Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Uploaded by
AnjiCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ptolus - Doctrine of Ghul PDFDocument31 pagesPtolus - Doctrine of Ghul PDFAmbre100% (1)
- Kan Essentials Formula GuideDocument60 pagesKan Essentials Formula GuideWinnie ChanNo ratings yet
- 12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesDocument13 pages12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesAnonymous yTdBi7100% (1)
- Aminat Siwes ReportDocument38 pagesAminat Siwes ReportPec Uliar86% (7)
- DkaDocument32 pagesDkanatheNo ratings yet
- Cardio Renal Hyperkalemia - EnglishDocument2 pagesCardio Renal Hyperkalemia - EnglishshaheershayanqaziNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalaemia Algorithm March 2014Document1 pageHyperkalaemia Algorithm March 2014ZosmasNo ratings yet
- Clin Management Dka or Hhs Web AlgorithmDocument6 pagesClin Management Dka or Hhs Web AlgorithmChoirotun HisanNo ratings yet
- Super Nis Summary 2017-18Document1 pageSuper Nis Summary 2017-18api-286560136No ratings yet
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Quick Reference Guide For Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument8 pagesManagement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Quick Reference Guide For Healthcare ProfessionalsAqilah SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Poster SetDocument5 pagesIV Fluid Poster SetAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests: Physical Examination:: Past Medical HistoryDocument1 pageLaboratory Tests: Physical Examination:: Past Medical HistoryJaymart BieNo ratings yet
- ATI MedicationsDocument1 pageATI MedicationsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- Genato - BSP3A - Case Study On Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument4 pagesGenato - BSP3A - Case Study On Alzheimer's DiseaseCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway Guidelines: Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesClinical Pathway Guidelines: Chronic Kidney DiseaseJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNo ratings yet
- Preop+++Goal Anaesthesia Record FormsDocument5 pagesPreop+++Goal Anaesthesia Record FormsShimelis AssefaNo ratings yet
- QR Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5th Edition) PDFDocument8 pagesQR Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5th Edition) PDFKai Xin100% (1)
- EsmoMetastatic Colorectal CancerDocument41 pagesEsmoMetastatic Colorectal CancerrafatrujNo ratings yet
- ATI A Pharm MedsDocument1 pageATI A Pharm MedsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument31 pagesCurriculum Vitaetrisya arthaputriNo ratings yet
- Guideline HHS or Honk in AdultDocument7 pagesGuideline HHS or Honk in AdultCarolina NauNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument5 pagesBlood ComponentsoxalateNo ratings yet
- Hyperchloremia PDFDocument2 pagesHyperchloremia PDFChezer KiethNo ratings yet
- HealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471729 Livewell Platinum Health Package - MaleDocument1 pageHealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471729 Livewell Platinum Health Package - MaleDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- Malepack PDFDocument1 pageMalepack PDFDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- Icu Journal ClubDocument19 pagesIcu Journal Clubapi-649066372No ratings yet
- 220 WHO Guidance and Specifics On Blood Pressure DevicesDocument18 pages220 WHO Guidance and Specifics On Blood Pressure DevicesImcu 6No ratings yet
- Major and Minor SurgeryDocument2 pagesMajor and Minor SurgerydelarakrishnafaithpNo ratings yet
- Dka AlgorithmDocument1 pageDka AlgorithmAbhinav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- AKI Pathway (Nottingham University Hospitals April 2015)Document3 pagesAKI Pathway (Nottingham University Hospitals April 2015)Yadi SupriyadiNo ratings yet
- CC2 TransDocument12 pagesCC2 TransAnathalea ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis SyndromesDocument1 pageVasculitis SyndromesamanNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFDocument20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFSurgery CSC1No ratings yet
- Tams NCP and DrugDocument5 pagesTams NCP and DrugNicholas Xavier VenturaNo ratings yet
- A Case of HypercalcaemiaDocument20 pagesA Case of HypercalcaemiasnipergirlNo ratings yet
