Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 3 Spring 2023 PHY111
Assignment 3 Spring 2023 PHY111
Uploaded by
MD. SABBIR AHAMEDOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 3 Spring 2023 PHY111
Assignment 3 Spring 2023 PHY111
Uploaded by
MD. SABBIR AHAMEDCopyright:
Available Formats
PHY 111 Semester: Spring, 2023
Department of Mathematics and Natural Sciences
PHY111 - Principles of Physics I
Assignment 3
Total marks: 25
Instructions:
1. Please write your name, ID and section on your script.
2. This assignment comprises of 2 questions. The points of each question is mentioned in the
particular question.
3. Please read the questions very carefully.
Question 1
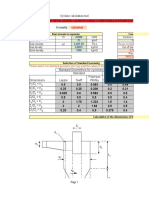
The figure shows a conical pendulum, in which the bob (the small object at the lower end of the
cord) moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The cord sweeps out a cone as the bob rotates
(see the figure). The bob has a mass of 0.04 kg, the string has length L = 0.90 m and negligible
mass, and the bob follows a circular path of circumference 0.94 m.
(a) Calculate the tension in the cord. 4
(b) Calculate the angular velocity and the period of the circular motion. 3+2
Question 2
A pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star that emits a radio beam the way a lighthouse emits
a light beam. We receive a radio pulse for each rotation of the star.The period T of rotation is
found by measuring the time between pulses. The pulsar in the Crab nebula has a current period
of rotation of T = 0.033 s that is increasing at the rate of 1.26 × 10−5 second/year.
(a) What is the pulsar’s angular acceleration α? 2
(b) If α is constant, how many years from now will the pulsar stop rotating? 3
(c) The pulsar originated in a supernova explosion seen in the year 1054.Assuming constant α,
find the initial T . 3
Question 3
The string in the figure L = 1.2 m long, has a ball attached to one end, and is fixed at its other
end. The distance d from the fixed end to a fixed peg at point P is 0.75 m. The peg basically stops
the rotation of the upper part of the rope. After the rope catches the peg, it moves in the circular
path of radius r. When the initially stationary ball is released with the string horizontal as shown,
it will swing along the dashed arc.
(a) What is its speed when it reaches its lowest point. 3
(b) Calculate the velocity at its highest point after the string catches on the peg? 5
You might also like
- Joaquim A. Batlle, Ana Barjau Condomines - Rigid Body Kinematics-Cambridge University Press (2020)Document305 pagesJoaquim A. Batlle, Ana Barjau Condomines - Rigid Body Kinematics-Cambridge University Press (2020)vuliencnNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan On Transverse and Longitudinal WavesDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan On Transverse and Longitudinal WavesMae Amor Enorio100% (4)
- Homework Week 7 - LightDocument3 pagesHomework Week 7 - LightMuhammad Waseem AbbasNo ratings yet
- PH-120-04 Homework Ch02 AnswersDocument3 pagesPH-120-04 Homework Ch02 AnswersJon KimballNo ratings yet
- Cyclone Calculation ToolDocument6 pagesCyclone Calculation ToolAli YasinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry NotesDocument160 pagesChemistry NotesSai TanushNo ratings yet
- Physics Problems WavesDocument3 pagesPhysics Problems WavesMalletNjonkemNo ratings yet
- PHY 1071 PHY 20 Apr 2023Document4 pagesPHY 1071 PHY 20 Apr 2023Xyz XyzNo ratings yet
- Challenging Practice Questions MixDocument62 pagesChallenging Practice Questions Mixmarjan familiNo ratings yet
- GJ 4 Waves Sound Jan2020Document29 pagesGJ 4 Waves Sound Jan2020Wilson ZhangNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry Module I Q&AnsDocument9 pagesApplied Chemistry Module I Q&Anskannankarthi3002No ratings yet
- An Atom Contains Electrons - PresentationDocument21 pagesAn Atom Contains Electrons - PresentationFatemaNo ratings yet
- Challenging Practice Questions MixDocument61 pagesChallenging Practice Questions MixKazimierz WojcikNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Arrangement of Electrons in AtomsDocument7 pagesChapter 4 - Arrangement of Electrons in AtomsEmily Zuber 2023No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Electronic StructureDocument62 pagesChapter 2 Electronic StructureLivan TuahNo ratings yet
