Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Key Notes
Key Notes
Uploaded by
John Linard Aningga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesThe document provides an overview of various math topics including:
- Working with fractions such as finding the lowest common denominator and cross-multiplying
- Factoring techniques like greatest common factor, difference of squares, and grouping
- Converting between decimals and fractions
- Properties of real numbers, sets, and absolute value
- Working with radicals and their properties
- Rational exponents and special product formulas
- Graphing linear functions from an equation
- Transforming functions through shifts, reflections, stretches, and shrinks
- Solving mixture problems using linear equations
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of various math topics including:
- Working with fractions such as finding the lowest common denominator and cross-multiplying
- Factoring techniques like greatest common factor, difference of squares, and grouping
- Converting between decimals and fractions
- Properties of real numbers, sets, and absolute value
- Working with radicals and their properties
- Rational exponents and special product formulas
- Graphing linear functions from an equation
- Transforming functions through shifts, reflections, stretches, and shrinks
- Solving mixture problems using linear equations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views3 pagesKey Notes
Key Notes
Uploaded by
John Linard AninggaThe document provides an overview of various math topics including:
- Working with fractions such as finding the lowest common denominator and cross-multiplying
- Factoring techniques like greatest common factor, difference of squares, and grouping
- Converting between decimals and fractions
- Properties of real numbers, sets, and absolute value
- Working with radicals and their properties
- Rational exponents and special product formulas
- Graphing linear functions from an equation
- Transforming functions through shifts, reflections, stretches, and shrinks
- Solving mixture problems using linear equations
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
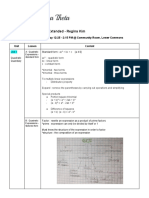
CH P Compound Fractions
* Get the LCD of denominators from fractions of both numerator
Fractions and denominator.
- Find LCD
- Cross-multiply Factoring
- Conversions GCF
- Factor out AC Method (Note of non-zero leading coeff.)
Special Factoring Formulas
Decimal to Fraction - A^2 – B^2 = (A + B)(A - B)
* Non-repeating: Multiply with 10^n, n being the amount of - A^2 + 2AB + B^2 = (A + B)^2
decimal. - A^2 – 2AB + B^2 = (A – B)^2
* Repeating: Multiply by powers of (10^n)x to isolate the repeating - A^3 – B^3 = (A – B)(A^2 + AB + B^2)
decimal, n being natural numbers, then subtract with another - A^3 + B^3 = (A + B)(A^2 – AB + B^2)
power of (10^n)x. Grouping (Grouped terms must have same ration with
other groups)
Properties of Real Numbers Completing-the-Square (Note of coeff. outside
1. Associative – Grouping parenthesis)
2. Commutative – Order Synthetic Division
3. Distributive – Distribution - Get possible zeros (c) as factor (x – c): Rational
Zeroes Theorem, p/q
Sets - Eliminate candidates via:
* Set = {Elements} o Remainder Theorem
* Element, Not element, Union, Intersection, Null set
o Descarte’s Rule of Signs
* Notations: Inset Builder Notations, Interval Notation
o Upper and Lower Bounds Theorem
Absolute Value: Complex Numbers
* |a| = +a (+), -a(-) - Complete Factorization Theorem
- Conjugate Zeroes Theorem
Radicals
Properties:
1. Multiplication: Can be combined in under 1 radical is
same index
2. Division: Can be separated or combined under 1 radical if
same index.
3. Multi-radical: Indexes can be multiplied to form single
radical.
4. If index is odd, retain the sign of radicand (+/-) on the
answer.
5. If index n is even, radicand is required to be positive, and
the result is in absolute value.
