Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 viewsCs1a05c Sol
Cs1a05c Sol
Uploaded by
Chau Minnie1. The document contains multiple word problems involving the calculation of profit percentages and loss percentages for various business scenarios.
2. It provides the calculations to determine whether there was a profit or loss in each scenario based on the selling price and cost price.
3. The problems are solved by setting up equations involving the cost price, selling price, and profit/loss amounts and calculating the relevant percentages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Forage JP Morgan Ib Task 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesForage JP Morgan Ib Task 2 SolutionRohit Vasave100% (1)
- MphasisDocument12 pagesMphasisVenkyNo ratings yet
- Asahi Case SolutionDocument1 pageAsahi Case SolutionAmit BiswalNo ratings yet
- The Bond Market in GhanaDocument12 pagesThe Bond Market in GhanaJohn Kennedy Akotia100% (3)
- Chapter 10 Stock Valuation A Second LookDocument33 pagesChapter 10 Stock Valuation A Second LookshuNo ratings yet
- CS1A05D SolDocument4 pagesCS1A05D SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Cs1a05b SolDocument5 pagesCs1a05b SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Fin SolutionsDocument9 pagesFin SolutionsTania Kalila HernandezNo ratings yet
- MARY GRACE PANGANIBAN - 027 Cost-Volume-Profit and Business Scalability Exercise 2Document17 pagesMARY GRACE PANGANIBAN - 027 Cost-Volume-Profit and Business Scalability Exercise 2Mary Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Profit - Loss - Discount - P3-10 2Document8 pagesProfit - Loss - Discount - P3-10 2buck albinoNo ratings yet
- P5Maths Week 33Document4 pagesP5Maths Week 33အင္တာေနရွင္နယ္ေက်ာင္းမ်ား၏ ေမးခြန္လႊာဘာသာစံုျဖန္႕ခ်ီေရးNo ratings yet
- AkuntansiDocument2 pagesAkuntansiDenny CandraNo ratings yet
- Business Decisions Using Cost Behaviour: Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument11 pagesBusiness Decisions Using Cost Behaviour: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysismishabmoomin1524No ratings yet
- Chapter-12-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWDocument13 pagesChapter-12-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWallthehalls666No ratings yet
- $70 - $40 $30 $30 /times X 15,000 $450,000 $450,000 - $540,000 - $90,000 (Loss)Document9 pages$70 - $40 $30 $30 /times X 15,000 $450,000 $450,000 - $540,000 - $90,000 (Loss)longphungspNo ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Percentages I e SolDocument7 pagesOJM DSETraining Percentages I e Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- India's First Absolutely Free Online Bank Exam Coaching WWW - BANKKING.INDocument4 pagesIndia's First Absolutely Free Online Bank Exam Coaching WWW - BANKKING.INJagannath JagguNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss - SOLS - Concept 31 To 40Document11 pagesProfit & Loss - SOLS - Concept 31 To 40xyzNo ratings yet
- Derivations: - ComputationalDocument3 pagesDerivations: - ComputationalEdiane QuilezaNo ratings yet
- CVP Test SolutionDocument2 pagesCVP Test Solutionahsaankhan2811No ratings yet
- Module 3 - BreakevenDocument2 pagesModule 3 - BreakevenBern Austin EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Assgment 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Agung Rizal / 2201827622Document10 pagesAssgment 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Agung Rizal / 2201827622Agung Rizal DewantoroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Chapter 4 - Salsabila Putri Sabrina - 1181002040 - Corfin 42Document5 pagesTugas Chapter 4 - Salsabila Putri Sabrina - 1181002040 - Corfin 42SalspsNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: Assignment: 02Document5 pagesManagerial Accounting: Assignment: 02Asma HatamNo ratings yet
- Ma 13.2.2023Document7 pagesMa 13.2.2023Chit Myo HlaingNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss SolutionDocument20 pagesProfit & Loss SolutionAnkit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Biaya Variabe Harga Jual $ 7 $ 20Document6 pagesBiaya Variabe Harga Jual $ 7 $ 20Shelley TaniaNo ratings yet
- Ratio - Proportion - PercentDocument31 pagesRatio - Proportion - PercentRiyadh HaiderNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02 - SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment 02 - SolutionSuman Paul ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Phase 7 PresentationDocument13 pagesPhase 7 PresentationAnton BernardoNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss and DiscountDocument20 pagesProfit Loss and DiscountLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Ebook Contemporary Business Mathematics Canadian 10Th Edition Hummelbrunner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument57 pagesEbook Contemporary Business Mathematics Canadian 10Th Edition Hummelbrunner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkevinfryecqiozexkjy100% (13)
