Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 6 Test Answer
Unit 6 Test Answer
Uploaded by
Khue MinhCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- IIMC Consulting Casebook 2022-23Document147 pagesIIMC Consulting Casebook 2022-23Aarti Kumari100% (2)
- Unit 6 RevisionDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Revisionivy100% (1)
- 8.4 HW PropertiesRectRhomSquPracticeDocument2 pages8.4 HW PropertiesRectRhomSquPracticeERVIN DANCANo ratings yet
- P - Science - 4 - Language Worksheets - Unit 4Document4 pagesP - Science - 4 - Language Worksheets - Unit 4Khue Minh100% (2)
- Learn English 3 With Audio and Video: Learn English, #3From EverandLearn English 3 With Audio and Video: Learn English, #3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Astm A-615Document8 pagesAstm A-615bill_lee_24271% (7)
- Stats Tools PackageDocument44 pagesStats Tools PackageMuhammad Asif Khan100% (1)
- Unit 6 Test RevisionDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Test RevisionKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Movements of The Earth - Rotation and RevolutionDocument10 pagesMovements of The Earth - Rotation and Revolutionmanelyn mansibangNo ratings yet
- Science 7 (Q4 Module 6) Performance Task & Written WorksDocument12 pagesScience 7 (Q4 Module 6) Performance Task & Written WorksJOY SHERYL PADIANGANNo ratings yet
- Module 13 14 15 Earths Movement Seasonal Changes Perihelion and AphelionDocument10 pagesModule 13 14 15 Earths Movement Seasonal Changes Perihelion and AphelionYukazhaimaNo ratings yet
- The Universe - Social ScienceDocument3 pagesThe Universe - Social ScienceAn Mon te100% (1)
- Ministry of Education Grade Four Consolidated Worksheet Subject: Science Week 15Document6 pagesMinistry of Education Grade Four Consolidated Worksheet Subject: Science Week 15ezerah nuwagabaNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document3 pagesScience 1Michelle VallejoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 4Q Answer SheetDocument3 pagesScience 7 4Q Answer SheetIris Joy Lee GeniseNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesWorksheet - The Solar SystemMaria BNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 6 - Module 4Document16 pagesQ4 Science 6 - Module 4Giyu Tomioka100% (1)
- Scie6 4th w5 MelcDocument90 pagesScie6 4th w5 Melckristine BurlaosNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreEfmarie De Guzman RufinoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 q4Document5 pagesScience 7 q4cattleya abelloNo ratings yet
- Hernandez, Nathaniel R. BSECE 2A GEC CEA 36 LP 04 ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesHernandez, Nathaniel R. BSECE 2A GEC CEA 36 LP 04 ASSESSMENTHernandez, Nathaniel R.No ratings yet
- Earth 1. Think of Our Beautiful Planet. Answer The QuestionsDocument8 pagesEarth 1. Think of Our Beautiful Planet. Answer The QuestionsPavol VozárNo ratings yet
- Science Guide 2nd GradeDocument4 pagesScience Guide 2nd GradeBEATRIZ RODRIGUEZ SOTO100% (1)
- Science 6: Turn AroundDocument9 pagesScience 6: Turn Aroundfermina combisNo ratings yet
- Name: - Science ExamDocument3 pagesName: - Science ExamJose TiradoNo ratings yet
- Science 5: Quarter 4 - Week 5 Competency: LessonDocument7 pagesScience 5: Quarter 4 - Week 5 Competency: LessonJan Warren BunoanNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test in SCIENCE 5Document8 pages1st Summative Test in SCIENCE 5Noeme VillarealNo ratings yet
- LAS1Document9 pagesLAS1soleilramirez217No ratings yet
- Science IV 4th RatingDocument46 pagesScience IV 4th RatingXer WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Revolution of The EarthDocument9 pagesRevolution of The EarthRUBELYN BAQUIRANNo ratings yet
- Science7, q4, Week4 (Validated)Document13 pagesScience7, q4, Week4 (Validated)Gary DiazNo ratings yet
- U1.Our World WorksheetsDocument4 pagesU1.Our World WorksheetsLaxeNo ratings yet
- Activity LS2 Module 1 Why Do I Believe in Science ActivityDocument7 pagesActivity LS2 Module 1 Why Do I Believe in Science ActivityKrisjelyn GumzNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q2 Summative Test 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Q2 Summative Test 1MA. HAZEL TEOLOGO0% (1)
- Review Test Sci 6Document5 pagesReview Test Sci 6ANNALIZA FIECASNo ratings yet
- G3 Social WorksheetDocument5 pagesG3 Social WorksheetkishancpNo ratings yet
