Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ3400 3 Ps Tariffs
Econ3400 3 Ps Tariffs
Uploaded by
Wenqing XiaoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Econ3400 3 Ps Tariffs
Econ3400 3 Ps Tariffs
Uploaded by
Wenqing XiaoCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set 3: Tariffs
1. As a government protects its producers from foreign competition, what does it
encourage its economy to do?
a. Move closer to a state of free trade.
b. Move closer to a state of autarky.
c. Move closer to a state of interdependence.
d. Move closer to a state of global flows.
2. How can ‘job protection’ be used as an argument for trade barriers?
a. Import restrictions create a level playing field.
b. Import reductions stimulate domestic activity.
c. Import reduce welfare for everyone.
d. Imports undercut domestic production.
3. How can ‘standards of living’ be used as an argument for trade barriers?
a. Import restrictions create a level playing field.
b. Import reductions stimulate domestic activity.
c. Import reduce welfare for everyone.
d. Imports undercut domestic production.
4. How can ‘fairness’ be used as an argument for trade barriers?
a. Import restrictions create a level playing field.
b. Import reductions stimulate domestic activity.
c. Import reduce welfare for everyone.
d. Imports undercut domestic production.
5. What is the correct terminology for a tax levied on an imported product?
a. Import tariff
b. Protective tariff
c. Revenue tariff
d. Export tariff
6. What is the correct terminology for a tax imposed on an exported product?
a. Import tariff
b. Protective tariff
c. Revenue tariff
d. Export tariff
Spring 2023 ECON3400 1
7. What is the correct terminology for a tax designed to reduce the amount of imports
entering a country?
a. Import tariff
b. Protective tariff
c. Revenue tariff
d. Export tariff
8. What is the correct terminology for a tax imposed for the purpose of generating tax
revenues?
a. Import tariff
b. Protective tariff
c. Revenue tariff
d. Export tariff
9. Which of the following is an advantage of specific tariffs?
a. Tends to maintain a constant degree of protection for domestic producers during
periods of changing prices.
b. The determination of duties is subject to administrative complexities.
c. The degree of protection it affords domestic producers varies inversely with
changes in import prices.
d. It provides domestic producers more protection during a business recession
when cheaper products are purchased.
10. Which of the following is an advantage of ad valorem tariffs?
a. Tends to maintain a constant degree of protection for domestic producers during
periods of changing prices.
b. The determination of duties is subject to administrative complexities.
c. The degree of protection it affords domestic producers varies inversely with
changes in import prices.
d. It provides domestic producers more protection during a business recession
when cheaper products are purchased.
11. Under which circumstances will a tariff have a greater protective effect?
a. It will have a greater protective effect if it is combined with a high tariff on
imported inputs.
b. It will have a greater protective effect if it is combined with a high tariff on
exported inputs.
c. It will have a greater protective effect if it is combined with a low tariff on
imported inputs.
d. It will have a greater protective effect if it is combined with a low tariff on
exported inputs.
Spring 2023 ECON3400 2
12. What is to be understood as tax escalation?
a. A decrease in the nominal and effective protection at each stage of production.
b. An increase in the nominal and effective protection at each stage of production.
c. A decrease in the nominal but increase in effective protection at each stage of
production.
d. An increase in the nominal but decrease in effective protection at each stage of
production.
Questions 13 to 16 refer to the following scenario: Assume that X imports Good A from Y at
P=350 and imposes an import tariff of n= 12%.
13. How much will the government generate from the import tariff?
a. 32
b. 42
c. 52
d. 62
14. How much does the consumer pay for the product?
a. 308
b. 350
c. 374
d. 392
15. Now X’s components worth 150 are used in the assembly of Good A. How much will the
consumer pay with OAP?
a. 308
b. 350
c. 374
d. 392
16. Why does a government have an interest in OAP?
a. Parts of the production remain at home – assembled abroad vs. produced
abroad.
b. The entire production will be outsourced, and the government does not have to
worry anymore.
c. The value added is generated 100% abroad.
d. They don’t.
Spring 2023 ECON3400 3
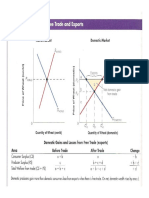
Questions 17 to 34 refer to the following scenario:
Conduct a welfare analysis for the domestic consumers and producers.
17. In the above market, the equilibrium price is
a. 5
b. 6
c. 7
d. 8
18. In the above market, the equilibrium quantity is
a. 5
b. 6
c. 7
d. 8
19. In the above market, consumer surplus is
a. 10.5
b. 12.5
c. 25
d. 50
20. In the above market, producer surplus is
a. 10.5
b. 12.5
c. 25
d. 50
Spring 2023 ECON3400 4
21. In the above market, total welfare is
a. 10.5
b. 12.5
c. 25
d. 50
Assume now the above market opens up to international trade. Domestic+World Supply is
at P = 4.