- Case Problem 3Document5 pagesCase Problem 3Marjorie PonceNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan Pratap SirDocument13 pagesProfit & Loss Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan Pratap Siramit kumarNo ratings yet
- Contribution Margin: Enter The Appropriate Amount in The Shaded Cells in Columns C and EDocument16 pagesContribution Margin: Enter The Appropriate Amount in The Shaded Cells in Columns C and EJames BagsicNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 - VPN: Tmar Vs VNPDocument2 pagesEjercicio 1 - VPN: Tmar Vs VNPRaul Quispe PedrazaNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis SolutionsDocument6 pagesCVP Analysis SolutionsAlaine Milka GosycoNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Jawaban Soal 1: Asst. Bagus, Elvira, & YogiDocument4 pagesJawaban Jawaban Soal 1: Asst. Bagus, Elvira, & YogiRavanellyNo ratings yet
- Markup On COGSDocument16 pagesMarkup On COGSJack LiuNo ratings yet
- Solution PricingDocument3 pagesSolution PricingDella BianchiNo ratings yet
- Derivations: - ComputationalDocument4 pagesDerivations: - ComputationalHAKUNA MATATANo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss Sheet SolutionDocument23 pagesProfit and Loss Sheet SolutionSahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- AO2 Worksheet 4 Absolute and Relative Changes AnswersDocument3 pagesAO2 Worksheet 4 Absolute and Relative Changes AnswersBhavishka ValraniNo ratings yet
- True or False: Basadre, Jessa G. Bsa 3 Yr Managerial Accounting Assignment No. 2 - CVP RelationshipDocument3 pagesTrue or False: Basadre, Jessa G. Bsa 3 Yr Managerial Accounting Assignment No. 2 - CVP RelationshipJessa BasadreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionsissy.he.7No ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 3 - CVP Analysis Answer Section: 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: A 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: A 5Document3 pagesTutorial No. 3 - CVP Analysis Answer Section: 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: A 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: A 5Hu-Ann KeymistNo ratings yet
- Profit, Loss and DiscountDocument5 pagesProfit, Loss and DiscountswagatamparidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ExcelDocument42 pagesChapter 13 ExcelMd Al Alif Hossain 2121155630No ratings yet
- FIE400E 2016 Spring SolutionsDocument4 pagesFIE400E 2016 Spring SolutionsSander Von Porat BaugeNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument7 pagesStudent Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisAasir NaQvi100% (1)
- F2 - MOCK A - ANSWERS NowDocument11 pagesF2 - MOCK A - ANSWERS NowRoronoa ZoroNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 ManKeu - Bella Fatma P - 2011070511Document4 pagesTugas 4 ManKeu - Bella Fatma P - 2011070511Bella FatmaNo ratings yet
- D E+ D X RD+ E D+ E X : Return Richard ExpectDocument5 pagesD E+ D X RD+ E D+ E X : Return Richard ExpectSu Suan TanNo ratings yet
- AKL Chapter9Document3 pagesAKL Chapter9Farrell DmNo ratings yet
- Percentage CDSDocument8 pagesPercentage CDSgladiatortorqueNo ratings yet
- Cs1a05a SolDocument6 pagesCs1a05a SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss 2023Document40 pagesProfit and Loss 2023netra7222No ratings yet
- Profit and Loss NewDocument34 pagesProfit and Loss NewPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 6 Bab 6Document4 pagesTugasan 6 Bab 6azwan88No ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 15 EpsDocument12 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 15 Epsfinn mertensNo ratings yet
- Activity #6Document3 pagesActivity #6ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Part 2Document47 pagesCorporate Finance Part 2sdfghjkNo ratings yet
- Hire Purchase (Part 2)Document7 pagesHire Purchase (Part 2)Kelly HibbertNo ratings yet
- Commercial Arithmetic (Solution) PDFDocument6 pagesCommercial Arithmetic (Solution) PDFagnelwaghelaNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- S&P CriteriaDocument57 pagesS&P CriteriaCairo AnubissNo ratings yet
- Solved 1 Herm S International Was A Family Owned Business For Many YearsDocument1 pageSolved 1 Herm S International Was A Family Owned Business For Many YearsJusta MukiriNo ratings yet
- Sonic R. SystemDocument2 pagesSonic R. Systemthang 1No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Academic Year 2011-2012 TutorialsDocument21 pagesCorporate Finance Academic Year 2011-2012 TutorialsSander Levert100% (1)
