Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Analysis and Design of Work
The Analysis and Design of Work
Uploaded by
Phương NgânCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- DVP - CPD Record - Assessment Activity 3 - Carmen Hofmeester - ResubmissionDocument2 pagesDVP - CPD Record - Assessment Activity 3 - Carmen Hofmeester - ResubmissionCarmen HofmeesterNo ratings yet
- Chap 004Document29 pagesChap 004ivan platiniNo ratings yet
- SESSION PLAN in Technical Drafting NCIIDocument61 pagesSESSION PLAN in Technical Drafting NCIIShiela Tala-oc Sapois-AndoNo ratings yet
- Bùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Document1 pageBùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Huong Bui Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document1 pageChap 4Nhứt Phú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Document1 pageName: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document1 pageLesson 4Bùi Thị Vân Anh 06No ratings yet
- Guide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation Brochure WebDocument4 pagesGuide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation Brochure WebChayanika MisraNo ratings yet
- Work Flow AnalysisDocument16 pagesWork Flow Analysisanjali_parekh37No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsMa Faith Angelica MoralesNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter-3Document12 pagesHRM Chapter-3KaiNo ratings yet
- 2024 03 11 Archimate Poster ENG DigitalDocument1 page2024 03 11 Archimate Poster ENG Digitalgecko123No ratings yet
- JobanalysisDocument25 pagesJobanalysismihir.chauhan1No ratings yet
- Performance Task in Chapters 4 and 5Document28 pagesPerformance Task in Chapters 4 and 5Jessica CerezaNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument4 pagesFlowchartclaudia duranNo ratings yet
- Computation of CompensationDocument22 pagesComputation of Compensationabdulrauf032119No ratings yet
- Motivational Design of Informal Learning SupportDocument1 pageMotivational Design of Informal Learning SupportAndreas SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Reviewer 2024Document29 pagesQualifying Exam Reviewer 20242023-106083No ratings yet
- Waode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Document4 pagesWaode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Sri SardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Brendah Oduori OutDocument1 pageBrendah Oduori OutWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- OTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationDocument45 pagesOTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationAshish PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Kisii University Main CampusDocument1 pageKisii University Main CampusWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 4Document13 pagesKuliah 4Yuliana WijayantiNo ratings yet
- (ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR) Motivation II: Applied ConceptsDocument10 pages(ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR) Motivation II: Applied ConceptsHueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Aisyah Nabihah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: Human Resource Management 3Document3 pagesCourse Syllabus: Human Resource Management 3Ayie Rose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Io Psych Chap2Document3 pagesIo Psych Chap2Gela FabianiaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Unit 7Document7 pagesPaper 1 Unit 7Ruchi MishraNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of ManagementDocument22 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Managementabhay.deshpande220No ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of ManagementDocument18 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Managementrajput91rahulNo ratings yet
- ML CanvasDocument1 pageML Canvasuday samalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document20 pagesChapter 3bimaka3527No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementSALIL DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Reviewer 2024Document29 pagesQualifying Exam Reviewer 20242023-106083No ratings yet
- Job Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsDocument28 pagesJob Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsSyrah Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- HRM PresentationDocument15 pagesHRM PresentationDarling Jerica IbanezNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackDocument1 pageMachine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackLeonard TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - JADocument18 pagesChapter 2 - JANeha KhereNo ratings yet
- Align Your Org: WorksheetDocument2 pagesAlign Your Org: WorksheetVictoria Salazar GómezNo ratings yet
