Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
Uploaded by
Karthikeyan LakshmananCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Build An Atom Worksheet-AnswersDocument3 pagesBuild An Atom Worksheet-AnswersBilly JoeNo ratings yet
- .Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018Document28 pages.Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018gno667533No ratings yet
- Pages From Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Mind MapDocument1 pagePages From Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Mind MapYuvarajNo ratings yet
- 2 Periodic Table: O SCIDocument2 pages2 Periodic Table: O SCISam KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdDocument17 pages2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdSai Shri Harshit DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Revision NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Revision NotesSREE GANESHNo ratings yet
- Trends & PeriodicityDocument32 pagesTrends & PeriodicityDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- CH 2. Periodic Classification (Chem +1)Document36 pagesCH 2. Periodic Classification (Chem +1)Shafin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties ResonanceDocument28 pagesPeriodic Properties ResonancePrince Singh100% (1)
- Chapter-3 Periodic ClassificationDocument12 pagesChapter-3 Periodic ClassificationMayank MishraNo ratings yet
- Why Chemistry?: Molecule AtomsDocument6 pagesWhy Chemistry?: Molecule Atomsvinnie0905No ratings yet
- Periodic Table & PeriodicityDocument22 pagesPeriodic Table & PeriodicityMike hunkNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Chapter - 03Document13 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Chapter - 03Yadhu Krishnan rNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument20 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Unacademy AtomicStructure MicroDocument43 pagesUnacademy AtomicStructure MicroHritik Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- KT Term Classification of ElementsDocument6 pagesKT Term Classification of ElementsAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument23 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- CHEM SPM Development of The Periodic Table UpdatedDocument11 pagesCHEM SPM Development of The Periodic Table Updatedangie0812No ratings yet
- Periodic Table IPEDocument15 pagesPeriodic Table IPEAdiChemAdi100% (4)
- Physical ChemistryDocument69 pagesPhysical Chemistrym.waseemNo ratings yet
- Peroidic Table NotesDocument52 pagesPeroidic Table Notesnil kumarNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument60 pagesPeriodic TableaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 08-1Document34 pagesNotes Chapter 08-1Biruk BtNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsBharatNo ratings yet
- 13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFDocument20 pages13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFP. E. I. AcademicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateTonald DrumpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Classification FinalsDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Classification FinalsSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table DPPDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table DPPUMA JoshiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserOblizinNo ratings yet
- 8 X Y 16 X 8 Y: 3. Compounds Are Composed of Atoms of More Than OneDocument10 pages8 X Y 16 X 8 Y: 3. Compounds Are Composed of Atoms of More Than OneSamantha DumagpiNo ratings yet
- Periodic P. (F)Document23 pagesPeriodic P. (F)Agriye KambojNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- 1 PeriodicDocument4 pages1 PeriodicAneeshTandonNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsDocument35 pagesPeriodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsJared MutindaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Development O F Peri O Dic Ta B L EDocument26 pagesPeriodic Table: Development O F Peri O Dic Ta B L Edevli falduNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument26 pagesPeriodic TableRethikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument1 pageAtomic Theory TimelineIsabella LeónNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Document51 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Abhishek NNo ratings yet
- Basics of Chemistry 2024Document49 pagesBasics of Chemistry 2024SP DevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Structure of Matter PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 The Structure of Matter PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument23 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNaisha JNo ratings yet
- Short - Notes - Trend in Periodic Table - pdf-42Document9 pagesShort - Notes - Trend in Periodic Table - pdf-42ICSE GURUNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification AakashDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification AakashAsmitNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 2 PDFDocument18 pagesPeriodic Table 2 PDFDiksha Bansal100% (1)
- Periodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFDocument37 pagesPeriodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFpallab mukherjee100% (1)
- Periodic Classification of Elements NotesDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Notesluubkhan037No ratings yet
