Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NAT Reviewer
NAT Reviewer
Uploaded by
Allen Aquino Prado0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views4 pagesThe document summarizes the structure and layers of the Earth. It is composed of three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost and thinnest layer, while the mantle makes up most of the Earth's volume and mass. Below the mantle is the core, which has an outer liquid layer and inner solid layer. The movement of tectonic plates on the mantle helps explain geological features via processes like seafloor spreading at mid-ocean ridges and subduction at trenches.
Original Description:
NAT reviewer
Original Title
NAT reviewer
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the structure and layers of the Earth. It is composed of three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost and thinnest layer, while the mantle makes up most of the Earth's volume and mass. Below the mantle is the core, which has an outer liquid layer and inner solid layer. The movement of tectonic plates on the mantle helps explain geological features via processes like seafloor spreading at mid-ocean ridges and subduction at trenches.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views4 pagesNAT Reviewer
NAT Reviewer
Uploaded by
Allen Aquino PradoThe document summarizes the structure and layers of the Earth. It is composed of three main layers - the crust, mantle, and core. The crust is the outermost and thinnest layer, while the mantle makes up most of the Earth's volume and mass. Below the mantle is the core, which has an outer liquid layer and inner solid layer. The movement of tectonic plates on the mantle helps explain geological features via processes like seafloor spreading at mid-ocean ridges and subduction at trenches.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
VI.
Summary/Synthesis/Feedback
•
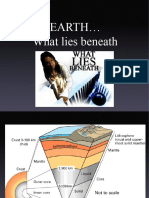
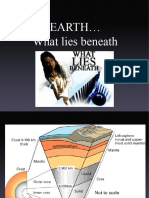
The Earth is composed of three major layers: the crust, mantle, and
core which is subdivided into outer an dinner core.
•
The crust is the outermost and thinnest layer of the Earth.
•
The mantle is the middle layer of the
Earth. It makes most of the Earth’s
volume and mass.
•
The crust and a part of the upper mantle make up the lithosphere.
The lithosphere is subdivided into portions called lithospheric plates.
•
The asthenosphere is the weak layer of the mantle on which the
lithosphere floats.
•
The outer core is made up of molten material and accounts for the
Earth’s magnetic field.
•
The inner core is the deepest layer of the Earth. It is made up of
solid nickel and iron. The temperature in the inner core reaches as
high as5000oC.
•
The speed, reflection and refraction properties of seismic waves
are used by scientists to study the structure and composition of
the
Earth’s interior.
•
The Continental Drift Theory of Alfred Wegener states that
the continents were once part of a large landmass called Pangaea
which drifted away from each other. The continents moved away
from each other towards their current positions.
•
Alfred Wegener based his theory one evidences from fossils
imbedded in rocks and rock formations.
•
Seafloor spreading is believed to occur as hot magma rises at the rift in
the mid-ocean ridge. This magma cools down and becomes the new
seafloor as it pushes the former.
•
The old seafloor is destroyed at the subduction zone and
melts inside the mantle.
•
The age of rocks and the magnetic stripes in the ocean floor support
the Seafloor Spreading Theory.
•
The Theory of Plate Tectonics helps explain the formation and
destruction of the Earth’s crust and
its movement over time.
Scientists believe that the plates’
movement is due to convection currents in the mantle.
According to the plate tectonics model, the entire lithosphere of
the Earth is broken into numerous segments called plates
• Each plate is slowly but
Continuously moving.
• As a result of the motion of the plates,
three types of plate boundaries
were formed: Divergent, Convergent
GRADE 10 SCIENCE (EARTH SCIENCE) FIRST QUARTER
Magma
is a mass of molten rock formed at depth, including dissolved gases and
crystals.
MODULE 1:PLATE TECTONICS Mid-ocean ridge
A continuous mass of land with long width and height on the ocean floor.
Plates
rigid sections of the lithosphere that move as a unit• According to the
plate tectonics model, the entire lithosphere of the Earth is broken into
numerous segments called
plates.
• Each plate is slowly but continuously moving• As a result of the motion
of the plates, three types of plate boundaries were formed:
Divergent, Convergent,and Transform
Fault boundaries.•
Divergent boundary
isformed when platesmove apart, creating azone of
tension.
•
Convergent boundary
ispresent when two
plates collide.
•
Transform fault
ischaracterized by platesthat are sliding past eachother.• Plate
tectonics give riseto several geologicfeatures and events.