22. With international trade, the equilibrium price is
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 8
23. With international trade, the equilibrium quantity is
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 8
24. With international trade, the imported quantity is
a. 2
b. 4
c. 6
d. 8
25. With international trade, the consumer surplus is
a. 2
b. 12.5
c. 24.5
d. 32
26 With international trade, the producer surplus is
a. 2
b. 12.5
c. 24.5
d. 32
27. With international trade, total welfare is
a. 31
b. 32
c. 33
d. 34
Spring 2023 ECON3400 5
Assume now the above market opens up to international trade. Domestic+World Supply is
at P = 4. And the domestic government imposes an import tariff n=1.
28. With an import tariff, the equilibrium price is
a. 4
b. 5
c. 6
d. 7
29. With an import tariff, the equilibrium quantity is
a. 4
b. 5
c. 6
d. 7
30. With an import tariff, the imported quantity is
a. 4
b. 5
c. 6
d. 7
31. With an import tariff, the consumer surplus is
a. 4.5
b. 12.5
c. 24.5
d. 32
32. With an import tariff, the producer surplus is
a. 4.5
b. 12.5
c. 24.5
d. 32
33. With an import tariff, the government generates in revenue
a. 4
b. 5
c. 6
d. 7
34. With an import tariff, total welfare is
a. 31
b. 32
c. 33
d. 34
Spring 2023 ECON3400 6
You might also like
- SIE Exam Practice Question Workbook: Seven Full-Length Practice Exams (2023 Edition)From EverandSIE Exam Practice Question Workbook: Seven Full-Length Practice Exams (2023 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Series 65 Exam Practice Question Workbook: 700+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)From EverandSeries 65 Exam Practice Question Workbook: 700+ Comprehensive Practice Questions (2023 Edition)No ratings yet
- Test Bank For Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 10th Edition Mishkin DownloadDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Economics of Money Banking and Financial Markets 10th Edition Mishkin Downloadveinalshoebill5wvbgNo ratings yet
- RB CAGMAT REVIEW Macroeconomics Reviewer - Yet Sample QuestionsDocument35 pagesRB CAGMAT REVIEW Macroeconomics Reviewer - Yet Sample QuestionsSylveth Novah Badal Denzo100% (1)
- First Quarter: Module 1 Sum-Up Exercises in Applied EconomicsDocument3 pagesFirst Quarter: Module 1 Sum-Up Exercises in Applied EconomicsRio Jaena DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsNora MYNo ratings yet
- ECN 221 With AnswersDocument29 pagesECN 221 With Answersmuyi kunleNo ratings yet
- FCE BINF Question Pool SolvedDocument109 pagesFCE BINF Question Pool SolvedGertaNo ratings yet
- Sample MC QuestionsDocument6 pagesSample MC QuestionsJoshua OhNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics MCQsDocument11 pagesMacroeconomics MCQsIAs100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions On Economics: C. Getting Greatest Satisfaction From Available ResourcesDocument8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Economics: C. Getting Greatest Satisfaction From Available Resourceszaidashraf007No ratings yet
- A. Okun's LawDocument40 pagesA. Okun's LawHaya AhmadNo ratings yet
- International Econ Quiz 2 FA 2022Document10 pagesInternational Econ Quiz 2 FA 2022Nhung HồngNo ratings yet
- International Economics Exam PaperDocument6 pagesInternational Economics Exam PaperAdrian FathanNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1PHƯƠNG ĐẶNG DƯƠNG XUÂNNo ratings yet
- Public Finance Exam A2 JHWVLDocument3 pagesPublic Finance Exam A2 JHWVLKhalid El SikhilyNo ratings yet
- IT - MidtermDocument8 pagesIT - MidtermNguyễn Trần Huệ AnhNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 MCDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 MCHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- Macro Multiple ChoiceDocument41 pagesMacro Multiple ChoiceNghi Lê Nguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 9Document13 pagesPractice Test 9Yer ChangNo ratings yet
- Mankiw-Test Chapter 10-22Document55 pagesMankiw-Test Chapter 10-22Nhật Lan PhươngNo ratings yet
- RB Cagmat Review Macroeconomics O - ADocument35 pagesRB Cagmat Review Macroeconomics O - AShainabe RivaNo ratings yet
- Economics 1A Revison Unit 1 Unit 9Document7 pagesEconomics 1A Revison Unit 1 Unit 9Tman LetswaloNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Final Eco120 - Set 1 QuestionDocument10 pages2022 - Final Eco120 - Set 1 QuestionNur Syaza Athirah ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- SYBBI - SAMPLE QUESTIONS - EVEN 2021 (MERGED PDF) - MinDocument71 pagesSYBBI - SAMPLE QUESTIONS - EVEN 2021 (MERGED PDF) - Minketan karmoreNo ratings yet