- Q4 Rotation and RevolutionDocument4 pagesQ4 Rotation and Revolutionmarites gallardoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 - L P 8 ILSWDocument6 pagesUNIT 6 - L P 8 ILSWNhi Ninh YếnNo ratings yet
- April 29 30 - MDL - Science 5Document2 pagesApril 29 30 - MDL - Science 5Rochelle May CascoNo ratings yet
- Scie5 Elem Module4 q4Document8 pagesScie5 Elem Module4 q4Elvie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sci5 Q4 Mod5 PDFDocument29 pagesSci5 Q4 Mod5 PDFMirabelNo ratings yet
- 4TH Monthly ExamDocument8 pages4TH Monthly ExamALVEN OYANGORINNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q4 Week 5Document7 pagesScience 7 Q4 Week 5dhangaguarri2No ratings yet
- Sci6 Q4 Mod5Document29 pagesSci6 Q4 Mod5Shefa CapurasNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Universe Student SheetDocument2 pagesFormation of The Universe Student SheetDubu Dubu DahyunieeNo ratings yet
- A Learning Module in Science and Health Iv: THE Exploration Around The SunDocument13 pagesA Learning Module in Science and Health Iv: THE Exploration Around The Sunleonel de veraNo ratings yet
- Science 1 FinalDocument2 pagesScience 1 FinalRona Mae NaviaNo ratings yet
- Grade6 4th QuarterDocument18 pagesGrade6 4th Quarterrex hussein lamosteNo ratings yet
- Cot - DLP - Science 5 by Sir John Cel P. FaustinoDocument4 pagesCot - DLP - Science 5 by Sir John Cel P. FaustinoMyrrh Balanay FloridaNo ratings yet
- CT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Document3 pagesCT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Chelsea Sharon Miranda SiregarNo ratings yet
- q3 Law Science 9 Weeks 7 8Document6 pagesq3 Law Science 9 Weeks 7 8zyrix perez bagoNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Week 4 LAS1Document2 pagesScience 6 Week 4 LAS1FRITZY PREMAYLONNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation Lesson Plan in Science 6Document5 pagesClassroom Observation Lesson Plan in Science 6MERLYNDA AMBINo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6: The Reason For The SeasonsDocument22 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 6: The Reason For The SeasonsJaken MackNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Earth Moon SunDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Earth Moon SunKirstyNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q4 Q2Document3 pagesScience 6 Q4 Q2preciousgiven.lachicaNo ratings yet
- Science6 - Q4 - Module 5 - Movements of The EarthDocument29 pagesScience6 - Q4 - Module 5 - Movements of The EarthSette-Angel LaudNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Activity Sheetsj Performance and AssessmentDocument11 pagesScience 7 Activity Sheetsj Performance and Assessmentdayshara9No ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument8 pagesSocial ScienceAn Mon teNo ratings yet
- Body 1Document17 pagesBody 1Vegilla Sinlao Ann JeehNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Week 4 LAS3Document2 pagesScience 6 Week 4 LAS3FRITZY PREMAYLONNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 4: SeasonsDocument24 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 4: SeasonsEverly Victorio SantosNo ratings yet
- Learn English 2 With Audio and Video.: Learn English, #2From EverandLearn English 2 With Audio and Video.: Learn English, #2Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Address To A HaggisDocument1 pageAddress To A HaggisKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Up in The Morning EarlyDocument1 pageUp in The Morning EarlyKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - TestDocument5 pagesUnit 9 - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- A Red, Red RoseDocument1 pageA Red, Red RoseKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (1) - TestDocument6 pagesUnit 8 (1) - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (2) - TestDocument6 pagesUnit 8 (2) - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 9.2 Answer TestDocument1 pageUnit 9.2 Answer TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- S1 W30 U8 HandwritingDocument2 pagesS1 W30 U8 HandwritingKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- One Fish Two Fish Red Fish Blue Fish by Dr. SeussDocument69 pagesOne Fish Two Fish Red Fish Blue Fish by Dr. SeussKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- G3 - Unit 1 Revision QuestionsDocument4 pagesG3 - Unit 1 Revision QuestionsKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Conductors and InsulatorsDocument1 pageConductors and InsulatorsKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- What Will We Do Today?: We Will Begin A New Unit in The BookDocument18 pagesWhat Will We Do Today?: We Will Begin A New Unit in The BookKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- CountriesDocument137 pagesCountriesKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Workbook Checking!Document13 pagesWorkbook Checking!Khue MinhNo ratings yet
