks on cryptosystems, and various cryptographic techniques throughout history including the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, polyalphabetic ciphers like the Vigenère cipher, the one-time pad, and transposition methods. It also covers cryptanalysis techniques like frequency analysis that can be used to break certain ciphers.
Original Description:
Original Title
Security2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several methods for key management, types of attacks on cryptosystems, and various cryptographic techniques throughout history including the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, polyalphabetic ciphers like the Vigenère cipher, the one-time pad, and transposition methods. It also covers cryptanalysis techniques like frequency analysis that can be used to break certain ciphers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views20 pagesSecurity 2
Security 2
Uploaded by
علي الورفليThe document discusses several methods for key management, types of attacks on cryptosystems, and various cryptographic techniques throughout history including the Caesar cipher, Playfair cipher, Hill cipher, polyalphabetic ciphers like the Vigenère cipher, the one-time pad, and transposition methods. It also covers cryptanalysis techniques like frequency analysis that can be used to break certain ciphers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 20
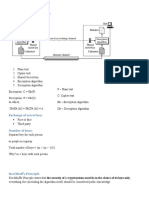
Key Management
! Using secret channel
! Encrypt the key
! Third trusted party
! The sender and the receiver generate key
" The key must be same
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Attacks
! Recover the message
! Recover the secret key
" Thus also the message
! Thus the number of keys possible must be
large!
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Steganography
! Conceal the existence of message
" Character marking
" Invisible ink
" Pin punctures
" Typewriter correction ribbon
! Cryptography renders message
unintelligible!
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Contemporary Equiv.
! Least significant bits of picture frames
" 2048x3072 pixels with 24-bits RGB info
" Able to hide 2.3M message
! Drawbacks
" Large overhead
" Virtually useless if system is known
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Caesar Cipher
! Replace each letter of message by a letter a
fixed distance away (use the 3rd letter on)
! Reputedly used by Julius Caesar
! Example:
L FDPH L VDZ L FRQTXHUHG
I CAME I SAW I CONGUERED
" The mapping is
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
DEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZABC
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Mathematical Model
! Description
" Encryption E(k) : i → i + k mod 26
" Decryption D(k) : i → i - k mod 26
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Cryptanalysis: Caesar Cipher
! Key space: 26
" Exhaustive key search
! Example
" GDUCUGQFRMPCNJYACJCRRCPQ
HEVDVHRGSNQDOKZBDKDSSDQR
" Plaintext:
JGXFXJTIUPSFQMBDFMFUUFSTKHYGYKUJVGRNCEGNG
VVGTU
" Ciphertext:
LIZHZLVKWRUHSODFHOHWWHUVMJAIAMWXSVITPEGI
PIXXIVW
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Character Frequencies
! In most languages letters are not equally common
" in English e is by far the most common letter
! Have tables of single, double & triple letter
frequencies
! Use these tables to compare with letter frequencies
in ciphertext,
" a monoalphabetic substitution does not change relative
letter frequencies
" do need a moderate amount of ciphertext (100+ letters)
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Letter Frequency Analysis
! Single Letter
" A,B,C,D,E,…..
! Double Letter
" TH,HE,IN,ER,RE,ON,AN,EN,….
! Triple Letter
" THE,AND,TIO,ATI,FOR,THA,TER,RES,…
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Modular Arithmetic Cipher
! Use a more complex equation to calculate
the ciphertext letter for each plaintext letter
! E(a,b) : i →a∗i + b mod 26
" Need gcd(a,26) = 1
" Otherwise, not reversible
" So, a≠2, 13, 26
" Caesar cipher: a=1
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Cryptanalysis
! Key space:23*26
" Brute force search
! Useletter frequency counts to guess a
couple of possible letter mappings
" frequency pattern not produced just by a shift
" use these mappings to solve 2 simultaneous
equations to derive above parameters
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Playfair Cipher
Used in WWI and WWII
s i/j m p l
e a b c d
f g h k n
o q r t u
v w x y z
Key: simple
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Playfair Cipher
! Use filler letter to separate repeated letters
! Encrypt two letters together
" Same row– followed letters
# ac--bd
" Same column– letters under
# qw--wi
" Otherwise—square’s corner at same row
# ar--bq
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Analysis
! Size of diagrams: 25!
