Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
Uploaded by
সাবরিন সুলতানাCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- MCI Communications CorporationDocument6 pagesMCI Communications Corporationnipun9143No ratings yet
- DoorDash Drive Catering OverviewDocument14 pagesDoorDash Drive Catering OverviewIgor RusuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PRICING STRATEGY & TACTICSDocument14 pagesChapter 1 PRICING STRATEGY & TACTICSSankary Caroll100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To Trend Following PDFDocument43 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Trend Following PDFsaingthy100% (4)
- Fishers EffectDocument14 pagesFishers EffectKiran NayakNo ratings yet
- Theories of Exchange RateDocument11 pagesTheories of Exchange RateNiharika Satyadev Jaiswal100% (1)
- IFM - Lecture 2.9 - IRP-PPP-IFE - IFE TheoryDocument23 pagesIFM - Lecture 2.9 - IRP-PPP-IFE - IFE TheoryKancherla Bhaskara RaoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - PARITY CONDITIONS IN INTERNATIONAL FINANCE AND CURRENCY FORECASTINGDocument37 pagesGroup 4 - PARITY CONDITIONS IN INTERNATIONAL FINANCE AND CURRENCY FORECASTINGadindaNo ratings yet
- FINALS - Global FinDocument11 pagesFINALS - Global Fincara0925100% (1)
- 67847bos54415-Cp9 (1) ExportDocument1 page67847bos54415-Cp9 (1) ExportreadorplaydigitalNo ratings yet
- Arbitrade (I.F.M.) FinalDocument3 pagesArbitrade (I.F.M.) Final0012 Shah Md. Arafat [C]No ratings yet
- Locational Arbitrage:: Rabea Rashed Mansoor - 20311562Document2 pagesLocational Arbitrage:: Rabea Rashed Mansoor - 20311562Rabea Rashed Al SabahiNo ratings yet
- Purchase Power Parity PrintDocument5 pagesPurchase Power Parity PrintTejaliNo ratings yet
- CFA L3 - MemorizeDocument2 pagesCFA L3 - Memorizeadham.abdelatyNo ratings yet
- Chapte R: International Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesChapte R: International Financial ManagementNiket GuptaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IPR, PPP & IFE TheoriesDocument1 pageComparison of IPR, PPP & IFE TheoriesTechnical networkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IFE, IRP)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IFE, IRP)doraemonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)doraemonNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Parity Conditions: International Parity Relations & Exchange Rate ForecastingDocument17 pages3.1 Parity Conditions: International Parity Relations & Exchange Rate ForecastingMunyaradzi MasendekeNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument3 pagesInterest Rate ParityPratik PatraNo ratings yet
- Spot and ForwardDocument11 pagesSpot and ForwardKajal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CHP 16 1 Foreign Exchange Rates Mechanism PDFDocument4 pagesCHP 16 1 Foreign Exchange Rates Mechanism PDFWaqar AmjadNo ratings yet
- Irpt & PPPTDocument3 pagesIrpt & PPPTKhabele LenkoeNo ratings yet
- 25444sm SFM Finalnewvol2 cp12Document72 pages25444sm SFM Finalnewvol2 cp12h.b. akshayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDocument6 pagesChapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDanica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDocument6 pagesChapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDanica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- International Financial Markets Part 2Document9 pagesInternational Financial Markets Part 2truthoverloveNo ratings yet
- F9 Notes (Risk Management)Document14 pagesF9 Notes (Risk Management)CHIAMAKA EGBUKOLENo ratings yet
- FOREX & Interest RiskDocument11 pagesFOREX & Interest Riskpercy mapetereNo ratings yet
- Theories of Exchange RateDocument37 pagesTheories of Exchange Ratedranita@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Group G IFM PrnstationDocument12 pagesGroup G IFM PrnstationMaryamNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument3 pagesInterest Rate ParityJayesh DessaiNo ratings yet
- Material Temas 3 y 4 - Tipo de Cambio y Paridad Poder de CompraDocument27 pagesMaterial Temas 3 y 4 - Tipo de Cambio y Paridad Poder de CompraReynerio VilledaNo ratings yet