Glossary of TermsContinental volcanic arcmountains
formed in part by igneousactivity associatedwith subduction of
oceaniclithospherebeneath a continent A
convergent boundary
is a boundary in whichtwo plates move towardeach other, causingone of
the slabs of thelithosphere to subductbeneath an overridingplate
Crust
the outer portion ofthe earth
Continental Crust
is thethick part of theEarth’s crust, not locatedunder the ocean
Plate tectonics
a theorythat suggeststhat Earth’s crust is
madeup of plates
thatinteract in various ways,thus producing
earthquakes
,
mountains
,
volcanoes
, andother geologic features
Primary (P) waves
are thefirst type of seismicwave to be recorded in aseismic station
Rocks
consolidatedmixture of minerals
Secondary (S) wave
thesecond type of earthquake wave to berecorded in a seismicstation
A seismogram
is a recordmade by aseismographSeismograph a deviceused to
recordearthquake waves
A subduction
is an eventin which a slab of rockthrusts into the mantle
Transform fault
boundarya boundaryproduced when two platesslide past eachother
Trench
a depression inthe seafloor produced by thesubduction process
Volcanic Island arc
achain of volcanoesthat develop parallel to atrenchMODULE 2:
THE EARTH’S INTERIOROceanic Crust
the thinpart of the Earth’scrust located under theoceans
You might also like
- Grade 10 Science Summary From BookDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Summary From BookRyzhenSanchez-Infante82% (22)
- ME-Tut 4Document2 pagesME-Tut 4Shekhar SinghNo ratings yet
- 6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths InteriorDocument41 pages6th Grade Science-Plate Tectonics and Earths Interiorleojohn2100% (1)
- 6th Grade - Plate TectonicsDocument40 pages6th Grade - Plate Tectonicsleojohn2100% (1)
- Summary in Module 2Document2 pagesSummary in Module 2Mabellee CabreraNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Grade 10)Document3 pagesScience Reviewer (Grade 10)Dove Mendelieve100% (7)
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument79 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsHyres Almerina AlturasNo ratings yet
- Eart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreDocument23 pagesEart H's Sub Syste M: Geo SPH EreRhiza Mae Lax100% (1)
- Plate Tectonic2Document27 pagesPlate Tectonic2eduardocarlbituin15No ratings yet
- 03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMDocument84 pages03 Earth and Life Science - EARTH - EARTH SUBSYTEMCarlo Bryan Ramento100% (1)
- Enviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedDocument26 pagesEnviro Geo Notes 3 CompressedAlaiza mae BongcayNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsShakerMahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsgildeddivaNo ratings yet
- Continental and Oceanic CrustDocument38 pagesContinental and Oceanic CrustEvelyn MayorNo ratings yet
- Science g10Document4 pagesScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNo ratings yet
- Geo SphereDocument17 pagesGeo SphereConsuelo BriceñoNo ratings yet
- L3 - Geosphere TectonicsDocument51 pagesL3 - Geosphere TectonicsbhaveshreddygunNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document46 pagesSession 1Shimaa MohammedNo ratings yet
- Earth Structure Plate TectonicsDocument47 pagesEarth Structure Plate TectonicsAl Jawad100% (3)
- 2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument33 pages2016 Layers of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKen Verona Ferrera100% (2)
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument39 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsKrysfer Secusana100% (2)
- PlatesDocument33 pagesPlatesJhana MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesJohn BenedictNo ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesvinod pNo ratings yet
- Theory of Global Plate TectonicsDocument11 pagesTheory of Global Plate TectonicsHannylet OcateNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalDocument7 pagesChapter - 10 - Notes Local Local LocalBryan YasgilNo ratings yet
- Presentation #1 Structure of The EarthDocument42 pagesPresentation #1 Structure of The EarthNathan McintoshNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsBoni Almueda Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument46 pagesPlate TectonicsKevin ChadwickNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022Document54 pagesGrade 10 Plate Tectonics 2022shanesha blackhood100% (1)
- Plate TechtonicsDocument37 pagesPlate Techtonicsapi-294510653No ratings yet
- PlatesDocument37 pagesPlatesMagistrado DrewNo ratings yet
- 4.1-4.2 Plate TectonicsDocument59 pages4.1-4.2 Plate TectonicsChristopher SparkmanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument37 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsnoelNo ratings yet
- Formation of EarthDocument54 pagesFormation of Earthniaz ahmedNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument36 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleBartclethon L. DelfinNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 11 WEEK 6c - Endogenic ProcessDocument57 pagesSCIENCE 11 WEEK 6c - Endogenic ProcessChristine CayosaNo ratings yet