- 5 - Shariah Analysis of Bitcoin - SFF 2017 - Marjan Muhammad - 8 Nov 2017 (FINAL)Document37 pages5 - Shariah Analysis of Bitcoin - SFF 2017 - Marjan Muhammad - 8 Nov 2017 (FINAL)rabtay100% (1)
- FMM Class 11Document15 pagesFMM Class 11YashshviNo ratings yet
- MBA4013 Management of Banking andDocument7 pagesMBA4013 Management of Banking andNurfaiqah AmniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Math20912 9 HandoutDocument9 pagesLecture Math20912 9 HandoutRimpy SondhNo ratings yet
- Grocery Inquiry Report - July 2008Document543 pagesGrocery Inquiry Report - July 2008Abdikadir AbdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Exchange RateDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - Exchange RateJuan Pablo León BenítezNo ratings yet
- Option Trading Tactics With Oliver Velez PDFDocument62 pagesOption Trading Tactics With Oliver Velez PDFhansondrew100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Overview of Se - MKTDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - Overview of Se - MKTHoàng Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Week-2-Chapter-3-Financial-Build-A-Mode LDocument7 pagesWeek-2-Chapter-3-Financial-Build-A-Mode LCrusty GirlNo ratings yet
- Dow Theory: Rail IndustrialDocument13 pagesDow Theory: Rail Industrialapi-281256227No ratings yet
- Secondary MarketDocument26 pagesSecondary MarketMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Futures and Options On Foreign Exchange: International Financial ManagementDocument50 pagesFutures and Options On Foreign Exchange: International Financial ManagementvijiNo ratings yet
- Rail Vikas Nigam Limited - Red Herring Prospectus PDFDocument523 pagesRail Vikas Nigam Limited - Red Herring Prospectus PDFChinuNo ratings yet
- Robi Axiata Limited: (As Per Prospectus)Document1 pageRobi Axiata Limited: (As Per Prospectus)রাফসান হোসেন রাব্বীNo ratings yet
- Quant Factsheet January 2023Document40 pagesQuant Factsheet January 2023DevendraNo ratings yet
- Commerce Sem 5Document3 pagesCommerce Sem 5Isha MoreNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return PDFDocument14 pagesRisk and Return PDFluv silenceNo ratings yet
- 9 Pdf&rendition 1.Document5 pages9 Pdf&rendition 1.boygenius21_39464798No ratings yet
- 53338bos42717 cp12Document71 pages53338bos42717 cp12VarunNo ratings yet
- Factsheet CNX High Beta IndexDocument2 pagesFactsheet CNX High Beta IndexSandeep BennurNo ratings yet
Cs1a05c Sol
Cs1a05c Sol
Uploaded by
Chau Minnie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views5 pages1. The document contains multiple word problems involving the calculation of profit percentages and loss percentages for various business scenarios.
2. It provides the calculations to determine whether there was a profit or loss in each scenario based on the selling price and cost price.
3. The problems are solved by setting up equations involving the cost price, selling price, and profit/loss amounts and calculating the relevant percentages.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document contains multiple word problems involving the calculation of profit percentages and loss percentages for various business scenarios.
2. It provides the calculations to determine whether there was a profit or loss in each scenario based on the selling price and cost price.
3. The problems are solved by setting up equations involving the cost price, selling price, and profit/loss amounts and calculating the relevant percentages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views5 pagesCs1a05c Sol
Cs1a05c Sol
Uploaded by
Chau Minnie1. The document contains multiple word problems involving the calculation of profit percentages and loss percentages for various business scenarios.
2. It provides the calculations to determine whether there was a profit or loss in each scenario based on the selling price and cost price.
3. The problems are solved by setting up equations involving the cost price, selling price, and profit/loss amounts and calculating the relevant percentages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
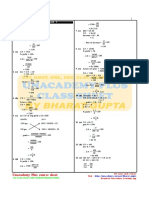
Consolidation Exercise 5C (P.5.
9)
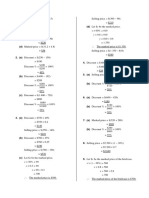
1. (b) ∵ $360 < $420 3. (a) Loss = $(50 − 42)
i.e. Selling price < cost price = $8
∴ There is a loss. Loss % =
$8
$50
× 100%
Loss = $(420 − 360)
= 16%
= $60
(c) ∵ $4 900 > $1 700
(b) Loss = $(300 − 180)
= $120
i.e. Selling price > cost price
∴
$120
There is a profit. Loss % = × 100%
$300
Profit = $(4 900 − 1 700) = 40%
= $3 200 (c) Selling price = $(65 − 39)
(d) ∵ $56.5 > $38 = $26
i.e. Selling price > cost price $39
∴ There is a profit.
