Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geeth Ews
Geeth Ews
Uploaded by
GEETH SREETHAMCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- GATE Questions On MOSFET, CMOS & Introduction To VLSI (1987 Till Date)Document15 pagesGATE Questions On MOSFET, CMOS & Introduction To VLSI (1987 Till Date)APNo ratings yet
- CMTS U2Document14 pagesCMTS U2rubu131813No ratings yet
- PARTS THAT BUILD UP A System UnitDocument64 pagesPARTS THAT BUILD UP A System UnitAwali, Eliazer A.No ratings yet
- Workshop 20technolog 01.1Document7 pagesWorkshop 20technolog 01.1Akshat KulhariaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing NC II Computer Parts and Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesComputer Systems Servicing NC II Computer Parts and Their Functionsracel orpiadaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- Summary Report in TRDocument9 pagesSummary Report in TREllie KimNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- Unit - 3. Science: 1. Information TechnologyDocument12 pagesUnit - 3. Science: 1. Information TechnologyRobert B. WeideNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop Job 1Document19 pagesComputer Workshop Job 1ayushkumar77447No ratings yet
- 22CSP-102 - Workshop Technology Lab ManualDocument63 pages22CSP-102 - Workshop Technology Lab ManualMehal KumarNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PartsDocument4 pagesMotherboard PartsabelNo ratings yet
- What Is Computers?Document6 pagesWhat Is Computers?Flores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodDocument7 pagesPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunNo ratings yet
- Write About Computer PartsDocument12 pagesWrite About Computer PartsThenaNo ratings yet
- Computer PartsDocument32 pagesComputer PartsSasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Document82 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Pastor Roy Onyancha CyberNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4Document12 pagesExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring SystemsDocument47 pagesInstalling and Configuring SystemsDonna Fe De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument22 pagesComputer Hardwareprinceisrael332No ratings yet
- CP and I AssigenmentDocument59 pagesCP and I Assigenmentfagixa3491No ratings yet
- 02 Itc 2K22-26Document20 pages02 Itc 2K22-26M IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocument7 pagesMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Richard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Document8 pagesRichard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Richard Anthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDocument12 pagesComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaNo ratings yet
- CSS Quarterly Exam 1Document18 pagesCSS Quarterly Exam 1seph bronNo ratings yet
- CHTDocument45 pagesCHTRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsDocument33 pagesMGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsTesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument42 pagesIntroduction To ComputersClark DomingoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan50% (2)
- Understanding Computer Hardware and PeripheralsDocument58 pagesUnderstanding Computer Hardware and Peripheralsligasan.cjNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationDocument138 pagesComputer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationSayyan Shaikh100% (2)
- Puter DocketsDocument58 pagesPuter DocketsMd ZakariaNo ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Document25 pagesLesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Archie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- S FDWDocument16 pagesS FDWSuyash PatilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing Jhs1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Computing Jhs1josephbliss04No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Structure of Modern ComputerDocument10 pagesUnit - I Structure of Modern ComputerxsaaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument5 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionnominnanaaespasolNo ratings yet
- Is The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerDocument5 pagesIs The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerAlfredo DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.1-3 Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripherals Parts of A Desktop ComputerDocument10 pagesInformation Sheet 1.1-3 Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripherals Parts of A Desktop ComputerManuelo VangieNo ratings yet