- Comment File Hematolog y (Updated)Document7 pagesComment File Hematolog y (Updated)Sakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- No More Nafld: The Nomenclature Is ChangingDocument4 pagesNo More Nafld: The Nomenclature Is ChanginghsiNo ratings yet
- Clcium GluconateDocument2 pagesClcium GluconatekarenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Imei UrinanalysisDocument3 pagesImei UrinanalysisRohitNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock PathoDocument1 pageCardiogenic Shock PathoCommunity BNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury PosterDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Postermmbire@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Hyper Kale Mia HPWDocument1 pageHyper Kale Mia HPWfredericktingsyNo ratings yet
- ( Û ) Questionnaire Hospital InformationDocument5 pages( Û ) Questionnaire Hospital InformationsjeloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway For Hyperglycemic Crisis For AdultsDocument2 pagesClinical Pathway For Hyperglycemic Crisis For AdultserikaNo ratings yet
- SAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015Document1 pageSAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015Joana woodsNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry BrochureDocument20 pagesClinical Chemistry Brochureyogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- PBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Document2 pagesPBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Ricardo Antonio Rivas SánchezNo ratings yet
- HealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471543 Livewell Health Package - BronzeDocument1 pageHealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471543 Livewell Health Package - BronzeDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- BookAppointmentTest Bronze. 1569462516.854957 PDFDocument1 pageBookAppointmentTest Bronze. 1569462516.854957 PDFಬಸವರಾಜ ಎಂ ಜಮಖಂಡಿNo ratings yet
- ATI A Pharm MedsDocument1 pageATI A Pharm MedsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- BookAppointmentTest CareV2 Silver. 1579881536.8462949Document1 pageBookAppointmentTest CareV2 Silver. 1579881536.8462949ankitNo ratings yet
- Anemia Care PathwayDocument2 pagesAnemia Care PathwayArina FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Intial Evaluation On Arrival To ER For All PatientsDocument1 pageTable 1: Intial Evaluation On Arrival To ER For All PatientsHetoshima KeiNo ratings yet
- Pre Anesthetic EvaluationDocument1 pagePre Anesthetic EvaluationАндрій ДанильцівNo ratings yet
- QC-7 Hematology Westgard Rules in Good Performance LaboratoryDocument38 pagesQC-7 Hematology Westgard Rules in Good Performance LaboratoryWita100% (1)
- Ped501 Hypernatremia NewDocument7 pagesPed501 Hypernatremia NewMisoo KimNo ratings yet
- Table 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDocument1 pageTable 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Medical Check Up MatrixDocument1 pageMedical Check Up Matrixgardamas tunggal primaNo ratings yet
- TransfusionDocument3 pagesTransfusionjulissand10No ratings yet
- Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineSahera Nurhidayah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Week 3 HospDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Hospapi-507319784No ratings yet
- Expanding The Therapeutic Window For Acute Ischemic Stroke:: New Agents, New ApproachesDocument29 pagesExpanding The Therapeutic Window For Acute Ischemic Stroke:: New Agents, New ApproachesDr. RajibNo ratings yet
- HistorDocument2 pagesHistorbesoNo ratings yet
- Artic - NEJM - Tricomicosis Axilaris - 2022Document1 pageArtic - NEJM - Tricomicosis Axilaris - 2022Michelle OlveraNo ratings yet
- ICRPDocument67 pagesICRPGiovanni MateusNo ratings yet
- Ai Laboratory and Boarstud SectionDocument63 pagesAi Laboratory and Boarstud SectionrsuertoNo ratings yet
- Rawat Jalan ProsesDocument304 pagesRawat Jalan ProseshermanNo ratings yet
- Introductie Tot de VeevoedingDocument18 pagesIntroductie Tot de VeevoedingRayen Sheombar SingNo ratings yet
- BS - 6180 - 1995 - Barriers in and About BuildingsDocument36 pagesBS - 6180 - 1995 - Barriers in and About BuildingsjuanaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths by Vaccination StatusDocument18 pagesCOVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths by Vaccination StatusMike ParadisNo ratings yet
- Hospital Staffing PlanDocument1 pageHospital Staffing PlanMilin Anik'sNo ratings yet
- TFM 4Document8 pagesTFM 4Miguel de VivarNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 5 6 Vulnerability and Sector of Society Vulnerable To DisasterDocument3 pagesQ3 Lesson 5 6 Vulnerability and Sector of Society Vulnerable To DisasterShanayaNo ratings yet