- Fibs Lectures PDFDocument203 pagesFibs Lectures PDFadi irawantoNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - SuryanarayananDocument28 pagesThe Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - Suryanarayananchhavi nahataNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document33 pagesSession 2Soumik MutsuddiNo ratings yet
- For Ex 2Document2 pagesFor Ex 2aryans467698No ratings yet
- Module 4 Wed Bsacore6Document4 pagesModule 4 Wed Bsacore6Kryzzel JonNo ratings yet
- International Finance - Update - STDocument9 pagesInternational Finance - Update - STWorlex zakiNo ratings yet
- PPP IrpDocument29 pagesPPP IrpSam SmithNo ratings yet
- Parity RelationshipDocument11 pagesParity Relationshipkenedy simwingaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 & Chapter 18 (1) NewDocument66 pagesChapter 17 & Chapter 18 (1) NewAlief AmbyaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument8 pagesDocAhmad RahhalNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument22 pagesExchange Rate0119 ASIB BIN ABSARNo ratings yet
- Does PPP Eliminate Concerns About Long-Term Exchange Rate RiskDocument2 pagesDoes PPP Eliminate Concerns About Long-Term Exchange Rate RiskAriel Logacho100% (1)
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument44 pagesExchange Rate DeterminationYuhao HuangNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Theories: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolDocument69 pagesExchange Rate Theories: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business Schoolasifanis100% (2)
- Investment Analysis Farhan Javed M14MBA031Document76 pagesInvestment Analysis Farhan Javed M14MBA031Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4. Foreign Exchange Market and Management of Foreign Exchange RiskDocument56 pages3 & 4. Foreign Exchange Market and Management of Foreign Exchange RiskPanashe MachekepfuNo ratings yet
- tài chính quốc tế 1Document7 pagestài chính quốc tế 1Đạt Dương ThànhNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument1 pageInterest Rate Paritypavanmandowara3984No ratings yet
- Mba 4 Sem (Umang Rajput)Document20 pagesMba 4 Sem (Umang Rajput)Umang RajputNo ratings yet
- FERM Unit 2Document8 pagesFERM Unit 2vaishnavisoni1108No ratings yet
- If Unit 3Document6 pagesIf Unit 3gowrirao496No ratings yet
- Chapter 08 SolutionDocument22 pagesChapter 08 SolutionmaybelNo ratings yet
- Theories of Foreign Exchange Rate Movement and International Parity ConditionsDocument10 pagesTheories of Foreign Exchange Rate Movement and International Parity ConditionsSaravanakrishnan VNo ratings yet
- 2013.the Exchange Rate and EuropeDocument58 pages2013.the Exchange Rate and EuropeBogdan AvadaniNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate: Outline of DiscussionDocument3 pagesExchange Rate: Outline of DiscussionRiubenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review International Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parity International ArbitrageDocument9 pagesChapter Review International Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parity International ArbitrageWi SilalahiNo ratings yet
- AhmedDocument17 pagesAhmedmoizmeingNo ratings yet
- International Arbitrage and Interest Rate ParityDocument20 pagesInternational Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parityjahirul munnaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Strategy: Winning Strategies of Professional InvestmentFrom EverandQuantum Strategy: Winning Strategies of Professional InvestmentNo ratings yet
- Malpractice in Marketing WEB Advertising: Eduardo Ramón León Rodríguez Inglés 6 - G Centro de Idiomas UcsgDocument8 pagesMalpractice in Marketing WEB Advertising: Eduardo Ramón León Rodríguez Inglés 6 - G Centro de Idiomas UcsgEdu Leon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument22 pagesMarketing Mixdev1992100% (1)