Rational Exponents
*Always factor first
* If radical denominator, multiply with conjugate (Take note of the
root or power of the conjugate)
Special Product Formulas
1. (A+B)(A-B) = (A-B)^2
2. (A+B)^2 = A^2 + 2AB + B^2
3. (A-B)^2 = A^2 – 2AB + B^2
4. (A+B)^3 = A^3 + 3A^2B + 3AB^2 + B^3
5. (A-B)^3 = A^3 – 3A^2B + 3AB^2 - B^3
Making Linear Model from Graph
1) Determine the slope – a
2) Determine y value when x = 0 – b
3) Insert at y = ax + b
Transformation of Functions
a) Vertical/Horizontal Shifts
d) Even and Odd Functions
b) Reflecting Graphs
c) Vertical/Horizontal Stretching and Shrinking of Graphs
MIXTURE PROBLEMS
1. P66
2. P70
7. P78
3. P72
8. P78
4. P72
5. P72
6. P72
You might also like
- Artificial Intelligence in Recruitment-Case StudyDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence in Recruitment-Case StudyAnmol Lama100% (3)
- MIR Contactless Terminal Kernel Specification 2.1Document128 pagesMIR Contactless Terminal Kernel Specification 2.1yoron liu100% (1)
- Basics of Supply Chain Management (BSCM) Practice Questions - APICS CPIMDocument17 pagesBasics of Supply Chain Management (BSCM) Practice Questions - APICS CPIMCertico100% (1)
- SM EU109 WPiO12 Service Manual 2018 03Document92 pagesSM EU109 WPiO12 Service Manual 2018 03Jose PereiraNo ratings yet
- Ext 10 Study Guide by ReginaDocument18 pagesExt 10 Study Guide by Reginaapi-459788815No ratings yet
- CET Sail Mathematics, Algebra (2023)Document22 pagesCET Sail Mathematics, Algebra (2023)Dahlia OjalesNo ratings yet
- Gen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherDocument2 pagesGen. Math Chapter 1 4 OtherMary Beth Ed MartelNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xii Maths Lab Manual Scert 20Document4 pagesHsslive Xii Maths Lab Manual Scert 20VictoryNo ratings yet
- Algebra II Reference: Completing The Square and Quadratics PolynomialsDocument2 pagesAlgebra II Reference: Completing The Square and Quadratics PolynomialsTim_CNo ratings yet
- EigenmathDocument50 pagesEigenmathJohnny Parrado100% (1)
- Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Chemical Engineering Cl603, Optimization Endsem, 27 April 2018Document3 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Bombay Chemical Engineering Cl603, Optimization Endsem, 27 April 2018Lakshay ChhajerNo ratings yet
- Mat Lab ObservationDocument25 pagesMat Lab Observationabinash ayyappanNo ratings yet
- Simultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesDocument8 pagesSimultaneous Equations, Indices, Surds, Logarithms: Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall Revision NotesVikas PatelNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 SOL Things To RememberDocument5 pagesAlgebra 2 SOL Things To RememberLois BurkeNo ratings yet
- AsdasfagfDocument10 pagesAsdasfagfPeach ParkNo ratings yet
- (Combined PDF) (Inverse Trigonometry - 4.0)Document184 pages(Combined PDF) (Inverse Trigonometry - 4.0)Sohan Krishna100% (1)
- Northview High School AB Calculus AP Prerequisites PacketDocument11 pagesNorthview High School AB Calculus AP Prerequisites PacketPradyun GREEN CELL VOLUNTEERNo ratings yet
- MAT120 Lab AssignmentDocument3 pagesMAT120 Lab Assignmentshudipto.siamNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document6 pagesLecture 3د. سعد قاسم الاجهزة الطبيةNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Math OverviewDocument7 pagesUnit 3 Math OverviewmicjenNo ratings yet
- A1. Algebra: A1.1. Operations On Algebraic ExpressionsDocument19 pagesA1. Algebra: A1.1. Operations On Algebraic ExpressionsKrystel Monica ManaloNo ratings yet
- Module2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsDocument5 pagesModule2 Multiplying and Dividing Rational ExpressionsJoe ALNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document5 pagesPart 3AshokNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasAmir MustakimNo ratings yet
- Using Proc IML: Statistical Computing Spring 2014Document50 pagesUsing Proc IML: Statistical Computing Spring 2014Anthy AnthyNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document4 pagesHomework 2Majid GhNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity 1 - Introduction To MATLAB (Part1)Document8 pagesLaboratory Activity 1 - Introduction To MATLAB (Part1)Nigel ArugayNo ratings yet
- FPM Formula Sheet 2Document13 pagesFPM Formula Sheet 2Yolo Gamer DudeNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Maths - Short Notes - Exam Winner - Allen SirDocument21 pagesClass 11 Maths - Short Notes - Exam Winner - Allen SirfarazainaraNo ratings yet