- GDJES-NDEP-Accomplishment-Report-april 2024 .Document4 pagesGDJES-NDEP-Accomplishment-Report-april 2024 .Mark BaniagaNo ratings yet
- (GK - 01) Question Paper Limited Departmental Competitive Examination - 2006 For The Post of Chargeman-Gr - Ii (T) & (NT)Document5 pages(GK - 01) Question Paper Limited Departmental Competitive Examination - 2006 For The Post of Chargeman-Gr - Ii (T) & (NT)murthy gNo ratings yet
- Critical Review of School Health and Nutrition (SHN) Program To Achieving Advance Preventive Healthcare For Children in PunjabDocument15 pagesCritical Review of School Health and Nutrition (SHN) Program To Achieving Advance Preventive Healthcare For Children in PunjabJournal of Public Policy PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsDocument7 pagesDrug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- Broken Rib SymptomsDocument12 pagesBroken Rib Symptomsneleh grayNo ratings yet
- Eriksons Eigth Stages of Personality DevelopmentDocument1 pageEriksons Eigth Stages of Personality DevelopmentKristinne Claire Renol ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3b. RhinoplastyDocument122 pages3b. RhinoplastyKamal Saud100% (2)
- Chapter 4. 101. Week 7Document8 pagesChapter 4. 101. Week 7RAGOS Jeffrey Miguel P.No ratings yet
- Determining Training WorkloadsDocument15 pagesDetermining Training WorkloadsAriw AmpatNo ratings yet
- Research Methods NotesDocument8 pagesResearch Methods Notessxb3zk1No ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penggunaan Minyak Goreng Terhadap Kualitas Ayam GorengDocument14 pagesPengaruh Penggunaan Minyak Goreng Terhadap Kualitas Ayam GorengqonitahazzaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessDocument8 pagesTeaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessFernando PintoNo ratings yet
- Sma " Nasional" Malang: Ulangan Tengah Semester GanjilDocument4 pagesSma " Nasional" Malang: Ulangan Tengah Semester GanjilAqmarina Dianova BaharyNo ratings yet
- Self RegulationDocument2 pagesSelf RegulationDaniel Bernal0% (1)
- @anesthesia - Books 2014 Regional Anaesthesia - A Pocket GuideDocument168 pages@anesthesia - Books 2014 Regional Anaesthesia - A Pocket Guideraphael boechatNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways To Build Confidence in A Child With ADD/ADHDDocument3 pages5 Ways To Build Confidence in A Child With ADD/ADHDwildflowerNo ratings yet
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Uploaded by
AnjiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Management Algorithm For Adult With Hyperkalemia
Uploaded by
AnjiCopyright:
Available Formats
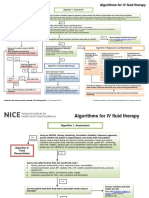
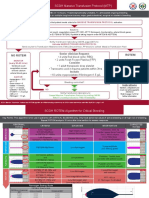
History Consistent with
Management Algorithm for Adults •
Hyperkalemia?
History of DM, CHF, CKD or No
Repeat K Testing
Consider spurious
with Hyperkalemia
and pseudo-HK
• Labs showing acidosis or elevated Cr (signs
of renal failure) or
(K> 5.5 mEq/L)
• Patient on medications known to cause
hyperkalemia
Yes No
Yes K>5.5mEq/L? EXIT
*All disposition and treatment recommendations should account for local standards of care and
should not supersede the clinical judgement of the treating physician.
New ECG Changes?
Recommended Doses for Acute Care Settings: • Arrhythmia (bradycardia, non-sinus
tachycardia, junctional rhythm)
Calcium Gluconate: 1 gram; Calcium Chloride: 1 ampule Consider Emergent Yes
Insulin (regular)/Dextrose: Hemodialysis • Prolonged Intervals (PR or QRS)
5 units (insulin naïve or CKD) ;10 units (not naïve)/ D50 1- 2 amps.
Repeat POC glucose in 30 mins & q1hr • Diminished P Wave amplitude ST or T
Albuterol: 10mg Nebulizer over 15mins
Wave Changes (elevation, depression,
Loop Diuretics: Adjust for GFR peaked T)
Bumetanide Dose: 1-2 mg IV once.
Furosemide Dose: 20-80 mg IV once.
Torsemide Dose: 10-40 mg IV once.
No
Oral binders:
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate 10-30 gm,
Patiromer 8.4g - 25.2g
SPS sodium polystyrene sulfonate 30 g Calcium Dosing
No • Give 1 gm IV push Calcium
Selection of therapeutic agents should account for safety profile,
availability, route of administration, tolerability, and patient clinical status. Yes Re-assessment
Gluconate
• Repeat ECG in 5 minutes.
K<6mEq/L? • If ECG changes persist, may repeat
calcium gluconate x 2
Treatment Options‡
Disposition K < 6 - Consider insulin/dextrose + albuterol ± oral
binders ± furosemide/fluids*.