- Principles of Quantam MechanicsDocument19 pagesPrinciples of Quantam Mechanicsమత్సా చంద్ర శేఖర్No ratings yet
- TuanAnh Chapter 1 AtomsDocument64 pagesTuanAnh Chapter 1 AtomsTrần Gia LinhNo ratings yet
- Dhselect 5Document9 pagesDhselect 5Biswanath Gouda (Biswanath)No ratings yet
- PCS125 Tutorial QuestionsDocument52 pagesPCS125 Tutorial Questionsfurbac321No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsmickey_disney93No ratings yet
- Worksheet 2Document3 pagesWorksheet 2Anushka GandhiNo ratings yet
- GeneralChemistry 1Document50 pagesGeneralChemistry 1peter168205No ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and Nuclei: Class XiiDocument12 pagesStructure of Atoms and Nuclei: Class XiiAmish ShahNo ratings yet
- Bpho Round 1 Section 1 15 November 2018 This Question Paper Must Not Be Taken Out of The Exam Room InstructionsDocument8 pagesBpho Round 1 Section 1 15 November 2018 This Question Paper Must Not Be Taken Out of The Exam Room InstructionsnadiaNo ratings yet
- P-2 Olympaid Paper - SP (NT Sir)Document4 pagesP-2 Olympaid Paper - SP (NT Sir)Subhankar TripathiNo ratings yet
- Transverse WavesDocument23 pagesTransverse WavesMundu Mustafa100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Quiz GroupDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Quiz GroupEnock KamugishaNo ratings yet
- 16th Chinese Physics Olympiad Semi FinalsDocument4 pages16th Chinese Physics Olympiad Semi FinalsPuneeth A100% (1)
- PHY1 June 2003Document2 pagesPHY1 June 2003api-3726022No ratings yet
- 0155 Cat-D Xi, Xii Physics Paper ADocument2 pages0155 Cat-D Xi, Xii Physics Paper ASayem PatelNo ratings yet
- Decoherence Objective Question PaperDocument7 pagesDecoherence Objective Question PaperYashashwi SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Mechanical of AtomsDocument44 pagesThe Quantum Mechanical of AtomsMutiara Wandini SamosirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - Atoms-Saju-Hsslive PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 12 - Atoms-Saju-Hsslive PDFAmiNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion FINAL - WatermarkDocument7 pagesCircular Motion FINAL - Watermark20 Subhojit Maji 10HNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument7 pagesCircular Motionwatawak457No ratings yet
- Atomsnotes 69472Document8 pagesAtomsnotes 69472ammonish08No ratings yet
- Principles of Physics 1 3 Semester 2018 2019Document4 pagesPrinciples of Physics 1 3 Semester 2018 2019tvan7426No ratings yet
- PH101: Tutorial-1 Kinematics in Polar CoordinatesDocument1 pagePH101: Tutorial-1 Kinematics in Polar CoordinatesPranoy BaishyaNo ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad 2010 PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics Olympiad 2010 PDFSayeed Mohammed100% (3)
- SHM WorksheetDocument1 pageSHM WorksheetAnita ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Sec Phys Waves ProblemsDocument19 pagesSec Phys Waves Problemsrixzylicoqui.salcedoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Class Task 1, L1, 25 July 2025 - 220721 - 210459Document2 pagesPre-Class Task 1, L1, 25 July 2025 - 220721 - 210459Kwandile JaftaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus WP 6 8Document6 pagesPre Calculus WP 6 8Janine Mae MujeNo ratings yet
- S6 Examen Physik Semester 2 2021 - 22 EN v.1 1Document5 pagesS6 Examen Physik Semester 2 2021 - 22 EN v.1 1danielemana17No ratings yet
- AtomsDocument26 pagesAtomsGiridhar MeruvalaNo ratings yet
- Report 13Document6 pagesReport 13Michael LunaNo ratings yet
- Electronics - Basic ConceptsDocument17 pagesElectronics - Basic ConceptsA B ShindeNo ratings yet
- PendulumDocument3 pagesPendulumvenkat krishnaNo ratings yet
- 2.1 MotionDocument18 pages2.1 MotioncetinNo ratings yet
- Practice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouDocument5 pagesPractice Usapho X: Kevin ZhouAkshat goyalNo ratings yet
- SHMDocument3 pagesSHMkemigishapatience369No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Set 1 - N 2016Document29 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Set 1 - N 2016monish gowda gNo ratings yet
- Hey HeyDocument1 pageHey HeyJitendra KaushikNo ratings yet
- Section B&C TipsDocument6 pagesSection B&C TipsNoor IrinaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Exercises M&R1: 1 Tutorial 1Document3 pagesConceptual Exercises M&R1: 1 Tutorial 1kaiNo ratings yet