Loss % =
$65
× 100%
Profit = $(56.5 − 38) = 60%
= $18.5 (d) Cost price = $(7.2 + 16.8)
(e) ∵ $840 < $960 = $24
$16.8
i.e. Selling price < cost price Loss % = × 100%
∴ There is a loss.
$24
= 70%
Loss = $(960 − 840)
$400
= $120 4. Profit % = × 100%
$640
= 62.5%
2. (a) Profit = $(90 − 60)
= $30
5. Loss = $(4 500 − 3 150)
$30
Profit % = × 100% = $1 350
$60
$1 350
= 50% Loss % = × 100%
$4 500
(b) Profit = $(350 − 280)
= 30%
= $70
$70
Profit % = × 100% 6. (a) Loss = $(360 − 180)
$280
= 25% = $180
$180
(c) Selling price = $(400 + 72) Loss % = × 100%
$360
= $472
= 50%
$72
Profit % = × 100% (b) Profit = $(360 − 180)
$400
= 18% = $180
$180
(d) Cost price = $(12.8 − 0.3) Profit % = × 100%
$180
= $12.5
= 100%
$0.3
Profit % = × 100%
$12.5
= 2.4% 7. Cost price = $(1 890 + 360)
= $2 250
$360 = $1 890
Loss % = × 100%
$2 250
= 16%
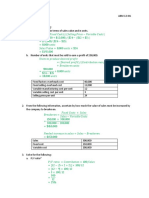
15. (a) Selling price = $x × (1 − 15%)
= $x × 0.85
$800
8. (a) Loss % = × 100% = $0.85x
$3 200
(b) 0.85x = 187
= 25%
x = 187 ÷ 0.85
(b) Cost price = $(3 200 + 800)
= 220
= $4 000
$800
∴ The cost price was $220.
Loss % = × 100%
$4 000
= 20% 16. Let $m be the cost price.
m × (1 + 80%) = 216
9. Profit = $45 000 × 28% m × 1.8 = 216
= $45 000 × 0.28 m = 216 ÷ 1.8
= $12 600 = 120
∴ Nancy paid $120 for the book.
10. Loss = $2 400 × 5%
= $2 400 × 0.05 17. (a) Total income = $15 × 8 × 5
= $120 = $600
11. Selling price = $770 × (1 − 30%) (b) Profit = $(600 − 300)
= $770 × 0.7 = $300
= $539 $300
Profit % = × 100%
$300
= 100%
12. Selling price = $9 600 × (1 + 2.5%)
= $9 600 × 1.025 18. (a) Total selling price = $(20 × 12 − 40) × 3.6
= $9 840
= $(240 − 40) × 3.6
= $200 × 3.6
13. Let $x be the cost price. = $720
x × 120% = 840 $30
Loss % = × 100%
x × 1.2 = 840 $(720 + 30)
x = 840 ÷ 1.2 = 4%
= 700 (b) Cost price of each dozen apples
∴ The cost price is $700. =
$(720 + 30)
20
= $37.5
14. Let $y be the cost price.
y × 30% = 810 19. Total cost price = $(2 500 + 3 900)
0.3y = 810 = $6 400
y = 810 ÷ 0.3 Loss = $(6 400 − 4 800)
= 2 700 = $1 600
∴ The cost price is $2 700. Loss % =
$1 600
× 100%
$6 400
Selling price = $(2 700 − 810)
= 25%
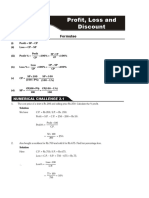
24. Let $x be the cost price of each T-shirt.
20. Paul’s profit = $(620 − 500) 8 000x × 60% = 288 000
= $120 8 000x × 0.6 = 288 000
$120 4 800x = 288 000
Paul’s profit % = × 100%
$500 x = 288 000 ÷ 4 800
= 24% = 60
Jason’s profit = $(1 620 − 1 500) ∴ The cost price of each T-shirt is $60.
= $120
$120 25. Let $y be the cost price of the bag of tea leaves.