Admit:
1. HK with unstable vitals K: 6-6.5 – Administer insulin/dextrose + albuterol ±
2. New onset HK furosemide/fluids*. Consider oral binders ± urgent
hemodialysis.
Discharge (consider): After 2-4 hrs
1. Chronic HK with K > 6.5 – Administer insulin/dextrose + albuterol ±
• stable vitals and ECG & furosemide/fluids*. Consider oral binders. Arrange
• K eliminated with binder or diuretics & for immediate hemodialysis.
• close follow up &
• Risk/benefit, shared decision of dc ‡ Consider bicarbonate for metabolic acidosis
discussed *Loop diuretics: use when eGFR≥45; Fluids: when eGFR≥45
and patient does not have CHF.
HK – hyperkalemia; K – serum potassium; DM – diabetes mellitus; CHF – congestive heart failure; CKD – chronic kidney disease; Cr – creatinine; ECG – electrocardiogram; IV – intravenous; dc – discharge;
You might also like
- Ptolus - Doctrine of Ghul PDFDocument31 pagesPtolus - Doctrine of Ghul PDFAmbre100% (1)
- Kan Essentials Formula GuideDocument60 pagesKan Essentials Formula GuideWinnie ChanNo ratings yet
- 12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesDocument13 pages12a Diabetic Emergencies DKA Case StudiesAnonymous yTdBi7100% (1)
- Aminat Siwes ReportDocument38 pagesAminat Siwes ReportPec Uliar86% (7)
- DkaDocument32 pagesDkanatheNo ratings yet
- Cardio Renal Hyperkalemia - EnglishDocument2 pagesCardio Renal Hyperkalemia - EnglishshaheershayanqaziNo ratings yet
- Hyperkalaemia Algorithm March 2014Document1 pageHyperkalaemia Algorithm March 2014ZosmasNo ratings yet
- Clin Management Dka or Hhs Web AlgorithmDocument6 pagesClin Management Dka or Hhs Web AlgorithmChoirotun HisanNo ratings yet
- Super Nis Summary 2017-18Document1 pageSuper Nis Summary 2017-18api-286560136No ratings yet
- Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Quick Reference Guide For Healthcare ProfessionalsDocument8 pagesManagement of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Quick Reference Guide For Healthcare ProfessionalsAqilah SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- IV Fluid Poster SetDocument5 pagesIV Fluid Poster SetAmisha VastaniNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Tests: Physical Examination:: Past Medical HistoryDocument1 pageLaboratory Tests: Physical Examination:: Past Medical HistoryJaymart BieNo ratings yet
- ATI MedicationsDocument1 pageATI MedicationsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- Genato - BSP3A - Case Study On Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument4 pagesGenato - BSP3A - Case Study On Alzheimer's DiseaseCHARLES RONALD GENATONo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway Guidelines: Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 pagesClinical Pathway Guidelines: Chronic Kidney DiseaseJohnBedaLatawanMalecdanNo ratings yet
- Preop+++Goal Anaesthesia Record FormsDocument5 pagesPreop+++Goal Anaesthesia Record FormsShimelis AssefaNo ratings yet
- QR Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5th Edition) PDFDocument8 pagesQR Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (5th Edition) PDFKai Xin100% (1)
- EsmoMetastatic Colorectal CancerDocument41 pagesEsmoMetastatic Colorectal CancerrafatrujNo ratings yet
- ATI A Pharm MedsDocument1 pageATI A Pharm MedsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument31 pagesCurriculum Vitaetrisya arthaputriNo ratings yet
- Guideline HHS or Honk in AdultDocument7 pagesGuideline HHS or Honk in AdultCarolina NauNo ratings yet
- Blood ComponentsDocument5 pagesBlood ComponentsoxalateNo ratings yet
- Hyperchloremia PDFDocument2 pagesHyperchloremia PDFChezer KiethNo ratings yet
- HealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471729 Livewell Platinum Health Package - MaleDocument1 pageHealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471729 Livewell Platinum Health Package - MaleDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- Malepack PDFDocument1 pageMalepack PDFDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- Icu Journal ClubDocument19 pagesIcu Journal Clubapi-649066372No ratings yet
