Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 2 Reteach: Geometric Proof
Lesson 2 Reteach: Geometric Proof
Uploaded by
INES MONTSERRAT VILLA VILLAOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 2 Reteach: Geometric Proof
Lesson 2 Reteach: Geometric Proof
Uploaded by
INES MONTSERRAT VILLA VILLACopyright:
Available Formats
NAME _____________________________________________ DATE __________________ PERIOD _________
Lesson 2 Reteach
Geometric Proof
The Proof Process
Step 1 List all given information.
Step 2 State what is to be proven.
Step 3 Create an argument by forming a chain of statements linking the given information to what you
are trying to prove.
Step 4 Justify each statement with a reason.
Step 5 State what it is you have proven.
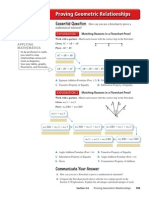
Example 1
Use the figure to complete the two-column proof to show that
if m∠1 + m∠2 = 180 and m∠1 + m∠4 = 180, then m∠2 = m∠4.
Given: m∠1 + m∠2 = 180 and m∠1 + m∠4 = 180 1
Prove: m∠2 = m∠4 2 4
3
Statements Reasons
a. m∠1 + m∠2 = 180; m∠1 + m∠4 = 180 Given
b. m∠1 + m∠2 = m∠1 + m∠4 Substitution
c. m∠2 = m∠4 Subtraction Property
of Equality
Proofs can also be written as paragraph proofs which involve writing a paragraph to
Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
explain why a conjecture is true. Each statement of the proof must still be supported by a
definition, algebraic property, or theorem.
Exercises b
Use the figure to complete the reasons in the two-column a
proof to show that if lines b and c are parallel and cut by c
1 2
transversal a, then ∠1 is congruent to ∠3.
3
Statements Reasons
a. Lines b and c are parallel
and cut by transversal a
b. m∠1 = m∠2
c. m∠2 = m∠3
d. m∠1 = m∠3
Course 3 • Chapter 5 Triangles and the Pythagorean Theorem 75
You might also like
- 4L80EDocument156 pages4L80EJames Winsor100% (14)
- Mathematics: Quarter IV-Week 1 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Document8 pagesMathematics: Quarter IV-Week 1 Learning Activity Sheets (LAS)Florame Algarme Melano100% (1)
- Component Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Parts List: ThermostatDocument101 pagesComponent Maintenance Manual With Illustrated Parts List: ThermostatGoutam SahaNo ratings yet
- Geometry 2.5Document6 pagesGeometry 2.5Carolina HuertasNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Writing A Proof (Both Direct and Indirect) - M8Ge-Iii-J-1Document14 pagesMathematics: Writing A Proof (Both Direct and Indirect) - M8Ge-Iii-J-1samantha buban100% (1)
- Extra Practice 1Document4 pagesExtra Practice 1John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Q3 - Week6 - Proving Right Triangles Theorem (DAY 3-4)Document20 pagesQ3 - Week6 - Proving Right Triangles Theorem (DAY 3-4)Athan JonathanNo ratings yet
- Textbook 2 6Document10 pagesTextbook 2 6api-293865618No ratings yet
- 2-8 Proving Angle RelationshipsDocument17 pages2-8 Proving Angle RelationshipsKia AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Casilac - Final ExamDocument3 pagesCasilac - Final Examrotshen casilacNo ratings yet
- Geometry Section 2 7Document11 pagesGeometry Section 2 7api-262621710100% (1)
- Pythagorean Triples Criteria BDocument3 pagesPythagorean Triples Criteria B2uh847No ratings yet
- Module 2 Lesson 4Document5 pagesModule 2 Lesson 4Raquel NavarezNo ratings yet
- Proof Involving Trigonometric FunctionsDocument7 pagesProof Involving Trigonometric FunctionsIm rich lolNo ratings yet
- Textbook 2 5Document6 pagesTextbook 2 5api-29386561833% (3)
- Different Methods of Proof Objectives: HSA Geometry Activities Activity 5Document57 pagesDifferent Methods of Proof Objectives: HSA Geometry Activities Activity 5Leomill Mendiola II0% (1)
- Laws of Exponent: Grade 9Document10 pagesLaws of Exponent: Grade 9Bernaliza CaserNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ExerciseDocument3 pagesChapter 5 ExerciseJurey VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Emelyn C. Sabadlab Noah Justine C. SaysonDocument6 pagesEmelyn C. Sabadlab Noah Justine C. SaysonRalph Rexor Macarayan BantuganNo ratings yet
- 3.2B Parallel Lines and Angles 1Document2 pages3.2B Parallel Lines and Angles 1Mahisa AgniNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - MathematicsDocument21 pagesGrade 8 - MathematicsChristeus Von SujeroNo ratings yet