- Simulated Examination in Agricultural Economics and Marketing (Post-Test) Name - Score - General DirectionsDocument10 pagesSimulated Examination in Agricultural Economics and Marketing (Post-Test) Name - Score - General Directionsmaica balaoasNo ratings yet
- Eco415 July2021Document7 pagesEco415 July2021Wan Nur Aqilah YusriNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions On Economics: A. NDP GDP-DepreciationDocument8 pagesMultiple Choice Questions On Economics: A. NDP GDP-Depreciationzaidashraf007No ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination Final AssessmentDocument13 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination Final AssessmentniklynNo ratings yet
- Time Allowance: 90 Minutes: Explanation) (0.3 Point/each Correct Answer)Document6 pagesTime Allowance: 90 Minutes: Explanation) (0.3 Point/each Correct Answer)Nguyễn Thùy LinhNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Fina4810Document9 pagesExam Questions Fina4810Bartholomew Szold75% (4)
- Introduction To Macroeconomics (Eco 1102) C. Théoret Practice Exam #1 Answers On Last PageDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics (Eco 1102) C. Théoret Practice Exam #1 Answers On Last Pagerei makiikoNo ratings yet
- International Trade Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesInternational Trade Practice QuestionsJaime SánchezNo ratings yet
- Economics MCQ SumsDocument19 pagesEconomics MCQ SumsAprajita SinghNo ratings yet
- ECON2103 Midterm 2 Fall2021+ (For+practice) +cindyDocument14 pagesECON2103 Midterm 2 Fall2021+ (For+practice) +cindyjocelyn.hy.chenNo ratings yet
- Review Midterm ExamDocument12 pagesReview Midterm ExamNgọc Ninh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Economics Important Mcqs From Past Papersof PPSC-2 PDFDocument18 pagesEconomics Important Mcqs From Past Papersof PPSC-2 PDFzuhaibNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Eco 1st TermDocument9 pagesGR 10 Eco 1st TermmaaheerjainNo ratings yet
- Macro Midterm 2018 Code ADocument11 pagesMacro Midterm 2018 Code Anoi baNo ratings yet
- C5 Final ExamDocument8 pagesC5 Final ExamFelicia DankwahNo ratings yet
- Mankiw-Test Chapter 10Document4 pagesMankiw-Test Chapter 10Vân Hà100% (1)
- Salvatore's International Economics - 10 Edition Test BankDocument5 pagesSalvatore's International Economics - 10 Edition Test BankMert CordukNo ratings yet
- International Trade Agricoolture-2Document42 pagesInternational Trade Agricoolture-2Nursana NinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: The Instruments of Trade Policy Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument13 pagesChapter 8: The Instruments of Trade Policy Multiple Choice QuestionsMian NomiNo ratings yet
- GTA Tutorials ECOM2201Document3 pagesGTA Tutorials ECOM2201kellaraydennNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document6 pagesAssignment 1wycliff brancNo ratings yet
- Surprise Quiz IDocument5 pagesSurprise Quiz I23pgp011No ratings yet
- 1 5 Mas - Lecture Notes Armin Glenn Araneta, Cpa EconomicsDocument5 pages1 5 Mas - Lecture Notes Armin Glenn Araneta, Cpa EconomicsDarelle Hannah MarquezNo ratings yet
- Economics Mcqs Test From Past Public Service Commission ExamsDocument43 pagesEconomics Mcqs Test From Past Public Service Commission Examslog man89% (9)
- Exam Code: 01: Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions: (1.6 Points Each)Document7 pagesExam Code: 01: Part 1: Multiple Choice Questions: (1.6 Points Each)Thế HùngNo ratings yet
- Macro Tut 1 HomeworkDocument7 pagesMacro Tut 1 HomeworkTạ ThưNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageDocument7 pagesPractice Problems Ch. 9 International Trade and Comparative AdvantageGabby CustodioNo ratings yet
- ECON 247 Practice Midterm ExaminationDocument9 pagesECON 247 Practice Midterm ExaminationRobyn ShirvanNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics Test 3Document26 pagesMicroeconomics Test 3a24dkNo ratings yet
- Eco162 104Document12 pagesEco162 104Abdullah RamlyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Discovery GridDocument16 pagesChapter Discovery GridjustinandbrendaNo ratings yet
- Shift The Supply Curve To The Right: An Increase in Price Increases RevenueDocument10 pagesShift The Supply Curve To The Right: An Increase in Price Increases RevenueAhmed Mahmoud AbouzaidNo ratings yet