! Difficult using frequency analysis
" But it still reveals the frequency information
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Hill Cipher
! Encryption
" Assign each letter an index
" C=KP mod 26
" Matrix K is the key
! Decryption
" P=K-1C mod 26
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Analysis
! Difficult
to use frequency analysis
! But vulnerable to known-plaintext attack
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Polyalphabetic Substitution
! Usemore than one substitution alphabet
! Makes cryptanalysis harder
" since have more alphabets to guess
" and flattens frequency distribution
# same plaintext letter gets replaced by several
ciphertext letter, depending on which alphabet is
used
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Vigenère Cipher
! Basically multiple Caesar ciphers
! key is multiple letters long
" K = k1 k2 ... kd
" ith letter specifies ith alphabet to use
" use each alphabet in turn, repeating from start after d
letters in message
! Plaintext THISPROCESSCANALSOBEEXPRESSED
Keyword CIPHERCIPHERCIPHERCIPHERCIPHE
Ciphertext VPXZTIQKTZWTCVPSWFDMTETIGAHLH
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
One-time Pad
! GilbertVernam (AT&T)
! Encryption
" C=P⊕K
! Decryption
" P=C⊕K
! Difficulty: key K is as long as message P
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
Transposition Methods
! Permutation of plaintext
! Example
" Write in a square in row, then read in column
order specified by the key
! Enhance: double or triple transposition
" Can reapply the encryption on ciphertext
CS595-Cryptography and Network Security
You might also like
- CIS Microsoft 365 Foundations Benchmark v1.5.0Document218 pagesCIS Microsoft 365 Foundations Benchmark v1.5.0md azamNo ratings yet
- SOC Analyst Course Content v3Document16 pagesSOC Analyst Course Content v3Halil YapraklıNo ratings yet
- GROUP 6 SWOT Analysis of SHOPEE CompanyDocument4 pagesGROUP 6 SWOT Analysis of SHOPEE CompanyTry Zega100% (1)
- SSL/TLS Under Lock and Key: A Guide to Understanding SSL/TLS CryptographyFrom EverandSSL/TLS Under Lock and Key: A Guide to Understanding SSL/TLS CryptographyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Cryptography and Network Security: Xiang-Yang LiDocument43 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Xiang-Yang Linadeem_skNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerDocument39 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: M. Odeo LecturerSNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques in Cryptography and Network SecurityDocument46 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques in Cryptography and Network SecurityEswin AngelNo ratings yet
- Cys505 Lecture02Document56 pagesCys505 Lecture02Abdirizak AbokarNo ratings yet
- Ch3 NISDocument37 pagesCh3 NIS410 Sarang JagdaleNo ratings yet
- Vignere Cipher EtcDocument72 pagesVignere Cipher EtcAhsan JameelNo ratings yet
- CNS LabmanualDocument21 pagesCNS LabmanualakiraNo ratings yet
- Cryptography: Information and Network SecurityDocument44 pagesCryptography: Information and Network SecurityLeng Hour lengNo ratings yet
- Classical Ciphers: by Mr. Fasee Ullah Cusit PeshawarDocument34 pagesClassical Ciphers: by Mr. Fasee Ullah Cusit PeshawarNewklear HurtedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cryptography: 1.1 PreliminariesDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Cryptography: 1.1 Preliminariesxcekax_net1666No ratings yet
- CryptographyDocument53 pagesCryptographySrinivas Likith RavulaNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security Pseudo-Random Number: Xiang-Yang LiDocument13 pagesCryptography and Network Security Pseudo-Random Number: Xiang-Yang LishahaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document49 pagesLecture 3Opoka John ModiNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption Techniques: Information System SecurityDocument54 pagesClassical Encryption Techniques: Information System SecurityYazanAlomariNo ratings yet
- NW &s Unit-2Document9 pagesNW &s Unit-2Sony ElipeNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument30 pagesClassical Encryption Techniquesextatic11No ratings yet