- Final Exam B - Spring 2021Document11 pagesFinal Exam B - Spring 2021eswarsai saiNo ratings yet
- Algebra FormulasDocument12 pagesAlgebra FormulasLuis Fernando De AlvarengaNo ratings yet
- Integrating Algebraic FractionsDocument8 pagesIntegrating Algebraic FractionsDark LordNo ratings yet
- Additional Mathematics SA2 Overall RevisDocument8 pagesAdditional Mathematics SA2 Overall RevisAnaya DonaldsonNo ratings yet
- Basic Operations in MATLAB:: Symbol OperationDocument6 pagesBasic Operations in MATLAB:: Symbol OperationKadiyam VijayNo ratings yet
- Q3 Mathematics Peer Tutoring: Students' Advisory BoardDocument93 pagesQ3 Mathematics Peer Tutoring: Students' Advisory BoardKiminiNo ratings yet
- Integer Exponents: A A A A ADocument5 pagesInteger Exponents: A A A A Achloe NavarroNo ratings yet
- Handouts of Maxima Software For Mathematics PracticalDocument5 pagesHandouts of Maxima Software For Mathematics PracticalUttam KhardeNo ratings yet
- Experiment - 1: Objective: To Implement General MATLAB Commands (General Purpose, Input/outputDocument30 pagesExperiment - 1: Objective: To Implement General MATLAB Commands (General Purpose, Input/outputNeelakantheswar KunkulaguntaNo ratings yet
- 8.indefinite IntegrationPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae SheetDocument6 pages8.indefinite IntegrationPROBLEM SOLVING TACTICSFormulae Sheetyodel23957No ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences MAT 120 Midterm Assignment SPRING 2021 SET: 14Document4 pagesDepartment of Mathematics and Natural Sciences MAT 120 Midterm Assignment SPRING 2021 SET: 14Life SummerNo ratings yet
- CNS - Unit 2Document29 pagesCNS - Unit 2alameenNo ratings yet
- HW 02 PDFDocument3 pagesHW 02 PDFQFTWNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFDocument9 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFkavinkumareceNo ratings yet
- Cat 1&2 - Sta 2204Document1 pageCat 1&2 - Sta 2204Lorna Makena KinyuaNo ratings yet
- IcmlDocument24 pagesIcmlAbhishek BansalNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesDocument17 pagesScheme of Work: Hrs Units Notes Examples ReferencesOluseye AkinNo ratings yet
- WS3 2 CorrDocument5 pagesWS3 2 CorrilianvegetaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper - Module 5: Definite IntegralDocument25 pagesLesson Proper - Module 5: Definite IntegralJack NapierNo ratings yet
- Add. Maths Form 4 Formula'sDocument16 pagesAdd. Maths Form 4 Formula'sArun JosephNo ratings yet
- Matrix Operations: dspmtrx3Document10 pagesMatrix Operations: dspmtrx3May Thet TunNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument12 pagesSeminar ReportFlorinNo ratings yet
- Updated-Numerical Solutions To CE ProblemsDocument24 pagesUpdated-Numerical Solutions To CE ProblemsPrincess MerryNo ratings yet
- m10111-1 2Document38 pagesm10111-1 2Jarrett LindseyNo ratings yet
- Matlab: Name:Mo Stafa Qasim TahrDocument16 pagesMatlab: Name:Mo Stafa Qasim TahrMostafa HamawandyNo ratings yet
- 12 Spec Test 1 2021 Marking KeyDocument9 pages12 Spec Test 1 2021 Marking KeyJeff TNo ratings yet
- CS 294-73 Software Engineering For Scientific Computing Lecture 8: Unstructured Grids and Sparse MatricesDocument25 pagesCS 294-73 Software Engineering For Scientific Computing Lecture 8: Unstructured Grids and Sparse MatricesEdmund ZinNo ratings yet
- 9.1 Intro To C9 and QuadraticsDocument4 pages9.1 Intro To C9 and QuadraticsChunesh BhallaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Linear Algebra University of Edinburgh Past Paper 2020-2021Document4 pagesNumerical Linear Algebra University of Edinburgh Past Paper 2020-2021Jonathan SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Algo VC Lecture24Document32 pagesAlgo VC Lecture24M HUZAIFANo ratings yet
- Intro To Graphing: Coordinate Plane: Plot The PointsDocument47 pagesIntro To Graphing: Coordinate Plane: Plot The PointsTheodore JonesNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Year at A GlanceDocument4 pagesYear at A GlanceJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - Methodology - CE4-3 - Aningga-Manalo-San Jose-VillafuerteDocument12 pagesCh3 - Methodology - CE4-3 - Aningga-Manalo-San Jose-VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Death BedDocument2 pagesDeath BedJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Application FormDocument6 pagesApplication FormJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Sample CADsDocument4 pagesSample CADsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- ReactionsDocument6 pagesReactionsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- APA Format: A Quick GuideDocument4 pagesAPA Format: A Quick GuideJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- F-0349-15 - Information SheetDocument2 pagesF-0349-15 - Information SheetJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test B PlansDocument5 pagesTest B PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test A PlansDocument8 pagesTest A PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Examples Dynamic Magnification FactorDocument4 pagesUnit 3 - Examples Dynamic Magnification FactorJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Test D PlansDocument6 pagesTest D PlansJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Matrix of Related LiteratureDocument19 pagesMatrix of Related LiteratureJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- 2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteDocument2 pages2TitleProposal - CE-4-3 - Aningga, Manalo, San Jose, VillafuerteJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- RrlmatirxDocument4 pagesRrlmatirxJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- CE Laws, Codes and EthicsDocument30 pagesCE Laws, Codes and EthicsJohn Linard AninggaNo ratings yet
- Comfort Zone of Air, For Most of UsDocument4 pagesComfort Zone of Air, For Most of UsshoaibNo ratings yet
- Lawrence Miriti Ndeke CVDocument3 pagesLawrence Miriti Ndeke CVlawrenceNo ratings yet
- Patient Care Management System DissertationDocument87 pagesPatient Care Management System DissertationShazy AmyNo ratings yet
- Summary About NetworkingDocument7 pagesSummary About Networkingdon dali100% (1)
- CPWE - CIP SecurityDocument125 pagesCPWE - CIP SecurityGreenOlive ControlsNo ratings yet
- Just Hit A Button Fashion 4.0 Designers As Cyborgs Experimenting and Designing With Generative AlgorithmsDocument11 pagesJust Hit A Button Fashion 4.0 Designers As Cyborgs Experimenting and Designing With Generative AlgorithmsanouknatalyawillyNo ratings yet
- Exponential Smoothing Example:: Single Years Quarter Period Sales Avg A (T) /avgDocument6 pagesExponential Smoothing Example:: Single Years Quarter Period Sales Avg A (T) /avgchikomborero maranduNo ratings yet
- Rotary Jhonson.Document2 pagesRotary Jhonson.Yonas MuluNo ratings yet
- DIGSI 5 Details - Control and Topology - V1.0 - en-USDocument23 pagesDIGSI 5 Details - Control and Topology - V1.0 - en-USKevin Luis Perez QuirozNo ratings yet
- Office of The Sangguniang Kabataan Municipal Federation Quarantine House Tour VlogDocument2 pagesOffice of The Sangguniang Kabataan Municipal Federation Quarantine House Tour VlogCessNo ratings yet
- (Object Oriented Programming) : CCS0023LDocument6 pages(Object Oriented Programming) : CCS0023LRhea KimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Cyber EthicsDocument44 pagesLesson 4 Cyber EthicsGina May DaulNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis World CupDocument13 pagesData Analysis World CupwhitespaceuseNo ratings yet
- 18MIS7020 - Lab 2Document8 pages18MIS7020 - Lab 2Abhinav GNo ratings yet
- NGL1 V1 Sec 7Document203 pagesNGL1 V1 Sec 7varatharajan g rNo ratings yet
- Lisette Lopez: Work ExperienceDocument1 pageLisette Lopez: Work ExperienceLisette LopezNo ratings yet
- Resensi Novel KilovegramDocument1,727 pagesResensi Novel KilovegramMutiara ArumNo ratings yet
- HW User Manual (CZNEWTON)Document14 pagesHW User Manual (CZNEWTON)PETER YINGNo ratings yet
- Sánchez - Modelado Termodinámico de Ciclos Avanzados para Propulsión de Alta VelocidadDocument97 pagesSánchez - Modelado Termodinámico de Ciclos Avanzados para Propulsión de Alta VelocidadSaraNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Extension Agr 355Document12 pagesAgricultural Extension Agr 355Eliza Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- IOT, Sumaiya KhanDocument22 pagesIOT, Sumaiya Khanshashank kumarNo ratings yet
- ISTQB CTAL TTA v4 - 0 Sample Exam Answers Set ADocument32 pagesISTQB CTAL TTA v4 - 0 Sample Exam Answers Set AAnand AzhagarNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic Characteristics Analysis of Rotor Blade Based On ANSYSDocument11 pagesThe Dynamic Characteristics Analysis of Rotor Blade Based On ANSYSFrancisco HidalgoNo ratings yet
- AIX Training-D1P1Document39 pagesAIX Training-D1P1Akang Zaenal MasterMamayukeroNo ratings yet
- Harn Frequently Asked Questions (HarnFAQ) (Archive, 19-Sep-2005)Document17 pagesHarn Frequently Asked Questions (HarnFAQ) (Archive, 19-Sep-2005)D.T. Wilson50% (2)
- enDocument70 pagesenRegistr Registr93% (14)