- G3 - Day and NightDocument15 pagesG3 - Day and NightKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Peugeot 206 P Dag Owners ManualDocument119 pagesPeugeot 206 P Dag Owners ManualAlex Rojas AguilarNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Batch Fermentation Kinetics For Succinic Acid Production by Mannheneimia SucciniciproducensDocument9 pagesModeling of Batch Fermentation Kinetics For Succinic Acid Production by Mannheneimia SucciniciproducensRyuuara Az-ZahraNo ratings yet
- Suld United PPT2020.09Document31 pagesSuld United PPT2020.09Ulstuguldur Kh.No ratings yet
- Topic 6 Circular Motion Test P1Document11 pagesTopic 6 Circular Motion Test P1Sabrina_LGXNo ratings yet
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule (ForDocument8 pagesFleming's Left Hand Rule (Forb_geyl4286No ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of A Bisection-Exclusion Method To Find Zeros of Univariate Analytic FunctionsDocument39 pagesNumerical Analysis of A Bisection-Exclusion Method To Find Zeros of Univariate Analytic FunctionsLucas SantosNo ratings yet
- Leca Block ProjekteringDocument32 pagesLeca Block ProjekteringBashar AlshathirNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMA DE INGLES 11°jeDocument14 pagesPROGRAMA DE INGLES 11°jeJoséNo ratings yet
- SprinklersDocument2 pagesSprinklersMohamed El MorsyNo ratings yet
- Using Chinese Dumbass Notation To Find A PDFDocument12 pagesUsing Chinese Dumbass Notation To Find A PDFLucas KevinNo ratings yet
- 4G Wireless PresentationDocument26 pages4G Wireless PresentationArjun ShankaNo ratings yet
- Solve System of Equations Using GraphingDocument42 pagesSolve System of Equations Using Graphingapi-265481804No ratings yet
- Introducing MPLS Traffic Engineering Components-L01Document35 pagesIntroducing MPLS Traffic Engineering Components-L01Cuong HaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MixedDocument11 pagesWorksheet MixedBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- 23-Primary Treatment and Secondary Treatment-21!02!2023Document37 pages23-Primary Treatment and Secondary Treatment-21!02!2023Back upNo ratings yet
- El Volcan MombachoDocument10 pagesEl Volcan MombachoYossuara PittiNo ratings yet
- Revised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016Document14 pagesRevised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016undyingNo ratings yet
- Page Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesPage Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Evidence From QuranDocument6 pagesEvidence From QuranHaziq Hakeem Ahmad Affandi100% (1)
- SP-1102A Specification For Design of 33kV Overhead Power Lines On Wooden PolesDocument118 pagesSP-1102A Specification For Design of 33kV Overhead Power Lines On Wooden Polesarjunprasannan7No ratings yet
- Instruments Obs & Gynea PDFDocument19 pagesInstruments Obs & Gynea PDFVibes Usmlee100% (1)
- I/O Specifications: CPU Unit DescriptionsDocument10 pagesI/O Specifications: CPU Unit Descriptionsวรพงษ์ กอชัชวาลNo ratings yet
- Clean RoomDocument9 pagesClean Roomxyzscribd1988No ratings yet
- Prof. D. Pulla RaoDocument20 pagesProf. D. Pulla RaoAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNo ratings yet
- Portuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENDocument48 pagesPortuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENMiguel Chã AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Document8 pages36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Ovo OjasNo ratings yet
Unit 6 Test Answer
Unit 6 Test Answer
Uploaded by
Khue MinhOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 6 Test Answer
Unit 6 Test Answer
Uploaded by
Khue MinhCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:___________________________ Class:___________________ Date:__________________
Unit 6 Test Revision
Grade 4
PART 1. Identify the following terms to their definitions.