- Revision - Paper IDocument9 pagesRevision - Paper Iiyaad MubarakNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Adel S. Laureto, PH.DDocument5 pagesReviewer: Adel S. Laureto, PH.DCT Bacolod Lanao del NorteNo ratings yet
- Production Cost Questions With AnswersDocument2 pagesProduction Cost Questions With AnswersHamza Mohamed50% (2)
- FPQP Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2024 Edition)From EverandFPQP Practice Question Workbook: 1,000 Comprehensive Practice Questions (2024 Edition)No ratings yet
- The Trade and Climate Change Nexus: The Urgency and Opportunities for Developing CountriesFrom EverandThe Trade and Climate Change Nexus: The Urgency and Opportunities for Developing CountriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Role of Entrepreneurship in Economic DevelopmentDocument21 pagesRole of Entrepreneurship in Economic DevelopmentEmmanuel BurcerNo ratings yet
- RIIM Question Bank - Economics 2020Document8 pagesRIIM Question Bank - Economics 2020SahilRajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 InterestDocument76 pagesChapter 3 InterestShudipto PodderNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Economics Unit 4 KeytermsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Economics Unit 4 KeytermsNIRAJ VENKATNo ratings yet
- Marxism and The Law - Preliminary AnalysesDocument27 pagesMarxism and The Law - Preliminary AnalysesRubensBordinhãoNetoNo ratings yet
- ECON-120 - Group Analysis, GuyanaDocument17 pagesECON-120 - Group Analysis, GuyanaAliyah AliNo ratings yet
- Rubin & The Old and New Rubinists 2021Document18 pagesRubin & The Old and New Rubinists 2021smavroNo ratings yet
- Ajaran Keynes Sebagai Analisa "Disequilibrium": Oleh: J. Soedradjad DjiwandonoDocument22 pagesAjaran Keynes Sebagai Analisa "Disequilibrium": Oleh: J. Soedradjad DjiwandonoSiti AminaNo ratings yet
- Gold StandardDocument24 pagesGold StandardmetlougamarNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Macroeconomics ModuleDocument76 pagesIntermediate Macroeconomics ModuleKatunga MwiyaNo ratings yet
- Economic SystemsDocument3 pagesEconomic SystemsKamarulnizam ZainalNo ratings yet
- Negative Rates The Bank of Japan ExperienceDocument8 pagesNegative Rates The Bank of Japan ExperienceYash BhasinNo ratings yet
- A02Document16 pagesA02Vũ Hồng NhungNo ratings yet
- Time ValueDocument24 pagesTime ValueAditya BapnaNo ratings yet
- Historical Capitalism Write-UpDocument7 pagesHistorical Capitalism Write-UpTanica NgangbamNo ratings yet
- MKT310 Group AssignmentDocument15 pagesMKT310 Group AssignmentIyad AmeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Classification of Planning 2.1 Planning by Direction and Planning by Inducement 2.1.1. Planning by DirectionDocument9 pagesChapter Two Classification of Planning 2.1 Planning by Direction and Planning by Inducement 2.1.1. Planning by DirectionYohannes EndaleNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Parkin 11th Edition Solutions ManualDocument20 pagesMacroeconomics Parkin 11th Edition Solutions ManualEricaGatespxje100% (47)
- Dance of The Trillions - Book ReviewDocument15 pagesDance of The Trillions - Book ReviewRajat MishraNo ratings yet
- MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stDocument6 pagesMANAGERIAL ECONOMICS NOTES Unit-5 MBA 1stRUBA NASIMNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5:: Discount InterestDocument9 pagesLesson 5:: Discount InterestAngelica Sulay BalaodNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Demand I: Building The - Model: IS LMDocument40 pagesAggregate Demand I: Building The - Model: IS LMaditya prudhviNo ratings yet
- Dissertation of Karl MarxDocument5 pagesDissertation of Karl MarxNeedHelpWriteMyPaperUK100% (1)
- Monopoly Capital - An Essay On The American Economic and Social Order (PDFDrive)Document416 pagesMonopoly Capital - An Essay On The American Economic and Social Order (PDFDrive)Maks imilijanNo ratings yet
- Communist ManifestoDocument16 pagesCommunist ManifestoWisdomNo ratings yet
- The Keynesian EconomicsDocument17 pagesThe Keynesian EconomicsIshrat Jahan DiaNo ratings yet
- ECO 5 Theory of DistributionDocument26 pagesECO 5 Theory of DistributionJubair sultanNo ratings yet
- Exam 2011 Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesExam 2011 Questions and Answersqizen0804No ratings yet