- FALLSEM2022-23 PHY1701 ETH VL2022230106333 Reference Material I 29-09-2022 3matter Wave TheoryDocument13 pagesFALLSEM2022-23 PHY1701 ETH VL2022230106333 Reference Material I 29-09-2022 3matter Wave TheoryTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PresentationDocument15 pagesChemistry PresentationSubham KalwarNo ratings yet
- G9 - Quarter 3 - The Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument95 pagesG9 - Quarter 3 - The Quantum Mechanical ModelBea Mae AlazadaNo ratings yet
- SLG Chem1 LG 3.2 Quantum NumbersDocument11 pagesSLG Chem1 LG 3.2 Quantum NumbersLaw of Attraction Come trueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12ramcharanneeli4No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - IiDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure - IiSUMITH K SNo ratings yet
- ATOMSDocument20 pagesATOMSJanvi ShahiNo ratings yet
- 2022 Arxiv M2P2S6Document10 pages2022 Arxiv M2P2S6Arvind MauryaNo ratings yet
- Presentación Completa ArupDocument105 pagesPresentación Completa ArupCarlos Eduardo Rodriguez100% (1)
- Linear MeasurementDocument15 pagesLinear MeasurementFarisa ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Blazzers of The New TrailDocument8 pagesBlazzers of The New TrailLovedeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Exam-Style Questions: E. B G B G × eDocument1 pageExam-Style Questions: E. B G B G × ePhan Minh ViệtNo ratings yet
- Principle of FlightDocument52 pagesPrinciple of FlightDang KhaiNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws / Gases BehaviourDocument35 pagesGas Laws / Gases Behaviour9338-Anmol KatharNo ratings yet
- G7 Science Q1 - Week 6-Unsaturated and Saturated SolutionDocument14 pagesG7 Science Q1 - Week 6-Unsaturated and Saturated SolutionJessa-Bhel AlmueteNo ratings yet
- Sharp SF2216 Service Manual PDFDocument125 pagesSharp SF2216 Service Manual PDFRostocanieNo ratings yet
- Analisis Kekuatan Tarik, Kekerasan, Dan Struktur PengelasanDocument10 pagesAnalisis Kekuatan Tarik, Kekerasan, Dan Struktur PengelasanNurkholis NurkholisNo ratings yet
- Use of Demonstration Models in Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering EducationDocument44 pagesUse of Demonstration Models in Undergraduate Geotechnical Engineering EducationZana Jalal JudiNo ratings yet
- Applied PhysicsDocument6 pagesApplied PhysicsAbu Syeed Md. Aurangzeb Al MasumNo ratings yet
- ULOB Chem205l MARK LLOYD TRONDILLODocument6 pagesULOB Chem205l MARK LLOYD TRONDILLOCeilo TrondilloNo ratings yet
- Unsw Mechanical Thesis DatabaseDocument8 pagesUnsw Mechanical Thesis Databaserobynchampagnemanchester100% (2)
- Design of Connection-Spud & BargeDocument8 pagesDesign of Connection-Spud & Bargeakash808099No ratings yet
- Tension Test of Ofhc CopperDocument7 pagesTension Test of Ofhc CopperUsman ishaqNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - Test ReviewDocument2 pagesUnit 5 - Test Reviewria wuNo ratings yet
- ECAT Past Papers (Mathematics Portion) PDFDocument16 pagesECAT Past Papers (Mathematics Portion) PDFtanoligNo ratings yet
- Biosignals & Biosystems: Block 2. The Z-TransformDocument69 pagesBiosignals & Biosystems: Block 2. The Z-Transformmaria reverteNo ratings yet
- AphiweDocument16 pagesAphiweaphiweshozi18No ratings yet
- Preliminary Pharmaceutical Characterization of Some Flowers As Natural Indicator: Acid-Base TitrationDocument5 pagesPreliminary Pharmaceutical Characterization of Some Flowers As Natural Indicator: Acid-Base Titrationzainkhan1juneNo ratings yet
- Check List. SuperstructureDocument5 pagesCheck List. SuperstructureALI RAZANo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bachelor in Nautical ScienceDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Bachelor in Nautical ScienceSurabhi RtNo ratings yet
- Vector 1 - by TrockersDocument58 pagesVector 1 - by TrockersFerguson UtseyaNo ratings yet
- Simplified MELC Based BOL in Science 3 FINALDocument8 pagesSimplified MELC Based BOL in Science 3 FINALFranz Evhanne50% (2)
- Ebook Calculus Single and Multivariable 6Th Edition Hughes Hallett Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Calculus Single and Multivariable 6Th Edition Hughes Hallett Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFKaylaWalkerncas100% (14)
- Max. Working Condition: Nl/min NM /H SCFM Bar Ø In-Out PH/V/FR A B C D E F GDocument3 pagesMax. Working Condition: Nl/min NM /H SCFM Bar Ø In-Out PH/V/FR A B C D E F Gapi-3818336No ratings yet