TERMS DEFINITION
____________1. Revolve E. A.Not a perfect ellipse. This is the term used to describe the shape of the Earth’s
orbit
____________2. Orbit C B.We use ‘this’ to mean spring, summer, autumn, or winter.
____________3. Ellipse H C. the path is taken when an object such as a planet) moves around a larger object
such as the sun in space.
____________4. slight ellipse A D. Leaning at an angle. In this unit, we refer to the ‘this’ of the Earth on its axis
____________5. Year J E. To move in a circle around an object in the center
____________6. Season B F. A sphere represents the whole globe. ‘Hemi’ means ‘half, ' so this is half the
globe.
____________7. Tilt D G. The northernmost and southernmost points on the globe.
____________8. Hemisphere F H. an oval shape
____________9. North Pole and I.To move in a circle around an axis
South Pole G
____________10. Rotate I J. 365¼ days.
PART 2: Complete the following information in the model below.
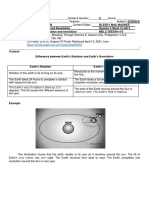
1. What shape is the Earth’s orbit around the sun? Slight ellipse
2. In which direction does the Earth orbit the sun? Anticlockwise
3. What is the imaginary line labeled X? Earth’s axis
4. What is the imaginary line labeled Y? Equator
5. How long does it take Earth to complete its orbit around the sun? 365¼ days
PART 3. Fill in the blanks. Use the words in the box.
sunrise dormant migration adapt
hibernation chlorophyll sunset
1. ______________. To make changes to fit a new situation. Adapt
2. ______________. The green substance in leaves. Chlorophyll
3. ______________. Sleeping. dormant
4. ______________.A time when an animal’s body processes slow down for a long period of time, such as in the
winter season. hibernate
5. ______________. The movement of large numbers of animals to a region where there is food or a region where
it is suitable for them to breed. migrate
6. ______________. The time when the sun appears to rise above the horizon in the morning. sunrise
7. ______________. The time when the sun appears to sink below the horizon in the evening. sunset
PART 4. Adaptations of plants and animals in hot, dry environments
1. Discuss how cacti adapt to their environment.
- They have thorns instead of leaves allowing them to lose less water, and their trunk or skin has a waxy coating
that stops water from escaping. They have a fat stem to store water and deep roots to find water.
2. Discuss how camels adapt to their environment.
- They have long eyelashes to keep sand out of their eyes, thick lips so they can eat thorny desert plants, humps
to store water, and wide tough feet so they can walk on hot sand.
PART 5. Adaptations of animals in wet environments
1. Discuss how fishes adapt to their environment.
- They have gills to breathe in the water and fins to swim faster.
2. Discuss how seabirds adapt to their environment.
- Seabirds have waterproof feathers so that they can dive for food. Seabirds also have special glands that get rid
of the salt that they take in when they drink seawater
PART 6. Match the predators with their prey in the pictures
Answer: Cheetah and antelope; spider and fly; polar bear and seal; hawk and lizard.