- Crypto LabDocument17 pagesCrypto LabwaqasbeforwardofficalNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOGRAPHYDocument23 pagesCRYPTOGRAPHYAnnarathna ANo ratings yet
- Traditional Symmetric Key CiphersDocument9 pagesTraditional Symmetric Key CiphersSamsung A30No ratings yet
- COMP202 Complexity of Algorithms Number Theory and Cryptography (See Relevant Sections of Chapter 10 in Goodrich and Tamassia.)Document81 pagesCOMP202 Complexity of Algorithms Number Theory and Cryptography (See Relevant Sections of Chapter 10 in Goodrich and Tamassia.)strokenfilledNo ratings yet
- Describe in Detail The Following Classical Cryptosystems With An Example Shift CipherDocument4 pagesDescribe in Detail The Following Classical Cryptosystems With An Example Shift CipherAneelaMalikNo ratings yet
- Course: Cryptography Code: CS-21123 Branch: M.Tech - IS 1 SemesterDocument28 pagesCourse: Cryptography Code: CS-21123 Branch: M.Tech - IS 1 SemesterManish BarlaNo ratings yet
- Cys535 Lecture02Document56 pagesCys535 Lecture02Waseem LaghariNo ratings yet
- Handout 7 - CryptographyDocument124 pagesHandout 7 - Cryptographyhordes-decker0gNo ratings yet
- Is Lab ManualDocument24 pagesIs Lab ManualAbhilashPadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Lec1 IntroDocument22 pagesLec1 IntroSaikarNo ratings yet
- CITS1003 2 CryptographyDocument51 pagesCITS1003 2 Cryptographytzarin372No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document39 pagesLecture 2Rahul BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Lab1 PDFDocument12 pagesLab1 PDFKhalil Al-khateebNo ratings yet
- Cryptography - Classical Encryption Techniques Substitution Ciphers - Simplest: ReplaceDocument9 pagesCryptography - Classical Encryption Techniques Substitution Ciphers - Simplest: Replacetharmaraj14No ratings yet
- Cryptology BasicsDocument11 pagesCryptology Basicsbuffet_jobsNo ratings yet
- Course: Cryptography and Network Security Code: CS-16104 Branch: B.Tech - CS 6 SemesterDocument26 pagesCourse: Cryptography and Network Security Code: CS-16104 Branch: B.Tech - CS 6 SemesterManav ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument14 pagesChapter ISreekanth RallapalliNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 - Part-IIIDocument7 pagesUnit-1 - Part-IIIRam Prasad Reddy SadiNo ratings yet
- Cryptography NotesDocument24 pagesCryptography NotesAsif KoujaganurNo ratings yet
- CSS Lab Manual - PrintDocument45 pagesCSS Lab Manual - PrintXavier TxANo ratings yet
- Worked Example - Scalable Key Cryptography:: The Set of N's As ModuliDocument10 pagesWorked Example - Scalable Key Cryptography:: The Set of N's As ModulighionoiucNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document33 pagesLecture 2Jasleen VirdiNo ratings yet
- Cryptology MIS 412Document4 pagesCryptology MIS 412stephNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document164 pagesChapter 3Ahmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- 1st LectureDocument10 pages1st LectureAHMED DARAJNo ratings yet
- L 05 Cryptographyandapplications 160825094546Document73 pagesL 05 Cryptographyandapplications 160825094546kavisandeepaniNo ratings yet
- Crypto Techniques VKDocument25 pagesCrypto Techniques VKVikas KNo ratings yet
- Assignment#02.... Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument9 pagesAssignment#02.... Classical Encryption TechniquesAdnan Adnan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Information Security Management - Cryptography: Computer ScienceDocument78 pagesInformation Security Management - Cryptography: Computer ScienceAbhishek Singh DeyolNo ratings yet
- Cryptography PDFDocument42 pagesCryptography PDFShreyaskar Singh100% (2)
- Lecture 9Document86 pagesLecture 9Alhussain DarbiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 E21cseu0021Document5 pagesAssignment 4 E21cseu0021sahilbhanotkNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Symmetric CiphersDocument51 pagesModule 1 Symmetric Ciphersshazia sulthanaNo ratings yet
- Classical Encryption TechniquesDocument36 pagesClassical Encryption TechniquesShashank VenkatNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security MsmeDocument27 pagesCryptography and Network Security Msmesanthosh n prabhuNo ratings yet