- 5.2 - Polynomial Functions 5.3 - Multiplication of Polynomials Textbook: Intermediate Algebra Aufmann and Lockwood 9E AimDocument4 pages5.2 - Polynomial Functions 5.3 - Multiplication of Polynomials Textbook: Intermediate Algebra Aufmann and Lockwood 9E AimCAROL_X1No ratings yet
- 1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulateDocument9 pages1.𝐴𝑅≅𝑆𝑅, 𝑊𝑅≅𝐷𝑅 1. Given 2. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 and ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 are vertical angles 2. Definition of vertical angles 3. ∠𝑊𝑅𝐴 ≅ ∠𝐷𝑅𝑆 3. Vertical Angle Theorem 4. Δ𝑅𝐴𝑊≅Δ𝑅𝑆𝐷 4. SAS Congruence PostulatenowilNo ratings yet
- Geometry Section 2 6Document10 pagesGeometry Section 2 6api-262621710No ratings yet
- Law of ExponentDocument8 pagesLaw of ExponentKyrie IrvingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - (Part 2) Reasoning and Proofs 02.11.21Document27 pagesLesson 2 - (Part 2) Reasoning and Proofs 02.11.21Rosalyn CalapitcheNo ratings yet
- Evaluating and Simplifying Algebraic ExpressionsDocument35 pagesEvaluating and Simplifying Algebraic ExpressionsMay CNo ratings yet
- Notes 2.5 2.6 Reasoning in Algebra and Geometry ProofsDocument4 pagesNotes 2.5 2.6 Reasoning in Algebra and Geometry ProofslowkeyonipadNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Geometric ProofsDocument3 pages2.6 Geometric ProofsKielvin MosquitoNo ratings yet
- Writing ProofsDocument10 pagesWriting ProofskiahjessieNo ratings yet
- 1 MATH 9 - M1 - Lesson 1A Final Qa DIGITAL 1Document10 pages1 MATH 9 - M1 - Lesson 1A Final Qa DIGITAL 1Timothy ArtusNo ratings yet
- Fractions II and Decimals: Mixed NumbersDocument6 pagesFractions II and Decimals: Mixed NumbersMuralee VeeramalaiNo ratings yet
- Proving Triangles Are Congruent: Notes Examples Worksheet Answer KeyDocument6 pagesProving Triangles Are Congruent: Notes Examples Worksheet Answer KeyYouth AllenNo ratings yet
- Table of SpecificationDocument3 pagesTable of SpecificationLeafy SamaNo ratings yet
- Q2W7L2 Reasoning With Geometry Part 1Document37 pagesQ2W7L2 Reasoning With Geometry Part 1joanna reignNo ratings yet
- CH 4 Review 1617 SWDocument4 pagesCH 4 Review 1617 SWabc123asdNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions PDFDocument2 pages2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions PDFShela RamosNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions PDFDocument2 pages2.1 Simplifying Algebraic Expressions PDFShela RamosNo ratings yet
- Learning Module in Math 8: How To Join The VSMART?Document7 pagesLearning Module in Math 8: How To Join The VSMART?Marvelous VillafaniaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Geometry ProofsDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Geometry ProofsNaufalzzNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Week 3Document12 pagesMath 7 Week 3Rey Mark RamosNo ratings yet
- Methods of Proof EqualityDocument5 pagesMethods of Proof Equalitygmshorr100% (1)
- Math PresentationDocument42 pagesMath Presentationhsjg5s75mvNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Blank Lessons PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 2 Blank Lessons PDFUthman BadmusNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1 Week 15 - With AnswerDocument4 pagesQ4 Week 1 Week 15 - With AnswerKizha JuanilloNo ratings yet
- 2-9 Study Guide and Intervention: Proving Lines ParallelDocument2 pages2-9 Study Guide and Intervention: Proving Lines ParallelReham Mohamed Ahmed NoufalNo ratings yet
- Module Week 1 2 Bus MathDocument13 pagesModule Week 1 2 Bus MathCamille CornelioNo ratings yet
- LeaP Math G9 Week 6 7 Q3Document10 pagesLeaP Math G9 Week 6 7 Q3fritzhervinalfonso7No ratings yet
- Axiomatic System PDF Two PDFDocument30 pagesAxiomatic System PDF Two PDFRusherNo ratings yet
- ML Geometry 2-6 Proving Statements About AnglesDocument8 pagesML Geometry 2-6 Proving Statements About Anglesmadhuraju778797No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Operations On Functions - DIVISIONDocument21 pagesLesson 7 Operations On Functions - DIVISIONLaurence SagumNo ratings yet