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument20 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyimislamianNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Sathish L RDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Sathish L RBhoomi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Hewlett Packard - Computer Systems Organisation: Selling To Enterprise CustomersDocument12 pagesHewlett Packard - Computer Systems Organisation: Selling To Enterprise Customersnavz88No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Equity ValuationDocument37 pagesAn Introduction To Equity ValuationAamir Hamza MehediNo ratings yet
- 7 7 100 10:30 PDF Ntu Cool PDF + 60% 3-4: Solution: (A)Document7 pages7 7 100 10:30 PDF Ntu Cool PDF + 60% 3-4: Solution: (A)歐怡君No ratings yet
- Build Relationship With Customer 2020Document28 pagesBuild Relationship With Customer 2020FelekePhiliphos100% (2)
- Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesLinear ProgrammingAngela HencherNo ratings yet
- CH16Document6 pagesCH16api-3731879No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Direct MarketingDocument75 pagesChapter 1 Direct MarketingalinaNo ratings yet
- Price Discrimination On Anand City TheatersDocument51 pagesPrice Discrimination On Anand City TheatersTusshar R Gadhiya NewNo ratings yet
- 02.mechanics of Futures MarketDocument8 pages02.mechanics of Futures MarketNg Jian LongNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Dawn BreadDocument10 pagesMarketing Strategies of Dawn BreadSaad RazaNo ratings yet
- Ugbs 201 T2Document3 pagesUgbs 201 T2richmannkansahNo ratings yet
- Porters 5 Forces AnalysisDocument2 pagesPorters 5 Forces AnalysisAmarnadhNo ratings yet
- 7 Powerful Secrets To Trade CFDs SuccessfullyDocument68 pages7 Powerful Secrets To Trade CFDs SuccessfullyconchunchunNo ratings yet
- Test 2 (Set C)Document2 pagesTest 2 (Set C)darshini mariappanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document39 pagesUnit 4Cuti PandaNo ratings yet
- Economics 2nd Edition Hubbard Test BankDocument48 pagesEconomics 2nd Edition Hubbard Test Bankmarthalouisaq6x100% (26)
- 56 Free Test Bank For Principles of Managerial Finance 13th Edition Gitman Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument16 pages56 Free Test Bank For Principles of Managerial Finance 13th Edition Gitman Multiple Choice QuestionsYeshey Choden0% (1)
- Group 6 Vora-and-CompanyDocument9 pagesGroup 6 Vora-and-CompanyAkanksha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Prob 1Document4 pagesProb 1asnescribNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions (Participation)Document4 pagesDiscussion Questions (Participation)Sam SamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Management AccountingDocument17 pagesAssignment On Management Accountingbaburangpur100% (2)
- Notes On Managerial EconomicsDocument28 pagesNotes On Managerial EconomicsShantilal HajeriNo ratings yet
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
Uploaded by
সাবরিন সুলতানাOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
IRP PPP IFE - PDF Version 1
Uploaded by
সাবরিন সুলতানাCopyright:
Available Formats
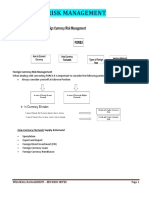
THEORY 1 THEORY 2 THEORY 3
(INTEREST RATE PARITY) (PURCHASING POWER PARITY) (INTERNATIONAL FISHER EFFECT)
Meaning Market forces cause the forward rate to differ It refers to a situation where the inflation It proposes that differences in nominal interest rates
from the spot rate by an amount that is differential between two countries is exactly between countries are reflective of differences in
sufficient to offset the interest rate differential offset by the depreciation of the higher expected inflation.
between the two currencies.
inflation currency.
Then, covered interest arbitrage is no longer
feasible, and the equilibrium state achieved is
referred to as interest rate parity (IRP).
Implication It basically implies that investor cannot earn a When PPP exists customers will be If interest rates in a country are higher, that is a sign of
rate of return higher than that attainable in his indifferent between purchasing goods in higher anticipated inflation. Hence, according to PPP the
or her home country by investing in foreign their own country versus purchasing goods higher interest currency will depreciate and investors will
market. in the foreign country. earn the same return whether they invest in the home
country or the foreign country.