- Computer ICTDocument20 pagesComputer ICTmobilelegendshelpcenter2022No ratings yet
- Roney CBLMDocument17 pagesRoney CBLMAdonis Abalos PradoNo ratings yet
- Lab 02 - EEDDocument18 pagesLab 02 - EEDAhmad MusabNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1Document106 pagesCycle 1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Global Institutes of Management & Emerging Technologies: Department of CSE Lab Manual of Data Communication (DC)Document38 pagesGlobal Institutes of Management & Emerging Technologies: Department of CSE Lab Manual of Data Communication (DC)Gagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- (M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computer - CapistranoDocument14 pages(M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computer - CapistranoRedd CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesComputer HardwareEhnan J LamitaNo ratings yet
- System Unit and Their FunctionsDocument30 pagesSystem Unit and Their Functionslex jhonNo ratings yet
- CSS Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesCSS Lesson Planirene cadizNo ratings yet
- Gilas PC MaintenanceDocument97 pagesGilas PC MaintenanceEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- (M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal ComputerDocument14 pages(M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computerchristianmendoza2004No ratings yet
- Hardware and NetworkingDocument6 pagesHardware and NetworkingdurailanNo ratings yet
- Comp. Maint Instal, Maint, and Config. Week 1 and 2Document21 pagesComp. Maint Instal, Maint, and Config. Week 1 and 2Emperor'l BillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1widiefreeNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument48 pagesMotherboardAce BorresNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Injection Molding Process Control of Servo-Hydraulic SystemDocument11 pagesApplied Sciences: Injection Molding Process Control of Servo-Hydraulic SystemTrung Kiên LêNo ratings yet
- 1-Attachment 1 Oversea Projects Experience ListDocument2 pages1-Attachment 1 Oversea Projects Experience Listhua tianNo ratings yet
- rfx75 Install Guide Cobra 29Document3 pagesrfx75 Install Guide Cobra 29Geraldrum Zyzcom HdzNo ratings yet
- JMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB LayoutDocument1 pageJMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB LayoutRenan Franzon GoettenNo ratings yet
- H.V.A.C.-R. Service TechnicianDocument2 pagesH.V.A.C.-R. Service Technicianapi-121390582No ratings yet
- Tail CompensationDocument4 pagesTail Compensationjammy700No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Ecosys FS-1750 Ecosys FS-3750Document222 pagesService Manual: Ecosys FS-1750 Ecosys FS-3750Ali OuchnNo ratings yet
- Alc3251 CGDocument1 pageAlc3251 CGAhmadNo ratings yet
- Octava Micro User Manual - NEW - 17 PDFDocument1 pageOctava Micro User Manual - NEW - 17 PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Vibration Measurement - Selecting and Using PickupsDocument62 pagesChapter 3: Vibration Measurement - Selecting and Using PickupsAndrey AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Gs26Clx LBP Compressor R404A/R507 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralDocument2 pagesGs26Clx LBP Compressor R404A/R507 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralmustafaNo ratings yet
- BREADBOARDING - TinkercadDocument2 pagesBREADBOARDING - TinkercadJustin NievaNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Automotive Terms 2Document519 pagesDictionary of Automotive Terms 2hahahaaNo ratings yet
- Service Man CHDocument287 pagesService Man CHAdan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Video Display DevicesDocument66 pagesVideo Display DevicesshabanaNo ratings yet
- GCE O/L ICT Source01Document5 pagesGCE O/L ICT Source01Mohamaad SihatthNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 1 QPDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 1 QPnssNo ratings yet
- Field-Circuit Co-Simulation of The Marx Generator: April 2015Document6 pagesField-Circuit Co-Simulation of The Marx Generator: April 2015KhyatiChavdaNo ratings yet
- SB Series: DC Magnetic ContactorsDocument3 pagesSB Series: DC Magnetic ContactorsAkmalNo ratings yet
- Form Pin TKDocument1 pageForm Pin TKnguyenlongquan2212No ratings yet
- Remote Releasing Module (RRM) InstallationDocument4 pagesRemote Releasing Module (RRM) InstallationIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- JHJHJHJH MergedDocument48 pagesJHJHJHJH Mergedhabaga1835No ratings yet
- Gaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2Document14 pagesGaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2api-581695353No ratings yet
- 1ETM (Extracted Timing Models) Basics - VLSI ConceptsDocument3 pages1ETM (Extracted Timing Models) Basics - VLSI ConceptsSudheer Gangisetty0% (1)
- Schematic Diagrams: XV-N210B, XV-N212S, XV-N310B, XV-N312SDocument10 pagesSchematic Diagrams: XV-N210B, XV-N212S, XV-N310B, XV-N312SKo AzaniNo ratings yet
- Tutsheet5 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutsheet5 SolutionsDevendra Singhaniya90% (10)
- Packaged Terminal Air Conditioner/Heat Pump Installation/Owner'S ManualDocument27 pagesPackaged Terminal Air Conditioner/Heat Pump Installation/Owner'S ManualMichael MartinNo ratings yet
- dt083 Yr4 Industrial Automation PT v2 0 PDFDocument110 pagesdt083 Yr4 Industrial Automation PT v2 0 PDFAldo RodNo ratings yet
- Gerber Attitude 2014Document119 pagesGerber Attitude 2014Rayner MontesNo ratings yet
Geeth Ews
Geeth Ews
Uploaded by
GEETH SREETHAMOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geeth Ews
Geeth Ews
Uploaded by
GEETH SREETHAMCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
ENGINEERING
WORKSHOP
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
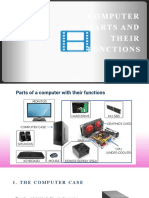
❖ EXPERIMENT 1: Peripherals of a
computer:
1. Monitor:
• The monitor displays the video and graphics information generated by the computer through
the video card. Monitors are very similar to televisions but usually display information at a much
higher resolution.
• The Monitor is Also Known As: screen, display, video display, video screen.
2. Keyboard:
• The keyboard is an input device designed to enter text, characters and other commands into a
computer or similar device.
• Many keyboards are wireless, communicating with the computer via Bluetooth or an RF receiver.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
3. Mouse:
• The mouse is an input device designed to manipulate objects on the computer screen.
• The Mouse is Also Known As: pointer
4. Cabinet:
• Computer cabinets are fitted with doors and side panels (which may or may not be removable).
Cabinets enclose a rack, which is a frame that provides a means for mounting electronic equipment.
• Cabinets come in a variety of styles, colors, and many contain baffles, fans, and other features.
5. SMPS:
• SMPS stands for Switched Mode Power Supply. It is basically a power supply unit in everything
from TVs to LCD monitors, camcorders to printers and fax machines. It's been in use in the military
before it made its way into consumer electronics.
• A Switched-mode power supply (also Switching-mode power supply, SMPS, or simply Switcher) is
an electronic Power Supply Unit (PSU) that incorporates a switching regulator in order to provide
the required output voltage.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
6. ATX Cable:
• ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended) is a motherboard form factor specification developed
by Intel in 1995 to improve on previous de facto standards like the AT form factor. mains voltage
switch with the four pins connected to wires from a four-core cable.
7. Motherboard:
• The motherboard serves to connect all of the parts of a computer together. The CPU, Memory
drives and other ports and expansion cards all connect to the motherboard directly or via cables.
• The motherboard can be thought of as the "back bone" of the computer.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
8. Processor:
• The processor (CPU, for Central Processing Unit) is the computer's brain.
• It allows the processing of numeric data, meaning information entered in binary form, and the
execution of instructions stored in memory.
9. Heat Sink fan:
• A component designed to lower the temperature of an electronic device by dissipating heat into the
surrounding air. All modern CPUs require a heat sink. Some also require a fan.
• A heat sink without a fan is called a passive heat sink; a heat sink with a fan is called an active heat
sink. Heat sinks are generally made of an aluminium alloy and often have fins.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
10. North Bridge:
• The northbridge is part of a family of Intel microchips, used to manage data
communications between a CPU and a motherboard within Intel chipsets based on . It is designed to
be paired with a second support chip known as a south bridge.
• The northbridge has historically been one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a PC
motherboard, the other being the southbridge. Increasingly these functions have migrated to the CPU
chip itself, beginning with memory and graphics controllers.