- Peroidic Table NotesDocument53 pagesPeroidic Table NotesmonikaNo ratings yet
- New Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDocument12 pagesNew Classification of Elements and PeriodicityValli Priya KNo ratings yet
- 1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFDocument60 pages1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFAce PTNo ratings yet
- PeriodicitySession 09 (Last)Document105 pagesPeriodicitySession 09 (Last)Bhvya SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Periodic Classification of ElementskunalNo ratings yet
- Workbook 1 Structure of The AtomDocument16 pagesWorkbook 1 Structure of The AtomAbologyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument3 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elementsvivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Early Classification of Elements NotesDocument5 pagesEarly Classification of Elements NotesosasosasyeyNo ratings yet
- 1st Term - Chapter One - 2nd Secondary - ChemistryDocument64 pages1st Term - Chapter One - 2nd Secondary - ChemistryMahmoud LotfyNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Matter RadiologyDocument5 pagesThe Structure of Matter RadiologyRozlyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumFrom EverandPhysics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- quantum chemistry electron: ρ is the electron τ the kinetic energy density. D is expected to be small inDocument2 pagesquantum chemistry electron: ρ is the electron τ the kinetic energy density. D is expected to be small inZie BeaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity QsDocument15 pagesPeriodicity QsJack SmitNo ratings yet
- Lasers - Principles: (Laser Pointer - This Photo Was Provided by Physics World)Document6 pagesLasers - Principles: (Laser Pointer - This Photo Was Provided by Physics World)narendra.it12No ratings yet
- Raman Spectroscopy For Quality Assessment of Meat and FishDocument13 pagesRaman Spectroscopy For Quality Assessment of Meat and FishYashaswini NagarajNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Samuel Franco Palacio - Bill Nye - Atoms and Molecules WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Samuel Franco Palacio - Bill Nye - Atoms and Molecules Worksheetapi-438118584No ratings yet
- Lab1 SpectrophotometryDocument25 pagesLab1 SpectrophotometrynqwrgnbzhqNo ratings yet
- Vanga BhasmaDocument1 pageVanga Bhasmadrsa2No ratings yet
- DPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Document3 pagesDPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Scanning Electron MicrosDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Scanning Electron Microsalireza221369No ratings yet
- Ftir PDFDocument40 pagesFtir PDFWahyuni EkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesChapter 06 Lecture NotesNuradin AderNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument25 pagesAtomic Structuremichaeldevid7890No ratings yet
- Diagram Tanabe PoncoDocument10 pagesDiagram Tanabe PoncounsaniaNo ratings yet
- Quest Book Icse 9 ChemistryDocument24 pagesQuest Book Icse 9 ChemistryjapneetfirstNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 KN Sharma Atomic Structure (ClassicalDocument18 pagesChapter 4 KN Sharma Atomic Structure (Classicalajay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Unit 2: Solid State PhysicsDocument52 pagesUnit 2 Unit 2: Solid State Physicssgab cANo ratings yet
- Molecular SpectrosDocument51 pagesMolecular SpectrosYttrium PrasadNo ratings yet
- The ElementsDocument4 pagesThe ElementsHaider AliNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument30 pagesNotessureshmohanty.sailNo ratings yet
- Electronics: MTE 121 MTE 106Document28 pagesElectronics: MTE 121 MTE 106mustafa osmanNo ratings yet
- MCQs Biochemical TechniquesDocument15 pagesMCQs Biochemical TechniquesAmna Fatima GhayoorNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR REACTIONS - Lec2Document9 pagesNUCLEAR REACTIONS - Lec2jon alexNo ratings yet
- Optical Atomic SpectrosDocument61 pagesOptical Atomic SpectrosAristia MonequeNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesDocument18 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesGeorge MoshiashviliNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal WritingDocument27 pagesResearch Proposal WritingsanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic Tableritchelle ruerasNo ratings yet
- The History of The AtomDocument5 pagesThe History of The AtomEmilyAranas100% (2)
- Atom A Closer LookDocument34 pagesAtom A Closer LookJohn Nash100% (1)
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
Uploaded by
Karthikeyan LakshmananCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
A3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Min
Uploaded by
Karthikeyan LakshmananCopyright:
Available Formats
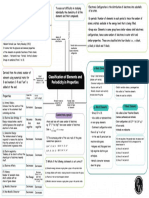
X Cl
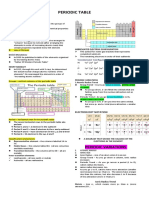
GENESIS OF CLASSIFICATION
Atomic
Mass
35.5
DOBEREINER'S TRIAD (1892) LAW OF OCTAVES (1865)
LOTHER MEYER MENDELEEV PERIODIC LAW
Middle element of each triads had J. Alexander Newlands arranged
Atomic an atomic weight about hay way Lothumeya found a periodc Properties of elements are a
the elements in increasing order
Number
17
between the atomic weight of of their atomic weight, every 8th pattern by plotting physical periodic function of their atomic
other two and also properties element had similar properties to properties like atomic volume, B.P weights.