- Engineering ManagementDocument6 pagesEngineering ManagementRy.KristNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis & Job DesignDocument19 pagesJob Analysis & Job DesignwardhantpeNo ratings yet
- Shaastra 2016 IIT Madras Consigliere Event Round-2: Management Development Institute Murshidabad (MDI-M)Document6 pagesShaastra 2016 IIT Madras Consigliere Event Round-2: Management Development Institute Murshidabad (MDI-M)Agastya KumarNo ratings yet
- Za Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicDocument4 pagesZa Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicAgung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- A Framework To Analyze Most Critical Wor PDFDocument10 pagesA Framework To Analyze Most Critical Wor PDFAbrham AbebeNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Unit 3 Work DesignDocument4 pagesWuolah Free Unit 3 Work Designjuan1710reynaldoNo ratings yet
- Title Author Name Published Date Objectives Research Methodolgy Analysis and Interpretation ConclusionDocument5 pagesTitle Author Name Published Date Objectives Research Methodolgy Analysis and Interpretation ConclusionDixith NagarajanNo ratings yet
- System Dynamics Modeling To Manage Performance Ased On Scope Change For Software Development ProjectsDocument10 pagesSystem Dynamics Modeling To Manage Performance Ased On Scope Change For Software Development ProjectsJosip StjepandicNo ratings yet
- Finding WasteDocument2 pagesFinding WasteBrendan CrowleyNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Innovation Tactics: People & CultureDocument1 page11 Types of Innovation Tactics: People & CultureClyde GulleNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Baanworkflow2Document12 pagesWhitepaper Baanworkflow2feewangNo ratings yet
- Person-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work AnalysisDocument11 pagesPerson-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work Analysispdhb5sqmzpNo ratings yet
- Action Research TableDocument2 pagesAction Research Tableapi-374992021No ratings yet
- ERP Trends Macola 021617Document1 pageERP Trends Macola 021617Tarik MudrovNo ratings yet
- Modern Management ToolsDocument1 pageModern Management ToolsJohanna HolzerNo ratings yet
- Perspectives On Models of Job Performance: Chockalingam Viswesvaran and Deniz S. OnesDocument11 pagesPerspectives On Models of Job Performance: Chockalingam Viswesvaran and Deniz S. OnesanitaNo ratings yet
- Person-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work AnalysisDocument11 pagesPerson-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work Analysispdhb5sqmzpNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Process Management - Joining Process Model With Everyday Work RoutineDocument2 pagesAdaptive Process Management - Joining Process Model With Everyday Work RoutineAndreas SchmidtNo ratings yet
- WSM - ReviewerDocument12 pagesWSM - ReviewerTini GarciaNo ratings yet
- LD Concept and ConductDocument9 pagesLD Concept and ConductSakshi Singh YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsFrom EverandHandbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsNo ratings yet
- MQP - MBA - Sem2 - Management Information System (DMBA204) PDFDocument3 pagesMQP - MBA - Sem2 - Management Information System (DMBA204) PDFsanjeev misraNo ratings yet
- Final Proctor and Gamble Strategy Case Analysis FinalDocument9 pagesFinal Proctor and Gamble Strategy Case Analysis FinalMurielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Anticipating More ScrutinyDocument23 pagesAnticipating More ScrutinyNorberto PernaNo ratings yet
- ARTIGO Lean AccountingDocument9 pagesARTIGO Lean AccountingAmanda LimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Art Science of MarketingDocument41 pagesChapter 12 - Art Science of MarketingCem YurdakulNo ratings yet
- Managerial Competencies and Their InflueDocument15 pagesManagerial Competencies and Their InflueJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- 05 Po Sync Faq Sheet (v5.1)Document5 pages05 Po Sync Faq Sheet (v5.1)jairam_911431562No ratings yet
- Roject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDDocument22 pagesRoject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDKandagatla KamalNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Template From ShopifyDocument31 pagesBusiness Plan Template From ShopifyGhing-Ghing ZitaNo ratings yet
- Case Study by AkhilDocument24 pagesCase Study by AkhilAsha RajNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Notes by TarunDocument8 pagesBusiness Analytics Notes by Taruntarun ranaNo ratings yet
- Resume Nur Syazana Najihah SuhaimyDocument14 pagesResume Nur Syazana Najihah SuhaimysyazasuhaimyNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument30 pagesPlanningAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Effective-Plant-Course Brochure NovDocument8 pagesEffective-Plant-Course Brochure NovAzri HafiziNo ratings yet