Jason’s profit % = × 100%
$1 500 y × (1 + 40%) = 5 600
= 8%
∵
1.4y = 5 600
24% ≠ 8%
∴
y = 5 600 ÷ 1.4
They didn’t make the same profit per cent.
= 4 000
∴ The cost price of the bag of tea leaves is
21. (a) Selling price = $80 000 × (1 + 15%) $4 000.
= $80 000 × 1.15 Profit = $(5 600 − 4 000)
= $92 000 = $1 600
(b) Profit = $(92 000 + 2 400 − 80 000)
= $14 400 26. (a) Let $k be the cost price of a bottle of tea.
$14 400
Profit % = × 100% k × (1 + 75%) = 9.8
$80 000
1.75k = 9.8
= 18%
k = 9.8 ÷ 1.75
= 5.6
22. (a) Selling price = $30 000 × (1 − 20%)
= $30 000 × 0.8
∴ The cost price of a bottle of tea is $5.6.
(b) Special price = $[3 × 5.6 × (1 + 25%)]
= $24 000
= $16.8 × 1.25
(b) Loss = $(24 000 − 21 600)
= $21
= $2 400
$2 400
Loss % = × 100%
$24 000 27. (a) Let $m be the cost price of the vase.
= 10% m × (1 − 40%) = 32 400
m × 0.6 = 32 400
23. (a) Profit = $600 000 × 20% m = 32 400 ÷ 0.6
= $120 000 = 54 000
(b) Let $x be the cost price. ∴ The cost price of the vase is $54 000.
x × (1 + 20%) = 600 000 (b) Loss = $(54 000 − 48 600)
1.2x = 600 000 = $5 400
x = 600 000 ÷ 1.2 $5 400
Loss % = × 100%
= 500 000 $54 000
∴ The cost price is $500 000. = 10%
Profit = $(600 000 − 500 000) ∵ 10% < 15%
= $100 000 ∴ The deal can be made.
m × (1 + 10%) = 792
28. Let $n be the cost price of the sofa. m × 1.1 = 792
n × (1 + 50%) = 3 600 m = 792 ÷ 1.1
n × 1.5 = 3 600 = 720
n = 3 600 ÷ 1.5 ∴ The cost price of the jacket is $720.
= 2 400
∴
(b) Original profit = $(792 − 720)
The cost price of the sofa is $2 400.
= $72
New profit = $(3 600 + 240 − 2 400)
New profit = $72 × (1 + 25%)
= $1 440
= $72 × 1.25
$1 440
New profit % = × 100% = $90
$2 400
New selling price = $(720 + 90)
= 60%
= $810
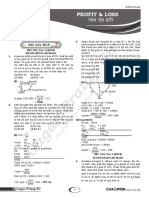
29. Let $x be the cost price of the oven.
x × (1 − 4%) = 1 200 32. (a) Total cost price = $(9 000 + 6 000)
x × 0.96 = 1 200 = $15 000
x = 1 200 ÷ 0.96 Total selling price
= 1 250 = $[9 000 × (1 − 10%) + 6 000 × (1 + 20%)]
∴ The cost price of the oven is $1 250. = $(9 000 × 0.9 + 6 000 × 1.2)
(a) Loss = $(1 250 − 950) = $15 300
= $300 ∵ $15 300 > $15 000
$300 i.e. Total selling price > total cost price
Loss % =
$1 250
× 100%
∴ He made a profit.
= 24% (b) Overall profit %
(b) Selling price = $1 250 × (1 + 36%) $(15 300 − 15 000)
= × 100%
$15 000
= $1 250 × 1.36
$300
= $1 700 = × 100%
$15 000
= 2%
30. (a) Let $y be the selling price of the camera.
y × 60% = 1 800 33. (a) Total selling price
y × 0.6 = 1 800 = $[ 15 × 200 × (1 + 40%) +
y = 1 800 ÷ 0.6 4 × 1 000 × (1 + 5%)]
= 3 000
∴
= $(3 000 × 1.4 + 4 000 × 1.05)
The selling price of the camera is
= $8 400
$3 000.
(b) Total cost price = $(15 × 200 + 4 × 1 000)
(b) Cost price = $(3 000 + 1 800) = $7 000
= $4 800 Overall profit = $(8 400 − 7 000)
$1 800
Loss % = × 100% = $1 400
$4 800
$1 400
= 37.5% Overall profit % = × 100%
$7 000
= 20%
31. (a) Let $m be the cost price of the jacket.