Element Name between the other two.
Eg. (Li, Na, K), (Ca, Sr, Ba).
1st element.
Eg. Li resembles with Na.
and M.P against atomic weight. Mendeleev periodic elements
Eka-Aluminium as Gallium. CHLORINE
NEED FOR CLASSIFICATION MODERN PERIODIC TABLE
• Modern Periodic Law: Physical and chemical properties of
To make it easier to understand the chemistry of all elements are periodic functions of their atomic number.
the elements and their compounds separately. • Father of modern periodic table: Dimitri Mendeleev
• 7 Horizontal rows: Periods; 18 Vertical columns: Groups
TRENDS IN PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Properties Group Period 2
1 3
(a) Atomic Radius
Distance between the Atomic
nucleus and the outermost Increases Decreases
shell containing electron.
(b) Electron Gain Enthalpy
Energy released when an
electron is added to the Decreases Increases
valance shell of an isolated
Gaseous Atom.
(c) Ionisation Energy
Amount of energy required
to remove an electron from
an isolated gaseous atom.
Decreases Increases
7 4 NOMENCLATURE OF ELEMENTS (ATOMIC NO. > 100)
(d) Electronegativity Digit Name Abbreviation
Tendency of an element to Derived from Atomic
Decreases Increases
attract shared electrons number of Element 0 nil n
towards itself. 1 un u
using numerical roots
5
2 bi b
6
(e) Metallic Character Increases Decreases for 0 and number 1-9 3 tri t
nad 'ium' is added at the 4 quad a
(f) None-Metallic Character Decreases Decreases end of name 5 pent p
6 hex n
7 sept s
8 oct o
9 enn e
TRENDS IN CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
STUDY OF PERIODIC TABLE
• The valance of representative elements is generally CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
equal to valence electron or (8-valence electrons).
•
•
Anomalous behaviour of 2nd period elements is due to
their small size, large charge/radius radio, high
AND S-Block Elements
(i) Electronic configuration: ns 1-2
P-Block Elements
(i) Electronic configuration: ns2np1-6
(ii) Consist of Group 1 (alkali metals) (ii) Consist of Group 1 to 18
pERIODICITY IN pROPERTIES
electronegativity and only 4 valence orbitals.
(iii) and also group 2 (alkali (iii) Also known as Representative
• Diagonal relationship: Li and Be is more similar to Mg as earth metals) or main group Elements.
Al respectively.
• The normal oxides formed by the element on wxtreme
D-Block Elements F-Block Elements
left is most basic (E.g. Na2O) and formed by elements on
(i) Electronic configuration: (i) Electronic configuration:
extreme right is most acidic (E.g. Cl2O7).
(n-1)d1-10ns0-2 (n-2)f1-14 (n-1)d0-1ns2
• Oxides of centre Elements are amphoteric (Eg. Al2O3) or (ii) Consist of Group 3 to 12 (z = 58-71) (z = 90-103)
neutral (Eg. N2O) (iii) also known as transition (ii) Consist of Lanthanoids and Actinoids
Elements (iii) also known as Inner
Amphoteric oxides are basic in acidic medium and vice transition Elements
versa.