- FRM at A Glance PDFDocument2 pagesFRM at A Glance PDFhasanNo ratings yet
- Audit+Report+-+Part+1+Document14 pagesAudit+Report+-+Part+1+Karan BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Columbia Business School Exec Ed PortfolioDocument7 pagesColumbia Business School Exec Ed PortfolioMoises GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of Inventory ManagementDocument2 pagesDisadvantages of Inventory ManagementAarti RaneNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Cover LetterDocument2 pagesPraveen Kumar Cover Letterjagan venkatNo ratings yet
- Testimonial DuduDocument2 pagesTestimonial Dudududu kamalNo ratings yet
- ch06 Human Resources ManagementDocument19 pagesch06 Human Resources ManagementRakin Feruz ShaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Genet GezehagnNo ratings yet
- Developing Product Brand Value in Response To Customer Satisfaction Participation in Building and Customer. Experience ManagementDocument6 pagesDeveloping Product Brand Value in Response To Customer Satisfaction Participation in Building and Customer. Experience ManagementThe IjbmtNo ratings yet
- Elements of Effective Strategic Planning 1675049469Document2 pagesElements of Effective Strategic Planning 1675049469Editorial LandmarkbooksNo ratings yet
- Organisation Behaviour EssayDocument15 pagesOrganisation Behaviour EssayMarian NeaguNo ratings yet
- Lessons From OWLET PitchDocument2 pagesLessons From OWLET PitchwanytaufikNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Trends of Managers in Commercial Banks in Taif Governorate Towards The Application Knowledge Management ProcessesDocument25 pagesAn Analysis of The Trends of Managers in Commercial Banks in Taif Governorate Towards The Application Knowledge Management Processesabrar shibanNo ratings yet
- XOM Business Performance ROI FDocument24 pagesXOM Business Performance ROI FFaustina GaryNo ratings yet
- Priya ResumeDocument4 pagesPriya ResumePriya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Success Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects ProjectDocument17 pagesSuccess Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects Projectbeast mickeyNo ratings yet
The Analysis and Design of Work
The Analysis and Design of Work
Uploaded by
Phương NgânOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Analysis and Design of Work
The Analysis and Design of Work
Uploaded by
Phương NgânCopyright:
Available Formats
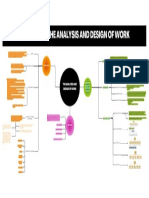
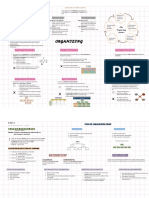
The number and nature of the outputs selected create
challenges for how to process the inputs to generate the Redesign is similar to analyze a job that has not yet exist.
outputs effectively. For example: McDonald recorded their Analyzing Work Outputs Work Redesign A firm often seeks to redesign work to make it more
worst speed-of performance metrics following the launch efficient or effective.
of new menu items.
Work-flow design is the process of analyzing the tasks Managers analyze an organization’s human resource
Teams are not a panacea. For teams to be effective, it is Human Resource Planning needs in a dynamic environment and develop activities
needed for the production of a product or service, prior to
essential that the level of task interdependence (how that enable a firm to adapt to change.
allocating and assigning these tasks to a particular job
much they have to cooperate) matches the level of Analyzing Work Processes
category or person.
outcome interdependence (how much they share the To identify the most qualified applicant, it must determine
reward for task accomplishment). the task will be performed by the individual employed and
Selection
the knowledge, skills and abilities he/she must have to
These inputs can be broken down into the raw materials, perform effectively.
equipment, and human skills needed to perform the Analyzing Work Inputs
tasks. The Importance of Job Analysis The training will prepare individuals to perform the jobs
Training and Development effectively; and some training programs may be more
Centralization extensive than others.
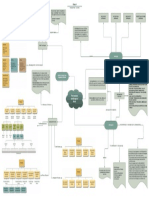
Dimensions of Structure
Departmentalization
Work-Flow Analysis and Organization Structure
Gathering information about how an employee behave
Performance Appraisal their work (effective or ineffective) and provide with
High levels of centralization tend to go naturally with justification for why the poor performance is disciplined.
functional departmentalization because individual units in
the structures are so specialized that members of the unit Functional Structure Matching an individual’s skills and aspirations with
may have a weak conceptualization of the overall Career Planning opportunities that are or may become available in the
organization mission. organization.