Variables Interest rate differential (%) Inflation Rate Differential (%) Interest rate differential (%)
Forward discount/premium of foreign country % Δ in the foreign currency’s spot rate % Δ in the foreign currency’s spot rate
Consider Political Risk Relationship not perfect even in the long run Holds during some time frames
Differential Tax Laws Use of inflation differentials is supported Based on PPP
Due to: confounding effects + lack of Will not hold when PPP does not hold
substitutes
Exact
Equation
Approximate
Equation
Md. Uzzal Hossain, MBA 24th Batch
You might also like
- MCI Communications CorporationDocument6 pagesMCI Communications Corporationnipun9143No ratings yet
- DoorDash Drive Catering OverviewDocument14 pagesDoorDash Drive Catering OverviewIgor RusuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PRICING STRATEGY & TACTICSDocument14 pagesChapter 1 PRICING STRATEGY & TACTICSSankary Caroll100% (1)
- The Ultimate Guide To Trend Following PDFDocument43 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Trend Following PDFsaingthy100% (4)
- Fishers EffectDocument14 pagesFishers EffectKiran NayakNo ratings yet
- Theories of Exchange RateDocument11 pagesTheories of Exchange RateNiharika Satyadev Jaiswal100% (1)
- IFM - Lecture 2.9 - IRP-PPP-IFE - IFE TheoryDocument23 pagesIFM - Lecture 2.9 - IRP-PPP-IFE - IFE TheoryKancherla Bhaskara RaoNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - PARITY CONDITIONS IN INTERNATIONAL FINANCE AND CURRENCY FORECASTINGDocument37 pagesGroup 4 - PARITY CONDITIONS IN INTERNATIONAL FINANCE AND CURRENCY FORECASTINGadindaNo ratings yet
- FINALS - Global FinDocument11 pagesFINALS - Global Fincara0925100% (1)
- 67847bos54415-Cp9 (1) ExportDocument1 page67847bos54415-Cp9 (1) ExportreadorplaydigitalNo ratings yet
- Arbitrade (I.F.M.) FinalDocument3 pagesArbitrade (I.F.M.) Final0012 Shah Md. Arafat [C]No ratings yet
- Locational Arbitrage:: Rabea Rashed Mansoor - 20311562Document2 pagesLocational Arbitrage:: Rabea Rashed Mansoor - 20311562Rabea Rashed Al SabahiNo ratings yet
- Purchase Power Parity PrintDocument5 pagesPurchase Power Parity PrintTejaliNo ratings yet
- CFA L3 - MemorizeDocument2 pagesCFA L3 - Memorizeadham.abdelatyNo ratings yet
- Chapte R: International Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesChapte R: International Financial ManagementNiket GuptaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of IPR, PPP & IFE TheoriesDocument1 pageComparison of IPR, PPP & IFE TheoriesTechnical networkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IFE, IRP)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IFE, IRP)doraemonNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)Document6 pagesAssignment 2 (Theories of Exchange Rates - PPP, IfE, IRP)doraemonNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Parity Conditions: International Parity Relations & Exchange Rate ForecastingDocument17 pages3.1 Parity Conditions: International Parity Relations & Exchange Rate ForecastingMunyaradzi MasendekeNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument3 pagesInterest Rate ParityPratik PatraNo ratings yet
- Spot and ForwardDocument11 pagesSpot and ForwardKajal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- CHP 16 1 Foreign Exchange Rates Mechanism PDFDocument4 pagesCHP 16 1 Foreign Exchange Rates Mechanism PDFWaqar AmjadNo ratings yet
- Irpt & PPPTDocument3 pagesIrpt & PPPTKhabele LenkoeNo ratings yet
- 25444sm SFM Finalnewvol2 cp12Document72 pages25444sm SFM Finalnewvol2 cp12h.b. akshayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDocument6 pagesChapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDanica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDocument6 pagesChapter 9: FOREX MARKET Key PointsDanica AbelardoNo ratings yet