- 220 WHO Guidance and Specifics On Blood Pressure DevicesDocument18 pages220 WHO Guidance and Specifics On Blood Pressure DevicesImcu 6No ratings yet
- Major and Minor SurgeryDocument2 pagesMajor and Minor SurgerydelarakrishnafaithpNo ratings yet
- Dka AlgorithmDocument1 pageDka AlgorithmAbhinav AggarwalNo ratings yet
- AKI Pathway (Nottingham University Hospitals April 2015)Document3 pagesAKI Pathway (Nottingham University Hospitals April 2015)Yadi SupriyadiNo ratings yet
- CC2 TransDocument12 pagesCC2 TransAnathalea ReyesNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis SyndromesDocument1 pageVasculitis SyndromesamanNo ratings yet
- High Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFDocument20 pagesHigh Yield Surgery Compatible Version PDFSurgery CSC1No ratings yet
- Tams NCP and DrugDocument5 pagesTams NCP and DrugNicholas Xavier VenturaNo ratings yet
- A Case of HypercalcaemiaDocument20 pagesA Case of HypercalcaemiasnipergirlNo ratings yet
- Comment File Hematolog y (Updated)Document7 pagesComment File Hematolog y (Updated)Sakesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- No More Nafld: The Nomenclature Is ChangingDocument4 pagesNo More Nafld: The Nomenclature Is ChanginghsiNo ratings yet
- Clcium GluconateDocument2 pagesClcium GluconatekarenmichellelecarozNo ratings yet
- Imei UrinanalysisDocument3 pagesImei UrinanalysisRohitNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock PathoDocument1 pageCardiogenic Shock PathoCommunity BNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury PosterDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Postermmbire@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Hyper Kale Mia HPWDocument1 pageHyper Kale Mia HPWfredericktingsyNo ratings yet
- ( Û ) Questionnaire Hospital InformationDocument5 pages( Û ) Questionnaire Hospital InformationsjeloNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathway For Hyperglycemic Crisis For AdultsDocument2 pagesClinical Pathway For Hyperglycemic Crisis For AdultserikaNo ratings yet
- SAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015Document1 pageSAHS HT Management Algorithm Medical Practitioner 2015Joana woodsNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry BrochureDocument20 pagesClinical Chemistry Brochureyogesh kumarNo ratings yet
- PBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Document2 pagesPBM Guidelines 4 Template Explanation of Base Excess Measurement Apr21Ricardo Antonio Rivas SánchezNo ratings yet
- HealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471543 Livewell Health Package - BronzeDocument1 pageHealthCheckupPlanHCK 1552471543 Livewell Health Package - BronzeDtftftfrNo ratings yet
- BookAppointmentTest Bronze. 1569462516.854957 PDFDocument1 pageBookAppointmentTest Bronze. 1569462516.854957 PDFಬಸವರಾಜ ಎಂ ಜಮಖಂಡಿNo ratings yet
- ATI A Pharm MedsDocument1 pageATI A Pharm MedsviankasmusicNo ratings yet
- BookAppointmentTest CareV2 Silver. 1579881536.8462949Document1 pageBookAppointmentTest CareV2 Silver. 1579881536.8462949ankitNo ratings yet
- Anemia Care PathwayDocument2 pagesAnemia Care PathwayArina FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Table 1: Intial Evaluation On Arrival To ER For All PatientsDocument1 pageTable 1: Intial Evaluation On Arrival To ER For All PatientsHetoshima KeiNo ratings yet
- Pre Anesthetic EvaluationDocument1 pagePre Anesthetic EvaluationАндрій ДанильцівNo ratings yet
- QC-7 Hematology Westgard Rules in Good Performance LaboratoryDocument38 pagesQC-7 Hematology Westgard Rules in Good Performance LaboratoryWita100% (1)
- Ped501 Hypernatremia NewDocument7 pagesPed501 Hypernatremia NewMisoo KimNo ratings yet
- Table 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDocument1 pageTable 4-16 - Use of Mood Stabilizing Medications For BipolarDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Medical Check Up MatrixDocument1 pageMedical Check Up Matrixgardamas tunggal primaNo ratings yet
- TransfusionDocument3 pagesTransfusionjulissand10No ratings yet