PART 7. Group predators according to their adaptations
You might also like
- IIMC Consulting Casebook 2022-23Document147 pagesIIMC Consulting Casebook 2022-23Aarti Kumari100% (2)
- Unit 6 RevisionDocument3 pagesUnit 6 Revisionivy100% (1)
- 8.4 HW PropertiesRectRhomSquPracticeDocument2 pages8.4 HW PropertiesRectRhomSquPracticeERVIN DANCANo ratings yet
- P - Science - 4 - Language Worksheets - Unit 4Document4 pagesP - Science - 4 - Language Worksheets - Unit 4Khue Minh100% (2)
- Learn English 3 With Audio and Video: Learn English, #3From EverandLearn English 3 With Audio and Video: Learn English, #3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Astm A-615Document8 pagesAstm A-615bill_lee_24271% (7)
- Stats Tools PackageDocument44 pagesStats Tools PackageMuhammad Asif Khan100% (1)
- Unit 6 Test RevisionDocument4 pagesUnit 6 Test RevisionKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Movements of The Earth - Rotation and RevolutionDocument10 pagesMovements of The Earth - Rotation and Revolutionmanelyn mansibangNo ratings yet
- Science 7 (Q4 Module 6) Performance Task & Written WorksDocument12 pagesScience 7 (Q4 Module 6) Performance Task & Written WorksJOY SHERYL PADIANGANNo ratings yet
- Module 13 14 15 Earths Movement Seasonal Changes Perihelion and AphelionDocument10 pagesModule 13 14 15 Earths Movement Seasonal Changes Perihelion and AphelionYukazhaimaNo ratings yet
- The Universe - Social ScienceDocument3 pagesThe Universe - Social ScienceAn Mon te100% (1)
- Ministry of Education Grade Four Consolidated Worksheet Subject: Science Week 15Document6 pagesMinistry of Education Grade Four Consolidated Worksheet Subject: Science Week 15ezerah nuwagabaNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document3 pagesScience 1Michelle VallejoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 4Q Answer SheetDocument3 pagesScience 7 4Q Answer SheetIris Joy Lee GeniseNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - The Solar SystemDocument3 pagesWorksheet - The Solar SystemMaria BNo ratings yet
- Q4 Science 6 - Module 4Document16 pagesQ4 Science 6 - Module 4Giyu Tomioka100% (1)
- Scie6 4th w5 MelcDocument90 pagesScie6 4th w5 Melckristine BurlaosNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreDocument4 pagesLearning Activity Worksheet Q4 Science 6 - Week 5: Name: - Section: - Rating/ScoreEfmarie De Guzman RufinoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 q4Document5 pagesScience 7 q4cattleya abelloNo ratings yet
- Hernandez, Nathaniel R. BSECE 2A GEC CEA 36 LP 04 ASSESSMENTDocument2 pagesHernandez, Nathaniel R. BSECE 2A GEC CEA 36 LP 04 ASSESSMENTHernandez, Nathaniel R.No ratings yet
- Earth 1. Think of Our Beautiful Planet. Answer The QuestionsDocument8 pagesEarth 1. Think of Our Beautiful Planet. Answer The QuestionsPavol VozárNo ratings yet
- Science Guide 2nd GradeDocument4 pagesScience Guide 2nd GradeBEATRIZ RODRIGUEZ SOTO100% (1)
- Science 6: Turn AroundDocument9 pagesScience 6: Turn Aroundfermina combisNo ratings yet
- Name: - Science ExamDocument3 pagesName: - Science ExamJose TiradoNo ratings yet
- Science 5: Quarter 4 - Week 5 Competency: LessonDocument7 pagesScience 5: Quarter 4 - Week 5 Competency: LessonJan Warren BunoanNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Test in SCIENCE 5Document8 pages1st Summative Test in SCIENCE 5Noeme VillarealNo ratings yet
- LAS1Document9 pagesLAS1soleilramirez217No ratings yet
- Science IV 4th RatingDocument46 pagesScience IV 4th RatingXer WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Revolution of The EarthDocument9 pagesRevolution of The EarthRUBELYN BAQUIRANNo ratings yet
- Science7, q4, Week4 (Validated)Document13 pagesScience7, q4, Week4 (Validated)Gary DiazNo ratings yet
- U1.Our World WorksheetsDocument4 pagesU1.Our World WorksheetsLaxeNo ratings yet
- Activity LS2 Module 1 Why Do I Believe in Science ActivityDocument7 pagesActivity LS2 Module 1 Why Do I Believe in Science ActivityKrisjelyn GumzNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q2 Summative Test 1Document2 pagesPhysical Science Q2 Summative Test 1MA. HAZEL TEOLOGO0% (1)