Structural Configurations Organization structure refers to the organization's
generally stable and formalized network of vertical and
Are not very efficient because of the redundancy Assessing the relative dollar value of each job to the
horizontal links between roles. Job Evaluation
associated with each group carrying its own functional organization to set up internally equitable pay structures.
Divisional Structure
specialists. It also “self-cannibalize” if the gains achieved
in one unit come at the expense of another unit. Managers must have detailed information about all the
jobs in their work group to understand the work-flow
The choice of structure also has implications for people process.
who would assume the jobs created in functional versus
divisional structures. Taller structures have implications Structure and the Nature of Jobs Managers need to understand the job requirements to
for organizational culture in terms of ethics and make informed hiring decisions.
accountability. The Importance of Job Analysis to Line Managers
A manager is responsible for ensuring that each
Changing the tasks or the way work is done in an existing individual is performing satisfactorily (or better).
job.
Managers ensure that the work is being done safely,
One must thoroughly comprehend the job as it exists (job Job Redesign identify potential hazards, and create an environment in
analysis) and its place (work-flow process) in the larger which individuals are allowed to avoid unsafe situations.
work unit’s work-flow process in order design jobs
effectively. TDRs are observable
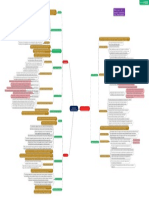
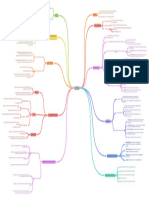
Job Description: a list of the tasks, duties and
Identifying the simplest way to structure work that responsibilities (TDRs) that a job consists. An effective balance between breadth and specificity
maximizes efficiency. This approach focuses on: task Job Analysis: the process of collecting detailed when constructing job descriptions.
THE ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF WORK information about jobs.
Nature of Information
specialization, skill simplification, and repetition.
Job Specification: a list of the knowledge, skills, abilities
Reducing the complexity of the work to make the work so and other characteristics (KSAOs) that a person must
simple that anyone can be trained quickly and easily to have to perform the job.
perform it. However, this can lead to unethical practice of
some companies in undeveloped countries. Job Analysis Information Assess the informal social network that exists within the
Mechanistic Approach formal organizational structure.
The organization reduces its need for high-ability (classical industrial engineering)
individuals and thus becomes less dependent on Although incumbents may provide the most accurate
individual workers. estimates, supervisors may be a more precise source of
Sources of Job Analysis Information Job Incumbent
information about the importance of job duties.
This approach are performed in developing countries
where there is a large supply of low-skilled labor and Other sources, such as customers, can be helpful,
relatively lax legal guidelines regarding safety standards. particularly for service jobs. External job analysts may be
However, this can lead to a backlash against companies the best source when it comes to analyzing skill levels.
that benefit from this unethical practice.
Information Input
Focus on increasing the meaningfulness of jobs through Job Design: the process of defining how work will
such interventions as job enlargement, job enrichment, be performed and the tasks that will be required Mental Processes
and the construction of jobs around socio-technical in a that job.
Motivational Approach (organizational psychology and Work Output
systems. Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ): one of the
management literature)
broadest and most well-researched instruments.
Creating meaningful work requires matching the right Relationships with other persons
type of person to the right type of task.
Job Context
Minimize physical strain on the worker by structuring the
physical work environment around the way the human Job Analysis Methods Other Characteristics
body works. Any job that creates a significant number of
injuries is a target for ergonomic redesign. Biological Approach Uses a common language that generalizes across jobs to
(ergonomics) describe the abilities, work styles, work activities, and
Programs also have a positive psychological effect on work context required for various occupations that are
workers by emphasizing an organizational climate that more broadly defined
values safety and health. The Occupational Information Network (O*NET)
Individuals who want to improve their ability to find
Improve reliability, safety, and user reactions by employment can obtain from the O*NET relatively
designing jobs to reduce their information-processing accurate information about what jobs they are qualified
requirements. for given their current literacy level.