- International Financial Markets Part 2Document9 pagesInternational Financial Markets Part 2truthoverloveNo ratings yet
- F9 Notes (Risk Management)Document14 pagesF9 Notes (Risk Management)CHIAMAKA EGBUKOLENo ratings yet
- FOREX & Interest RiskDocument11 pagesFOREX & Interest Riskpercy mapetereNo ratings yet
- Theories of Exchange RateDocument37 pagesTheories of Exchange Ratedranita@yahoo.comNo ratings yet
- Group G IFM PrnstationDocument12 pagesGroup G IFM PrnstationMaryamNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument3 pagesInterest Rate ParityJayesh DessaiNo ratings yet
- Material Temas 3 y 4 - Tipo de Cambio y Paridad Poder de CompraDocument27 pagesMaterial Temas 3 y 4 - Tipo de Cambio y Paridad Poder de CompraReynerio VilledaNo ratings yet
- Fibs Lectures PDFDocument203 pagesFibs Lectures PDFadi irawantoNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - SuryanarayananDocument28 pagesThe Foreign Exchange Market: Prepared For Class Discussion by Prof - Suryanarayananchhavi nahataNo ratings yet
- Session 2Document33 pagesSession 2Soumik MutsuddiNo ratings yet
- For Ex 2Document2 pagesFor Ex 2aryans467698No ratings yet
- Module 4 Wed Bsacore6Document4 pagesModule 4 Wed Bsacore6Kryzzel JonNo ratings yet
- International Finance - Update - STDocument9 pagesInternational Finance - Update - STWorlex zakiNo ratings yet
- PPP IrpDocument29 pagesPPP IrpSam SmithNo ratings yet
- Parity RelationshipDocument11 pagesParity Relationshipkenedy simwingaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 & Chapter 18 (1) NewDocument66 pagesChapter 17 & Chapter 18 (1) NewAlief AmbyaNo ratings yet
- DocDocument8 pagesDocAhmad RahhalNo ratings yet
- Exchange RateDocument22 pagesExchange Rate0119 ASIB BIN ABSARNo ratings yet
- Does PPP Eliminate Concerns About Long-Term Exchange Rate RiskDocument2 pagesDoes PPP Eliminate Concerns About Long-Term Exchange Rate RiskAriel Logacho100% (1)
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument44 pagesExchange Rate DeterminationYuhao HuangNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate Theories: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business SchoolDocument69 pagesExchange Rate Theories: Prof Mahesh Kumar Amity Business Schoolasifanis100% (2)
- Investment Analysis Farhan Javed M14MBA031Document76 pagesInvestment Analysis Farhan Javed M14MBA031Muhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- 3 & 4. Foreign Exchange Market and Management of Foreign Exchange RiskDocument56 pages3 & 4. Foreign Exchange Market and Management of Foreign Exchange RiskPanashe MachekepfuNo ratings yet
- tài chính quốc tế 1Document7 pagestài chính quốc tế 1Đạt Dương ThànhNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate ParityDocument1 pageInterest Rate Paritypavanmandowara3984No ratings yet
- Mba 4 Sem (Umang Rajput)Document20 pagesMba 4 Sem (Umang Rajput)Umang RajputNo ratings yet
- FERM Unit 2Document8 pagesFERM Unit 2vaishnavisoni1108No ratings yet
- If Unit 3Document6 pagesIf Unit 3gowrirao496No ratings yet
- Chapter 08 SolutionDocument22 pagesChapter 08 SolutionmaybelNo ratings yet
- Theories of Foreign Exchange Rate Movement and International Parity ConditionsDocument10 pagesTheories of Foreign Exchange Rate Movement and International Parity ConditionsSaravanakrishnan VNo ratings yet
- 2013.the Exchange Rate and EuropeDocument58 pages2013.the Exchange Rate and EuropeBogdan AvadaniNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate: Outline of DiscussionDocument3 pagesExchange Rate: Outline of DiscussionRiubenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review International Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parity International ArbitrageDocument9 pagesChapter Review International Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parity International ArbitrageWi SilalahiNo ratings yet