11. South Bridge:
• The southbridge is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a personal
computer (PC) motherboard, the other being the north bridge. The southbridge typically implements
the slower capabilities of the motherboard in a northbridge/southbridge chipset computer
architecture.
• In Intel chipset systems, the southbridge is named Input/Output Controller Hub (ICH). AMD,
beginning with its Fusion APUs, has given the label FCH, or Fusion Controller Hub, to its
southbridge.
• The southbridge can usually be distinguished from the northbridge by not being directly connected to
the CPU.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
12. CMOS:
• Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) is a technology for constructing integrated
circuits. CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM, and
other digital logic circuits.
• CMOS technology is also used for several analog circuits such as image sensors (CMOS
sensor), data converters, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication. Frank
Wanlass patented CMOS in 1967.
13. RAM:
• RAM is an acronym for random access memory, a type of computer that can be accessed randomly;
that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes. RAM is the most
common type of memory found in computers and other devices, such as printers.
14. CD – ROM:
• A CD-ROM is a pre-pressed compact disc which contains data. The name is an acronym which
stands for "Compact Disc Read-only memory". Computers can read CD-ROMs, but cannot write on
them.
• CD-ROMs are popularly used to distribute computer software, including video games and
multimedia applications, though any data can be stored (up to the capacity limit of a disc
• These are called enhanced CDs.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
15. BIOS:
• BIOS is a chip located on all motherboards that contain instructions and setup for how your system
should boot and how it operates.
• In the picture to the right, is an example of what a BIOS chip may look like on your computer
motherboard. In this example, this is a picture of an AMIBIOS, a type of BIOS manufacture by
the AMI another good example of a BIOS manufacturer is Phoenix.
16. Hard Disk
• A hard disk is part of a unit, often called a "disk drive," "hard drive," or "hard disk drive," that stores
and provides relatively quick access to large amounts of data on an electromagnetically charged
surface or set of surfaces.
• Today's computers typically come with a hard disk that contains several billion bytes (gigabytes)
of storage.
17. CD Drive:
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
• In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disk drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic
waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or
from optical discs.
• Some drives can only read from discs, but recent drives are commonly both readers and recorders,
also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical
media which can be read and recorded by such drives. Optical drive is the generic name; drives are
usually described as "CD" "DVD", or "Blu-ray", followed by "drive", "writer", etc.
18. Jumper Pin:
• In electronics and particularly computing, a jumper is a short length of conductor used to close a
break in, or bypass part of, an electrical circuit.
• Jumpers are typically used to set up or configure printed circuit boards, such as
the motherboards of computers.
19. SATA cable:
• Serial ATA (SATA) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage
devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives.
• Serial ATA replaces the older AT Attachment standard (ATA; later referred to as Parallel ATA or
PATA), offering several advantages over the older interface: reduced cable size and cost (seven
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
conductors instead of 40), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signalling rates,
and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol.
20. PCI Slots:
• PCI slots are general purpose slots that take a wide variety of cards, such as network cards and sound
cards.
• They only run at 33MHz and are slowly becoming obsolete as more cards are now being made for
the newer and faster PCI Express slots instead. When PCI slots appeared in computers they replaced
ISA slots, which you will only find in older PCs.
21. VGA Cable:
• A Video Graphics Array (VGA) connector is a three-row 15-pin DE-15 connector. The 15-pin
VGA connector is found on many video cards, computer monitors, and high definition
television sets.
• On laptop computers or other small devices, a mini-VGA port is sometimes used in place of the full-
sized VGA connector.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
22. Speakers:
• Computer speakers, or multimedia speakers, are speakers external to a computer, that disable the
lower fidelity built-in speaker.
• They often have a low-power internal amplifier. The standard audio connection is a 3.5 mm
(approximately 1/8 inch) stereo phone connector often color-coded lime green (following the PC
99 standard) for computer sound cards.
23. Printer:
• In computing, a printer is a peripheral which produces a representation of an electronic document on
physical media such as paper or transparency film.