- Management of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineDocument7 pagesManagement of Acute Coronary Syndrome / NSTEMI: Purpose of The GuidelineSahera Nurhidayah NasutionNo ratings yet
- Week 3 HospDocument2 pagesWeek 3 Hospapi-507319784No ratings yet
- Expanding The Therapeutic Window For Acute Ischemic Stroke:: New Agents, New ApproachesDocument29 pagesExpanding The Therapeutic Window For Acute Ischemic Stroke:: New Agents, New ApproachesDr. RajibNo ratings yet
- HistorDocument2 pagesHistorbesoNo ratings yet
- Artic - NEJM - Tricomicosis Axilaris - 2022Document1 pageArtic - NEJM - Tricomicosis Axilaris - 2022Michelle OlveraNo ratings yet
- ICRPDocument67 pagesICRPGiovanni MateusNo ratings yet
- Ai Laboratory and Boarstud SectionDocument63 pagesAi Laboratory and Boarstud SectionrsuertoNo ratings yet
- Rawat Jalan ProsesDocument304 pagesRawat Jalan ProseshermanNo ratings yet
- Introductie Tot de VeevoedingDocument18 pagesIntroductie Tot de VeevoedingRayen Sheombar SingNo ratings yet
- BS - 6180 - 1995 - Barriers in and About BuildingsDocument36 pagesBS - 6180 - 1995 - Barriers in and About BuildingsjuanaNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths by Vaccination StatusDocument18 pagesCOVID-19 Cases, Hospitalizations, and Deaths by Vaccination StatusMike ParadisNo ratings yet
- Hospital Staffing PlanDocument1 pageHospital Staffing PlanMilin Anik'sNo ratings yet
- TFM 4Document8 pagesTFM 4Miguel de VivarNo ratings yet
- Q3 Lesson 5 6 Vulnerability and Sector of Society Vulnerable To DisasterDocument3 pagesQ3 Lesson 5 6 Vulnerability and Sector of Society Vulnerable To DisasterShanayaNo ratings yet
- GDJES-NDEP-Accomplishment-Report-april 2024 .Document4 pagesGDJES-NDEP-Accomplishment-Report-april 2024 .Mark BaniagaNo ratings yet
- (GK - 01) Question Paper Limited Departmental Competitive Examination - 2006 For The Post of Chargeman-Gr - Ii (T) & (NT)Document5 pages(GK - 01) Question Paper Limited Departmental Competitive Examination - 2006 For The Post of Chargeman-Gr - Ii (T) & (NT)murthy gNo ratings yet
- Critical Review of School Health and Nutrition (SHN) Program To Achieving Advance Preventive Healthcare For Children in PunjabDocument15 pagesCritical Review of School Health and Nutrition (SHN) Program To Achieving Advance Preventive Healthcare For Children in PunjabJournal of Public Policy PractitionersNo ratings yet
- Drug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsDocument7 pagesDrug Dosing in Obese Patients: A Dilemma: International Journal of Advances in PharmaceuticsYuppie RajNo ratings yet
- Broken Rib SymptomsDocument12 pagesBroken Rib Symptomsneleh grayNo ratings yet
- Eriksons Eigth Stages of Personality DevelopmentDocument1 pageEriksons Eigth Stages of Personality DevelopmentKristinne Claire Renol ReyesNo ratings yet
- 3b. RhinoplastyDocument122 pages3b. RhinoplastyKamal Saud100% (2)
- Chapter 4. 101. Week 7Document8 pagesChapter 4. 101. Week 7RAGOS Jeffrey Miguel P.No ratings yet
- Determining Training WorkloadsDocument15 pagesDetermining Training WorkloadsAriw AmpatNo ratings yet
- Research Methods NotesDocument8 pagesResearch Methods Notessxb3zk1No ratings yet
- Pengaruh Penggunaan Minyak Goreng Terhadap Kualitas Ayam GorengDocument14 pagesPengaruh Penggunaan Minyak Goreng Terhadap Kualitas Ayam GorengqonitahazzaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessDocument8 pagesTeaching Clinical Handover With ISBAR: Review Open AccessFernando PintoNo ratings yet
- Sma " Nasional" Malang: Ulangan Tengah Semester GanjilDocument4 pagesSma " Nasional" Malang: Ulangan Tengah Semester GanjilAqmarina Dianova BaharyNo ratings yet
- Self RegulationDocument2 pagesSelf RegulationDaniel Bernal0% (1)
- @anesthesia - Books 2014 Regional Anaesthesia - A Pocket GuideDocument168 pages@anesthesia - Books 2014 Regional Anaesthesia - A Pocket Guideraphael boechatNo ratings yet
- 5 Ways To Build Confidence in A Child With ADD/ADHDDocument3 pages5 Ways To Build Confidence in A Child With ADD/ADHDwildflowerNo ratings yet