34. (a) Let $x be the cost price of the kettle. = $28
x × (1 − 60%) = 180 $28
Overall loss % = × 100%
x × 0.4 = 180 $700
= 4%
x = 180 ÷ 0.4
= 450
∴ The cost price of the kettle is $450.
Let $y be the cost price of the coffee
machine.
y × (1 + 60%) = 2 160
y × 1.6 = 2 160
y = 2 160 ÷ 1.6
= 1 350
∴ The cost price of the coffee machine is
$1 350.
(b) Total cost price = $(450 + 1 350)
= $1 800
Total selling price = $(180 + 2 160)
= $2 340
∵ $1 800 < $2 340
i.e. Total cost price < total selling price
∴ He made a profit.
(c) Overall profit = $(2 340 − 1 800)
= $540
$540
Overall profit % = × 100%
$1 800
= 30%
35. (a) Number of bags of chips = 180 ÷ 6
= 30
Profit = $(35 × 30 − 700)
= $350
$350
Profit % = × 100%
$700
= 50%
(b) (i) Total selling price
= $[35 × 12 + 14 × (30 − 12)]
= $672
∵ $700 > $672
i.e. Total cost price > total selling price
∴ He made a loss.
(ii) Overall loss = $(700 − 672)
You might also like
- Forage JP Morgan Ib Task 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesForage JP Morgan Ib Task 2 SolutionRohit Vasave100% (1)
- MphasisDocument12 pagesMphasisVenkyNo ratings yet
- Asahi Case SolutionDocument1 pageAsahi Case SolutionAmit BiswalNo ratings yet
- The Bond Market in GhanaDocument12 pagesThe Bond Market in GhanaJohn Kennedy Akotia100% (3)
- Chapter 10 Stock Valuation A Second LookDocument33 pagesChapter 10 Stock Valuation A Second LookshuNo ratings yet
- CS1A05D SolDocument4 pagesCS1A05D SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Cs1a05b SolDocument5 pagesCs1a05b SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Fin SolutionsDocument9 pagesFin SolutionsTania Kalila HernandezNo ratings yet
- MARY GRACE PANGANIBAN - 027 Cost-Volume-Profit and Business Scalability Exercise 2Document17 pagesMARY GRACE PANGANIBAN - 027 Cost-Volume-Profit and Business Scalability Exercise 2Mary Grace PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Profit - Loss - Discount - P3-10 2Document8 pagesProfit - Loss - Discount - P3-10 2buck albinoNo ratings yet
- P5Maths Week 33Document4 pagesP5Maths Week 33အင္တာေနရွင္နယ္ေက်ာင္းမ်ား၏ ေမးခြန္လႊာဘာသာစံုျဖန္႕ခ်ီေရးNo ratings yet
- AkuntansiDocument2 pagesAkuntansiDenny CandraNo ratings yet
- Business Decisions Using Cost Behaviour: Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument11 pagesBusiness Decisions Using Cost Behaviour: Cost-Volume-Profit Analysismishabmoomin1524No ratings yet
- Chapter-12-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWDocument13 pagesChapter-12-Worked-Solutions Year 11 Standard Maths Cambridge NSWallthehalls666No ratings yet
- $70 - $40 $30 $30 /times X 15,000 $450,000 $450,000 - $540,000 - $90,000 (Loss)Document9 pages$70 - $40 $30 $30 /times X 15,000 $450,000 $450,000 - $540,000 - $90,000 (Loss)longphungspNo ratings yet
- OJM DSETraining Percentages I e SolDocument7 pagesOJM DSETraining Percentages I e Sol林俊佑No ratings yet
- India's First Absolutely Free Online Bank Exam Coaching WWW - BANKKING.INDocument4 pagesIndia's First Absolutely Free Online Bank Exam Coaching WWW - BANKKING.INJagannath JagguNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss - SOLS - Concept 31 To 40Document11 pagesProfit & Loss - SOLS - Concept 31 To 40xyzNo ratings yet
- Derivations: - ComputationalDocument3 pagesDerivations: - ComputationalEdiane QuilezaNo ratings yet
- CVP Test SolutionDocument2 pagesCVP Test Solutionahsaankhan2811No ratings yet
- Module 3 - BreakevenDocument2 pagesModule 3 - BreakevenBern Austin EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Assgment 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Agung Rizal / 2201827622Document10 pagesAssgment 1 (Chapter 1-4) : Agung Rizal / 2201827622Agung Rizal DewantoroNo ratings yet
- Tugas Chapter 4 - Salsabila Putri Sabrina - 1181002040 - Corfin 42Document5 pagesTugas Chapter 4 - Salsabila Putri Sabrina - 1181002040 - Corfin 42SalspsNo ratings yet
- Managerial Accounting: Assignment: 02Document5 pagesManagerial Accounting: Assignment: 02Asma HatamNo ratings yet