Similar to the mechanistic approach, this approach Most inaccuracy is likely to result from job descriptions
generally decreases the job’s cognitive demands. simply being outdated. The job analysis process must
Perceptual-Motor Approach also detect changes in the nature of jobs.
(human-factors literature)
The new technology serves as a source of distraction Dynamic Elements of Job Analysis
from the primary task, reducing performance and A trend referred to as “dejobbing” in organizations -
increasing the opportunities for errors. consisting of viewing organizations as a field of work
needing to be done rather than a set of discrete jobs held
Team-based work design is a central component in terms by specific individuals.
of strategy and competitive advantage
You might also like
- DVP - CPD Record - Assessment Activity 3 - Carmen Hofmeester - ResubmissionDocument2 pagesDVP - CPD Record - Assessment Activity 3 - Carmen Hofmeester - ResubmissionCarmen HofmeesterNo ratings yet
- Chap 004Document29 pagesChap 004ivan platiniNo ratings yet
- SESSION PLAN in Technical Drafting NCIIDocument61 pagesSESSION PLAN in Technical Drafting NCIIShiela Tala-oc Sapois-AndoNo ratings yet
- Bùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Document1 pageBùi Ngọc Minh Hương - 31211021957 - CHAPTER 4Huong Bui Ngoc MinhNo ratings yet
- Chap 4Document1 pageChap 4Nhứt Phú NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Name: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Document1 pageName: Oàn V Hào Student ID: 31201028653 Class: HRM-DH46ISB-01Nguyễn Huỳnh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document1 pageLesson 4Bùi Thị Vân Anh 06No ratings yet
- Guide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation Brochure WebDocument4 pagesGuide Chart-Profile Method of Job Evaluation Brochure WebChayanika MisraNo ratings yet
- Work Flow AnalysisDocument16 pagesWork Flow Analysisanjali_parekh37No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 4 Analyzing Work and Designing JobsMa Faith Angelica MoralesNo ratings yet
- HRM Chapter-3Document12 pagesHRM Chapter-3KaiNo ratings yet
- 2024 03 11 Archimate Poster ENG DigitalDocument1 page2024 03 11 Archimate Poster ENG Digitalgecko123No ratings yet
- JobanalysisDocument25 pagesJobanalysismihir.chauhan1No ratings yet
- Performance Task in Chapters 4 and 5Document28 pagesPerformance Task in Chapters 4 and 5Jessica CerezaNo ratings yet
- FlowchartDocument4 pagesFlowchartclaudia duranNo ratings yet
- Computation of CompensationDocument22 pagesComputation of Compensationabdulrauf032119No ratings yet
- Motivational Design of Informal Learning SupportDocument1 pageMotivational Design of Informal Learning SupportAndreas SchmidtNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Reviewer 2024Document29 pagesQualifying Exam Reviewer 20242023-106083No ratings yet
- Waode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Document4 pagesWaode Sardiyanti (16522024) Phase 1Sri SardiyantiNo ratings yet
- Brendah Oduori OutDocument1 pageBrendah Oduori OutWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- OTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationDocument45 pagesOTH RFP Response Standardized TransformationAshish PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Kisii University Main CampusDocument1 pageKisii University Main CampusWilliams Grant MaxwelNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 4Document13 pagesKuliah 4Yuliana WijayantiNo ratings yet
- (ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR) Motivation II: Applied ConceptsDocument10 pages(ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR) Motivation II: Applied ConceptsHueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Aisyah Nabihah Mohd ZakiNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus: Human Resource Management 3Document3 pagesCourse Syllabus: Human Resource Management 3Ayie Rose HernandezNo ratings yet
- Io Psych Chap2Document3 pagesIo Psych Chap2Gela FabianiaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Unit 7Document7 pagesPaper 1 Unit 7Ruchi MishraNo ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of ManagementDocument22 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Managementabhay.deshpande220No ratings yet