- S1ExamSupplement KeyDocument4 pagesS1ExamSupplement KeyDwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- Mat102 Week 5 AnnotatedDocument4 pagesMat102 Week 5 Annotatedsanjanabulusu07No ratings yet
- Geometry Q2M1 Wk1and2 SY21.22Document9 pagesGeometry Q2M1 Wk1and2 SY21.22IMCOOL LUAGNo ratings yet
- Starting Algebraic Proofs 2 ColumnDocument10 pagesStarting Algebraic Proofs 2 Columnapi-265481804100% (1)
- Maths T P 1 2014 - Pahang (Q)Document4 pagesMaths T P 1 2014 - Pahang (Q)mk.foo123No ratings yet
- Warm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Holt Geometry Holt Mcdougal GeometryDocument23 pagesWarm Up Lesson Presentation Lesson Quiz: Holt Mcdougal Geometry Holt Geometry Holt Mcdougal Geometryrmm0415No ratings yet
- Reading 4: ProofsDocument8 pagesReading 4: ProofsBharat NarumanchiNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus Q3 W6Document5 pagesBasic Calculus Q3 W6Rufina RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Algebraic Formulaenaza9775100% (1)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 7No ratings yet
- Iso 7966 1993Document11 pagesIso 7966 1993Sci KelayNo ratings yet
- PC3000 6 PDFDocument8 pagesPC3000 6 PDFRocioSanchezCalderonNo ratings yet
- Sharp Edge OrificeDocument2 pagesSharp Edge Orificeleo.caguimbal6433No ratings yet
- Resistances, Voltages and Current in CircuitsDocument21 pagesResistances, Voltages and Current in CircuitsHisyamAl-MuhammadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: TidesDocument40 pagesChapter 9: TidesCarol GirottoNo ratings yet
- Virtual Synchronous Control For Grid-Connected DFIG-Based Wind TurbinesDocument13 pagesVirtual Synchronous Control For Grid-Connected DFIG-Based Wind TurbinesWILLIAM FERNEY RINCON MELONo ratings yet
- Revit Programming For Beginners: Dan Mapes Senior BIM Coordinator/Developer at ME EngineersDocument17 pagesRevit Programming For Beginners: Dan Mapes Senior BIM Coordinator/Developer at ME EngineersjeanNo ratings yet
- The Dino GameDocument1 pageThe Dino Game296 004 Aditya ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Nepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Document52 pagesNepal National Building Code: Draft Final NBC 205: 2012Sudan ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Anggaran ElektronikaDocument12 pagesAnggaran ElektronikaSeptian IswanjayaNo ratings yet
- SK 135 SR 3Document327 pagesSK 135 SR 3Trung Cuong100% (1)
- 3 Generations of Human RightsDocument1 page3 Generations of Human RightsDzenan HakalovicNo ratings yet
- Proposal Nur Azizah 2315059 R1Document34 pagesProposal Nur Azizah 2315059 R1zizieNo ratings yet
- Earth Dams Foundation & Earth Material InvestigationDocument111 pagesEarth Dams Foundation & Earth Material Investigationmustafurade1No ratings yet
- Module 5 in Eed 114: ReviewDocument6 pagesModule 5 in Eed 114: ReviewYvi BenrayNo ratings yet
- Benstones Instruments IMPAQ ELITE 4 CanalesDocument8 pagesBenstones Instruments IMPAQ ELITE 4 CanalesmauriciojjNo ratings yet
- Dry Concentrator IntroductionDocument6 pagesDry Concentrator Introductionmanuel3021No ratings yet
- Lab6 Phase Locked LoopsDocument20 pagesLab6 Phase Locked Loopsuitce2011No ratings yet
- Manas Arora 3 Year - B Roll No. 3 Vastu Kala AcademyDocument12 pagesManas Arora 3 Year - B Roll No. 3 Vastu Kala AcademyManasAroraNo ratings yet
- Brac Bank LimitedDocument1 pageBrac Bank LimitedMd Mojibar RahmanNo ratings yet
- Start With Why SummaryDocument6 pagesStart With Why SummaryAnurag100% (1)
- 2127 - Mahatma Gandhi Missions College of Engineering, Hingoli RD, NandedDocument8 pages2127 - Mahatma Gandhi Missions College of Engineering, Hingoli RD, NandedAjit DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- 10 1039@d0mh00081gDocument20 pages10 1039@d0mh00081gHuấn BùiNo ratings yet
- OB Mid-Term AssignmentDocument9 pagesOB Mid-Term AssignmentAshish PatelNo ratings yet
- Reasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorDocument2 pagesReasons For Diminishing Returns To A FactorRobert AyalaNo ratings yet
- ACDC - Lucina - DatasheetDocument1 pageACDC - Lucina - Datasheetwincad_sgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Part 1Document13 pagesLecture 1 Part 1Marianna KlosNo ratings yet