•
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/neetplus
You might also like
- Build An Atom Worksheet-AnswersDocument3 pagesBuild An Atom Worksheet-AnswersBilly JoeNo ratings yet
- .Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018Document28 pages.Trashed 1702966745 1700327617018gno667533No ratings yet
- Pages From Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Mind MapDocument1 pagePages From Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Mind MapYuvarajNo ratings yet
- 2 Periodic Table: O SCIDocument2 pages2 Periodic Table: O SCISam KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdDocument17 pages2 - PERIODIC TABLE SYNOPSIS-59-75.pmdSai Shri Harshit DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Revision NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 3 - Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Revision NotesSREE GANESHNo ratings yet
- Trends & PeriodicityDocument32 pagesTrends & PeriodicityDelano PeteNo ratings yet
- CH 2. Periodic Classification (Chem +1)Document36 pagesCH 2. Periodic Classification (Chem +1)Shafin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties ResonanceDocument28 pagesPeriodic Properties ResonancePrince Singh100% (1)
- Chapter-3 Periodic ClassificationDocument12 pagesChapter-3 Periodic ClassificationMayank MishraNo ratings yet
- Why Chemistry?: Molecule AtomsDocument6 pagesWhy Chemistry?: Molecule Atomsvinnie0905No ratings yet
- Periodic Table & PeriodicityDocument22 pagesPeriodic Table & PeriodicityMike hunkNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Chapter - 03Document13 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties: Chapter - 03Yadhu Krishnan rNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument20 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesELVIS BoradNo ratings yet
- Unacademy AtomicStructure MicroDocument43 pagesUnacademy AtomicStructure MicroHritik Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- KT Term Classification of ElementsDocument6 pagesKT Term Classification of ElementsAnkit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument23 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Revision Notes Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesPriyanshuNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument19 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsARNAV DEYNo ratings yet
- CHEM SPM Development of The Periodic Table UpdatedDocument11 pagesCHEM SPM Development of The Periodic Table Updatedangie0812No ratings yet
- Periodic Table IPEDocument15 pagesPeriodic Table IPEAdiChemAdi100% (4)
- Physical ChemistryDocument69 pagesPhysical Chemistrym.waseemNo ratings yet
- Peroidic Table NotesDocument52 pagesPeroidic Table Notesnil kumarNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument60 pagesPeriodic TableaieyinHengNo ratings yet
- Notes Chapter 08-1Document34 pagesNotes Chapter 08-1Biruk BtNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument17 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsBharatNo ratings yet
- 13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFDocument20 pages13.periodic Table and Periodicity PDFP. E. I. AcademicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Periodic Table and Atomic Structure: Name: - Class: - DateTonald DrumpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Classification FinalsDocument13 pagesChapter 5 Classification FinalsSarveshyaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table DPPDocument19 pagesPeriodic Table DPPUMA JoshiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table Knowledge OrganiserOblizinNo ratings yet
- 8 X Y 16 X 8 Y: 3. Compounds Are Composed of Atoms of More Than OneDocument10 pages8 X Y 16 X 8 Y: 3. Compounds Are Composed of Atoms of More Than OneSamantha DumagpiNo ratings yet
- Periodic P. (F)Document23 pagesPeriodic P. (F)Agriye KambojNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFDocument10 pagesChapter 2 S - Block Elements PDFHong Hong WongNo ratings yet
- 1 PeriodicDocument4 pages1 PeriodicAneeshTandonNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsDocument35 pagesPeriodic Trends: Elemental Properties and PatternsJared MutindaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Development O F Peri O Dic Ta B L EDocument26 pagesPeriodic Table: Development O F Peri O Dic Ta B L Edevli falduNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument26 pagesPeriodic TableRethikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory TimelineDocument1 pageAtomic Theory TimelineIsabella LeónNo ratings yet
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Document51 pagesClassification of Elements & Periodic Table Part-A (Periodic Table)Abhishek NNo ratings yet
- Basics of Chemistry 2024Document49 pagesBasics of Chemistry 2024SP DevNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Structure of Matter PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 The Structure of Matter PDFLee DonghyuckNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument23 pagesPeriodic Classification of ElementsNaisha JNo ratings yet