- 1 CryptoDocument83 pages1 Cryptomhming1103No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document47 pagesLecture 2Talha MehmoodNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Cryptography ch02Document38 pagesWilliam Stallings Cryptography ch02Suganya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Cryptography and Network Security: Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture Slides by Lawrie BrownDocument39 pagesCryptography and Network Security: Third Edition by William Stallings Lecture Slides by Lawrie BrownhussainbedsNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Cryptography: Fundamental concepts of Encryption, Milestones, Mega-Trends and sustainable Change in regard to Secret Communications and its NomenclaturaFrom EverandTransformation of Cryptography: Fundamental concepts of Encryption, Milestones, Mega-Trends and sustainable Change in regard to Secret Communications and its NomenclaturaNo ratings yet
- New Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNAFrom EverandNew Frontiers in Cryptography: Quantum, Blockchain, Lightweight, Chaotic and DNANo ratings yet
- 300+ (UPDATED) CISSP MCQs and Answers (PDF)Document25 pages300+ (UPDATED) CISSP MCQs and Answers (PDF)Pierre-Marie Diambra0% (1)
- Data Embassy Correction 1Document2 pagesData Embassy Correction 1Donald bhai ModiNo ratings yet
- TIB SpotWebPlay 4.0.2 InstallationManualDocument101 pagesTIB SpotWebPlay 4.0.2 InstallationManualsrgaurNo ratings yet
- The Permutation CipherDocument19 pagesThe Permutation CipherAman HandaNo ratings yet
- Apple Platform Security GuideDocument196 pagesApple Platform Security Guideazm9sNo ratings yet
- Webinar 6Document3 pagesWebinar 6Mark Israel SantosNo ratings yet
- Topics To LearnDocument26 pagesTopics To LearnVidhya MohananNo ratings yet
- Unified Endpoint Management and Security 2022Document5 pagesUnified Endpoint Management and Security 2022Mathieu LEROYNo ratings yet
- Christopher Whyte - Information Warfare in The Age of Cyber ConflictDocument271 pagesChristopher Whyte - Information Warfare in The Age of Cyber ConflictyuryumaoNo ratings yet
- Nis-1 5Document5 pagesNis-1 5comedy loverNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Technical Reference Guide For CMMC v2 - (Public Preview) - 20220304Document280 pagesMicrosoft Technical Reference Guide For CMMC v2 - (Public Preview) - 20220304Malik100% (1)
- Sqli InjectionDocument7 pagesSqli Injectionprem_kumar_kushawahaNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Baseline Requirements PolicyDocument3 pagesBluetooth Baseline Requirements PolicyMohamed SihanNo ratings yet
- Adapting To The Cyber Domain: Comparing US and UK Institutional, Legal, and Policy InnovationsDocument40 pagesAdapting To The Cyber Domain: Comparing US and UK Institutional, Legal, and Policy InnovationsHoover InstitutionNo ratings yet
- How Bitcoin Achieves DecentralizationDocument77 pagesHow Bitcoin Achieves DecentralizationRithvik RajaniNo ratings yet
- Consent Statement - Supplier Accreditation 2019Document4 pagesConsent Statement - Supplier Accreditation 2019Emmanuel Joseph AnggonNo ratings yet
- The Golden Tax Department and Emergence of Goldenspy MalwareDocument26 pagesThe Golden Tax Department and Emergence of Goldenspy MalwarerodrigoduocNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Maze of Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics - Anything ConnectedDocument23 pagesNavigating The Maze of Cyber Security Intelligence and Analytics - Anything ConnectedBhuNo ratings yet
- Scientific Paper Alexandru TrifuDocument6 pagesScientific Paper Alexandru TrifuAlexandru TrifuNo ratings yet
- CIS Palo Alto Firewall 10 Benchmark v1.1.0Document210 pagesCIS Palo Alto Firewall 10 Benchmark v1.1.0awaissadiq45No ratings yet
- Request For Proposal Intranet SharePoint Project 1Document40 pagesRequest For Proposal Intranet SharePoint Project 1Rodgers MoondeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document31 pagesChapter 3Nithya NairNo ratings yet
- Comp3632 ProtocolsDocument41 pagesComp3632 ProtocolsKavya BalajiNo ratings yet
- HqpassDocument314 pagesHqpassPsic MNo ratings yet
- CSS322Y09S2E01 Midterm Exam AnswersDocument16 pagesCSS322Y09S2E01 Midterm Exam AnswersHassanein Al-hadadNo ratings yet
- Malware AnalysisDocument15 pagesMalware AnalysisJosue OuattaraNo ratings yet