- AhmedDocument17 pagesAhmedmoizmeingNo ratings yet
- International Arbitrage and Interest Rate ParityDocument20 pagesInternational Arbitrage and Interest Rate Parityjahirul munnaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Strategy: Winning Strategies of Professional InvestmentFrom EverandQuantum Strategy: Winning Strategies of Professional InvestmentNo ratings yet
- Malpractice in Marketing WEB Advertising: Eduardo Ramón León Rodríguez Inglés 6 - G Centro de Idiomas UcsgDocument8 pagesMalpractice in Marketing WEB Advertising: Eduardo Ramón León Rodríguez Inglés 6 - G Centro de Idiomas UcsgEdu Leon RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Marketing MixDocument22 pagesMarketing Mixdev1992100% (1)
- Blue Ocean StrategyDocument20 pagesBlue Ocean StrategyimislamianNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Sathish L RDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Sathish L RBhoomi GoyalNo ratings yet
- Hewlett Packard - Computer Systems Organisation: Selling To Enterprise CustomersDocument12 pagesHewlett Packard - Computer Systems Organisation: Selling To Enterprise Customersnavz88No ratings yet
- An Introduction To Equity ValuationDocument37 pagesAn Introduction To Equity ValuationAamir Hamza MehediNo ratings yet
- 7 7 100 10:30 PDF Ntu Cool PDF + 60% 3-4: Solution: (A)Document7 pages7 7 100 10:30 PDF Ntu Cool PDF + 60% 3-4: Solution: (A)歐怡君No ratings yet
- Build Relationship With Customer 2020Document28 pagesBuild Relationship With Customer 2020FelekePhiliphos100% (2)
- Linear ProgrammingDocument8 pagesLinear ProgrammingAngela HencherNo ratings yet
- CH16Document6 pagesCH16api-3731879No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Direct MarketingDocument75 pagesChapter 1 Direct MarketingalinaNo ratings yet
- Price Discrimination On Anand City TheatersDocument51 pagesPrice Discrimination On Anand City TheatersTusshar R Gadhiya NewNo ratings yet
- 02.mechanics of Futures MarketDocument8 pages02.mechanics of Futures MarketNg Jian LongNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategies of Dawn BreadDocument10 pagesMarketing Strategies of Dawn BreadSaad RazaNo ratings yet
- Ugbs 201 T2Document3 pagesUgbs 201 T2richmannkansahNo ratings yet
- Porters 5 Forces AnalysisDocument2 pagesPorters 5 Forces AnalysisAmarnadhNo ratings yet
- 7 Powerful Secrets To Trade CFDs SuccessfullyDocument68 pages7 Powerful Secrets To Trade CFDs SuccessfullyconchunchunNo ratings yet
- Test 2 (Set C)Document2 pagesTest 2 (Set C)darshini mariappanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document39 pagesUnit 4Cuti PandaNo ratings yet
- Economics 2nd Edition Hubbard Test BankDocument48 pagesEconomics 2nd Edition Hubbard Test Bankmarthalouisaq6x100% (26)
- 56 Free Test Bank For Principles of Managerial Finance 13th Edition Gitman Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument16 pages56 Free Test Bank For Principles of Managerial Finance 13th Edition Gitman Multiple Choice QuestionsYeshey Choden0% (1)
- Group 6 Vora-and-CompanyDocument9 pagesGroup 6 Vora-and-CompanyAkanksha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Prob 1Document4 pagesProb 1asnescribNo ratings yet
- Discussion Questions (Participation)Document4 pagesDiscussion Questions (Participation)Sam SamNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Management AccountingDocument17 pagesAssignment On Management Accountingbaburangpur100% (2)
- Notes On Managerial EconomicsDocument28 pagesNotes On Managerial EconomicsShantilal HajeriNo ratings yet