- Ma 13.2.2023Document7 pagesMa 13.2.2023Chit Myo HlaingNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss SolutionDocument20 pagesProfit & Loss SolutionAnkit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Biaya Variabe Harga Jual $ 7 $ 20Document6 pagesBiaya Variabe Harga Jual $ 7 $ 20Shelley TaniaNo ratings yet
- Ratio - Proportion - PercentDocument31 pagesRatio - Proportion - PercentRiyadh HaiderNo ratings yet
- Assignment 02 - SolutionDocument4 pagesAssignment 02 - SolutionSuman Paul ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Phase 7 PresentationDocument13 pagesPhase 7 PresentationAnton BernardoNo ratings yet
- Profit Loss and DiscountDocument20 pagesProfit Loss and DiscountLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Ebook Contemporary Business Mathematics Canadian 10Th Edition Hummelbrunner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument57 pagesEbook Contemporary Business Mathematics Canadian 10Th Edition Hummelbrunner Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFkevinfryecqiozexkjy100% (13)
- Case Problem 3Document5 pagesCase Problem 3Marjorie PonceNo ratings yet
- Profit & Loss Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan Pratap SirDocument13 pagesProfit & Loss Last 5 Year Best Questions by Gagan Pratap Siramit kumarNo ratings yet
- Contribution Margin: Enter The Appropriate Amount in The Shaded Cells in Columns C and EDocument16 pagesContribution Margin: Enter The Appropriate Amount in The Shaded Cells in Columns C and EJames BagsicNo ratings yet
- Ejercicio 1 - VPN: Tmar Vs VNPDocument2 pagesEjercicio 1 - VPN: Tmar Vs VNPRaul Quispe PedrazaNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis SolutionsDocument6 pagesCVP Analysis SolutionsAlaine Milka GosycoNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Jawaban Soal 1: Asst. Bagus, Elvira, & YogiDocument4 pagesJawaban Jawaban Soal 1: Asst. Bagus, Elvira, & YogiRavanellyNo ratings yet
- Markup On COGSDocument16 pagesMarkup On COGSJack LiuNo ratings yet
- Solution PricingDocument3 pagesSolution PricingDella BianchiNo ratings yet
- Derivations: - ComputationalDocument4 pagesDerivations: - ComputationalHAKUNA MATATANo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss Sheet SolutionDocument23 pagesProfit and Loss Sheet SolutionSahil GuptaNo ratings yet
- AO2 Worksheet 4 Absolute and Relative Changes AnswersDocument3 pagesAO2 Worksheet 4 Absolute and Relative Changes AnswersBhavishka ValraniNo ratings yet
- True or False: Basadre, Jessa G. Bsa 3 Yr Managerial Accounting Assignment No. 2 - CVP RelationshipDocument3 pagesTrue or False: Basadre, Jessa G. Bsa 3 Yr Managerial Accounting Assignment No. 2 - CVP RelationshipJessa BasadreNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 SolutionDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 Solutionsissy.he.7No ratings yet
- Tutorial No. 3 - CVP Analysis Answer Section: 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: A 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: A 5Document3 pagesTutorial No. 3 - CVP Analysis Answer Section: 1. ANS: B 2. ANS: A 3. ANS: B 4. ANS: A 5Hu-Ann KeymistNo ratings yet
- Profit, Loss and DiscountDocument5 pagesProfit, Loss and DiscountswagatamparidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ExcelDocument42 pagesChapter 13 ExcelMd Al Alif Hossain 2121155630No ratings yet
- FIE400E 2016 Spring SolutionsDocument4 pagesFIE400E 2016 Spring SolutionsSander Von Porat BaugeNo ratings yet
- Student Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument7 pagesStudent Solutions Chapter 8 Cost Volume Profit AnalysisAasir NaQvi100% (1)
- F2 - MOCK A - ANSWERS NowDocument11 pagesF2 - MOCK A - ANSWERS NowRoronoa ZoroNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 ManKeu - Bella Fatma P - 2011070511Document4 pagesTugas 4 ManKeu - Bella Fatma P - 2011070511Bella FatmaNo ratings yet