- Principles and Practices of ManagementDocument18 pagesPrinciples and Practices of Managementrajput91rahulNo ratings yet
- ML CanvasDocument1 pageML Canvasuday samalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document20 pagesChapter 3bimaka3527No ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Resource ManagementDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Human Resource ManagementSALIL DHIMANNo ratings yet
- Qualifying Exam Reviewer 2024Document29 pagesQualifying Exam Reviewer 20242023-106083No ratings yet
- Job Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsDocument28 pagesJob Analysis: MBA 120: Personnel and Employee RelationsSyrah Mae ColomaNo ratings yet
- HRM PresentationDocument15 pagesHRM PresentationDarling Jerica IbanezNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackDocument1 pageMachine Learning Canvas: Background Solution Data Modeling FeedbackLeonard TVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - JADocument18 pagesChapter 2 - JANeha KhereNo ratings yet
- Align Your Org: WorksheetDocument2 pagesAlign Your Org: WorksheetVictoria Salazar GómezNo ratings yet
- Engineering ManagementDocument6 pagesEngineering ManagementRy.KristNo ratings yet
- Job Analysis & Job DesignDocument19 pagesJob Analysis & Job DesignwardhantpeNo ratings yet
- Shaastra 2016 IIT Madras Consigliere Event Round-2: Management Development Institute Murshidabad (MDI-M)Document6 pagesShaastra 2016 IIT Madras Consigliere Event Round-2: Management Development Institute Murshidabad (MDI-M)Agastya KumarNo ratings yet
- Za Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicDocument4 pagesZa Deloitte Intelligent Mining InfographicAgung SupriyantoNo ratings yet
- A Framework To Analyze Most Critical Wor PDFDocument10 pagesA Framework To Analyze Most Critical Wor PDFAbrham AbebeNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Unit 3 Work DesignDocument4 pagesWuolah Free Unit 3 Work Designjuan1710reynaldoNo ratings yet
- Title Author Name Published Date Objectives Research Methodolgy Analysis and Interpretation ConclusionDocument5 pagesTitle Author Name Published Date Objectives Research Methodolgy Analysis and Interpretation ConclusionDixith NagarajanNo ratings yet
- System Dynamics Modeling To Manage Performance Ased On Scope Change For Software Development ProjectsDocument10 pagesSystem Dynamics Modeling To Manage Performance Ased On Scope Change For Software Development ProjectsJosip StjepandicNo ratings yet
- Finding WasteDocument2 pagesFinding WasteBrendan CrowleyNo ratings yet
- 11 Types of Innovation Tactics: People & CultureDocument1 page11 Types of Innovation Tactics: People & CultureClyde GulleNo ratings yet
- Whitepaper Baanworkflow2Document12 pagesWhitepaper Baanworkflow2feewangNo ratings yet
- Person-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work AnalysisDocument11 pagesPerson-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work Analysispdhb5sqmzpNo ratings yet
- Action Research TableDocument2 pagesAction Research Tableapi-374992021No ratings yet
- ERP Trends Macola 021617Document1 pageERP Trends Macola 021617Tarik MudrovNo ratings yet
- Modern Management ToolsDocument1 pageModern Management ToolsJohanna HolzerNo ratings yet
- Perspectives On Models of Job Performance: Chockalingam Viswesvaran and Deniz S. OnesDocument11 pagesPerspectives On Models of Job Performance: Chockalingam Viswesvaran and Deniz S. OnesanitaNo ratings yet
- Person-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work AnalysisDocument11 pagesPerson-Job-Environment Fit: Job and Work Analysispdhb5sqmzpNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Process Management - Joining Process Model With Everyday Work RoutineDocument2 pagesAdaptive Process Management - Joining Process Model With Everyday Work RoutineAndreas SchmidtNo ratings yet
- WSM - ReviewerDocument12 pagesWSM - ReviewerTini GarciaNo ratings yet