- Science 10 1st Grading Module 1Document27 pagesScience 10 1st Grading Module 1vinesseNo ratings yet
- I. Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesI. Plate TectonicsChristian GanganNo ratings yet
- Week 1 NotesDocument12 pagesWeek 1 Notessaifulislam9442No ratings yet
- Lecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesLecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Plate TectonicsQP0125 Vu Song HaNo ratings yet
- SciencemidtermDocument9 pagesSciencemidtermapi-281100019No ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument71 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsJANICE FRANCELOSONo ratings yet
- Plates SSE Grade 11Document26 pagesPlates SSE Grade 11Noor AlDiniNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicsDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The Earth and Plate TectonicshatdoghatdogNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - TectonicsDocument21 pagesLab 1 - TectonicsPatrick TiernanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument20 pagesEarth ScienceAida100% (1)
- Plate TectonicsDocument35 pagesPlate TectonicsSyed sikander ali shah SyedNo ratings yet
- ch03 Sec1 RevisedDocument35 pagesch03 Sec1 Revisedapi-239353579No ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Engineering SeismologyDocument55 pagesUnit - 3 Engineering Seismologyci_balaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 First Quarter SummaryDocument3 pagesGrade 10 First Quarter SummaryAdrian Tastar100% (1)
- Layer Chage OptionDocument36 pagesLayer Chage OptionKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- LayerDocument36 pagesLayerKarthik MadhuNo ratings yet
- Layers of Earth For FoldabaleDocument37 pagesLayers of Earth For FoldabaleJade QuitoNo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah Konsep GeologiDocument107 pagesMateri Kuliah Konsep GeologiPandu Riyadi ShalihinNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Gregory M Sped841 UnitlessonDocument1 pageGregory M Sped841 Unitlessonapi-271896767No ratings yet
- Binomial FiltersDocument5 pagesBinomial FiltersverdosNo ratings yet
- Micropolar Fluid Lubrication of Finite Rough Porous Journal Bearing With Squeezing EffectDocument28 pagesMicropolar Fluid Lubrication of Finite Rough Porous Journal Bearing With Squeezing EffectIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Am2xx enDocument34 pagesAm2xx enpham linhNo ratings yet
- 08 03 Lab ReportDocument5 pages08 03 Lab ReportDenise QuinnNo ratings yet
- Location of PakistanDocument14 pagesLocation of PakistanPotatoNo ratings yet
- Limitations of MLDocument10 pagesLimitations of MLNavneet LalwaniNo ratings yet
- Voice Recognition SystemDocument18 pagesVoice Recognition SystemArun Sharma75% (16)
- Types of FittingsDocument22 pagesTypes of Fittingsroronoa zoro100% (1)
- CS3251 Programming in C - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument96 pagesCS3251 Programming in C - by WWW - Learnengineering.inTishbian MeshachNo ratings yet
- Hash Function Instruction CountDocument6 pagesHash Function Instruction Countapi-1752250No ratings yet
- Probability and Statistical Analysis: Chapter FiveDocument25 pagesProbability and Statistical Analysis: Chapter Fiveyusuf yuyuNo ratings yet
- VBA12 - Monte Carlo SimulationDocument3 pagesVBA12 - Monte Carlo SimulationzarasettNo ratings yet
- Classical Item and Test Analysis Report Hasil Run Kelompok 6Document20 pagesClassical Item and Test Analysis Report Hasil Run Kelompok 6Khinasih NoerwotoNo ratings yet
- TutorialDocument46 pagesTutorialGurpreet Singh SohalNo ratings yet
- Project STA108Document25 pagesProject STA108meliszaNo ratings yet
- PROVA cm-07Document10 pagesPROVA cm-07hidrologia05No ratings yet
- Condensate Pumps 4100 SERIES: Steel TankDocument2 pagesCondensate Pumps 4100 SERIES: Steel TankruzlaNo ratings yet
- Long Quiz 1-BDocument11 pagesLong Quiz 1-BEthel FajardoNo ratings yet
- Act Design GuideDocument49 pagesAct Design GuideRodney LeamanNo ratings yet
- EXP Series - : Standard Chemical Process PumpsDocument6 pagesEXP Series - : Standard Chemical Process PumpsMohsen ParpinchiNo ratings yet
- Um TQ GC Ms 7000e 7010c Series Concepts Guide g7006 90008 en AgilentDocument52 pagesUm TQ GC Ms 7000e 7010c Series Concepts Guide g7006 90008 en AgilentxdshkiperNo ratings yet
- Homework 2 IENG584Document3 pagesHomework 2 IENG584Frida YoungNo ratings yet
- Large Data Set Lds-EdexcelDocument146 pagesLarge Data Set Lds-EdexcelhadzNo ratings yet
- GC ADS - Hydrocarbon Dew PointDocument4 pagesGC ADS - Hydrocarbon Dew Pointmajid maheriNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI VNS-L31C432B160 Software Upgrade GuidelineDocument9 pagesHUAWEI VNS-L31C432B160 Software Upgrade GuidelineAlessandroCarlàNo ratings yet
- RelevoDocument10 pagesRelevocarlos cruzNo ratings yet
- Journal of Hydraulic ResearchDocument11 pagesJournal of Hydraulic ResearchfernandoNo ratings yet
- SequencesDocument16 pagesSequencesAnjali BodaniNo ratings yet