• Many printers are local peripherals connected directly to a nearby personal computer. Individual
printers are often designed to support both local and network connected users at the same time.
• Some printers can print documents stored on memory cards or from digital cameras and scanners.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
24. Parallel ports:
• A parallel port is a type of interface found on computers (personal and otherwise) for connecting
peripherals. In computing, a parallel port is a parallel communication physical interface.
• It is also known as a printer port or Centronics port. It was a de facto industry standard for many
years, and was finally standardized as IEEE 1284 in the late 1990s, which defined a bi-directional
version of the port.
25. Serial Ports:
• In computing, a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information
transfers in or out one bit at a time (in contrast to a parallel port).
• Throughout most of the history of personal computers, data was transferred through serial ports
connected the computer to devices such as terminals and various peripherals.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
26. NIC Card:
• A network interface controller (NIC) (also known as a network interface card, network
adapter, LAN adapter and by similar terms) is a computer hardware component that connects
a computer to a computer network.
27. Graphic Card:
• A video card (also called a video adapter, display card, graphics card, graphics board, display
adapter or graphics adapter) is an expansion card which generates a feed of output images to a
display.
• Most video cards offer various functions such as accelerated rendering of 3Dscenes and 2D
graphics, MPEG-2/MPEG-4 decoding, TV output, or the ability to connect multiple monitors (multi-
monitor).
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
28. LAN Card:
• With the increasing use of the computers and the networking the local area network of the LAN is
one such network type which links the two computers in a connection.
• For this connection a Local area network card or the LAN card is required which enables the
connection of the computers in a network. It is a piece of hardware which is connected inside the PC
linking the computer network.
29. USB:
❖ Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines
the cables, connectors and communications protocols used in a bus for connection,
communication andpower supply between computers and electronic devices.
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
❖ EXPERIMENT 2: CERTIFICATE
GAYATRI VIDYA PARISHAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
(AUTONOMOUS)
MADHURAWADA, VISHAKAPATNAM -530048
CERTIFICATE
Certified that this is a bonafide record of practical work done by
ROLL NO of B.Tech
Semester in the _ Lab, in the Department of during the
Academic Year.
No of Experiments done:
Signature of Faculty
Signature of Internal examiner:
Signature of External examiner:
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
❖ EXPERIMENT 3 : DOCUMENT
GRAVITY
In physics, gravity from latin gravitas 'weight' is a
fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between
all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of
the four fundamental interactions, approximately 10 38 times
weaker than the strong interaction, 1036 times weaker than
the electromagnetic force and 1029 times weaker than the weak
interaction. As a result, it has no significant influence at the level
of subatomic particles. However, gravity is the most significant
interaction between objects at the macroscopic scale, and it
determines
the motion of planets,stars,galaxies and even light.
ON earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects, and the moon gravity
is responsible for sublunar tides in the oceans (the corresponding antipodal tide
is caused by the inertia of the Earth and Moon orbiting one another). Gravity also
has many important biological functions, helping to guide the growth of
plants through the process of gravitopism and influencing the circulation of
fluids in multicellular organisms. Investigation into the effects of weightlessness
has shown that gravity may play a role in immune system function and
cell differentiation within the human body .
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravity
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
❖ EXPERIMENT 4: ABSTRACT
E-WASTE
❖ ABSTRACT:
Electronic waste (e-waste) has emerged as a pressing
global environmental challenge, fueled by the rapid pace of technological advancements and the
resulting obsolescence of electronic devices.The improper disposal and inadequate management of e-waste
pose significant risks to human health, as well as to the environment due to the presence of hazardous
substances. This abstract highlights the urgency of addressing the e-waste crisis and presents sustainable
solutions to effectively manage and reduce e-waste.