- Review Test Sci 6Document5 pagesReview Test Sci 6ANNALIZA FIECASNo ratings yet
- G3 Social WorksheetDocument5 pagesG3 Social WorksheetkishancpNo ratings yet
- Q4 Rotation and RevolutionDocument4 pagesQ4 Rotation and Revolutionmarites gallardoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 6 - L P 8 ILSWDocument6 pagesUNIT 6 - L P 8 ILSWNhi Ninh YếnNo ratings yet
- April 29 30 - MDL - Science 5Document2 pagesApril 29 30 - MDL - Science 5Rochelle May CascoNo ratings yet
- Scie5 Elem Module4 q4Document8 pagesScie5 Elem Module4 q4Elvie ReyesNo ratings yet
- Sci5 Q4 Mod5 PDFDocument29 pagesSci5 Q4 Mod5 PDFMirabelNo ratings yet
- 4TH Monthly ExamDocument8 pages4TH Monthly ExamALVEN OYANGORINNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q4 Week 5Document7 pagesScience 7 Q4 Week 5dhangaguarri2No ratings yet
- Sci6 Q4 Mod5Document29 pagesSci6 Q4 Mod5Shefa CapurasNo ratings yet
- Formation of The Universe Student SheetDocument2 pagesFormation of The Universe Student SheetDubu Dubu DahyunieeNo ratings yet
- A Learning Module in Science and Health Iv: THE Exploration Around The SunDocument13 pagesA Learning Module in Science and Health Iv: THE Exploration Around The Sunleonel de veraNo ratings yet
- Science 1 FinalDocument2 pagesScience 1 FinalRona Mae NaviaNo ratings yet
- Grade6 4th QuarterDocument18 pagesGrade6 4th Quarterrex hussein lamosteNo ratings yet
- Cot - DLP - Science 5 by Sir John Cel P. FaustinoDocument4 pagesCot - DLP - Science 5 by Sir John Cel P. FaustinoMyrrh Balanay FloridaNo ratings yet
- CT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Document3 pagesCT Science BJU Chapter 8 and 9Chelsea Sharon Miranda SiregarNo ratings yet
- q3 Law Science 9 Weeks 7 8Document6 pagesq3 Law Science 9 Weeks 7 8zyrix perez bagoNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Week 4 LAS1Document2 pagesScience 6 Week 4 LAS1FRITZY PREMAYLONNo ratings yet
- Classroom Observation Lesson Plan in Science 6Document5 pagesClassroom Observation Lesson Plan in Science 6MERLYNDA AMBINo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6: The Reason For The SeasonsDocument22 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 6: The Reason For The SeasonsJaken MackNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Earth Moon SunDocument4 pagesGrade 7 Earth Moon SunKirstyNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Q4 Q2Document3 pagesScience 6 Q4 Q2preciousgiven.lachicaNo ratings yet
- Science6 - Q4 - Module 5 - Movements of The EarthDocument29 pagesScience6 - Q4 - Module 5 - Movements of The EarthSette-Angel LaudNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Activity Sheetsj Performance and AssessmentDocument11 pagesScience 7 Activity Sheetsj Performance and Assessmentdayshara9No ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument8 pagesSocial ScienceAn Mon teNo ratings yet
- Body 1Document17 pagesBody 1Vegilla Sinlao Ann JeehNo ratings yet
- Science 6 Week 4 LAS3Document2 pagesScience 6 Week 4 LAS3FRITZY PREMAYLONNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 4: SeasonsDocument24 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 4: SeasonsEverly Victorio SantosNo ratings yet
- Learn English 2 With Audio and Video.: Learn English, #2From EverandLearn English 2 With Audio and Video.: Learn English, #2Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Address To A HaggisDocument1 pageAddress To A HaggisKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Up in The Morning EarlyDocument1 pageUp in The Morning EarlyKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 - TestDocument5 pagesUnit 9 - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- A Red, Red RoseDocument1 pageA Red, Red RoseKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (1) - TestDocument6 pagesUnit 8 (1) - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 (2) - TestDocument6 pagesUnit 8 (2) - TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Unit 9.2 Answer TestDocument1 pageUnit 9.2 Answer TestKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- S1 W30 U8 HandwritingDocument2 pagesS1 W30 U8 HandwritingKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- One Fish Two Fish Red