- Short - Notes - Trend in Periodic Table - pdf-42Document9 pagesShort - Notes - Trend in Periodic Table - pdf-42ICSE GURUNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification AakashDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification AakashAsmitNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 2 PDFDocument18 pagesPeriodic Table 2 PDFDiksha Bansal100% (1)
- Periodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFDocument37 pagesPeriodicity - of - Elements - Prince Sir PDFpallab mukherjee100% (1)
- Periodic Classification of Elements NotesDocument6 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elements Notesluubkhan037No ratings yet
- Peroidic Table NotesDocument53 pagesPeroidic Table NotesmonikaNo ratings yet
- New Classification of Elements and PeriodicityDocument12 pagesNew Classification of Elements and PeriodicityValli Priya KNo ratings yet
- 1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFDocument60 pages1819 Physical and Inorganic Summary PDFAce PTNo ratings yet
- PeriodicitySession 09 (Last)Document105 pagesPeriodicitySession 09 (Last)Bhvya SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Periodic Classification of ElementskunalNo ratings yet
- Workbook 1 Structure of The AtomDocument16 pagesWorkbook 1 Structure of The AtomAbologyNo ratings yet
- Periodic Classification of ElementsDocument3 pagesPeriodic Classification of Elementsvivek_theeasywaysNo ratings yet
- Early Classification of Elements NotesDocument5 pagesEarly Classification of Elements NotesosasosasyeyNo ratings yet
- 1st Term - Chapter One - 2nd Secondary - ChemistryDocument64 pages1st Term - Chapter One - 2nd Secondary - ChemistryMahmoud LotfyNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Matter RadiologyDocument5 pagesThe Structure of Matter RadiologyRozlyn Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumFrom EverandPhysics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic MediumRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- quantum chemistry electron: ρ is the electron τ the kinetic energy density. D is expected to be small inDocument2 pagesquantum chemistry electron: ρ is the electron τ the kinetic energy density. D is expected to be small inZie BeaNo ratings yet
- Periodicity QsDocument15 pagesPeriodicity QsJack SmitNo ratings yet
- Lasers - Principles: (Laser Pointer - This Photo Was Provided by Physics World)Document6 pagesLasers - Principles: (Laser Pointer - This Photo Was Provided by Physics World)narendra.it12No ratings yet
- Raman Spectroscopy For Quality Assessment of Meat and FishDocument13 pagesRaman Spectroscopy For Quality Assessment of Meat and FishYashaswini NagarajNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Samuel Franco Palacio - Bill Nye - Atoms and Molecules WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Samuel Franco Palacio - Bill Nye - Atoms and Molecules Worksheetapi-438118584No ratings yet
- Lab1 SpectrophotometryDocument25 pagesLab1 SpectrophotometrynqwrgnbzhqNo ratings yet
- Vanga BhasmaDocument1 pageVanga Bhasmadrsa2No ratings yet
- DPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Document3 pagesDPP 25C Goc Mesomeric 1686185793412Aditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Scanning Electron MicrosDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Scanning Electron Microsalireza221369No ratings yet
- Ftir PDFDocument40 pagesFtir PDFWahyuni EkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06 Lecture NotesDocument57 pagesChapter 06 Lecture NotesNuradin AderNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument25 pagesAtomic Structuremichaeldevid7890No ratings yet
- Diagram Tanabe PoncoDocument10 pagesDiagram Tanabe PoncounsaniaNo ratings yet
- Quest Book Icse 9 ChemistryDocument24 pagesQuest Book Icse 9 ChemistryjapneetfirstNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 KN Sharma Atomic Structure (ClassicalDocument18 pagesChapter 4 KN Sharma Atomic Structure (Classicalajay mauryaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Unit 2: Solid State PhysicsDocument52 pagesUnit 2 Unit 2: Solid State Physicssgab cANo ratings yet
- Molecular SpectrosDocument51 pagesMolecular SpectrosYttrium PrasadNo ratings yet
- The ElementsDocument4 pagesThe ElementsHaider AliNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument30 pagesNotessureshmohanty.sailNo ratings yet
- Electronics: MTE 121 MTE 106Document28 pagesElectronics: MTE 121 MTE 106mustafa osmanNo ratings yet
- MCQs Biochemical TechniquesDocument15 pagesMCQs Biochemical TechniquesAmna Fatima GhayoorNo ratings yet
- NUCLEAR REACTIONS - Lec2Document9 pagesNUCLEAR REACTIONS - Lec2jon alexNo ratings yet
- Optical Atomic SpectrosDocument61 pagesOptical Atomic SpectrosAristia MonequeNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesDocument18 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesGeorge MoshiashviliNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal WritingDocument27 pagesResearch Proposal WritingsanelisofuturemoyoNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic Tableritchelle ruerasNo ratings yet
- The History of The AtomDocument5 pagesThe History of The AtomEmilyAranas100% (2)
- Atom A Closer LookDocument34 pagesAtom A Closer LookJohn Nash100% (1)