❖ APPROACH:
Overviewing of the different approaches importance
of implementing comprehensive e-waste management systems that encompass various stages of the
product lifecycle, from design to disposal. This includes encouraging manufacturers to adopt eco-friendly
design practices, such as modular and upgradable components, as well as promoting the use of
environmentally friendly materials. Additionally, the abstract discusses the significance of proper
collection, recycling, and responsible disposal processes, with an emphasis on the role of government
policies, public awareness campaigns, and collaboration between stakeholders can be some of the solutions.
❖ CONCLUSION:
In conclusion, addressing the e-waste crisis requires a
holistic approach that integrates sustainable practices across the entire electronic product lifecycle.
By implementing eco-friendly design strategies, improving collection and recycling infrastructure, and
fostering collaboration among stakeholders, it is possible to mitigate the environmental and health risks
associated with e-waste
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
ENGINEERING WORKSHOP COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING SECTION -03
❖ EXPERIMENT 8: TIME TABLE BY
USING EXEL
M.V.S.GEETH SREETHAM ROLL NO: 322103310137
You might also like
- GATE Questions On MOSFET, CMOS & Introduction To VLSI (1987 Till Date)Document15 pagesGATE Questions On MOSFET, CMOS & Introduction To VLSI (1987 Till Date)APNo ratings yet
- CMTS U2Document14 pagesCMTS U2rubu131813No ratings yet
- PARTS THAT BUILD UP A System UnitDocument64 pagesPARTS THAT BUILD UP A System UnitAwali, Eliazer A.No ratings yet
- Workshop 20technolog 01.1Document7 pagesWorkshop 20technolog 01.1Akshat KulhariaNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing NC II Computer Parts and Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesComputer Systems Servicing NC II Computer Parts and Their Functionsracel orpiadaNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in SomeDocument20 pages1.0 Motherboard DEFINITION: Is The Central Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in Somekadilobari100% (3)
- Summary Report in TRDocument9 pagesSummary Report in TREllie KimNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument27 pagesMotherboardமகான் சிறோன்No ratings yet
- Unit - 3. Science: 1. Information TechnologyDocument12 pagesUnit - 3. Science: 1. Information TechnologyRobert B. WeideNo ratings yet
- Computer Workshop Job 1Document19 pagesComputer Workshop Job 1ayushkumar77447No ratings yet
- 22CSP-102 - Workshop Technology Lab ManualDocument63 pages22CSP-102 - Workshop Technology Lab ManualMehal KumarNo ratings yet
- Motherboard PartsDocument4 pagesMotherboard PartsabelNo ratings yet
- What Is Computers?Document6 pagesWhat Is Computers?Flores Carl JosephNo ratings yet
- Practical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodDocument7 pagesPractical-3: Specify The Difference Between Desktop Motherboard, Laptop and Server MethodAarunain PandavdraNo ratings yet
- Maxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsDocument16 pagesMaxim Nyansa I.T Solution (Nigeria) : Note On Computer RepairsOlúwaṣẹ́gunNo ratings yet
- Write About Computer PartsDocument12 pagesWrite About Computer PartsThenaNo ratings yet
- Computer PartsDocument32 pagesComputer PartsSasi RekhaNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Document82 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Personal Computer System - 02Pastor Roy Onyancha CyberNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitDocument35 pagesBasic Parts of A Computer: - Monitor - Keyboard - Mouse - System UnitShenny CariscalNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4Document12 pagesExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheNo ratings yet
- Installing and Configuring SystemsDocument47 pagesInstalling and Configuring SystemsDonna Fe De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument22 pagesComputer Hardwareprinceisrael332No ratings yet
- CP and I AssigenmentDocument59 pagesCP and I Assigenmentfagixa3491No ratings yet