Fish Blue Fish by Dr. SeussDocument69 pagesOne Fish Two Fish Red Fish Blue Fish by Dr. SeussKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- G3 - Unit 1 Revision QuestionsDocument4 pagesG3 - Unit 1 Revision QuestionsKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Conductors and InsulatorsDocument1 pageConductors and InsulatorsKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- What Will We Do Today?: We Will Begin A New Unit in The BookDocument18 pagesWhat Will We Do Today?: We Will Begin A New Unit in The BookKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- CountriesDocument137 pagesCountriesKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Workbook Checking!Document13 pagesWorkbook Checking!Khue MinhNo ratings yet
- G3 - Day and NightDocument15 pagesG3 - Day and NightKhue MinhNo ratings yet
- Peugeot 206 P Dag Owners ManualDocument119 pagesPeugeot 206 P Dag Owners ManualAlex Rojas AguilarNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Batch Fermentation Kinetics For Succinic Acid Production by Mannheneimia SucciniciproducensDocument9 pagesModeling of Batch Fermentation Kinetics For Succinic Acid Production by Mannheneimia SucciniciproducensRyuuara Az-ZahraNo ratings yet
- Suld United PPT2020.09Document31 pagesSuld United PPT2020.09Ulstuguldur Kh.No ratings yet
- Topic 6 Circular Motion Test P1Document11 pagesTopic 6 Circular Motion Test P1Sabrina_LGXNo ratings yet
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule (ForDocument8 pagesFleming's Left Hand Rule (Forb_geyl4286No ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of A Bisection-Exclusion Method To Find Zeros of Univariate Analytic FunctionsDocument39 pagesNumerical Analysis of A Bisection-Exclusion Method To Find Zeros of Univariate Analytic FunctionsLucas SantosNo ratings yet
- Leca Block ProjekteringDocument32 pagesLeca Block ProjekteringBashar AlshathirNo ratings yet
- PROGRAMA DE INGLES 11°jeDocument14 pagesPROGRAMA DE INGLES 11°jeJoséNo ratings yet
- SprinklersDocument2 pagesSprinklersMohamed El MorsyNo ratings yet
- Using Chinese Dumbass Notation To Find A PDFDocument12 pagesUsing Chinese Dumbass Notation To Find A PDFLucas KevinNo ratings yet
- 4G Wireless PresentationDocument26 pages4G Wireless PresentationArjun ShankaNo ratings yet
- Solve System of Equations Using GraphingDocument42 pagesSolve System of Equations Using Graphingapi-265481804No ratings yet
- Introducing MPLS Traffic Engineering Components-L01Document35 pagesIntroducing MPLS Traffic Engineering Components-L01Cuong HaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet MixedDocument11 pagesWorksheet MixedBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- 23-Primary Treatment and Secondary Treatment-21!02!2023Document37 pages23-Primary Treatment and Secondary Treatment-21!02!2023Back upNo ratings yet
- El Volcan MombachoDocument10 pagesEl Volcan MombachoYossuara PittiNo ratings yet
- Revised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016Document14 pagesRevised LRS BRS Booklet-2015-2016undyingNo ratings yet
- Page Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument44 pagesPage Proofs: Continuous Probability DistributionsApoorva PanchalNo ratings yet
- Evidence From QuranDocument6 pagesEvidence From QuranHaziq Hakeem Ahmad Affandi100% (1)
- SP-1102A Specification For Design of 33kV Overhead Power Lines On Wooden PolesDocument118 pagesSP-1102A Specification For Design of 33kV Overhead Power Lines On Wooden Polesarjunprasannan7No ratings yet
- Instruments Obs & Gynea PDFDocument19 pagesInstruments Obs & Gynea PDFVibes Usmlee100% (1)
- I/O Specifications: CPU Unit DescriptionsDocument10 pagesI/O Specifications: CPU Unit Descriptionsวรพงษ์ กอชัชวาลNo ratings yet
- Clean RoomDocument9 pagesClean Roomxyzscribd1988No ratings yet
- Prof. D. Pulla RaoDocument20 pagesProf. D. Pulla RaoAppan Kandala VasudevacharyNo ratings yet
- Portuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENDocument48 pagesPortuguese Market Outlook Up To 2040: A Report To APRENMiguel Chã AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Document8 pages36 - 4 - New York - 08-91 - 1478Ovo OjasNo ratings yet