- LD Concept and ConductDocument9 pagesLD Concept and ConductSakshi Singh YaduvanshiNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsFrom EverandHandbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, The Handbook of Selecting and Implementing Performance InterventionsNo ratings yet
- MQP - MBA - Sem2 - Management Information System (DMBA204) PDFDocument3 pagesMQP - MBA - Sem2 - Management Information System (DMBA204) PDFsanjeev misraNo ratings yet
- Final Proctor and Gamble Strategy Case Analysis FinalDocument9 pagesFinal Proctor and Gamble Strategy Case Analysis FinalMurielle FajardoNo ratings yet
- Anticipating More ScrutinyDocument23 pagesAnticipating More ScrutinyNorberto PernaNo ratings yet
- ARTIGO Lean AccountingDocument9 pagesARTIGO Lean AccountingAmanda LimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Art Science of MarketingDocument41 pagesChapter 12 - Art Science of MarketingCem YurdakulNo ratings yet
- Managerial Competencies and Their InflueDocument15 pagesManagerial Competencies and Their InflueJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- 05 Po Sync Faq Sheet (v5.1)Document5 pages05 Po Sync Faq Sheet (v5.1)jairam_911431562No ratings yet
- Roject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDDocument22 pagesRoject Anagement: B. Sravanthi Asst. Prof CEDKandagatla KamalNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Template From ShopifyDocument31 pagesBusiness Plan Template From ShopifyGhing-Ghing ZitaNo ratings yet
- Case Study by AkhilDocument24 pagesCase Study by AkhilAsha RajNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Notes by TarunDocument8 pagesBusiness Analytics Notes by Taruntarun ranaNo ratings yet
- Resume Nur Syazana Najihah SuhaimyDocument14 pagesResume Nur Syazana Najihah SuhaimysyazasuhaimyNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument30 pagesPlanningAshutosh SinghNo ratings yet
- Effective-Plant-Course Brochure NovDocument8 pagesEffective-Plant-Course Brochure NovAzri HafiziNo ratings yet
- FRM at A Glance PDFDocument2 pagesFRM at A Glance PDFhasanNo ratings yet
- Audit+Report+-+Part+1+Document14 pagesAudit+Report+-+Part+1+Karan BhavsarNo ratings yet
- Columbia Business School Exec Ed PortfolioDocument7 pagesColumbia Business School Exec Ed PortfolioMoises GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Disadvantages of Inventory ManagementDocument2 pagesDisadvantages of Inventory ManagementAarti RaneNo ratings yet
- Praveen Kumar Cover LetterDocument2 pagesPraveen Kumar Cover Letterjagan venkatNo ratings yet
- Testimonial DuduDocument2 pagesTestimonial Dudududu kamalNo ratings yet
- ch06 Human Resources ManagementDocument19 pagesch06 Human Resources ManagementRakin Feruz ShaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Genet GezehagnNo ratings yet
- Developing Product Brand Value in Response To Customer Satisfaction Participation in Building and Customer. Experience ManagementDocument6 pagesDeveloping Product Brand Value in Response To Customer Satisfaction Participation in Building and Customer. Experience ManagementThe IjbmtNo ratings yet
- Elements of Effective Strategic Planning 1675049469Document2 pagesElements of Effective Strategic Planning 1675049469Editorial LandmarkbooksNo ratings yet
- Organisation Behaviour EssayDocument15 pagesOrganisation Behaviour EssayMarian NeaguNo ratings yet
- Lessons From OWLET PitchDocument2 pagesLessons From OWLET PitchwanytaufikNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of The Trends of Managers in Commercial Banks in Taif Governorate Towards The Application Knowledge Management ProcessesDocument25 pagesAn Analysis of The Trends of Managers in Commercial Banks in Taif Governorate Towards The Application Knowledge Management Processesabrar shibanNo ratings yet
- XOM Business Performance ROI FDocument24 pagesXOM Business Performance ROI FFaustina GaryNo ratings yet
- Priya ResumeDocument4 pagesPriya ResumePriya BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Success Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects ProjectDocument17 pagesSuccess Factors in Project Management: Key Words: Projects Projectbeast mickeyNo ratings yet