- 02 Itc 2K22-26Document20 pages02 Itc 2K22-26M IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Motherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardDocument7 pagesMotherboard: Personal Computers Printed Circuit Board Computers Apple Logic BoardMustafa MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Richard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Document8 pagesRichard Anthony C. Rivera BSIT 2A (MT 7:00-8:30am)Richard Anthony RiveraNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDocument12 pagesComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaNo ratings yet
- CSS Quarterly Exam 1Document18 pagesCSS Quarterly Exam 1seph bronNo ratings yet
- CHTDocument45 pagesCHTRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- MGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsDocument33 pagesMGU-TASFA-EDSI-IT-101 - Module 2 - Hardware and Operating SystemsTesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputersDocument42 pagesIntroduction To ComputersClark DomingoNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan50% (2)
- Understanding Computer Hardware and PeripheralsDocument58 pagesUnderstanding Computer Hardware and Peripheralsligasan.cjNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationDocument138 pagesComputer Hardware Maintenance and AdministrationSayyan Shaikh100% (2)
- Puter DocketsDocument58 pagesPuter DocketsMd ZakariaNo ratings yet
- What Is A MotherboardDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MotherboardManpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Lesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Document25 pagesLesson3 141205082141 Conversion Gate02Archie CuyacotNo ratings yet
- S FDWDocument16 pagesS FDWSuyash PatilNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing Jhs1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Computing Jhs1josephbliss04No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemDocument50 pagesLesson 1: Understanding The Computer SystemR-Yel Labrador BaguioNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Structure of Modern ComputerDocument10 pagesUnit - I Structure of Modern ComputerxsaaNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocument5 pagesMotherboard Components and FunctionnominnanaaespasolNo ratings yet
- Is The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerDocument5 pagesIs The Enclosure For All The Other Main Interior Components of A Computer. It Is Also Called The Computer Case, Computer Chassis, or Computer TowerAlfredo DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.1-3 Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripherals Parts of A Desktop ComputerDocument10 pagesInformation Sheet 1.1-3 Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripherals Parts of A Desktop ComputerManuelo VangieNo ratings yet
- Computer ICTDocument20 pagesComputer ICTmobilelegendshelpcenter2022No ratings yet
- Roney CBLMDocument17 pagesRoney CBLMAdonis Abalos PradoNo ratings yet
- Lab 02 - EEDDocument18 pagesLab 02 - EEDAhmad MusabNo ratings yet
- Cycle 1Document106 pagesCycle 1Srinivas KanakalaNo ratings yet
- Global Institutes of Management & Emerging Technologies: Department of CSE Lab Manual of Data Communication (DC)Document38 pagesGlobal Institutes of Management & Emerging Technologies: Department of CSE Lab Manual of Data Communication (DC)Gagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- (M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computer - CapistranoDocument14 pages(M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computer - CapistranoRedd CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument4 pagesComputer HardwareEhnan J LamitaNo ratings yet
- System Unit and Their FunctionsDocument30 pagesSystem Unit and Their Functionslex jhonNo ratings yet
- CSS Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesCSS Lesson Planirene cadizNo ratings yet
- Gilas PC MaintenanceDocument97 pagesGilas PC MaintenanceEmmanuel Jimenez-Bacud, CSE-Professional,BA-MA Pol SciNo ratings yet
- (M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal ComputerDocument14 pages(M3-TECHNICAL) Hardware Components of Personal Computerchristianmendoza2004No ratings yet