- D E+ D X RD+ E D+ E X : Return Richard ExpectDocument5 pagesD E+ D X RD+ E D+ E X : Return Richard ExpectSu Suan TanNo ratings yet
- AKL Chapter9Document3 pagesAKL Chapter9Farrell DmNo ratings yet
- Percentage CDSDocument8 pagesPercentage CDSgladiatortorqueNo ratings yet
- Cs1a05a SolDocument6 pagesCs1a05a SolChau MinnieNo ratings yet
- Profit and Loss 2023Document40 pagesProfit and Loss 2023netra7222No ratings yet
- Profit and Loss NewDocument34 pagesProfit and Loss NewPranjal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tugasan 6 Bab 6Document4 pagesTugasan 6 Bab 6azwan88No ratings yet
- Sol. Man. - Chapter 15 EpsDocument12 pagesSol. Man. - Chapter 15 Epsfinn mertensNo ratings yet
- Activity #6Document3 pagesActivity #6ScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Part 2Document47 pagesCorporate Finance Part 2sdfghjkNo ratings yet
- Hire Purchase (Part 2)Document7 pagesHire Purchase (Part 2)Kelly HibbertNo ratings yet
- Commercial Arithmetic (Solution) PDFDocument6 pagesCommercial Arithmetic (Solution) PDFagnelwaghelaNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- S&P CriteriaDocument57 pagesS&P CriteriaCairo AnubissNo ratings yet
- Solved 1 Herm S International Was A Family Owned Business For Many YearsDocument1 pageSolved 1 Herm S International Was A Family Owned Business For Many YearsJusta MukiriNo ratings yet
- Sonic R. SystemDocument2 pagesSonic R. Systemthang 1No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Academic Year 2011-2012 TutorialsDocument21 pagesCorporate Finance Academic Year 2011-2012 TutorialsSander Levert100% (1)
- 5 - Shariah Analysis of Bitcoin - SFF 2017 - Marjan Muhammad - 8 Nov 2017 (FINAL)Document37 pages5 - Shariah Analysis of Bitcoin - SFF 2017 - Marjan Muhammad - 8 Nov 2017 (FINAL)rabtay100% (1)
- FMM Class 11Document15 pagesFMM Class 11YashshviNo ratings yet
- MBA4013 Management of Banking andDocument7 pagesMBA4013 Management of Banking andNurfaiqah AmniNo ratings yet
- Lecture Math20912 9 HandoutDocument9 pagesLecture Math20912 9 HandoutRimpy SondhNo ratings yet
- Grocery Inquiry Report - July 2008Document543 pagesGrocery Inquiry Report - July 2008Abdikadir AbdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Exchange RateDocument20 pagesChapter 4 - Exchange RateJuan Pablo León BenítezNo ratings yet
- Option Trading Tactics With Oliver Velez PDFDocument62 pagesOption Trading Tactics With Oliver Velez PDFhansondrew100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Overview of Se - MKTDocument23 pagesChapter 1 - Overview of Se - MKTHoàng Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Week-2-Chapter-3-Financial-Build-A-Mode LDocument7 pagesWeek-2-Chapter-3-Financial-Build-A-Mode LCrusty GirlNo ratings yet
- Dow Theory: Rail IndustrialDocument13 pagesDow Theory: Rail Industrialapi-281256227No ratings yet
- Secondary MarketDocument26 pagesSecondary MarketMohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Futures and Options On Foreign Exchange: International Financial ManagementDocument50 pagesFutures and Options On Foreign Exchange: International Financial ManagementvijiNo ratings yet
- Rail Vikas Nigam Limited - Red Herring Prospectus PDFDocument523 pagesRail Vikas Nigam Limited - Red Herring Prospectus PDFChinuNo ratings yet
- Robi Axiata Limited: (As Per Prospectus)Document1 pageRobi Axiata Limited: (As Per Prospectus)রাফসান হোসেন রাব্বীNo ratings yet
- Quant Factsheet January 2023Document40 pagesQuant Factsheet January 2023DevendraNo ratings yet
- Commerce Sem 5Document3 pagesCommerce Sem 5Isha MoreNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return PDFDocument14 pagesRisk and Return PDFluv silenceNo ratings yet
- 9 Pdf&rendition 1.Document5 pages9 Pdf&rendition 1.boygenius21_39464798No ratings yet
- 53338bos42717 cp12Document71 pages53338bos42717 cp12VarunNo ratings yet
- Factsheet CNX High Beta IndexDocument2 pagesFactsheet CNX High Beta IndexSandeep BennurNo ratings yet