- Hardware and NetworkingDocument6 pagesHardware and NetworkingdurailanNo ratings yet
- Comp. Maint Instal, Maint, and Config. Week 1 and 2Document21 pagesComp. Maint Instal, Maint, and Config. Week 1 and 2Emperor'l BillNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1widiefreeNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument48 pagesMotherboardAce BorresNo ratings yet
- PLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.From EverandPLC: Programmable Logic Controller – Arktika.: EXPERIMENTAL PRODUCT BASED ON CPLD.No ratings yet
- Applied Sciences: Injection Molding Process Control of Servo-Hydraulic SystemDocument11 pagesApplied Sciences: Injection Molding Process Control of Servo-Hydraulic SystemTrung Kiên LêNo ratings yet
- 1-Attachment 1 Oversea Projects Experience ListDocument2 pages1-Attachment 1 Oversea Projects Experience Listhua tianNo ratings yet
- rfx75 Install Guide Cobra 29Document3 pagesrfx75 Install Guide Cobra 29Geraldrum Zyzcom HdzNo ratings yet
- JMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB LayoutDocument1 pageJMPGuitars 18 Watt Tremolo TMB LayoutRenan Franzon GoettenNo ratings yet
- H.V.A.C.-R. Service TechnicianDocument2 pagesH.V.A.C.-R. Service Technicianapi-121390582No ratings yet
- Tail CompensationDocument4 pagesTail Compensationjammy700No ratings yet
- Service Manual: Ecosys FS-1750 Ecosys FS-3750Document222 pagesService Manual: Ecosys FS-1750 Ecosys FS-3750Ali OuchnNo ratings yet
- Alc3251 CGDocument1 pageAlc3251 CGAhmadNo ratings yet
- Octava Micro User Manual - NEW - 17 PDFDocument1 pageOctava Micro User Manual - NEW - 17 PDFJohn DoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Vibration Measurement - Selecting and Using PickupsDocument62 pagesChapter 3: Vibration Measurement - Selecting and Using PickupsAndrey AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Gs26Clx LBP Compressor R404A/R507 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralDocument2 pagesGs26Clx LBP Compressor R404A/R507 220-240V 50Hz: GeneralmustafaNo ratings yet
- BREADBOARDING - TinkercadDocument2 pagesBREADBOARDING - TinkercadJustin NievaNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Automotive Terms 2Document519 pagesDictionary of Automotive Terms 2hahahaaNo ratings yet
- Service Man CHDocument287 pagesService Man CHAdan MartinezNo ratings yet
- Video Display DevicesDocument66 pagesVideo Display DevicesshabanaNo ratings yet
- GCE O/L ICT Source01Document5 pagesGCE O/L ICT Source01Mohamaad SihatthNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Effects 1 QPDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Effects 1 QPnssNo ratings yet
- Field-Circuit Co-Simulation of The Marx Generator: April 2015Document6 pagesField-Circuit Co-Simulation of The Marx Generator: April 2015KhyatiChavdaNo ratings yet
- SB Series: DC Magnetic ContactorsDocument3 pagesSB Series: DC Magnetic ContactorsAkmalNo ratings yet
- Form Pin TKDocument1 pageForm Pin TKnguyenlongquan2212No ratings yet
- Remote Releasing Module (RRM) InstallationDocument4 pagesRemote Releasing Module (RRM) InstallationIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- JHJHJHJH MergedDocument48 pagesJHJHJHJH Mergedhabaga1835No ratings yet
- Gaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2Document14 pagesGaby Lau Gel55 Mae 3780 Individual Final Report Fall 2021 2api-581695353No ratings yet
- 1ETM (Extracted Timing Models) Basics - VLSI ConceptsDocument3 pages1ETM (Extracted Timing Models) Basics - VLSI ConceptsSudheer Gangisetty0% (1)
- Schematic Diagrams: XV-N210B, XV-N212S, XV-N310B, XV-N312SDocument10 pagesSchematic Diagrams: XV-N210B, XV-N212S, XV-N310B, XV-N312SKo AzaniNo ratings yet
- Tutsheet5 SolutionsDocument5 pagesTutsheet5 SolutionsDevendra Singhaniya90% (10)
- Packaged Terminal Air Conditioner/Heat Pump Installation/Owner'S ManualDocument27 pagesPackaged Terminal Air Conditioner/Heat Pump Installation/Owner'S ManualMichael MartinNo ratings yet
- dt083 Yr4 Industrial Automation PT v2 0 PDFDocument110 pagesdt083 Yr4 Industrial Automation PT v2 0 PDFAldo RodNo ratings yet
- Gerber Attitude 2014Document119 pagesGerber Attitude 2014Rayner MontesNo ratings yet